When you launch a new website or publish fresh content, the last thing you want is to wait days—or even weeks—for Google to notice it.
I’ve been there, hitting refresh on Search Console, wondering when my pages will finally show up.
The truth is, you don’t have to just wait and hope. There are several proactive steps you can take to speed up the indexing process.
In this post, we’ll walk you through 10 effective ways you can quickly get your site indexed by Google, so your content can start ranking and driving traffic as soon as possible.

Table Of Contents
- What is Google Indexing?
- How to Check if Google Has Indexed Your Site
- How to Index Your Site on Google
- Check WordPress Settings for Search Engine Visibility
- Submit Your Sitemap
- Use Instant Indexing
- Monitor Your Indexing Status
- Check robots.txt for Crawl Issues
- Make Sure There’s No Duplication of Pages
- Remove Unwanted Noindex Tags
- Check for Nofollow Internal Links
- Use Clean, SEO-Friendly URLs
- Build Powerful Internal Links
- Build High-Quality Backlinks
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
1 What is Google Indexing?
When you publish a new page on your website, one of the first things you want is for Google to find it—and that’s where indexing comes in.
Google indexing is the process where Google discovers your web pages, reads through the content, and stores all that information in its database, known as the Google Index. Once your page is indexed, it can show up in search results when someone searches for something related.
