Are you struggling with indexing issues on Google? It can be frustrating when your carefully crafted content doesn’t appear in search results. However, you’re not alone.
In this knowledgebase article, we’ll help you identify, fix, and validate common page indexing issues in Google Search Console.

Table Of Contents
-
Common Google Page Indexing Issues and How to Fix Them
- Not Found (404)
- Excluded by ‘noindex’ tag
- Server error (5xx)
- Page with redirect
- Soft 404
- Blocked due to access forbidden (403)
- Duplicate without user-selected canonical
- Alternate page with proper canonical tag
- Crawled – currently not indexed
- Blocked by robots.txt
- Duplicate, Google chose different canonical than user
- Blocked due to other 4xx issue
- Indexed, though blocked by robots.txt
- Page indexed without content
- Validating Indexing Fixes in Search Console
1 Common Google Page Indexing Issues and How to Fix Them
Before we start, you’ll want to identify these errors by logging in to your Google Search Console account and navigating to the Pages section. Then, ensure the “Not Indexed” tab is enabled, as shown below.
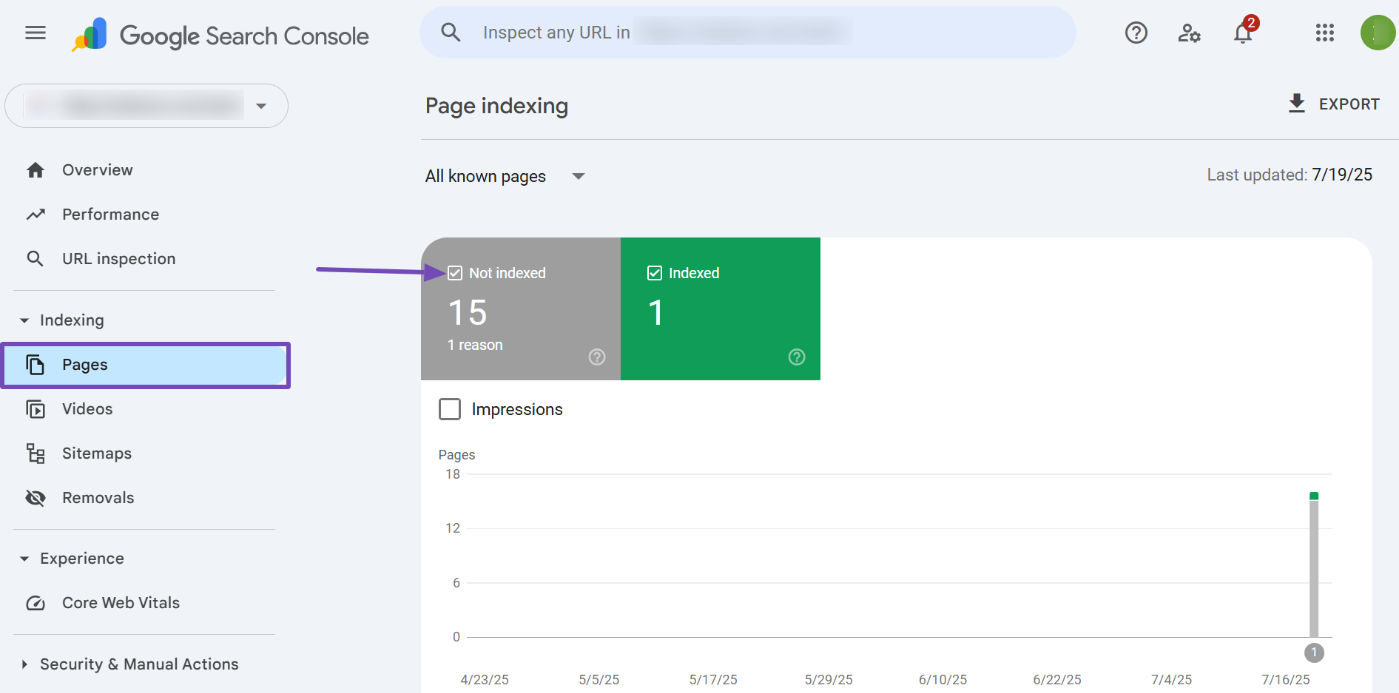
This will provide a detailed list of your page indexing issues.
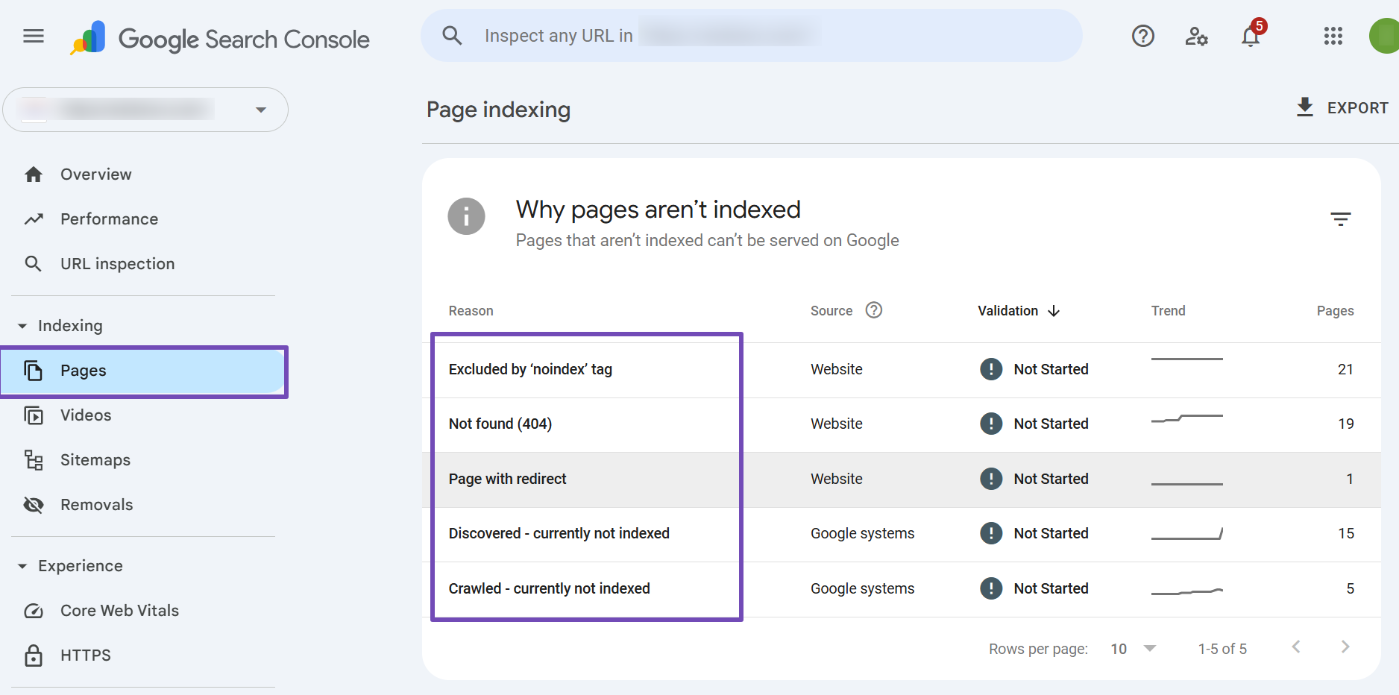
Let’s discuss the common indexing issues you might encounter and how to fix them.
1.1 Not Found (404)
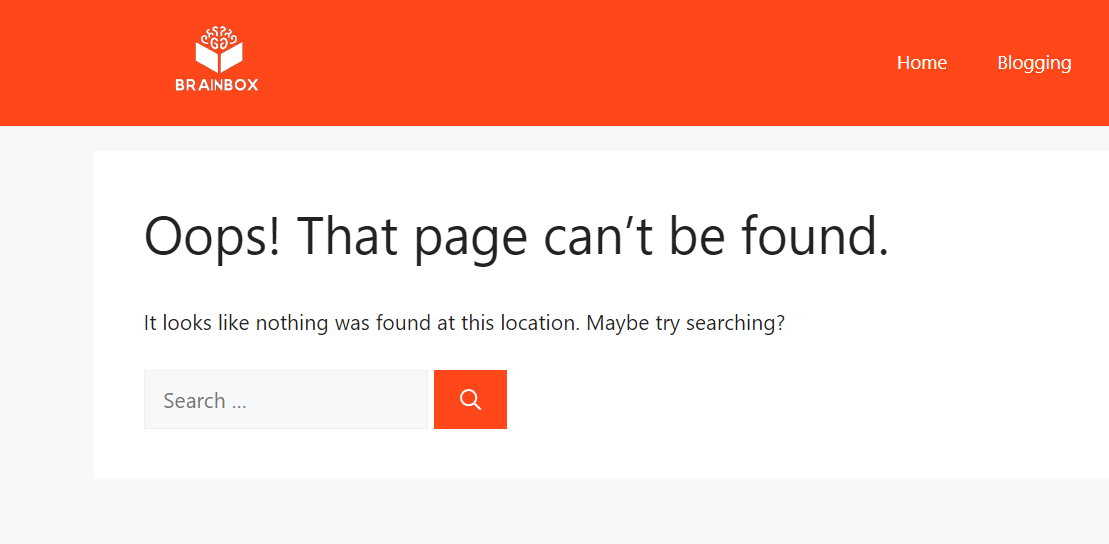
A “Not Found (404)” error occurs when a user or Googlebot tries to access a URL on your website that does not exist. This can happen if the page has been removed, the URL is incorrect, or broken links point to a non-existent page.
The error typically appears like this on most sites.
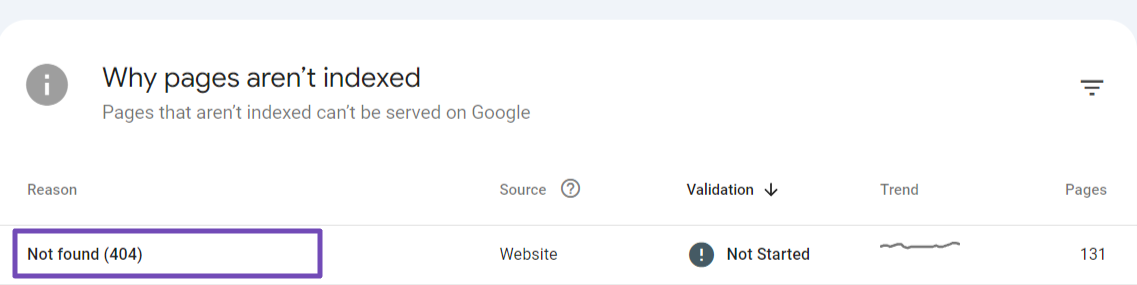
When accessing the “Pages” section in Google Search Console (GSC), the error message will be displayed.
