With millions and millions of content getting uploaded to websites every day, search engines like Google crawl and index web pages based on the importance and value you provide in your content. Sometimes you might even don’t know whether your content has been indexed or not.
Fortunately, with Rank Math SEO you can now check the index status of pages/ posts/ CPTs from your WordPress site itself.
In this guide, we will discuss how to activate the URL Inspection API Integration feature in Rank Math. We will also cover how Rank Math helps you understand the index status of the pages and discover any underlying issues preventing the page from getting indexed.
Table of Contents
1 What is Search Console URL Inspection API?
Search Console URL Inspection API gives you the opportunity to inspect the data of your webpages directly from your WordPress site.
With the new URL Inspection API, you can now get a better understanding of how Google’s algorithm views your content, and get access to any index data that Google has for the specific URLs.
2 How to Enable URL Inspection API Integration in Rank Math?
As mentioned earlier, Rank Math helps you to have an overview of the index status of your content. But in order to take advantage of this feature, you’d need to follow the steps we walk you through in this tutorial:
2.1 Enable Analytics Module from Rank Math Dashboard
The first and foremost step is to enable the Analytics module from Rank Math. To do so, head over to WordPress Dashboard → Rank Math SEO and activate the Analytics module, as shown below.
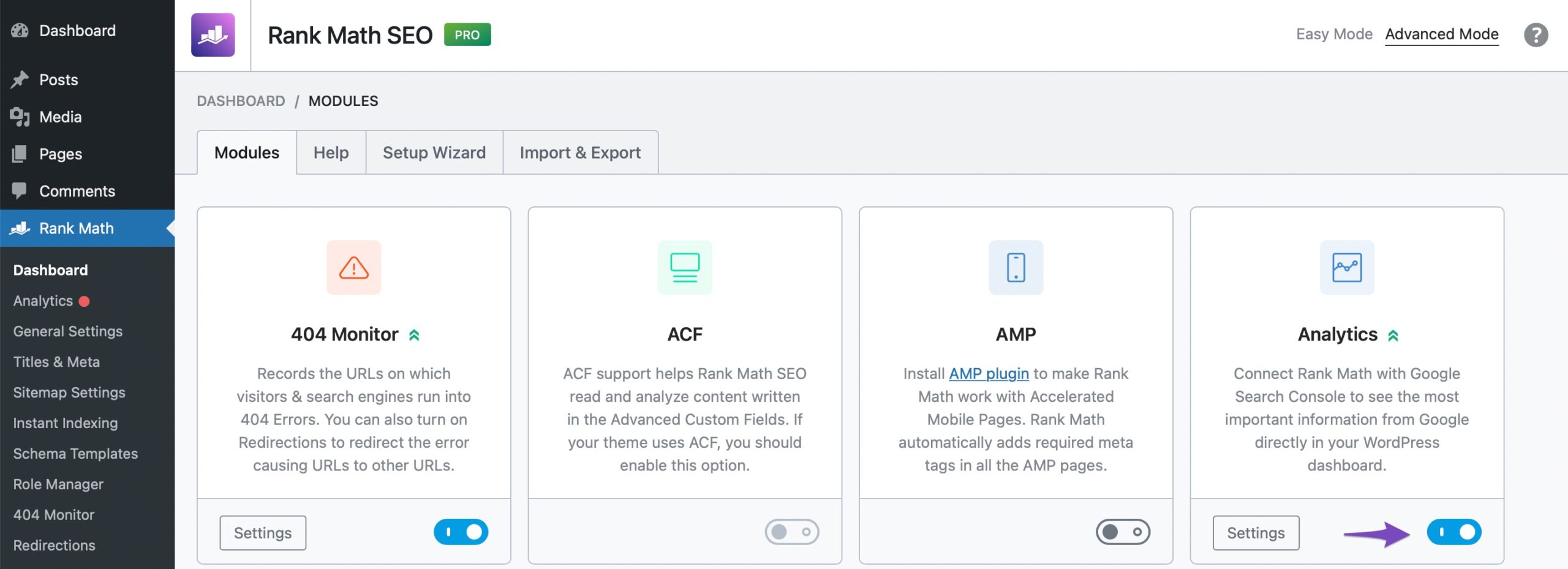
2.2 Connect Rank Math with Google Services
Now go to Rank Math SEO → Analytics and choose to Connect Your Rank Math Account if you haven’t already. You can select the email account you want to connect with Rank Math and then grant all the permissions to connect with your Google account. You can refer to our dedicated KB to connect your Google Account with Rank Math.
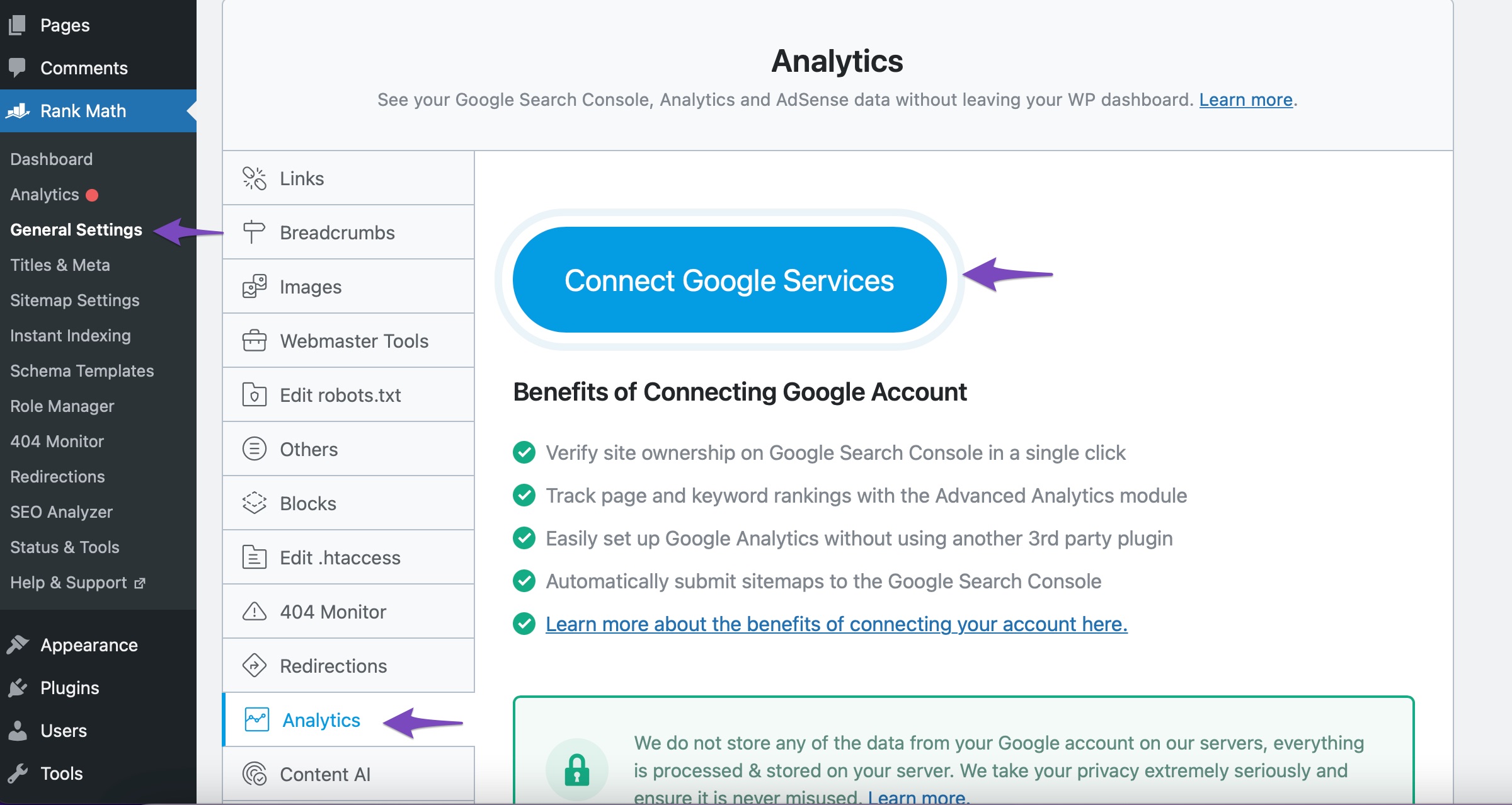
If the site is already connected with the Analytics module, then Rank Math will automatically fetch the Index Stats data for the first time.