Here’s how it works: Google sends out bots—called crawlers—to scan your site. These bots look at your text, images, links, and other elements to understand what your page is about. If everything looks good and follows Google’s guidelines, your page gets added to the index.
If your site isn’t indexed, it won’t appear in search results, no matter how helpful or well-written your content is. That’s why indexing is such an important first step in SEO.
For example, when I published a blog post about Schema Markup, I made sure Google could index it properly. Once it was indexed, the page became visible in search results. So now, when someone searches for Schema Markup, my blog post can show up, because Google recognizes it as a relevant and useful resource.

2 How to Check if Google Has Indexed Your Site
The quickest method is to do a site-specific search using Google using search operators. Just type site:yourwebsite.com into the Google search bar (replacing yourwebsite.com with your actual domain). This will show you a list of all the pages from your site that Google has indexed.
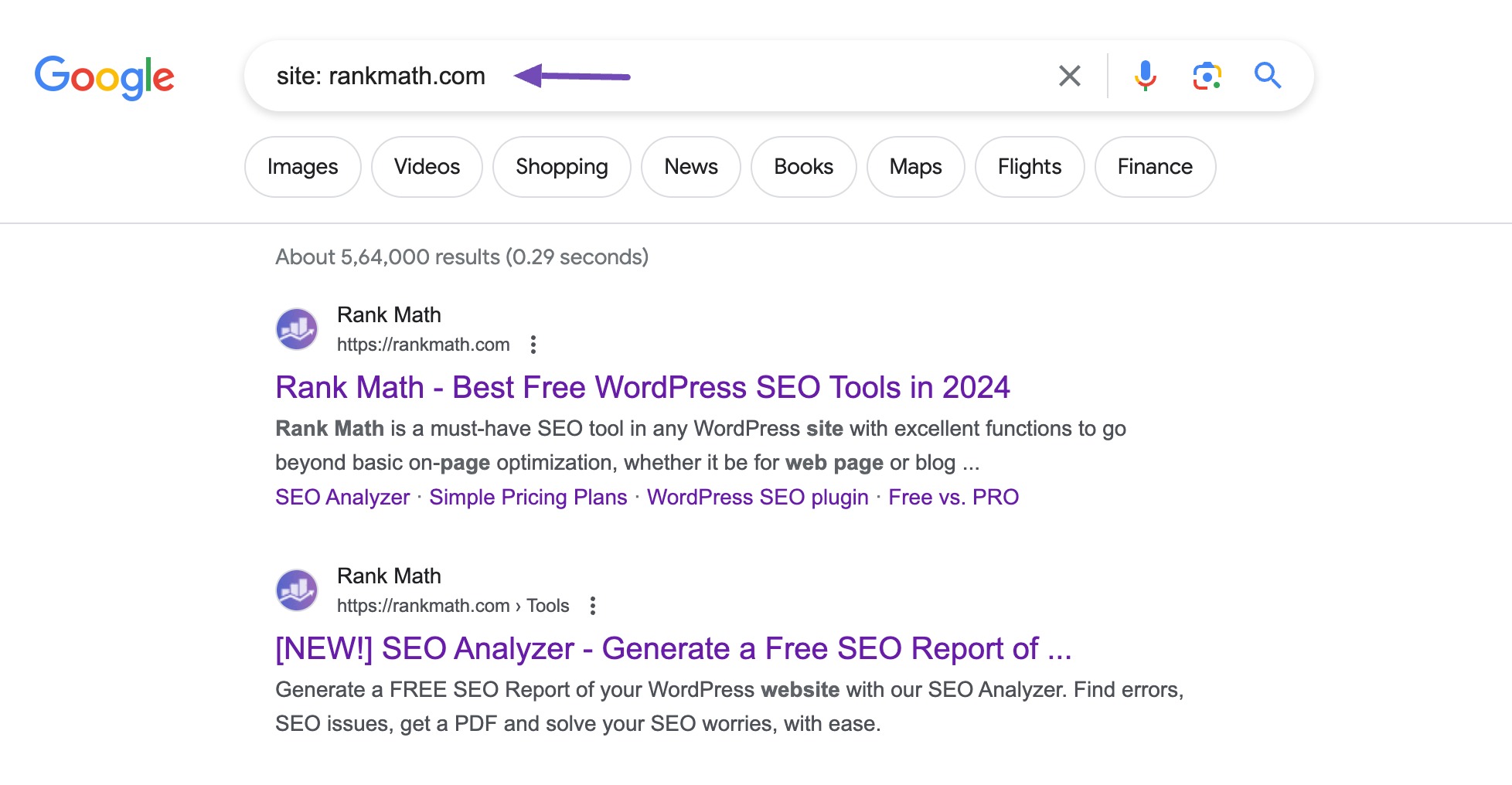
Another reliable option is to use the URL Inspection tool in Google Search Console. Enter the page URL to check if it is indexed or not in the URL Inspection tool.
If the page is indexed, you’ll notice a message saying the URL is on Google, as shown below.

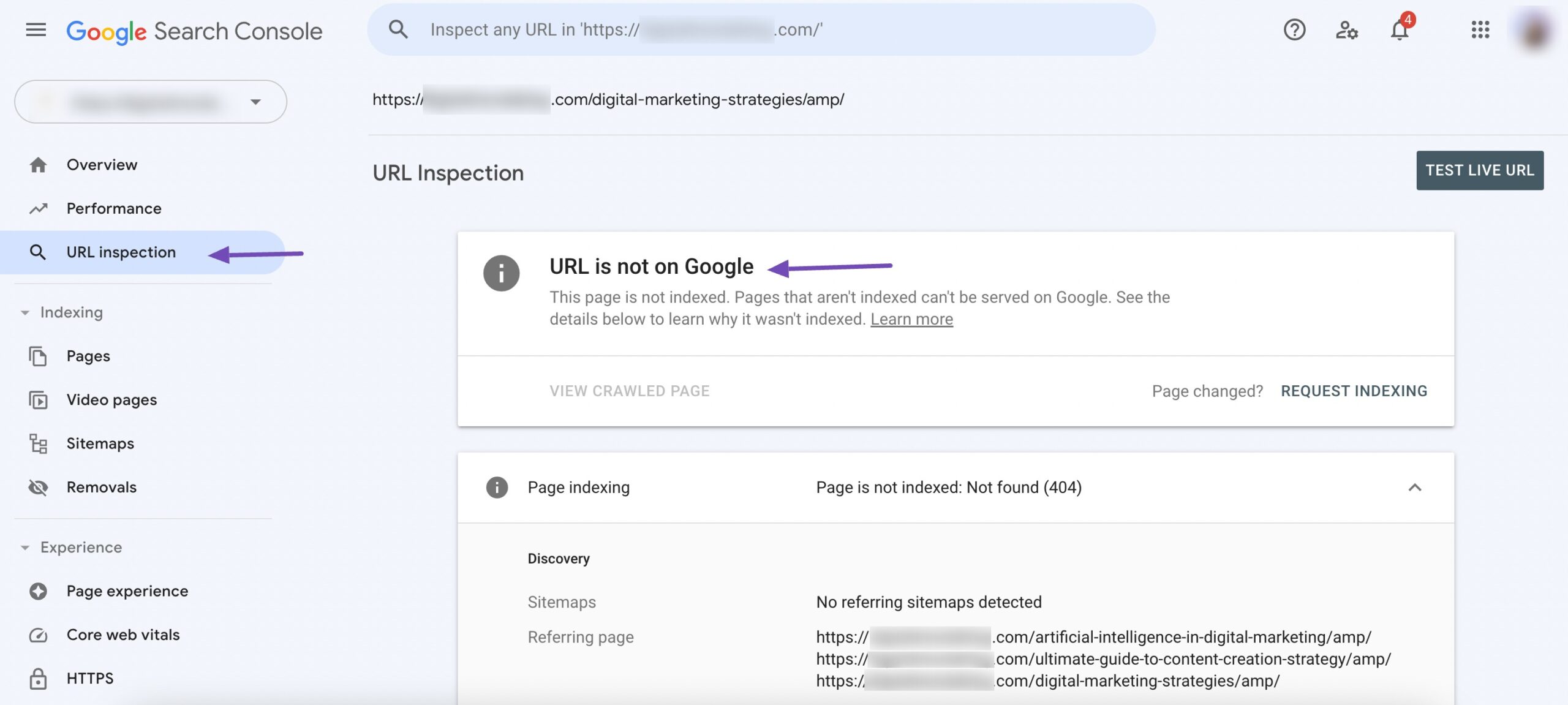
If the page is not indexed, the following message will be displayed in Google Search Console.
