What is the Google Search Algorithm?
Google search algorithm refers to the complex set of rules, equations, and instructions that Google uses to determine the rankings of the content it displays on its search results pages.
The term “Google search algorithm” actually refers to a set of algorithms rather than a single algorithm. These algorithms work together to analyze various signals from a webpage and determine its quality and relevance to a search query.
In this article, we’ll cover:
Importance of the Google Search Algorithm
The Google Search algorithm determines how webpages are ranked and displayed on Google search engine results pages (SERPs). Specifically, the algorithm filters and organizes the webpages in Google’s index and then returns a ranked list of the most relevant, high-quality results for each query.
For example, when we search for “yoga for beginners,” Google returns the results below. Google returned these results because its algorithm determined they are relevant and helpful to the user.
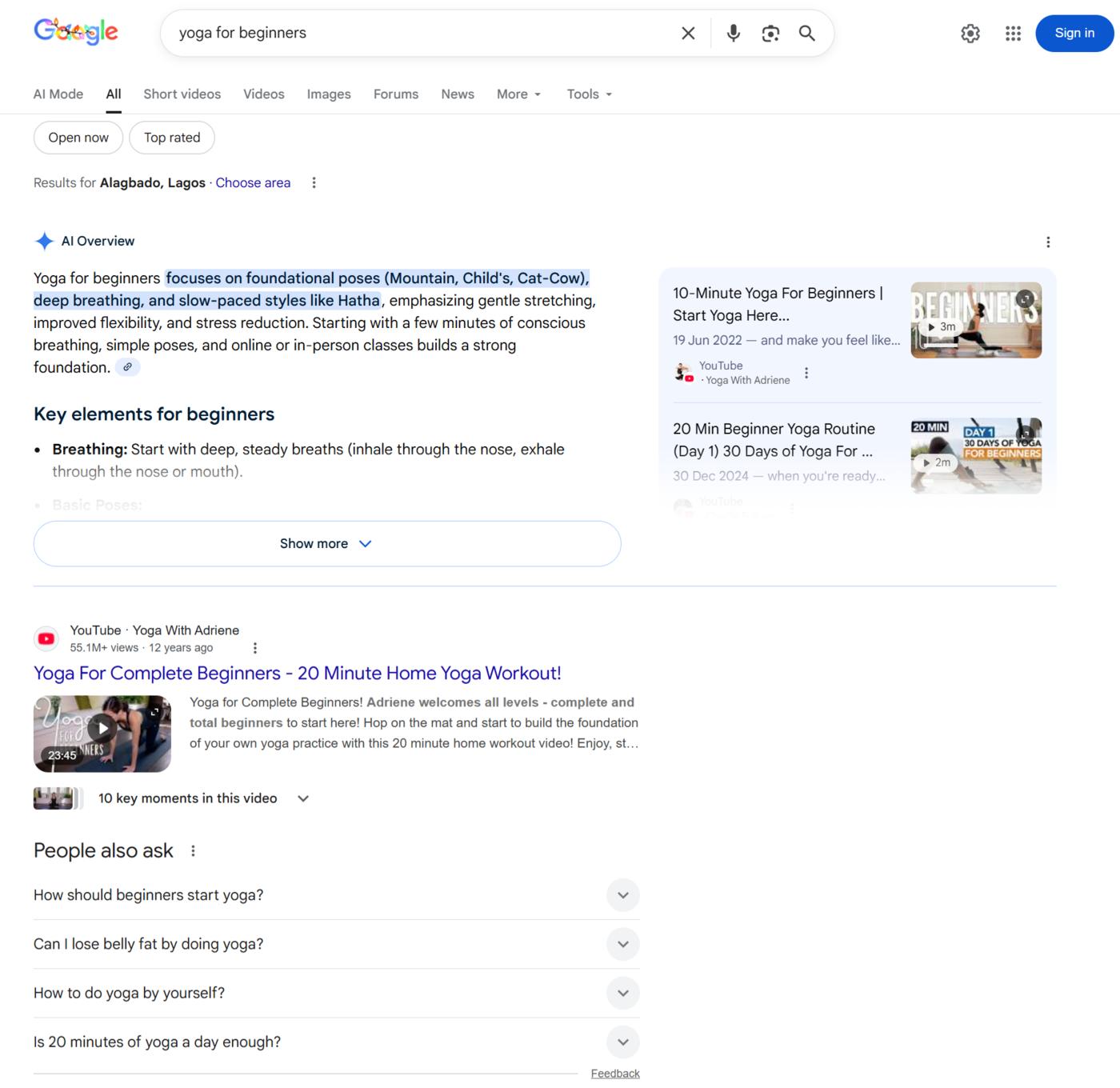
For bloggers, the Google Search algorithm directly influences their visibility, organic traffic, and overall online success.