2.3 Enable the Index Status tab Under Search Console
Then head over to Rank Math SEO → General Settings → Analytics and, under the Search Console settings, ensure that the option “Enable the Index Status tab” is toggled on.
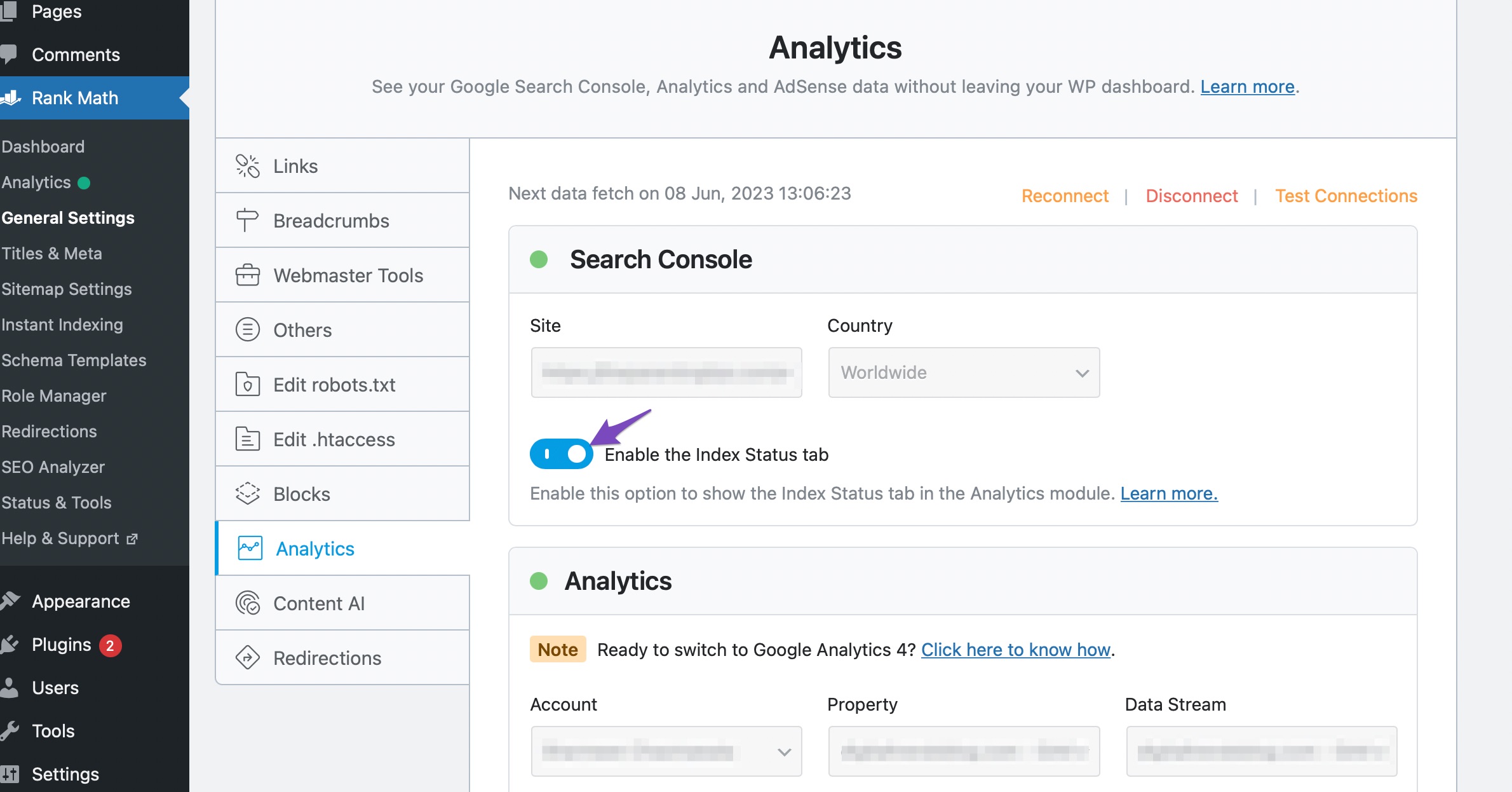
Then click the Save Changes button at the bottom of the page. Now that you have enabled the integration and saved the changes, Rank Math would start to fetch the data automatically, and you may need to wait for an hour to start seeing the initial results from the URL Inspection API.
This timeframe is only for the initial data fetch, and when this data gets updated, Rank Math will update them along with the data fetch schedule for Google Analytics and Google Search Console — which is different for Free (every 7 days) and PRO users (every 3 days).
| Features | Free | PRO |
| Max no. of URLs fetched in each schedule | 2000 URLs | 6000 URLs |
| Fetching Frequency | Every 7 days | Every 3 days |
| Top Statuses | ||
| Presence on Google | ||
| Filtering posts by Index Status | ||
| Overall Index Status | ||
| Indexing Allowed | ||
| Rich Results | ||
| Crawled As | ||
| Robots State | ||
| Page Fetch | ||
| Index Status Result | ||
| Last Crawl Date | ||
| Rich Results Errors |
Note: If the Enable the Index Status tab option is grayed out and unclickable, switch to a Chromium-based browser like Google Chrome and navigate to Rank Math SEO → General Settings → Analytics to toggle it on.