3 How to Index Your Site on Google
If you want your site to appear in search results, it needs to be indexable by Google. Let’s start with a quick check on your WordPress settings.
3.1 Check WordPress Settings for Search Engine Visibility
Sometimes, WordPress settings may block search engines without you realizing it. To make sure your site can be indexed:
- Go to your WordPress dashboard.
- Click Settings → Reading.
- Look for the Search engine visibility section.
You’ll see a checkbox labelled Discourage search engines from indexing this site, as shown below.
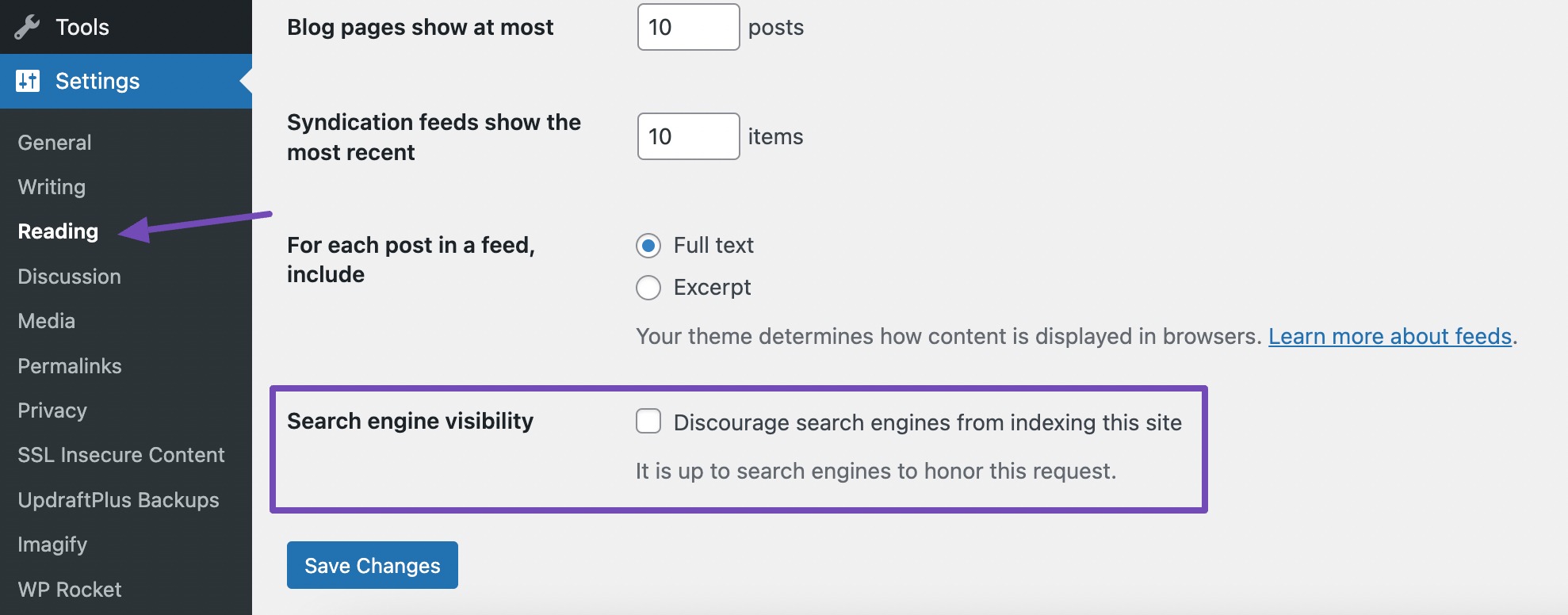
If this box is checked, your site is telling search engines not to index it, which means it won’t appear in Google search results. Make sure the box is unchecked, then click Save Changes.