Now, click on the error to identify the affected pages. Scroll down to the “Examples” section to see the pages where these errors occur.
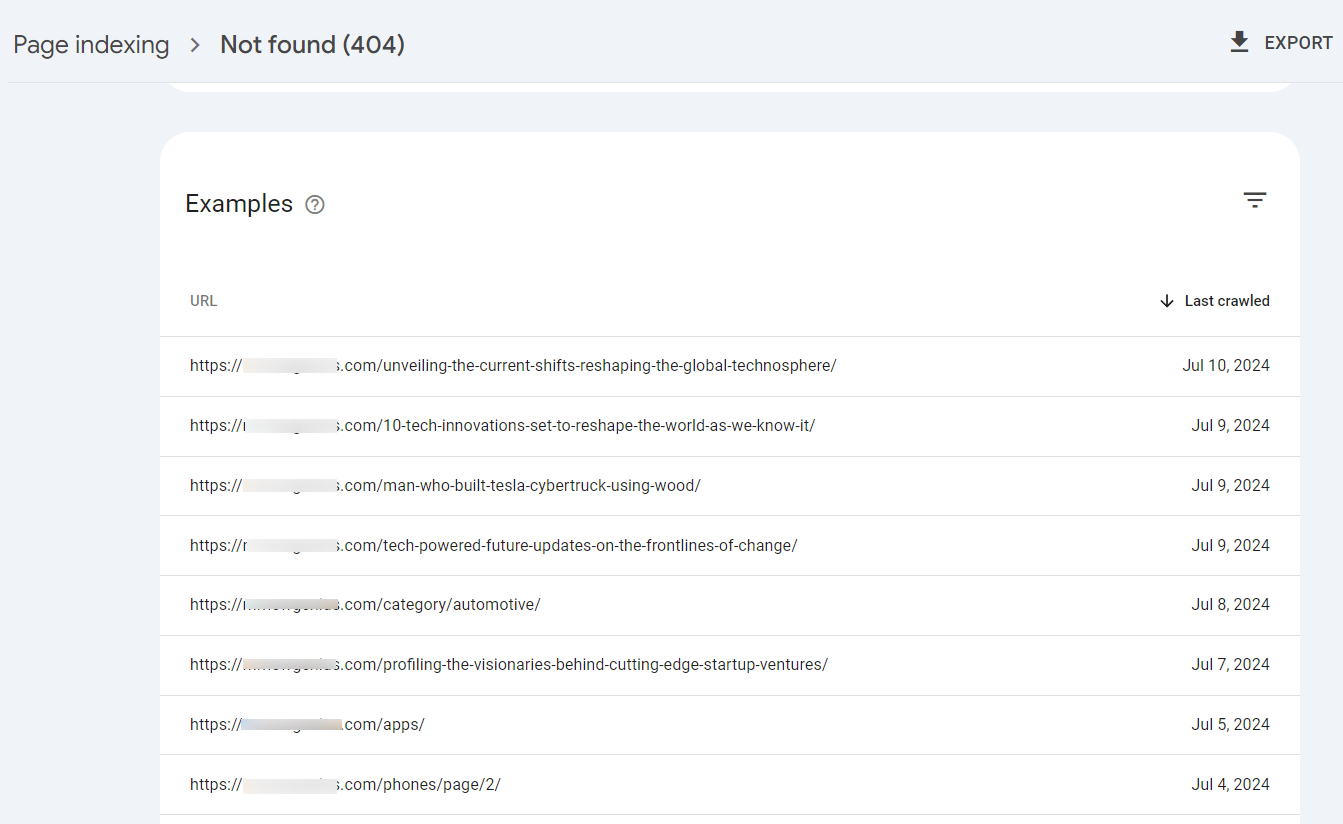
To fix the “Not Found (404)” error:
- Redirect Removed Pages: If the page has moved, create a 301 redirect from the old URL to the new one. This helps preserve any link equity from the old URL. Refer to our guide on how to do this.
- Fix Broken Links: Check internal and external links pointing to the missing page and update them accordingly. If possible, reach out to the sites linking to your deleted pages and request an update to the correct URL.
- Create a Custom 404 Page: Design a user-friendly 404 page that guides visitors to helpful content on your site. Include links to popular posts or a search bar to help users find what they want.
1.2 Excluded by ‘noindex’ tag
This error indicates that Google found a “noindex” meta tag on the page, instructing it not to include the page in its search index.
You may have purposefully added ‘noindex’ tags to non-essential pages or unintentionally, perhaps through a plugin or theme active on your site.

When you click on this error in your search console, it will reveal the pages on your site affected by the “Excluded by ‘noindex’ tag” error.
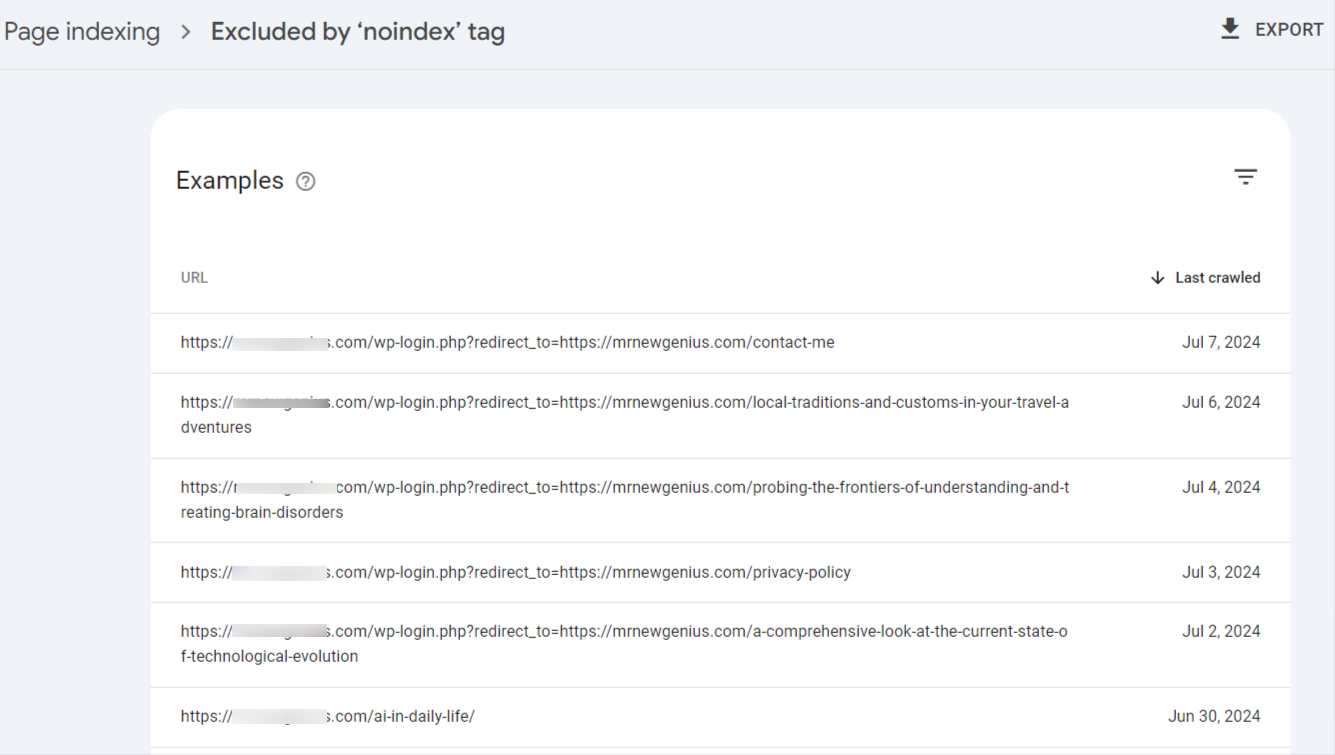
To fix the error:
- Remove the “noindex” tag: If you want the page to be indexed, remove the “noindex” meta tag from the page’s HTML code.
- Review plugins and themes. Look for those that might add the “noindex” tag to your site and disable or modify them accordingly.
For more details, refer to our guide on how to fix the “Excluded by NoIndex Tag” error in Google Search Console.
1.3 Server error (5xx)
The server error (5xx) indicates a general server-side issue preventing Googlebot from accessing your page.
This broad category encompasses various specific error codes, such as 500, 502, 503, etc., indicating different server problems.
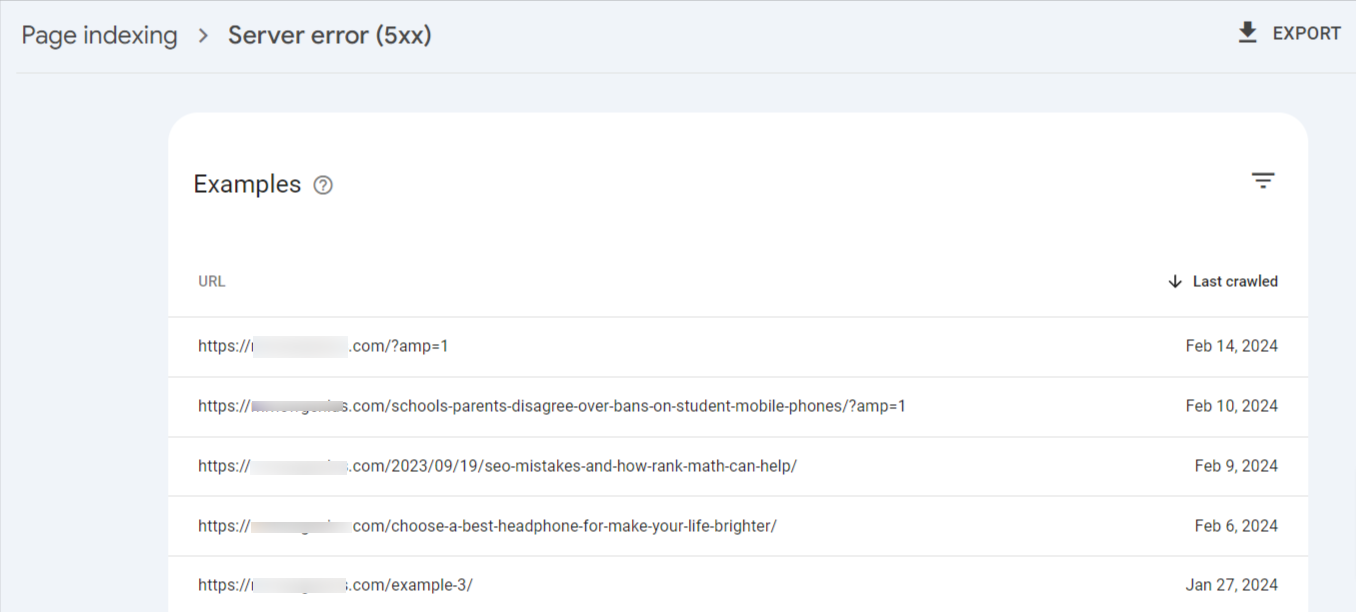
To help fix this error, follow these steps after detecting the affected pages:
- Review server logs: Analyze server logs to pinpoint the error and cause.