Those that create and maintain content and sites that align with Google’s ranking signals (called ranking factors) are more likely to appear at the top of search results for relevant queries than those that do not.
This makes understanding how the algorithm works a necessity for bloggers who want to rank on Google. You must understand how it works and how to create content that aligns with its ranking factors.
How the Google Search Algorithm Works
Google is secretive about its algorithm. It has never revealed the details on how it works or even how many algorithms are there and how they work together to power Google Search.
Google does this to prevent creators from gaming the system. However, it also means that bloggers that create high-quality content may not understand how to optimize their content and site so that it ranks high on Google search engine results pages.
Nonetheless, we know Google uses ranking factors to identify high-quality content and sites on the web. It then displays this content to visitors if it is relevant to the search term they used.
Overall, instead of focusing on the Google Search algorithm itself, it is better to understand Google’s ranking factors and how Google Search works. You then create content that aligns with them.
How Google Search Works
The process of Google discovering content published on the web and displaying it on search engine result pages is a three-step process involving:
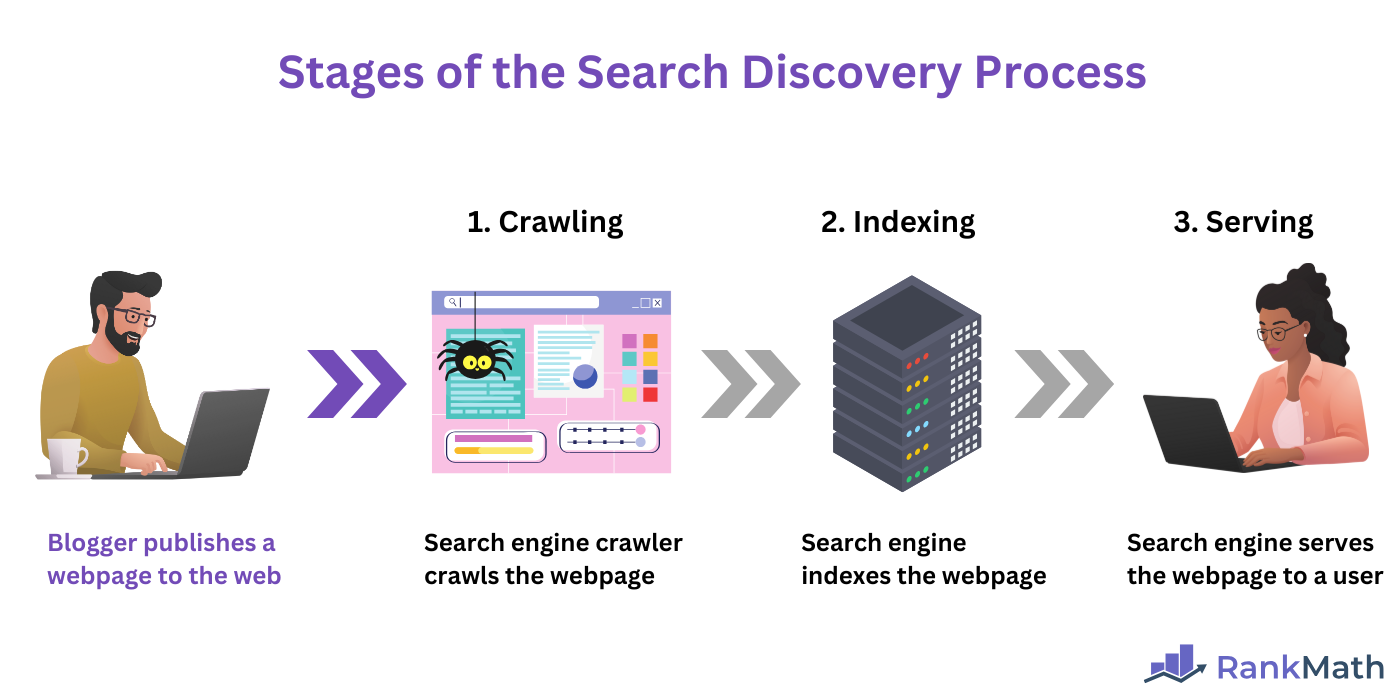
Let us briefly address them one after another.