2.4 Using Search Console Index Status
Once the data is fetched, you can check Index Status under Rank Math SEO → Analytics → Index Status tab. Under this tab, you will get the real data/status of your pages as well as their presence on Google.
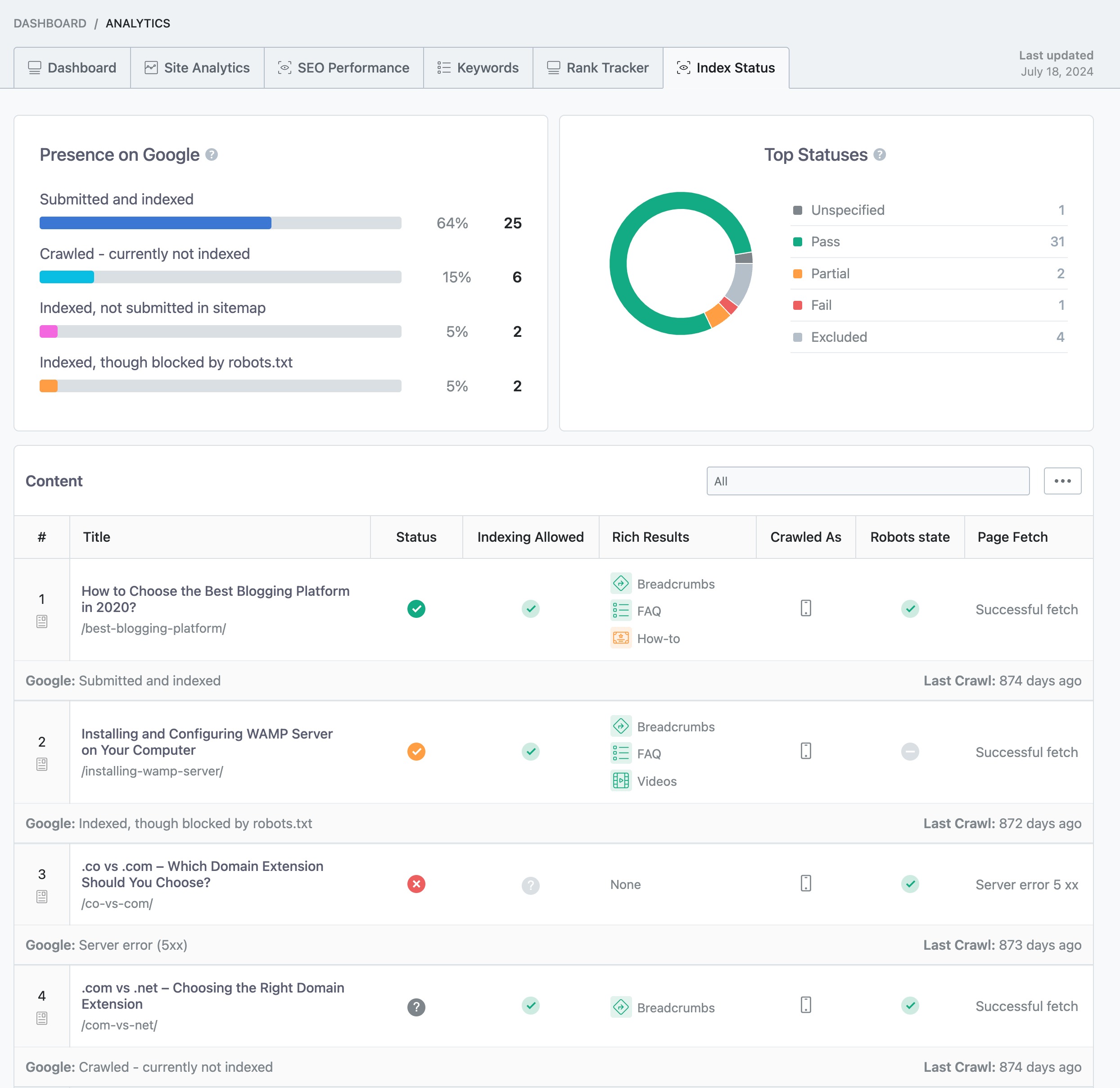
Let’s start by understanding the different widgets that Rank Math presents in the Index status tab.
3 Top Statuses PRO
The Top Statuses widget is available exclusively in the PRO version of Rank Math and shows a pie chart to give you an overview of the index status of the pages overall. On the right, Rank Math also lists down the number of pages under each status.
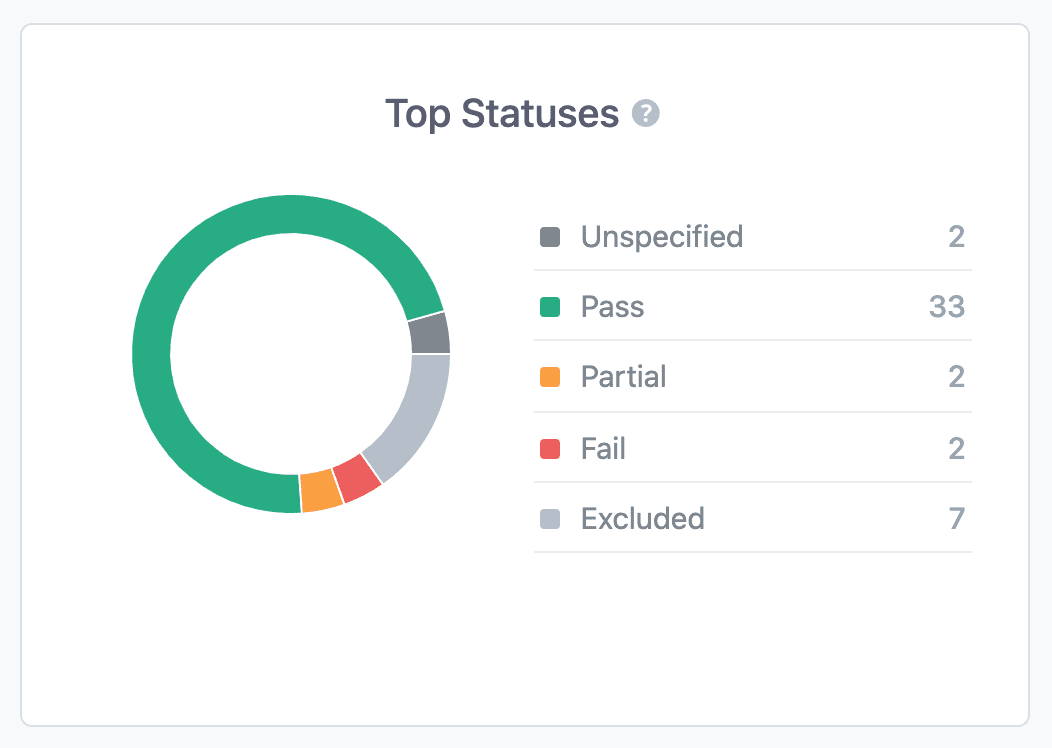
The following are the statuses shown in Rank Math and what they correspond to in Google Search Console:
Unspecified (No data available) – These are the data that are not available. Sometimes due to some technical glitches, it happens.