- Check for overload signs: Look for overload indications, such as slow response times or high CPU usage.
- Verify settings: Ensure you use the correct settings for your site’s PHP, database, and other relevant components.
- Contact hosting provider: If the issue persists, reach out to your hosting provider for support.
1.4 Page with redirect
A “Page with redirect” error in Google Search Console indicates that Googlebot has detected a redirect on a URL. However, the redirect may not be properly configured or be causing issues with crawling and indexing.
This can happen when you use 301 redirects, redirect loops, or temporary redirects (302) instead of permanent redirects (301).

In your search console, click on the error to see the affected pages.
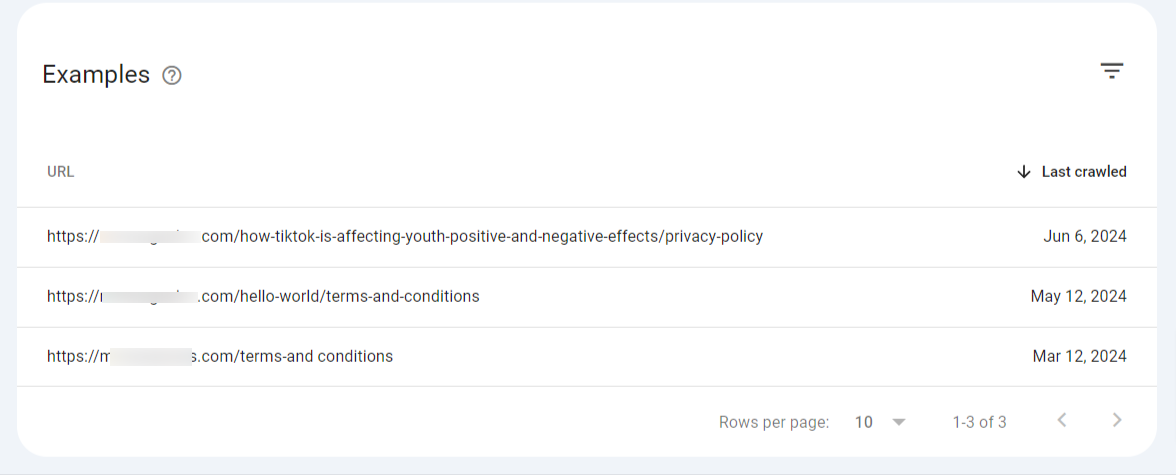
To fix the “Page with redirect” error, follow these tips:
- Simplify redirects: Minimize the number of redirects and ensure they are correctly configured to point to the final destination URL.
- Avoid redirect loops: Identify and fix any redirect loops by ensuring that redirects point to a final, crawlable URL.
- Use 301 redirects: If possible, replace temporary (302) redirects with permanent (301) redirects, which are more crawlable by Googlebot.
- Use canonical URLs: Specify a canonical URL for pages with redirects to help Googlebot understand the preferred version of the page.
For more details, refer to our guide on how to fix the “Page with redirect” error in Google Search Console.
1.5 Soft 404
A soft 404 is a deceptive error where a page returns a 200 OK status code (indicating success) but actually lacks substantial content or is irrelevant to the user’s search query.
Essentially, it’s a page that should have returned a 404 Not Found error but didn’t.

When you click on this error in your search console, it will reveal the affected pages.
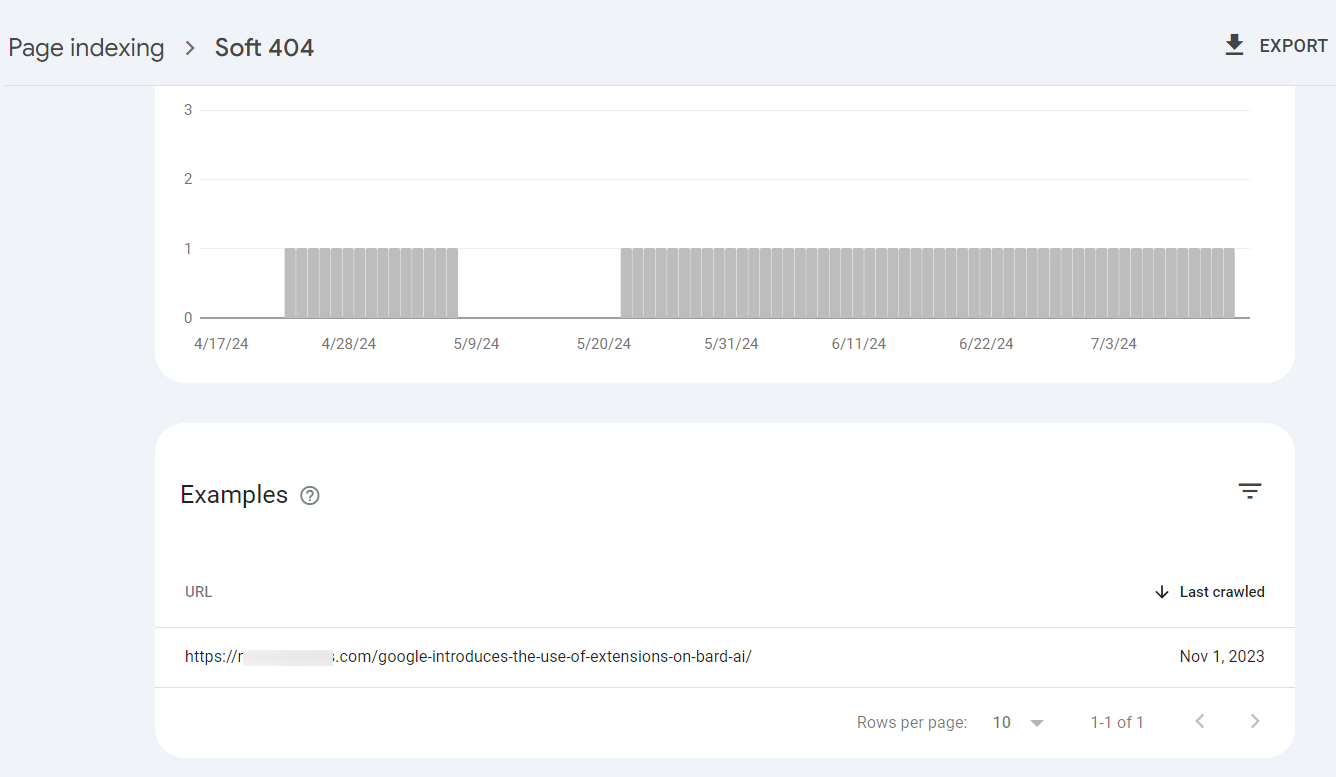
To fix soft 404 errors, follow these tips:
- Review flagged pages: Ensure that flagged pages contain substantial, relevant content and avoid placeholder or empty pages that provide little value to users.
- Configure 404 status codes: Set up pages that should return a “404 Not Found” status to actually return a “404” status code or create a 301 redirect to a more appropriate page.
For more details about the Soft 404 error and how to fix it, refer to our guide here.
1.6 Blocked due to access forbidden (403)
This error signifies that Googlebot was denied access to a page on your website. The server returned a 403 status code, indicating that the request is understood but forbidden.

So, you will need to click the error to reveal the affected pages.
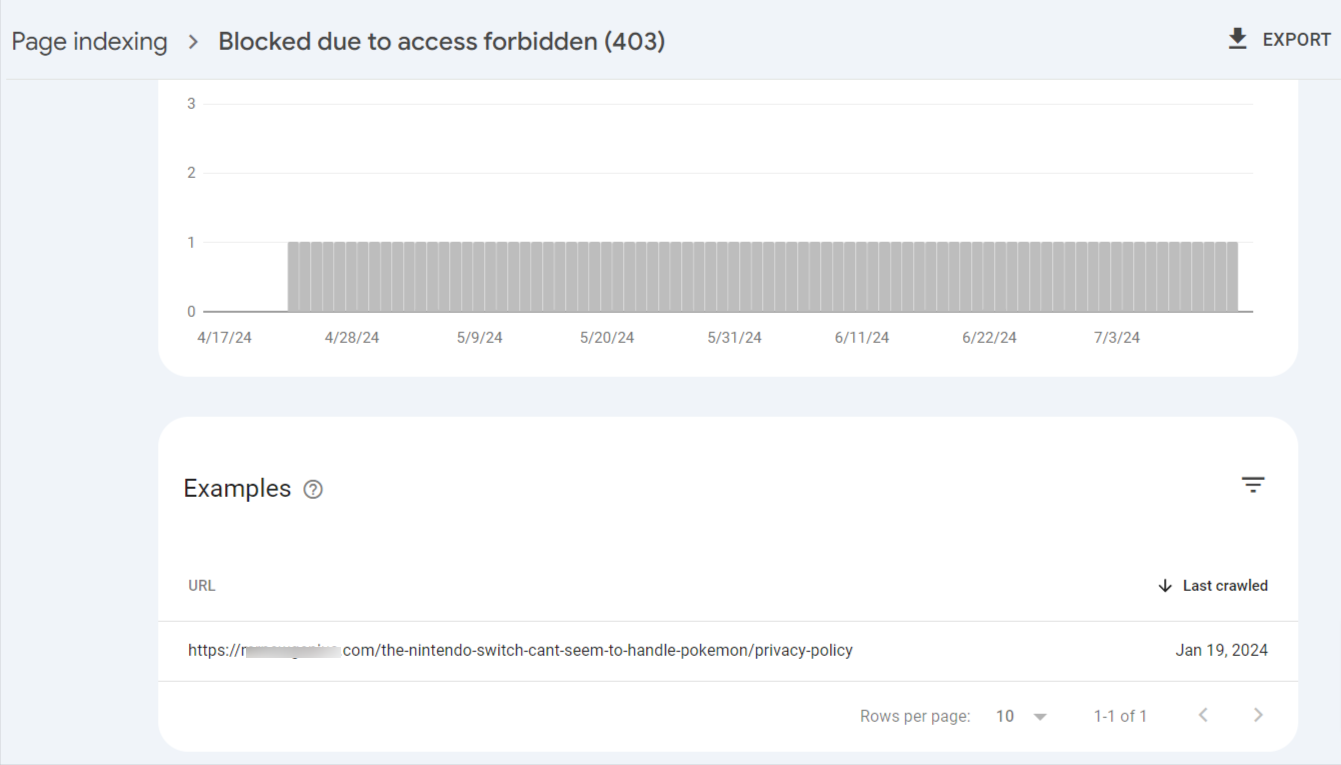
To fix this error, follow these tips:
- Check file permissions: Ensure correct permissions for files and directories accessible to the web server.