a. Crawling
Crawling is the first step in the Google Search process. This is where Google’s web crawler, known as Googlebot, visits a webpage and downloads its content. This includes the text, images, videos, and any other relevant element on the webpage.
b. Indexing
Indexing is the second step in the Google Search process. Here, Google analyzes the text, images, videos, and other elements on the page for relevance and quality. Once done, it stores the elements (along with their details such as their metadata) in a database called an index.
c. Serving
Serving is the third and final step in the Google Search process. This is the point where Google retrieves relevant and high-quality content from its index and presents it on its search engine results page. This step occurs after a visitor enters a search term (also called a search query) into Google.
This is a rundown on how Google Search works. When a user enters a search term into Google, Google analyzes its keywords along with the context in which they are used. This allows Google to understand the searcher’s intent.
Once done, the Google Search algorithm evaluates relevant content in its index against its ranking factors. Those that pass Google’s ranking factors are considered the most relevant and are shown to the user on the Google search engine results page.
Google Search Algorithm Ranking Factors
Google ranking factors determine which results appear on the Google Search results page and what order they appear. For a blogger, the ranking factor determines whether your content will appear on the results page and where it appears.
The number of ranking factors that Google uses remains a closely guarded secret. However, bloggers and SEOs speculate that it is between 200 and 700. Some confirmed ones include:
- Content quality
- Page experience
- Inbound links (backlinks)
- Internal links
- Anchor text
- Content freshness
- Content relevance
- Content usability
- URL structure
- Search history
- Openness
Note: Ranking factors are not created equal. Some have a significant effect on rankings, while others have a minor effect. Some ranking factors also affect all searches, while others only apply to specific searches.
a. Content Quality
Many bloggers and SEOs believe content quality is Google’s most important ranking factor. This makes sense, considering Google only wants to display high-quality content on the search results pages.
A high quality content is usually in-depth and original. It is frequently updated to include new information and remove redundant ones. It is also well formatted, includes relevant media, and has great E-E-A-T signals.
b. Page Experience
Google wants visitors to have a great user experience. So, it uses the page experience to evaluate how your visitors experienced your site.
The page experience relies on multiple signals including your Core Web Vitals, mobile-friendliness, and HTTPS usage, and absence of intrusive interstitials. It is also closely linked to technical SEO, which can impact the crawlability and indexability of your webpages.
c. Inbound Links
Inbound links (also called backlinks) are a significant Google ranking factor. Google treats them, especially when they are set to dofollow and originate from a contextually relevant webpage, as endorsements from other bloggers.
The more authoritative the originating site, the greater the link equity and PageRank passed to the destination page. Overall, helpful and high-quality content are the likelier to receive backlinks from other webpages.
d. Internal Links
Internal links are hyperlinks that originate and point to different webpages on the same site. These links help visitors and search engines to navigate the site. It also allows search engines to understand the site’s structure and understand how its pages are related to one another.
e. Anchor Text
The anchor text is the clickable text used in an hyperlink. In this case, it is used in an external link. A descriptive and relevant anchor text helps Google understand the topic, context, and relationship between the referring and destination pages.
f. Content Freshness
Content freshness refers to how recently a page was published or updated. However, this ranking factor does not affect all webpages. Instead, it only affects webpages that appear for search terms visitors use when they require current information.
g. Content Relevance
Content relevance measures how well a page satisfies the user’s query. Google evaluates whether the content aligns with search intent and provides comprehensive coverage of the topic. Overall, highly relevant content is more likely to rank higher because it delivers value to searchers.
h. Content Usability
Content usability focuses on how easily users can consume and interact with a page. This includes readability, layout, mobile responsiveness, and visual clarity. Pages that are easy to use encourage longer visits and lower bounce rates, which positively influence rankings.
i. URL Structure
Google uses the URL structure to understand a page’s content. However, this is a minor ranking factor and is mostly relevant when Google discovers but is yet to access the webpage. Make sure to keep your URL structure clean and descriptive with relevant keywords.
j. Search History
Google sometimes uses a user’s search history to tailor the results page to them. This means Google may surface certain webpages to specific users when it decides that the user is interested in them.
k. Openness
Openness refers to a business’s operating hours. Google wants to refer visitors to businesses that are open at the time of search. So, it evaluates its index for businesses that are open and surfaces them on its local search results pages and local pack.