Pass (Indexed) – This status indicates the pages are valid and have been indexed. There are no issues or warnings.
Partial (Indexed) – A warning is a statement that something bad might happen if you ignore the warning signal. Here the URLs are submitted and pages are indexed. But, there can be an issue that you need to be aware of. You need to give utmost importance to these warning signals.
Fail (Not indexed) – This status says that your website has not been indexed due to an error. You can refer to the specific error type description on each page (which we’d cover shortly in this article) to identify what’s happening on the page and how you could fix it. In addition, you need to take care of these problems first.
Excluded (Not indexed) – This status includes those pages/ URLs that are deliberately excluded from indexing by you or those with duplicate content.
4 Presence on Google PRO
Rank Math gives an overview of the status reasons for a better understanding of the indexed and not indexed pages. The following chart displays the percentage and count of posts for each status reason:
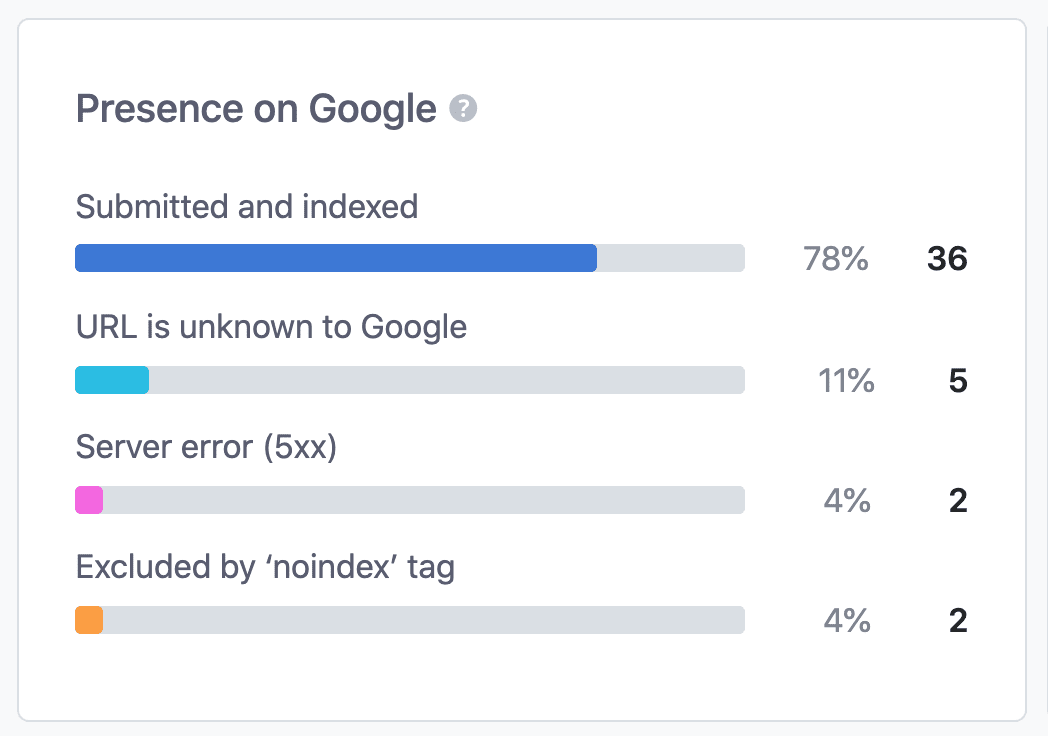
Here are some of the most common status reasons you’d come across.
Not indexed
Server error (5xx): This indicates that when Google attempted to crawl the page, your server returned a 500-level error, and if this continues, you should look into your server & fix the issue.
Redirect error: When Google attempted to crawl your page, it experienced a redirect error. This could be a long redirect chain, redirect loop, bad URLs in the redirect chain, or a redirect URL that exceeded the max URL length.
Submitted URL marked ‘noIndex’: Indicates that you’ve submitted a page for indexing; however, something in the page (noindex meta tag or HTTP header) instructs Google not to index this page.
Soft 404: Google believes this page has returned a soft 404 error (user-friendly 404 pages) and excluded this page from the Index. If you think this is incorrect, you’d need to look at the contents and layout of the page.
Blocked due to unauthorized request (401): This indicates that Googlebot was blocked from accessing the page by request for authorization. If this page is supposed to be indexed, you’d need to remove the authorization requirements for Googlebot.
Not found (404): Google has discovered this 404 page through some means, although it was not submitted directly. Google will attempt to crawl this page less often. In case this page is moved, then you can add 301 redirections.
Blocked due to access forbidden (403): Your server wrongly served the 403 forbidden access error when Google attempted to crawl the page. You should fix this issue or prevent this page from being crawled through the robots.txt rule or using noindex.
Blocked due to other 4xx issue: When Google attempted to crawl this page, the server returned a 4xx error, which is different from the ones we covered earlier.
Blocked by page removal tool: This page is blocked from indexing through a URL removal request.
Crawled – currently not indexed: Although you’ve submitted the page and Google has crawled the page in response, it has decided not to index the page for now. You’ll need to keep a note to work on these pages to ensure the page gets indexed.
Discovered – currently not indexed: This indicates Google has discovered the page, and even wants to crawl the page. But this was expected to cause an overload on the site, hence Google has rescheduled the crawl. As a result, Google may delay this crawl for several days after it has been discovered and crawl status would remain empty until then.
Alternate page with proper canonical tag: This indicates Google has recognized this page as a duplicate of a canonical.
Duplicate without user-selected canonical: Google has recognized this page and several other similar pages as duplicate, but none of them includes a canonical. We recommend explicitly marking the canonical page.
Duplicate, Google chose different canonical than user: This implies that you’ve marked this page as canonical but Google thinks another page could be a better choice for the canonical.