- Review firewall settings: Adjust firewall rules to allow Googlebot access.
- Inspect .htaccess file: Edit and fix corrupted
.htaccessfiles that control various functions of your site. - Check for IP address blocking: Ensure Googlebot’s IP addresses are not blocked.
To learn more about this error and how to fix it, refer to our detailed guide here.
1.7 Duplicate without user-selected canonical
This error occurs when Google identifies duplicate content on your website but can’t determine the page’s preferred (canonical) version.
This situation arises when multiple pages have similar or identical content, and you haven’t specified the original. Consequently, search engines struggle to decide which page to index and rank.
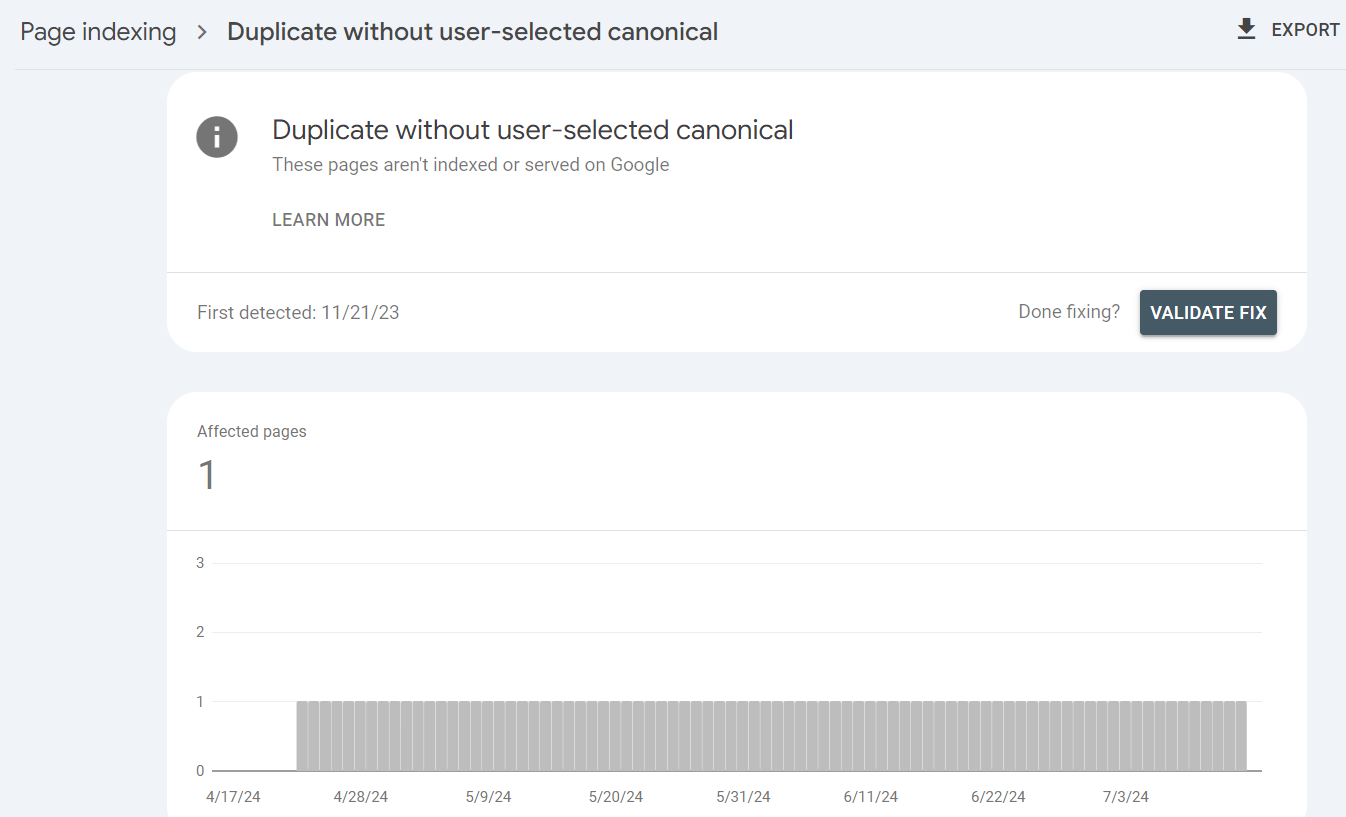
When you encounter this error in your Google Search Console, it’s crucial to take action. Here’s how to address the issue:
- Specify the Preferred Version: Add a canonical tag to the head section of duplicate pages. This informs search engines which page to prioritize.
- Consolidate Content: Where feasible, combine similar content into a single page to minimize duplication.
- Implement Redirects: Use 301 redirects to guide traffic from duplicate pages to the preferred version, preserving link equity.
For more information on how to fix the “Duplicate without user-selected canonical” error, refer to our detailed guide here.
1.8 Alternate page with proper canonical tag
The “Alternate page with proper canonical tag” status in Google Search Console indicates that Google has found two or more pages with the same canonical URL.

When you click on the error, it will display the pages causing the issue.
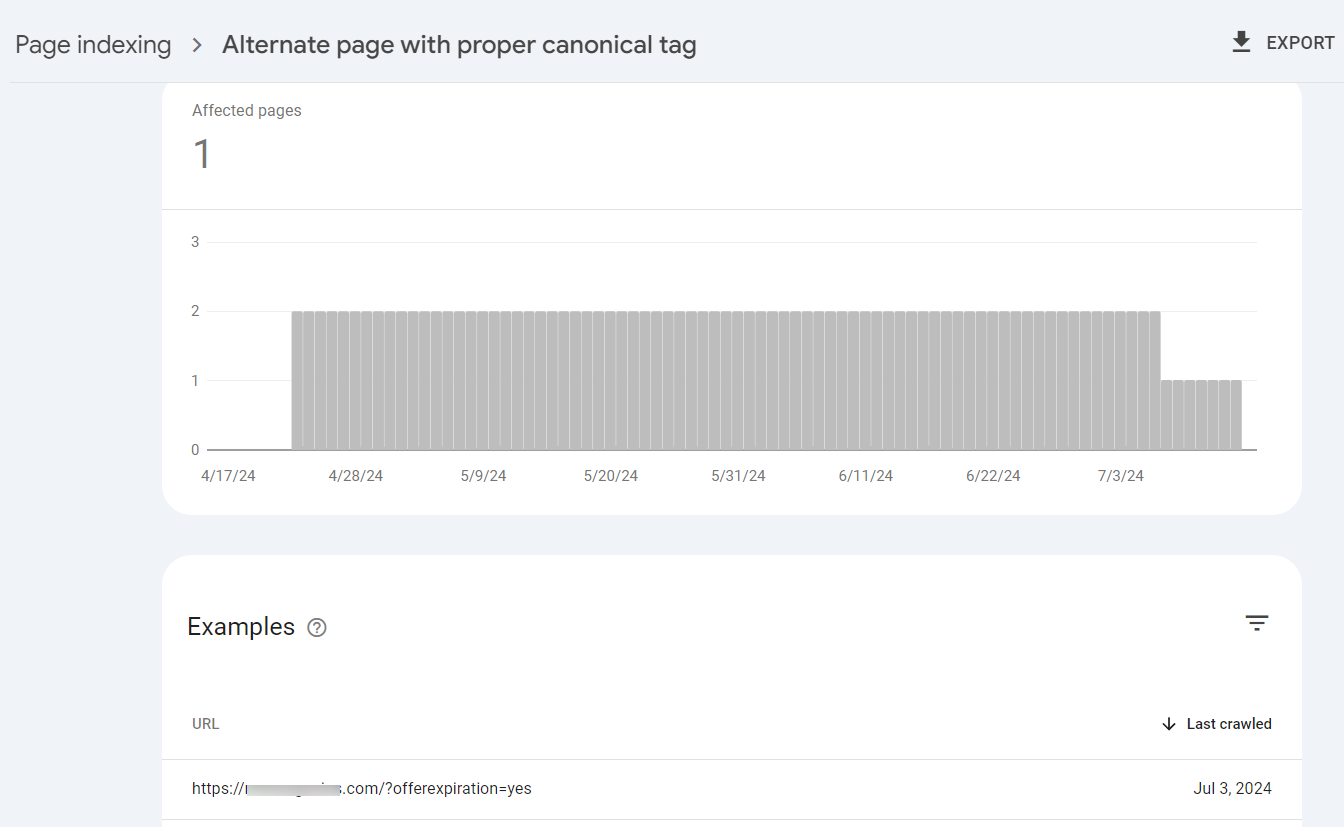
These pages have correctly implemented the canonical tag pointing to the same preferred version. Generally, this is a good thing. It means you’ve correctly addressed duplicate content issues by specifying the canonical version.
Google will likely prioritize the canonical page and exclude the alternates from the search index.
However, double-check that the canonical tag points to the correct page. There might be cases where the canonicalization is unintended or incorrect.
Learn more about the “Alternate page with proper canonical tag” error in Google Search Console here.
1.9 Crawled – currently not indexed
This status indicates that Google has crawled the page but has not yet indexed it. This can happen for various reasons, including quality issues, duplication, or Google simply needing more time to evaluate the page.

Before fixing this error, click on it to see the affected pages.