You may have observed that these confirmed ranking factors correlate with the four major types of SEO: on-page SEO, off-page SEO, technical SEO, and local SEO.
- On-page SEO: Optimizing the content and HTML elements on the webpage
- Off-page SEO: Building inbound links (backlinks) that point to the webpage
- Technical SEO: Optimizing the website’s code, server infrastructure, and technical elements
- Local SEO: Optimizing the page’s elements for location-based searches and local results pages
Overall, while the Google Search algorithm and ranking factors are generally unclear and can be open to guesses and speculations, these four types of SEO are well-known to a large extent.
So, when you optimize your site for them, you should expect that they would satisfy the Google Search algorithm and ranking factors and increase your chances of appearing on the Google search engine results page.
Google Algorithm Updates: How They Affect Ranking
When Google announces an update (either directly or through third-parties), we call such update a confirmed update. On the other hand, when Google does not announce the update, we call it an unconfirmed update.
For instance, Google announces major updates to its core algorithm about three or four times a year.
Google also announces major updates to its other algorithms and systems multiple times a year. These updates typically cover its spam, link spam, and review systems.
Sometimes, Google introduces entirely new algorithms to its ranking system. Two examples of such are the Hidden Gems algorithm update that surfaced under-recognized valuable content and the Helpful Content Update that promotes content written primarily for users rather than for SEO.
In many instances, Google even later ingests these new algorithms into its existing core algorithm.
These confirmed and unconfirmed algorithm updates can significantly impact the Google search engine results pages. Depending on their scope, even large and established sites can gain or lose substantial traffic overnight.
Within blogging circles, this sudden change is referred to as a “SERP volatility” (search engine results page volatility) and is often how bloggers detect unconfirmed algorithm updates. In some cases, bloggers have even used these volatilities to identify confirmed updates before they were officially announced by Google.
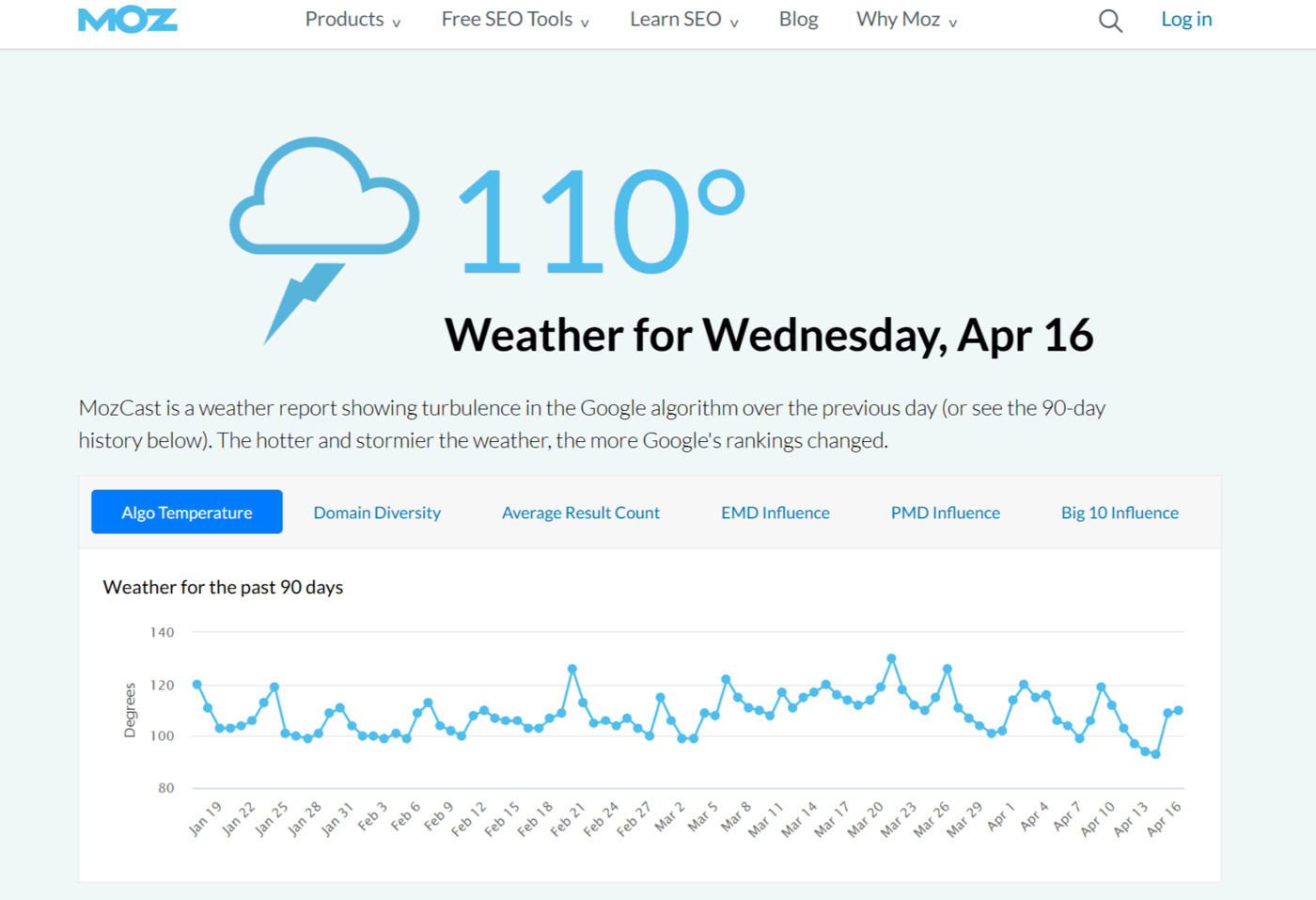
Overall, if you want to rank on Google, then it is important that you monitor these updates, understand their intent, and track their effects on your site. You can refer to this page to monitor confirmed and unconfirmed algorithm updates released by Google.
Google Search Algorithm Best Practices
If we were to sum up Google Search algorithm best practices in a single sentence, it would be: Create trustworthy, helpful, high-quality content and optimize it for SEO. Such content typically satisfies multiple Google ranking factors, which increases its chances of ranking on Google.