Page with redirect: This page includes a redirect, so Google excluded the page from Index.
URL is unknown to Google: This indicates that Google has not discovered this URL before and has not been crawled yet.
Excluded by ‘noindex’ tag: When Google crawled this page, it noticed a noindex tag and excluded this page from Index. If this noindex tag was added correctly, then no issues, but if it wasn’t supposed to be added, then you’d need to remove them.
Blocked by robots.txt: This page has been blocked from indexing through the robots.txt file on your site. If you think this is incorrect, then you should update the robots.txt rules.
Duplicate, submitted URL not selected as Canonical: These include duplicate URLs that are not explicitly marked as canonical. You can review these pages and consider adding the rel="canonical" tag to these duplicate pages.
Indexed
Indexed, though blocked by robots.txt: Implies that your robots.txt file blocked this page from crawling, but Google managed to index this page. Although Google respects the robots.txt file, if someone else links to this page, then Google can use that information to index the page.
Page indexed without content: This indicates that your page is added to Google’s index. But for some reason, Google could not read the page’s contents. It is possible that the page could be cloaked for Google or might not be in a format that Google couldn’t index.
Submitted and Indexed: Implies that the URL you have submitted through the sitemap has been indexed successfully.
Indexed, not submitted in sitemap: The URL was discovered by Google and indexed. However, this page was not submitted through a sitemap, and Google has discovered the page through other means.
Ideally, you’d want most of your article’s presence on Google as Submitted and Indexed, so they could rank for relevant keywords and start driving organic traffic for your site.
5 Index Status of Posts
Now that we have an overview of the site’s index status, let us dive deep into the status reasons of the individual pages and debug issues that prevent the page from getting indexed and its visibility in the search results.
The last section in the Index tab would list all posts, pages, and CPTs on your website and their corresponding index status.
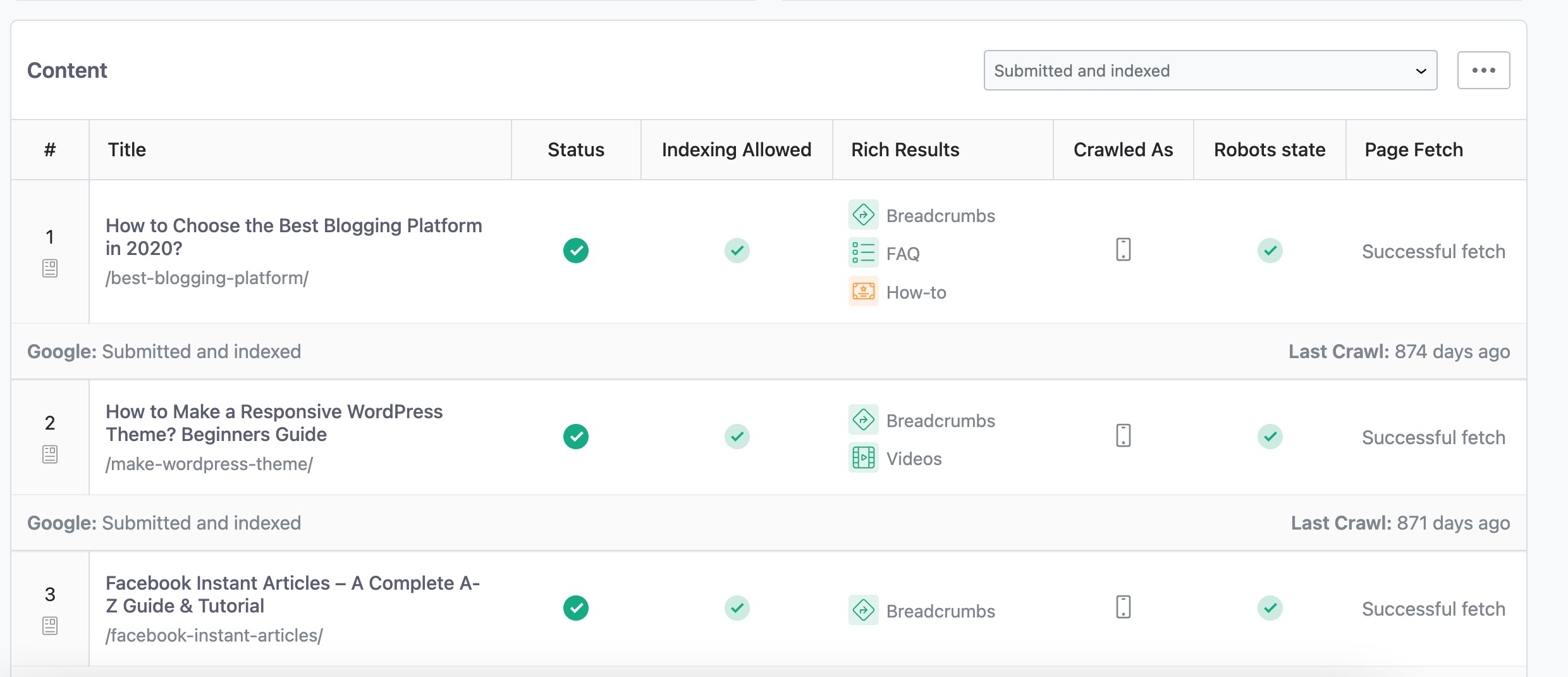
Before we analyze the individual posts’ index status, let’s look at a few options that Rank Math offers in handling a huge volume of data.