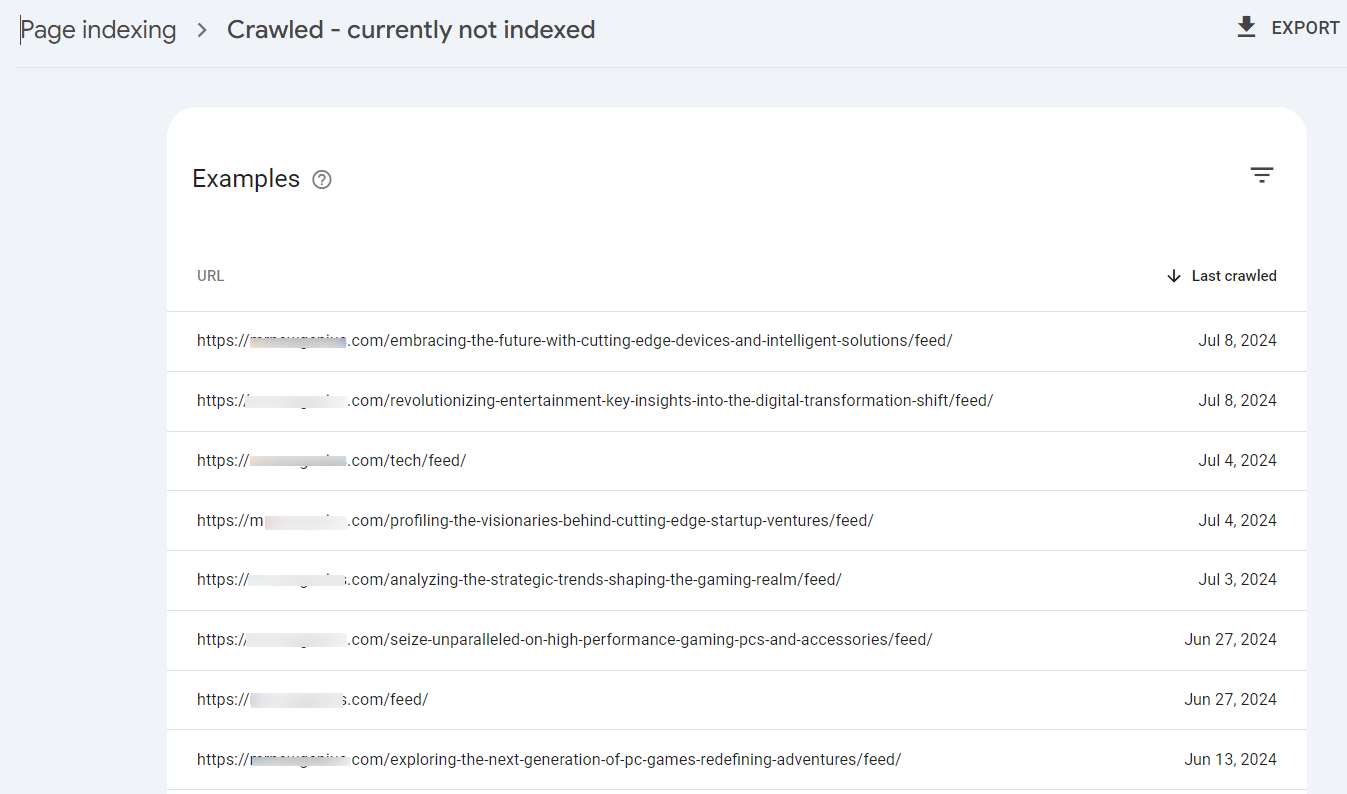
Now, go through these affected pages to determine if:
- It’s a new page, as Google needs more time to process and index new pages.
- Your content is unique, valuable, and comprehensive.
- It’s a thin, duplicate content, or needs a better user experience.
- You used strong internal links that lead to high traffic and relevant pages on your site.
For more details on how to resolve this error, refer to our guide here.
1.10 Discovered – currently not indexed
A “Discovered – currently not indexed” error in Google Search Console indicates that Google has found the page (discovered it through links or your sitemap) but has not yet crawled or indexed it.
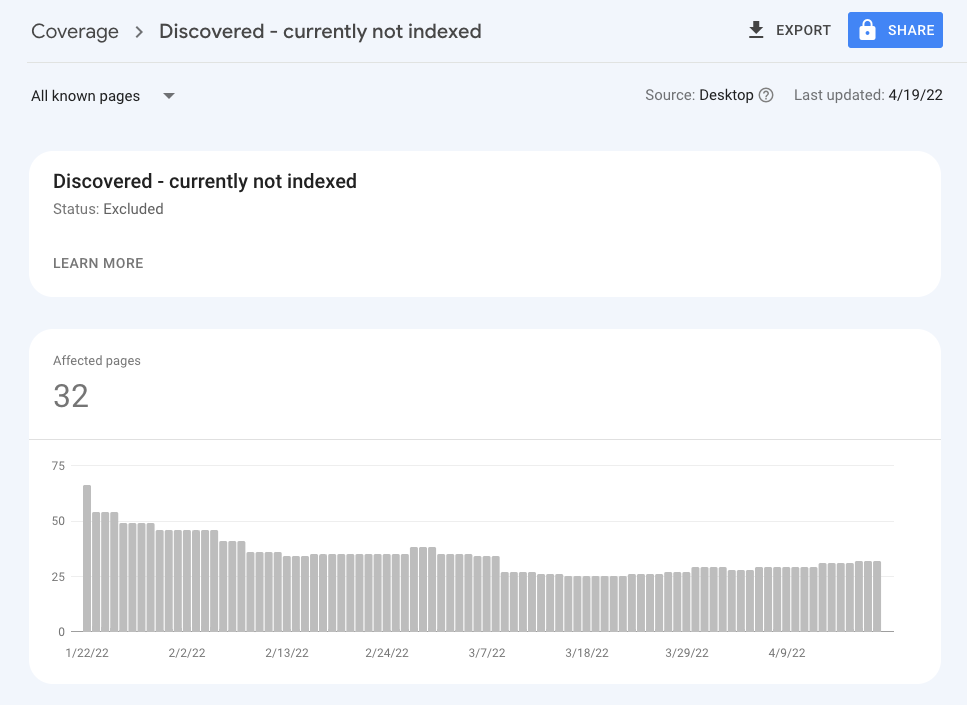
This can be due to various reasons, including prioritization issues, content quality, or technical problems. It could also mean that Google needs time to process these pages, as it will eventually crawl and index them.
While it’s normal for some pages to be “Discovered – currently not indexed,” many pages in this status might indicate underlying issues. To address this, follow these steps:
- Check for and fix any technical problems that might prevent crawling, such as robots.txt restrictions, slow load times, or broken links.
- Include internal links to the page from other high-traffic and relevant pages on your site.
- Avoid thin and duplicate content, and make sure the page provides significant value to users.
For more details on how to fix the “Discovered – currently not indexed” error, refer to our guide here.
1.11 Blocked by robots.txt
When Google identifies that a page is blocked by robots.txt, it means the file contains directives preventing Googlebot from crawling specific pages or sections of your site. This can happen intentionally or unintentionally.
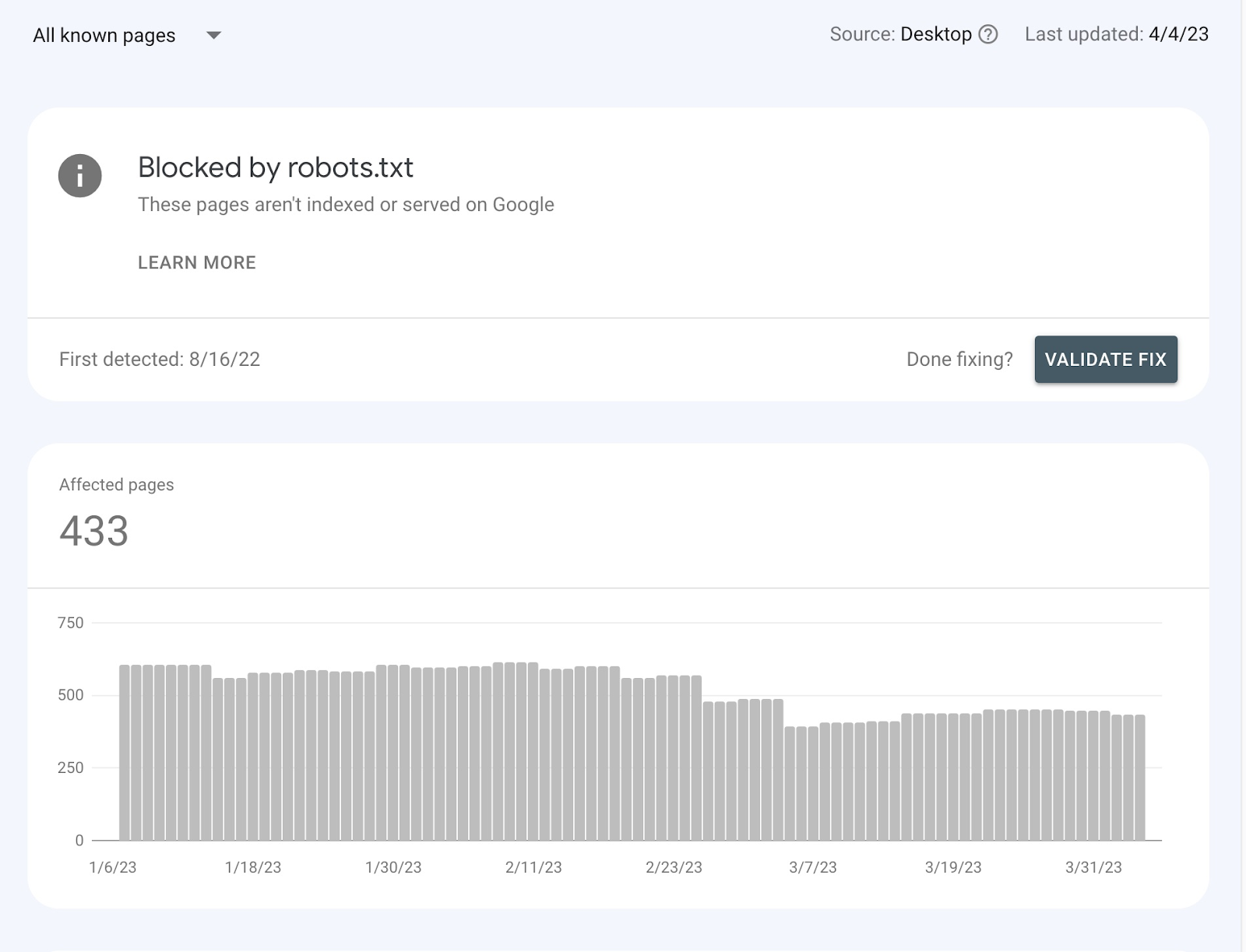
To resolve this error, follow these steps:
- Access your robots.txt file: Locate the file on your website (typically at yourdomain.com/robots.txt).