1 Create Helpful and High-Quality Content for People
Always create helpful high-quality content for people and not search engines. For the best results, such content should be original and offer new and unique insights into the topic instead of just repeating what already exists online.
This type of content often attracts visitors and natural backlinks, such as editorial links, which causes Google to improve its rankings on its results pages.
The content should also satisfy the search intent. Specifically, you should understand the type of search query and ensure to optimize the content for it.
With that said, the types of search queries include:
- Informational queries: Used by visitors looking to learn something
- Navigational queries: Used by visitors who want to visit a specific webpage
- Commercial queries: Used by visitors who are researching a product or service
- Transactional queries: Used by visitors who want to make a purchase
2 Optimize Your Site and Content for Multiple Types of SEO
Search engine optimization ensures your content is discoverable and accessible to users and search engines. To get the best results, ensure to optimize for the main types of SEO along with the additional types that are relevant to you.
The main types of SEO are on-page SEO, off-page SEO, and technical SEO. If you want to rank for local results, then optimize for local SEO. You should also optimize your images for image SEO and videos for video SEO.
If you should run an online store, make sure to optimize for WooCommerce SEO. If you want visitors and search engines to easily navigate through your taxonomies, such as your categories and tags, then optimize for taxonomy SEO. You should also learn to optimize your category pages.
If your content is intended for an international audience, then you should also optimize for international SEO. And if you are a large organization with multiple websites, then you should consider enterprise SEO.
Overall, there are multiple types of SEO and you will have to optimize for multiple types depending on the intent and scope of your site.
3 Demonstrate Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness (E-E-A-T)
Experience, expertise, authoritativeness, and trustworthiness (E-E-A-T) are the set of signals that Google uses to determine the quality and credibility of a webpage.
- Experience: The firsthand knowledge the content creator has on the topic
- Expertise: The skill, education, or specialized knowledge the author possesses on the topic
- Authoritativeness: The credibility of the author or website as a reliable source on the topic
- Trustworthiness: The degree to which the content and site are honest, safe, and reliable
Trustworthiness is the most important of the four, so even if your content demonstrates the other three but shows low trust, Google will rank your content low.
Overall, you should ensure that your content demonstrates E-E-A-T. This signals to Google that it is worthy enough to be displayed on the search results page.