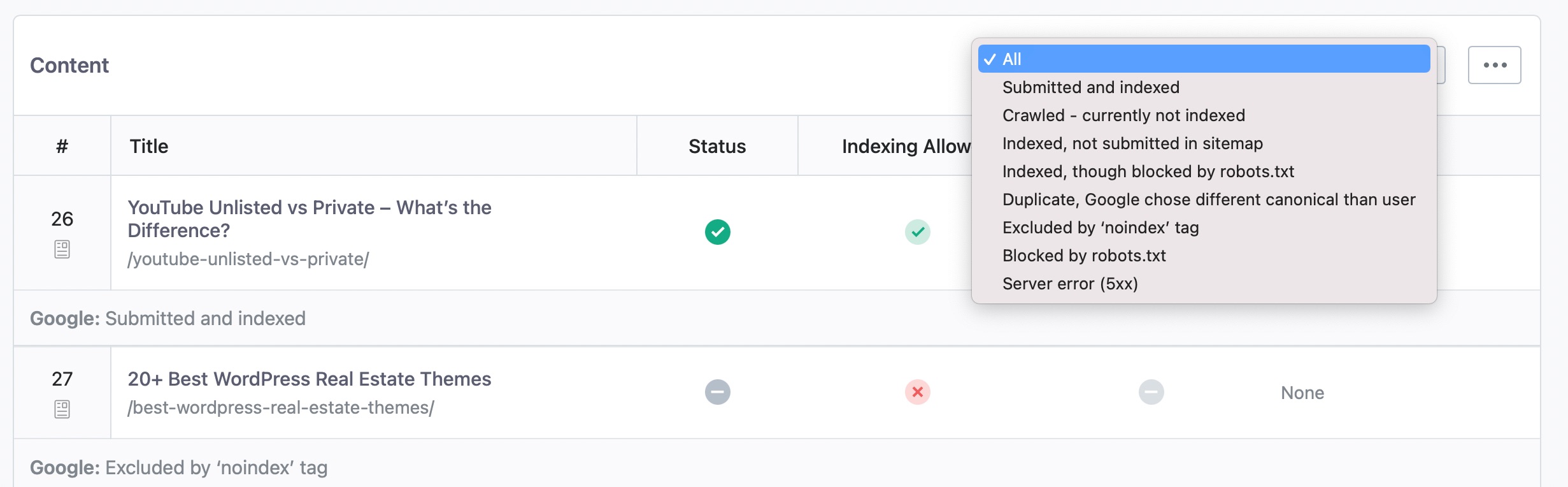
5.1 Filter by Index Status PRO
Rank Math PRO users can filter the posts by index status using this drop-down menu. When you select a specific status, you’ll be able to see all posts that share the same index status.
5.2 Adding/Removing Columns
You can also choose to display only the essential columns in the table to keep it clutter-free. To add/remove columns, click the three horizontal dots icon you see in the top-right and choose the columns you prefer.
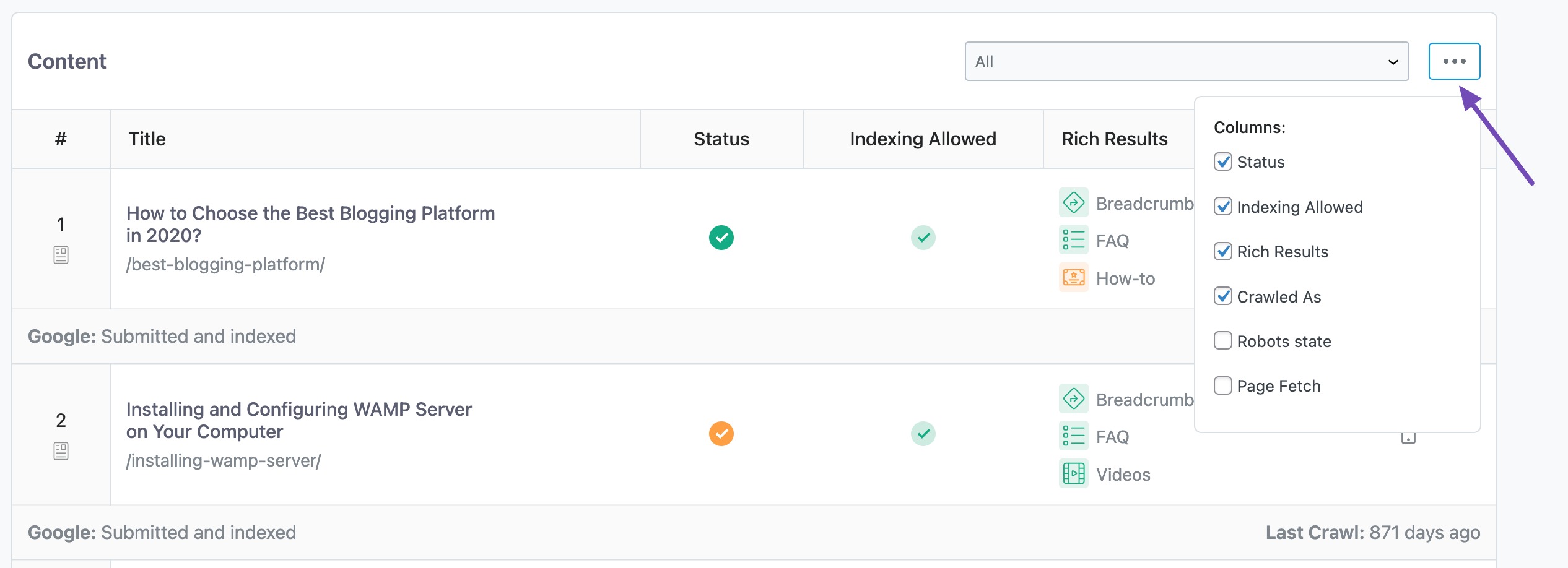
Here are the available columns:
- Status PRO – indicates the overall index status.
- Indexing Allowed – indicates whether the URL is marked with the index or noindex directive.
- Rich Results – indicates the rich snippets Google has detected for the page.
- Crawled As PRO – indicates the user agent Google crawled this page with (mobile or desktop)
- Robots State PRO – whether the page is blocked for crawling or not.
- Page Fetch – indicates whether Google could retrieve your page from the server.
Note: The columns Status, Crawled As, and Robots state are available to select only in the PRO version of Rank Math.
5.3 Submit Post for Indexing
If you’ve installed and configured the Instant Indexing for Google plugin, then Rank Math will display an option beside the pages yet to be indexed on Google.
Simply click the Submit now with Instant Indexing option as shown below, and Rank Math will get your pages submitted to Google using the Instant Indexing API to get your pages indexed.
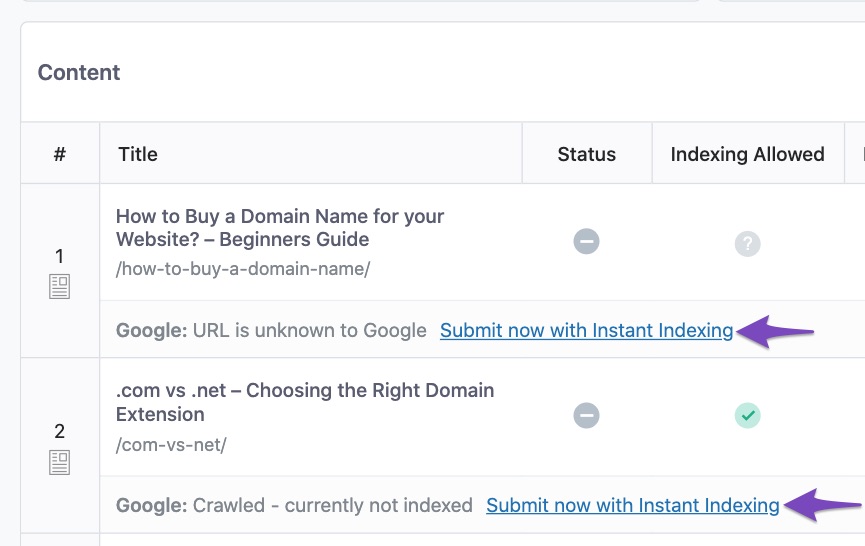
Refer to our dedicated blog post to set up the Instant Indexing plugin on your website.