- Review the file: Carefully examine the content for any ‘Disallow’ directives blocking the page.
- Remove or modify directives: If you find relevant ‘Disallow’ directives, remove or adjust them to allow Googlebot access to the page.
For more details on fixing the “Blocked by robots.txt” error, refer to our comprehensive guide here.
1.12 Duplicate, Google chose different canonical than user
This error indicates a disagreement between you and Google regarding the preferred version (canonical) of a page with duplicate content.
You’ve specified a canonical URL using a rel="canonical" tag, but Google has chosen a different URL to represent the content in its search index.

When you encounter the ‘Duplicate, Google chose different canonical than user’ error in your search console, click on the error to identify the affected pages.
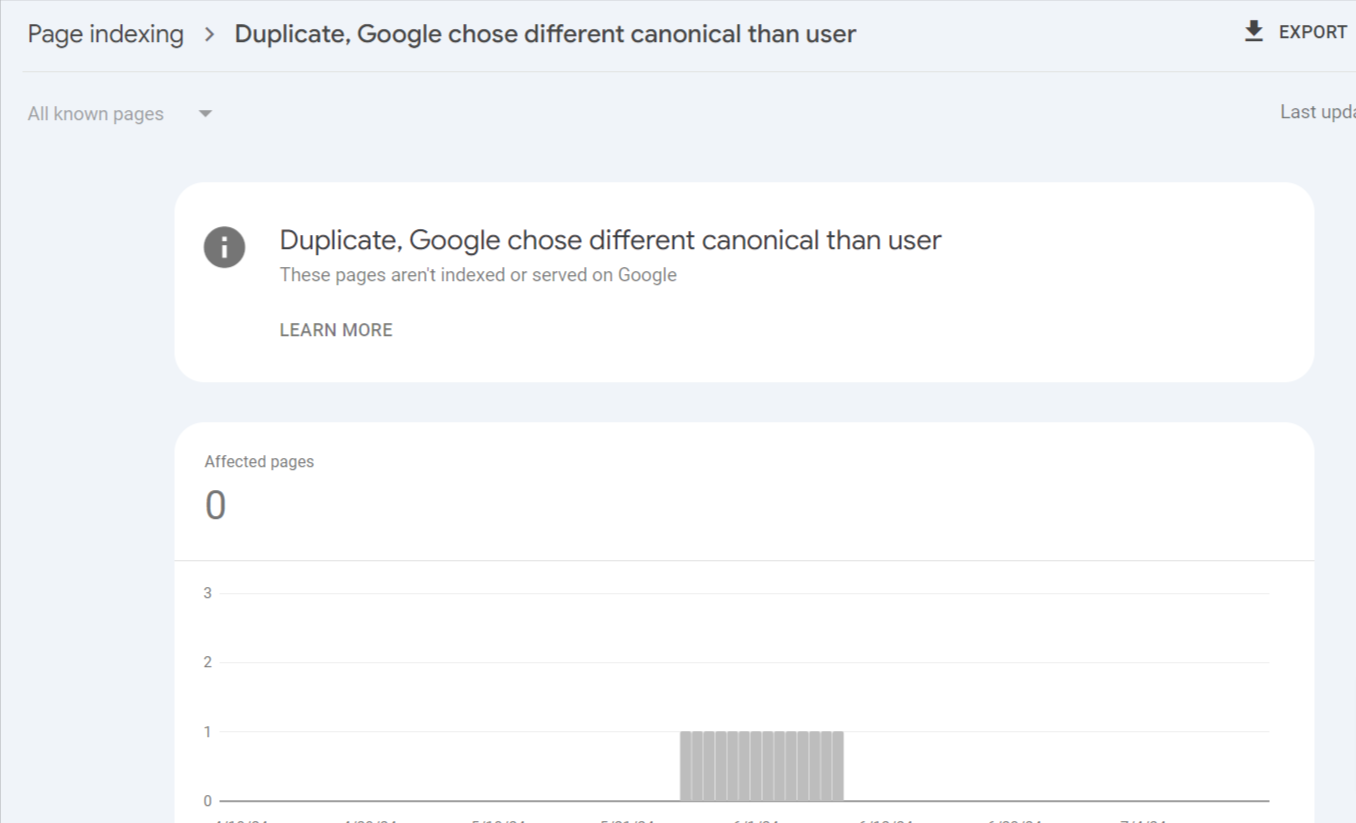
Once you’ve identified the pages, follow these steps:
- Double-check that the specified canonical URL is correct, accessible, and represents the best version of the content.
- Update or change the user-selected canonical if it is incorrect so it points to the most appropriate version.
- Implement 301 redirects from duplicate pages to the preferred canonical URL.
For more details about this error and how to fix it, refer to our detailed guide here.
1.13 Blocked due to other 4xx issue
This error message in Google Search Console indicates that Googlebot encountered a 4xx client-side error that isn’t a typical 404 (Not Found), 401 (Unauthorized), or 403 (Forbidden).
These “other 4xx” errors prevent Googlebot from accessing and indexing the page.

When you encounter this error, click on it to discover the pages triggering the issue.
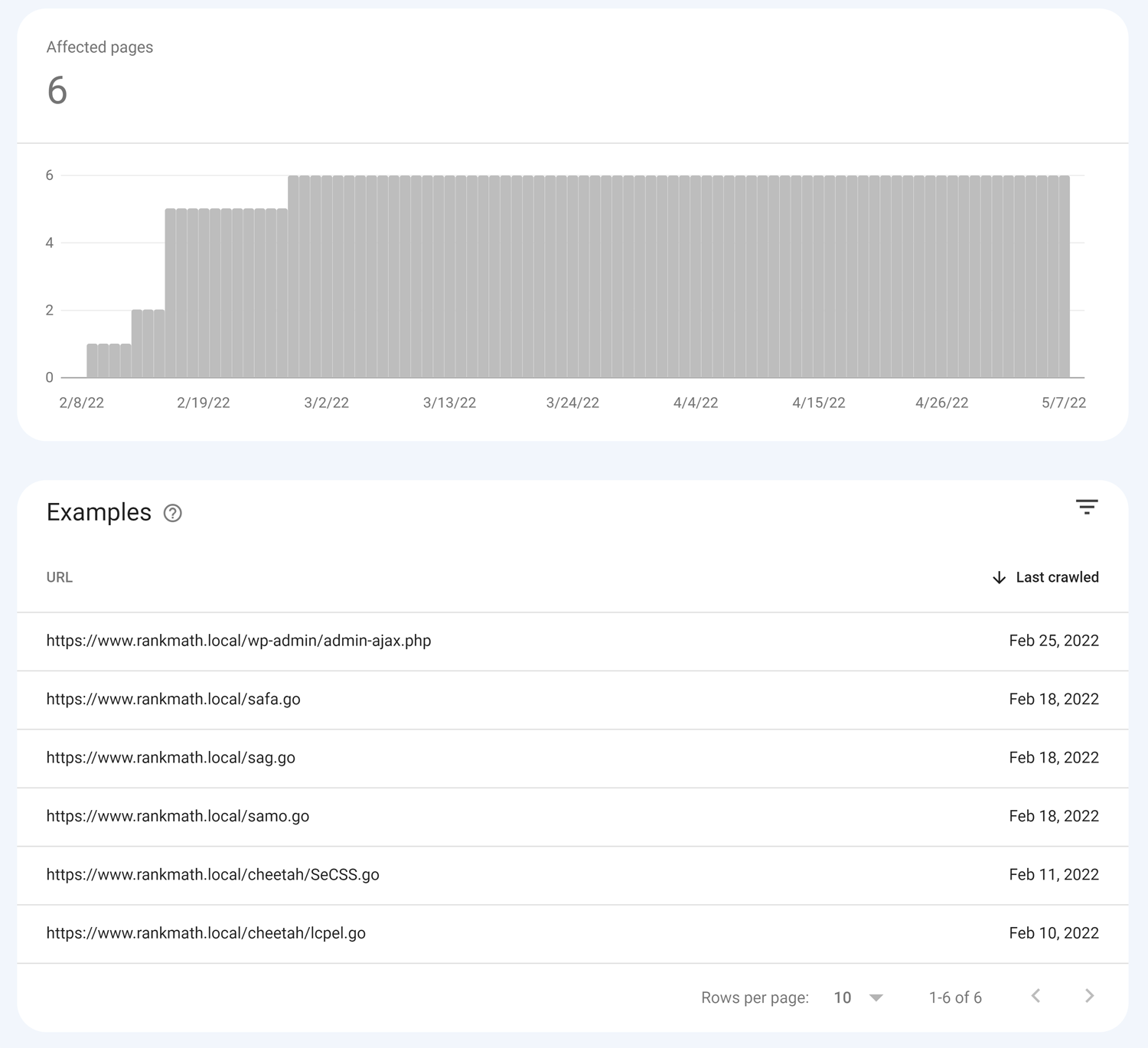
To fix this error, follow these tips:
- Set up redirects for 404 errors so that visitors will be redirected to another page of your site.
- Adjust your .htaccess file and robots.txt file to manage 403 and 401 errors, respectively.
- For temporary server issues, work with your hosting provider to identify and resolve the underlying cause.
For more details, refer to our guide on how to fix the “Blocked due to other 4xx issue” error.
1.14 Indexed, though blocked by robots.txt
This message in Google Search Console indicates that Google has already indexed a URL on your website, but a directive in your robots.txt file is blocking access to that URL.
This creates a conflict: Google knows the page exists but is instructed not to show it in search results.
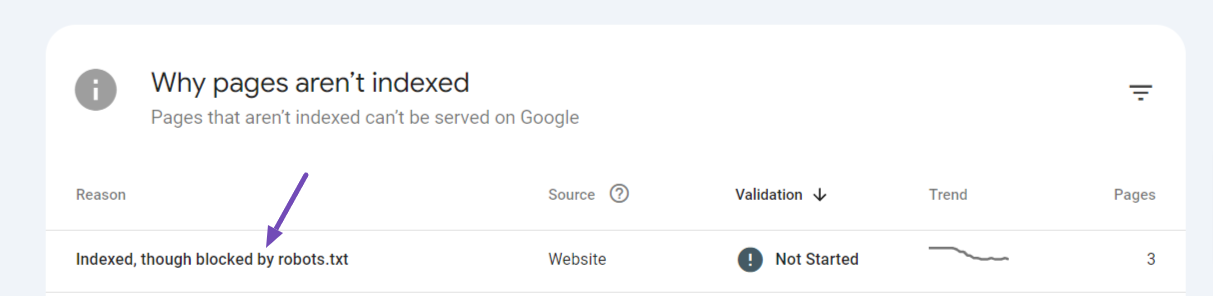
This error can occur if the page has external links pointing to it or if it was crawled and indexed before being blocked by the robots.txt file.