5.4 Color Codes
To make sense of the various indexing metrics, Rank Math presents all the data in the table with a color-code so you could quickly grasp the status of each page. The data is color-coded as follows:
- A green stamp with a tick means Pass
- A orange stamp with a tick means Partial
- A red stamp with a X means Fail
- And a gray stamp with a question mark means Unspecified
6 Index Status Result PRO
Now Rank Math PRO users can dive deep into each post’s indexing metrics and results as they click the individual post. Here is what the result would look like:
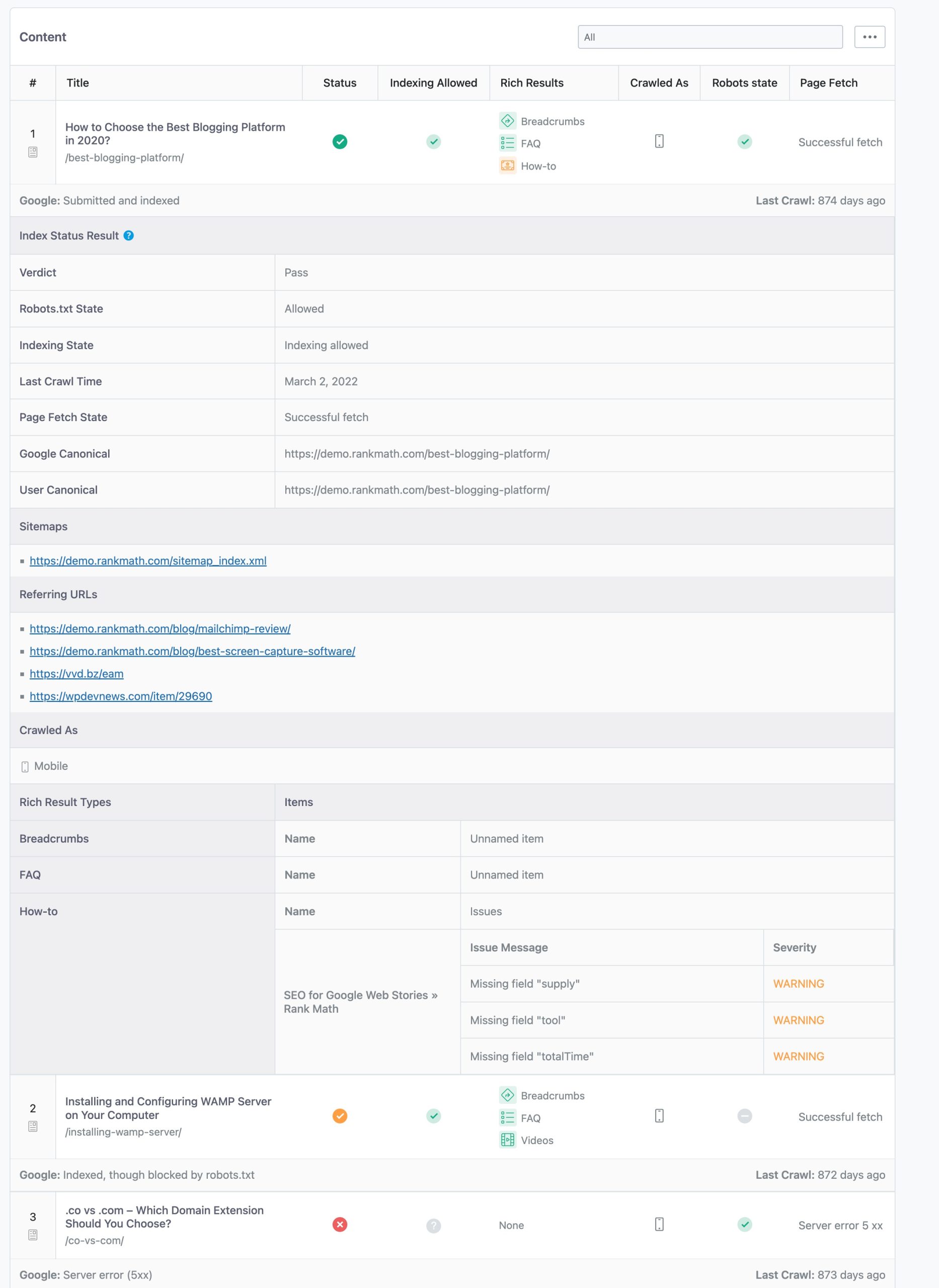
Note: Before we look into the data, please note the data provided URL Inspection API dates from the time when Google indexed your page or last tried to index your page. If you’re looking for the current status of the URL, you’ll need to use the Test Live URL feature in Google Search Console.
6.1 Verdict
This provides information on whether the submitted page is indexed or not.
PRO Tip: Assuming you want to get the page indexed and rank them for targeted keywords, you’d need to start looking into the pages that are not indexed and identify the underlying issues. Once these issues are fixed, you can validate these pages with a live URL test in Search Console.
6.2 Robots.txt State
This indicates whether or not the page is blocked to Google by a robots.txt rule. Depending on whether your robots.txt restricts the crawling of this page, you’d see one of the three values:
- Unspecified – An unknown robots.txt state because the page wasn’t fetched or found or because robots.txt itself couldn’t be reached.
- Allowed – The page is allowed to be crawled by the robots.txt rules.
- Disallowed – The page is not allowed to be crawled by the robots.txt rules.
PRO Tip: To identify the exact robots.txt rule preventing the page from being accessed, you can use the robots.txt tester and run a test as Googlebot. Once you’ve identified the issue, you can change the robots.txt file using Rank Math.
6.3 Indexing State
The indexing state shows whether or not the page blocks indexing through a noindex meta tag or HTTP Header. The result could be any of the four below-mentioned values:
- Unspecified – Unknown Indexing Status of the URL.
- Indexing Allowed – Indexing is allowed for the submitted URL.
- Blocked by Meta Tag – Indexing not allowed, ‘noindex’ detected in ‘robots’ meta tag.
- Blocked by HTTP Header – Indexing not allowed, ‘noindex’ detected in the ‘X-Robots-Tag’ http header.
Note: If your pages are incorrectly blocked with noindex robots meta tag, then follow these steps to remove the noindex meta tag.
6.4 Last Crawl Time
It shows the last time this URL was crawled by Google using the primary crawler. This result would not be available if the page has not been crawled successfully yet.