To resolve this issue:
- Carefully examine your robots.txt file for any directives blocking the affected URL.
- If you find a rule blocking the URL and want it to be indexed, remove the corresponding line or adjust it to allow access.
- If external links are the cause, allow Google to reindex the page.
You can learn more about this error and how to fix it by referring to our detailed guide here.
1.15 Page indexed without content
This status signifies that Google indexed a page on your website but couldn’t find meaningful content.
Though the page exists, it lacks information for search engines to understand its value.
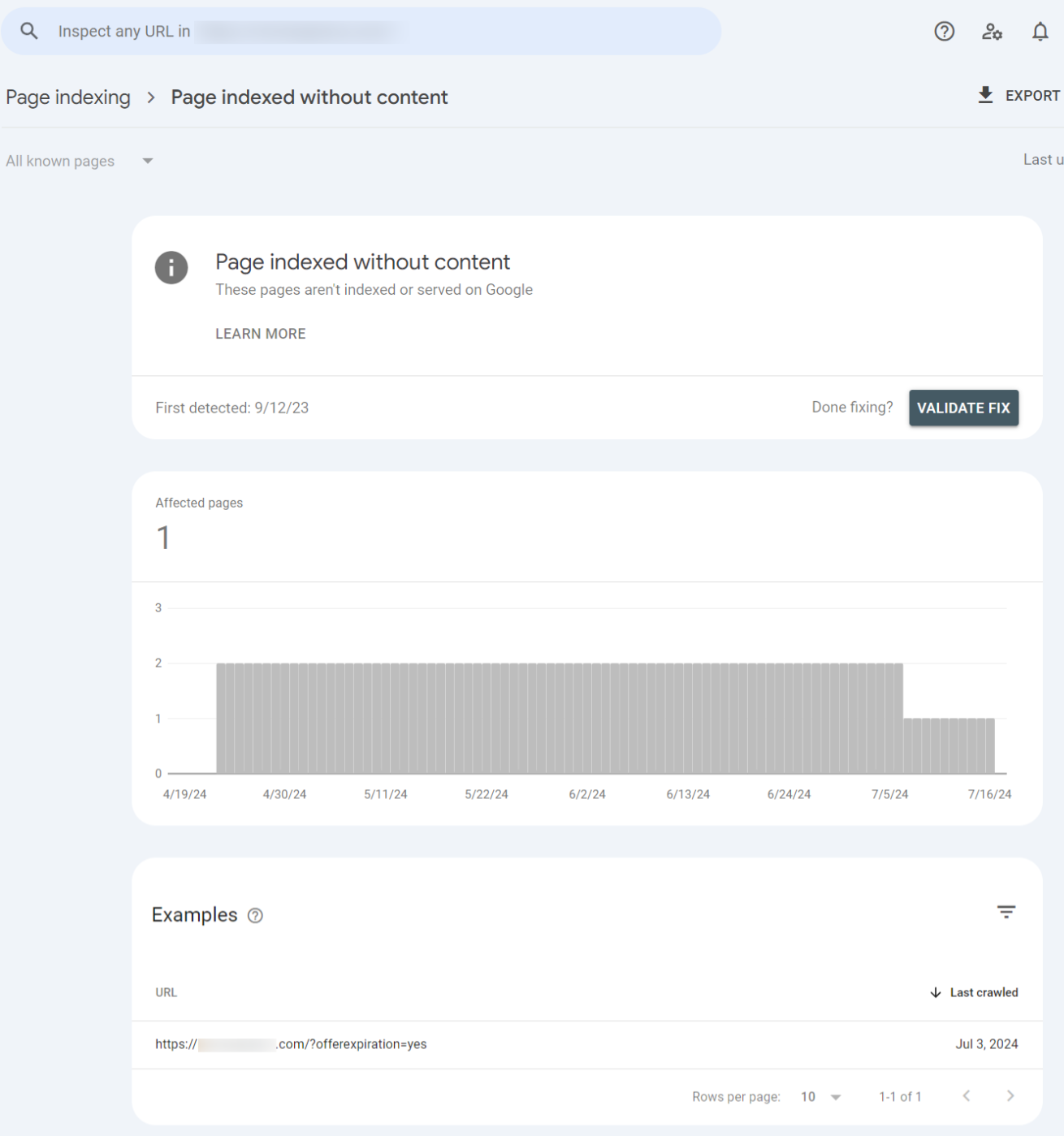
This error can occur if your pages have little or no content or your site’s robots.txt file is corrupted.
To resolve this error:
- Check the structure of your site to see if the pages are well-linked together.
- Ensure the affected page has informative, well-written content that addresses user needs and search intent.
- Ensure that your robots.txt file doesn’t prevent Google from indexing the page.
For more information on how to fix this error, refer to our detailed guide here.
2 Validating Indexing Fixes in Search Console
After fixing indexing issues identified in the Search Console, you need to validate the changes to ensure Google recognizes the fixes. Here’s how:
Navigate to the Pages section of your GSC and find the specific error you addressed (e.g., “Not Found (404)”). Click on the error category.
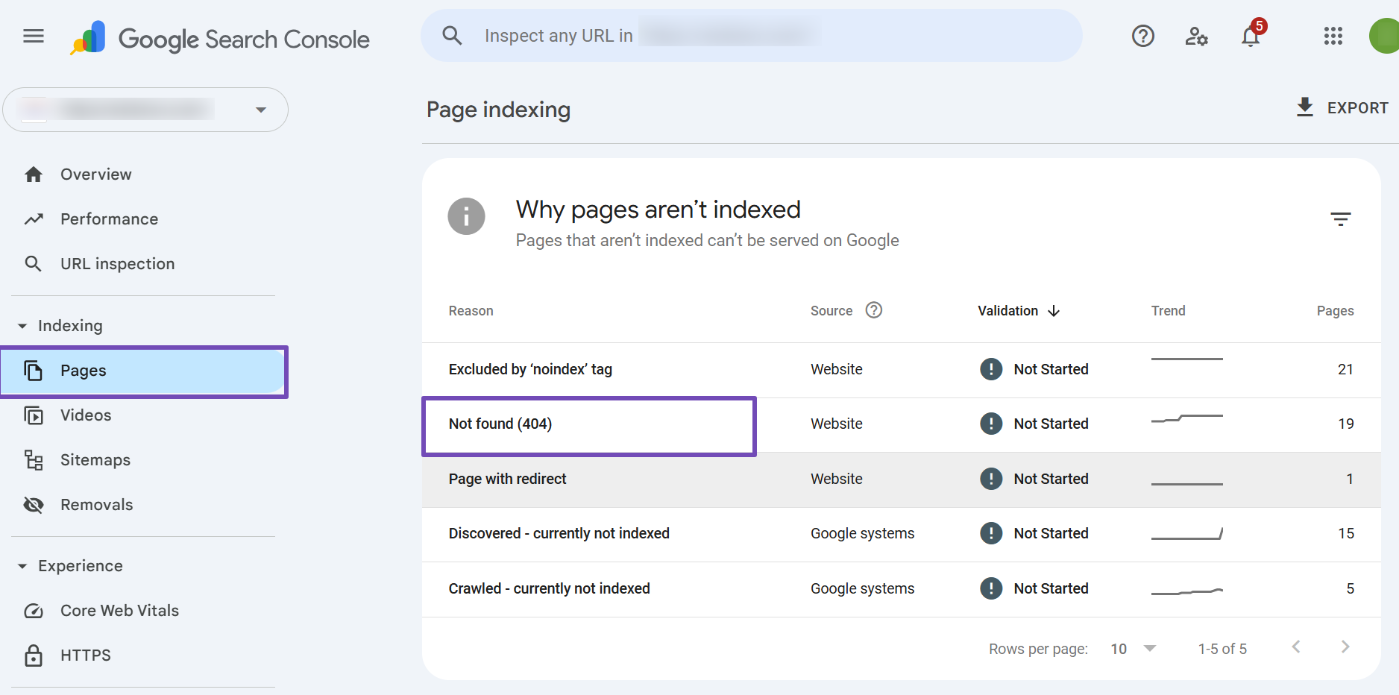
On the error details page, look for the VALIDATE FIX button and click it.
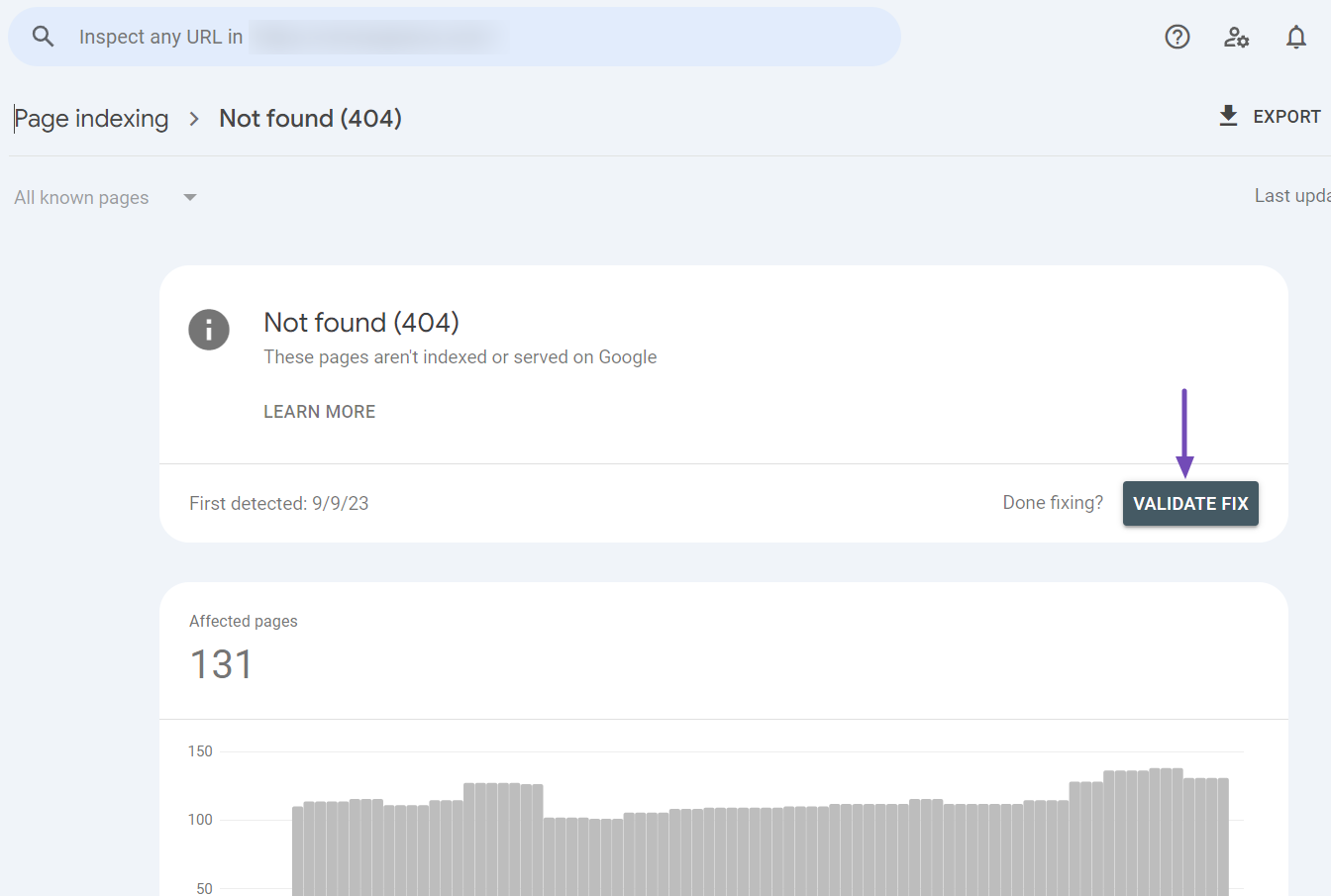
Google will notify you via email or a message in GSC’s top right corner (bell icon) that validation has begun.
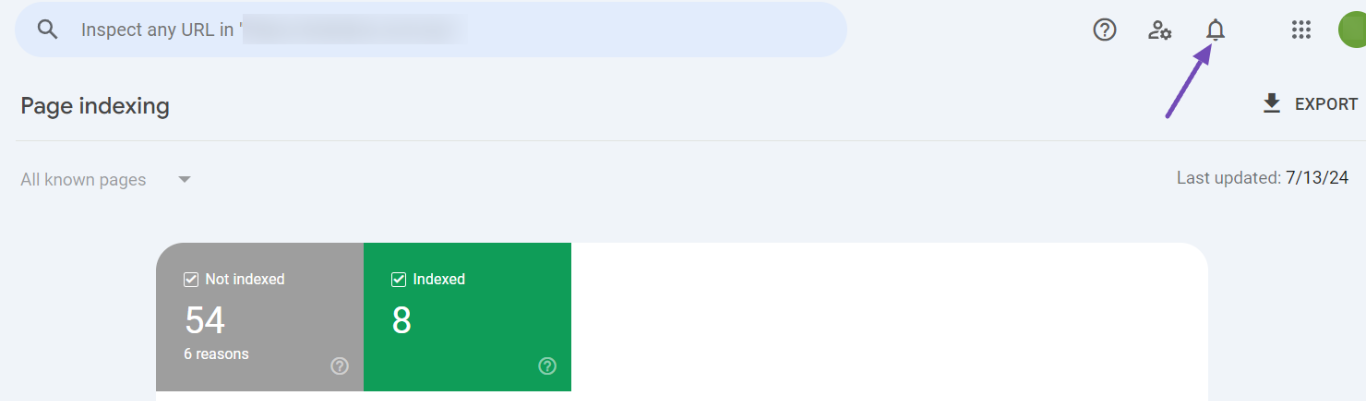
When you click on the icon, the messages will appear. Then, give Google time to complete the validation process.
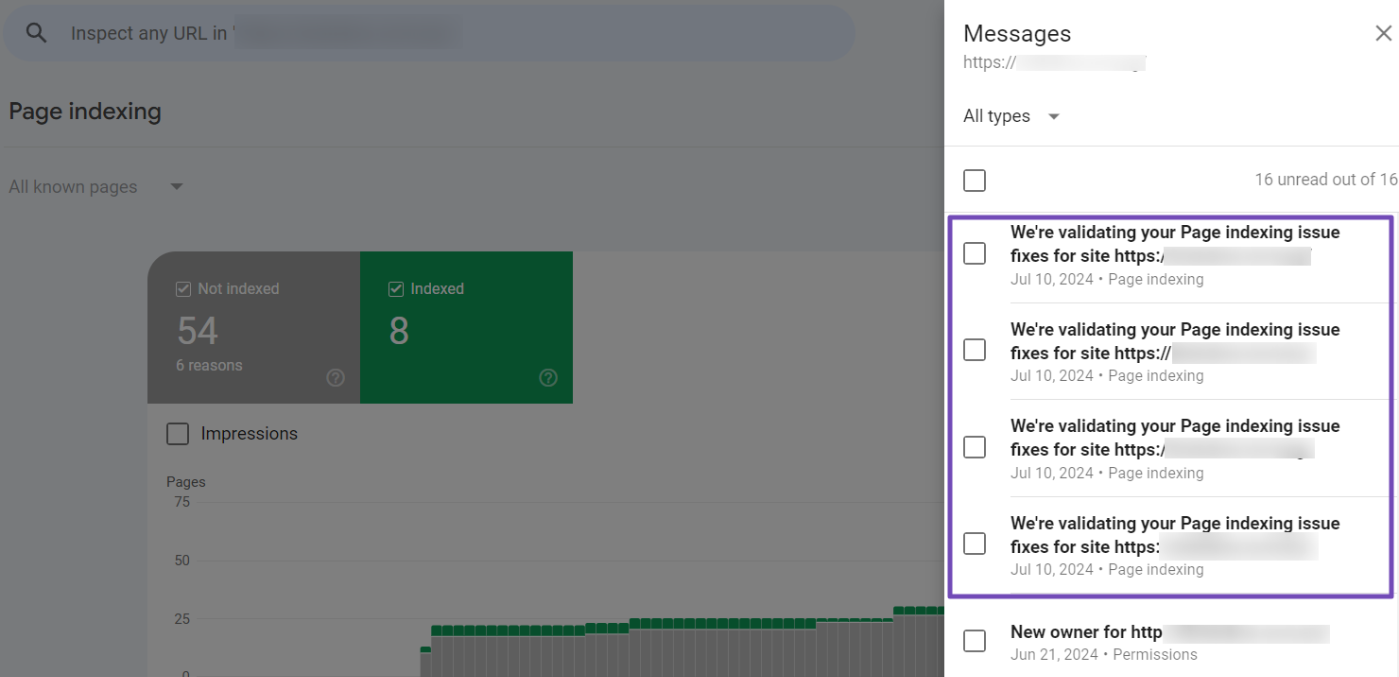
Once finished, Google will notify you again. You can also check the validation status back in the Pages section where the error initially appeared.
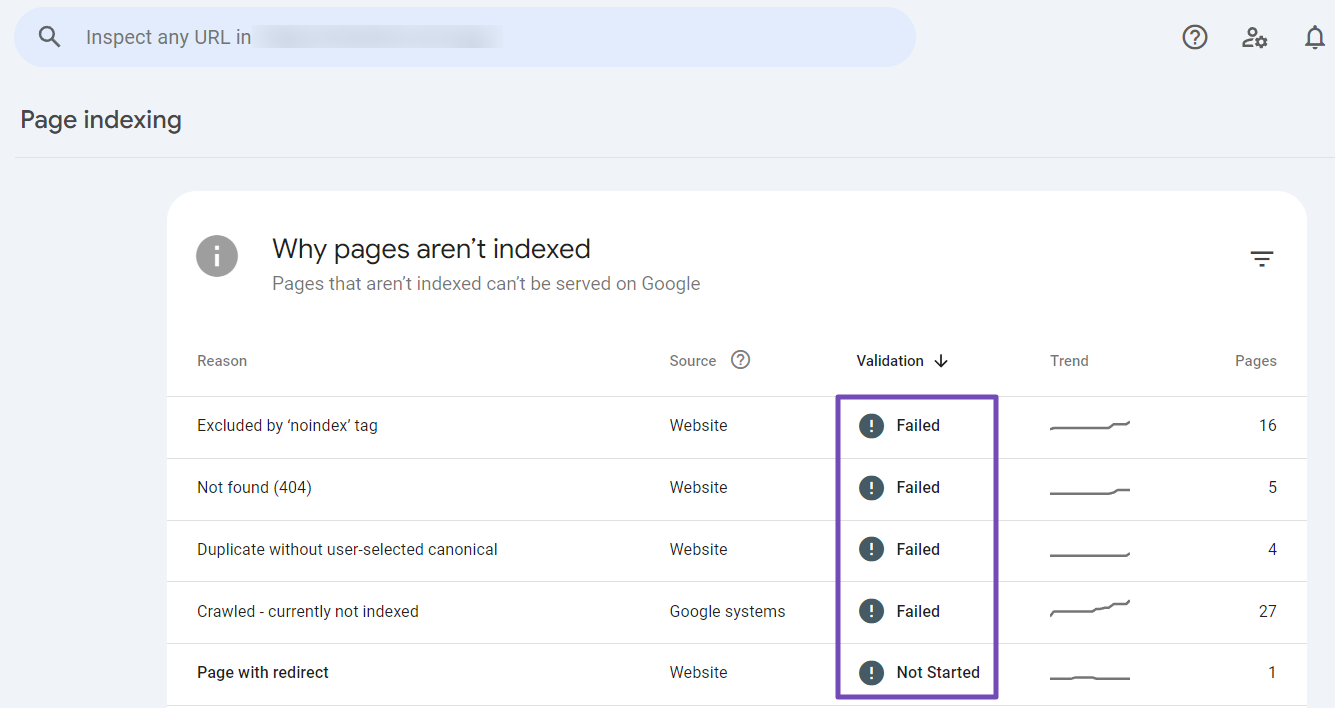
And that’s it! We hope you can fix the page indexing issues in the Google Search Console. If you have any questions, feel free to contact our dedicated support team. We’re available 24/7, 365 days a year.