PRO Tip: If your page has not been crawled recently, then you can help Google understand the importance of this page by improving the quality of this page, gaining backlinks, and linking internally to this page from other articles.
6.5 Page Fetch State
The Page Fetch state indicates whether Googlebot was able to retrieve the page from your server or not. The value shown here could be one of the following:
- Unknown fetch state
- Successful fetch
- Soft 404
- Blocked by robots.txt
- Not found (404)
- Blocked due to unauthorized request (401)
- Server error (5xx)
- Redirection error
- Blocked due to access forbidden (403)
- Blocked due to other 4xx issue (not 403, 404)
- Internal error
- Invalid URL
Note: Ideally, you want Google to fetch the page successfully. But, if you see any other error, you need to troubleshoot what causes this error. In case you’re facing any issues or need any help in fixing these issues, we’re always here to help.
6.6 Google Canonical
Google uses the canonical URL to display the preferred version of the page on the search results. While you can explicitly declare the canonical URL of the page, Google can decide not to go with them and select a canonical on their own.
This field indicates the Canonical URL Google has selected for the page. If this page was not indexed, then this result will not be available.
6.7 User Canonical
This field indicates the canonical URL you’ve declared on the page. If the page does not include any canonical tag, this result will be unavailable.
However, if you’re using Rank Math, this is unlikely, as Rank Math would automatically add self-referencing canonical tags for all pages that are set to index (unless you set custom canonicals)
6.8 Sitemaps
This result includes any known sitemaps that point to this page. Having said that, this result includes only the sitemaps submitted to Google using the search console or listed down in the robots.txt file, and any sitemap discovered through other means would not be listed.
PRO Tip: We recommend having an XML Sitemap for your site, as it helps you to let Google know all the indexable pages on your site. If you’ve configured the Analytics module of Rank Math, then Rank Math will automatically submit your sitemap to Google.
6.9 Referring URLs
Here you can find URLs that Google possibly used to discover this page. The referring page might directly have a link to this page or through a chain of linked pages.
If the page you’re inspecting does not display any referring pages, it only means that the referring pages may be inaccessible or the URL Inspection API could not pull this information for now.
6.10 Crawled As
This includes the primary crawler (desktop or mobile) that Google has used to crawl the page.
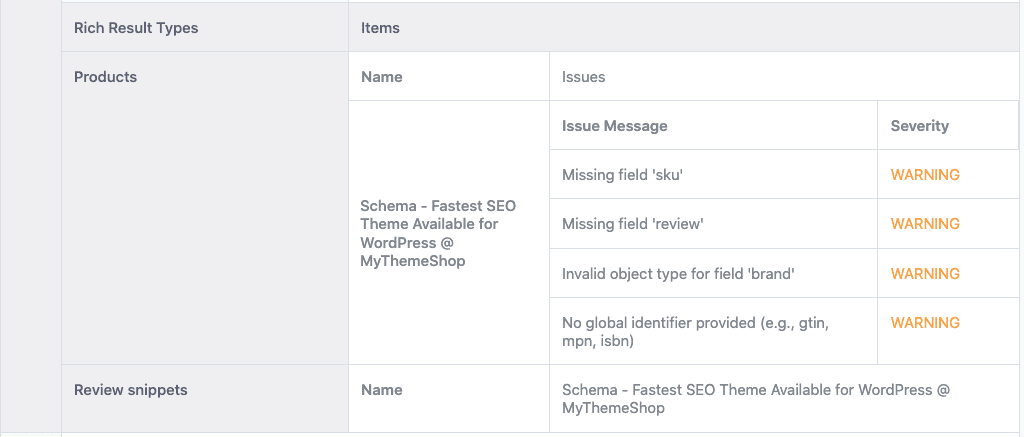
6.11 Rich Result Types
Rank Math lists down all the rich results that Google detected for the page and any Schema errors on the page. As a matter of fact, the Schema errors that you see here are the exact feedback that Google provides in the Rich Results Test.
If no rich results are found, then you will see it as absent.
7 Frequently Asked Questions
How can I integrate Rank Math with Google Search Console URL Inspection API?
Rank Math offers one-click integration with Google Search Console URL Inspection API. Head over to Rank Math SEO → General Settings → Analytics and toggle on Enable the Index Status tab under Search Console settings. Click Save Changes.
In case, you haven’t connected Rank Math with Google Account, you’ll need to connect first before integrating.
How many URLs can I fetch?
The URL Inspection API includes a daily usage limit of 2000 queries per day. So in the free version, Rank Math fetches a maximum of 2000 URLs, and in the PRO version, Rank Math fetches a maximum of 6000 URLs (when the posts on the site are more than 2000) by scheduling the fetching over a period of 3 days.
Can I test the indexability of a live URL?
No, the URL Inspection API provides the status of URLs dating from the time when Google indexed the page or attempted to index the page. It could not be used for inspecting the current status of a URL.
Why is my URL not ranking, even if it is marked as ‘Submitted and Indexed’?
To make it clear, a page getting indexing doesn’t necessarily mean it is also ranking for the targeting keywords. Google takes into account hundreds of factors before ranking these indexed URLs. The best you could do here is to ensure the page is of high quality and answers the searchers’ intent.
Does the URL Inspection API account for manual actions?
No, the URL Inspection API does not account for any manual actions. So before you start diagnosing your pages with the API, looking for the manual actions in your Google Search Console account is recommended.
What if the Index Status Tab does not update, displays zeros, or is missing some pages?
You can rectify this by re-fetching your analytics data from Google. To do so, update Rank Math to the latest version and head over to Rank Math SEO → Status & Tools → Database Tools and Rebuild Index for Analytics, as shown here.
Once done, head to Rank Math SEO → General Settings → Analytics → Analytics Database. Click Delete data. Then, click Update data manually, as shown here. Rank Math will then re-fetch your analytics data from Google.
Why is the Index Status option disabled/not working on my site?
Our plugin doesn’t fully support fetching data from domain properties. You’ll have to connect the URL-prefix property to fetch the data properly in Rank Math Analytics and Index Status. The URL-prefix property also helps keep your sitemap in sync with Google Search Console as we submit it automatically for you.
So if you’re using domain property, please reconnect your Google account from WordPress Dashboard → Rank Math SEO → General Settings → Analytics and connect the URL-prefix property. After that, you can try to enable the Index Status tab again.
8 Final Thoughts
That’s it! We hope this tutorial has helped you enable the URL Inspection API Integration feature in Rank Math.

If you have any doubts or questions related to this matter, please don’t hesitate to reach out to our support team. We are available 24×7, 365 days a year, and are happy to help you with any issues you might face.