By doing so, you’re allowing Google and other search engines to crawl and index your site properly.
3.2 Submit Your Sitemap
Submitting your sitemap is one of the easiest ways to help Google find and index all the important pages on your site.
If you’re using WordPress, Rank Math makes this process quick and simple.
Install and activate the Rank Math plugin on your WordPress website if you haven’t already.
Once activated, follow the setup wizard to configure your basic site details, like your website name, type, and SEO preferences.
Below are the sitemap settings that you can configure in the setup wizard.
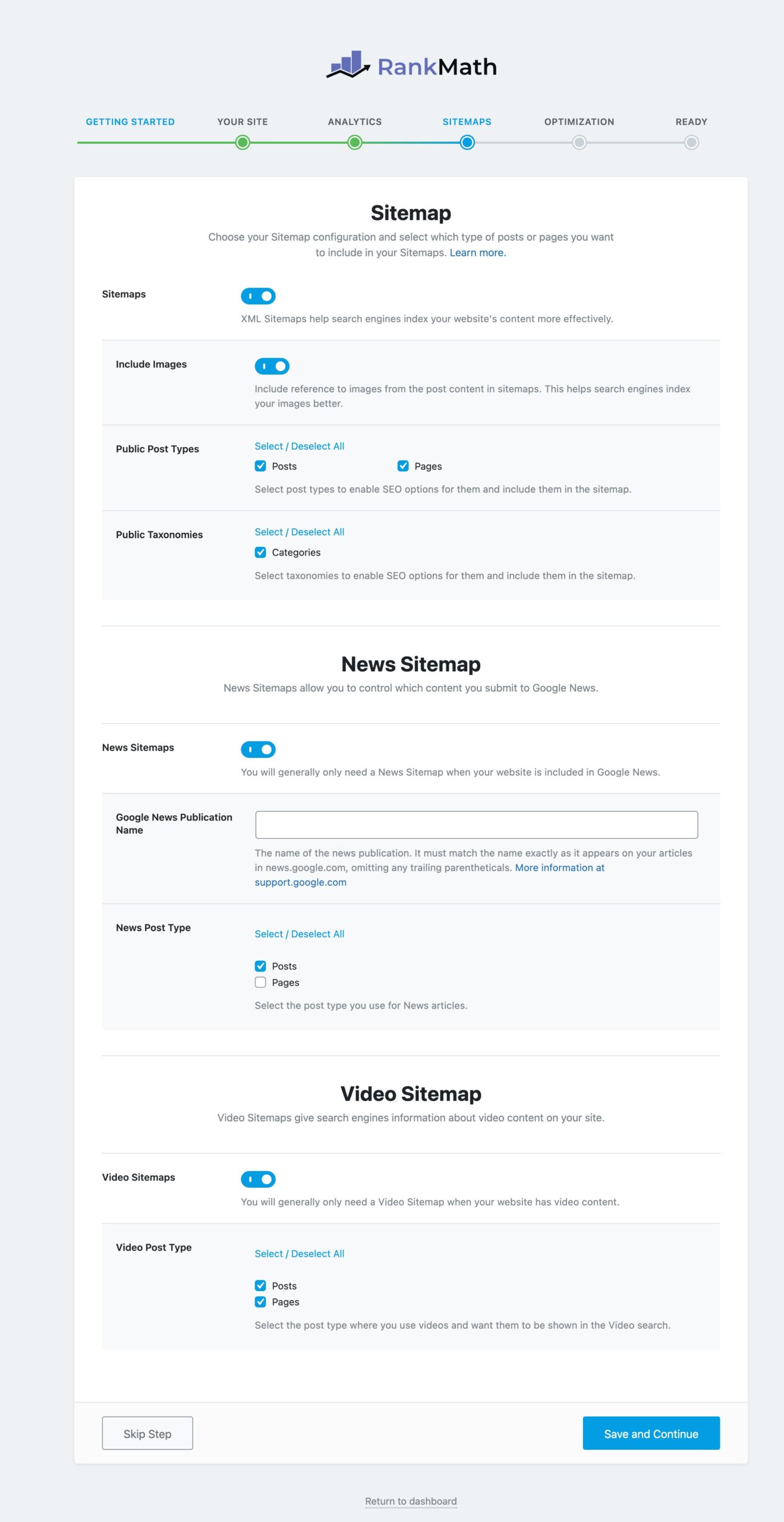
To locate your sitemap, navigate to your WordPress dashboard and navigate to Rank Math SEO→ Sitemap Settings. Here, you’ll find the URL of your sitemap file.
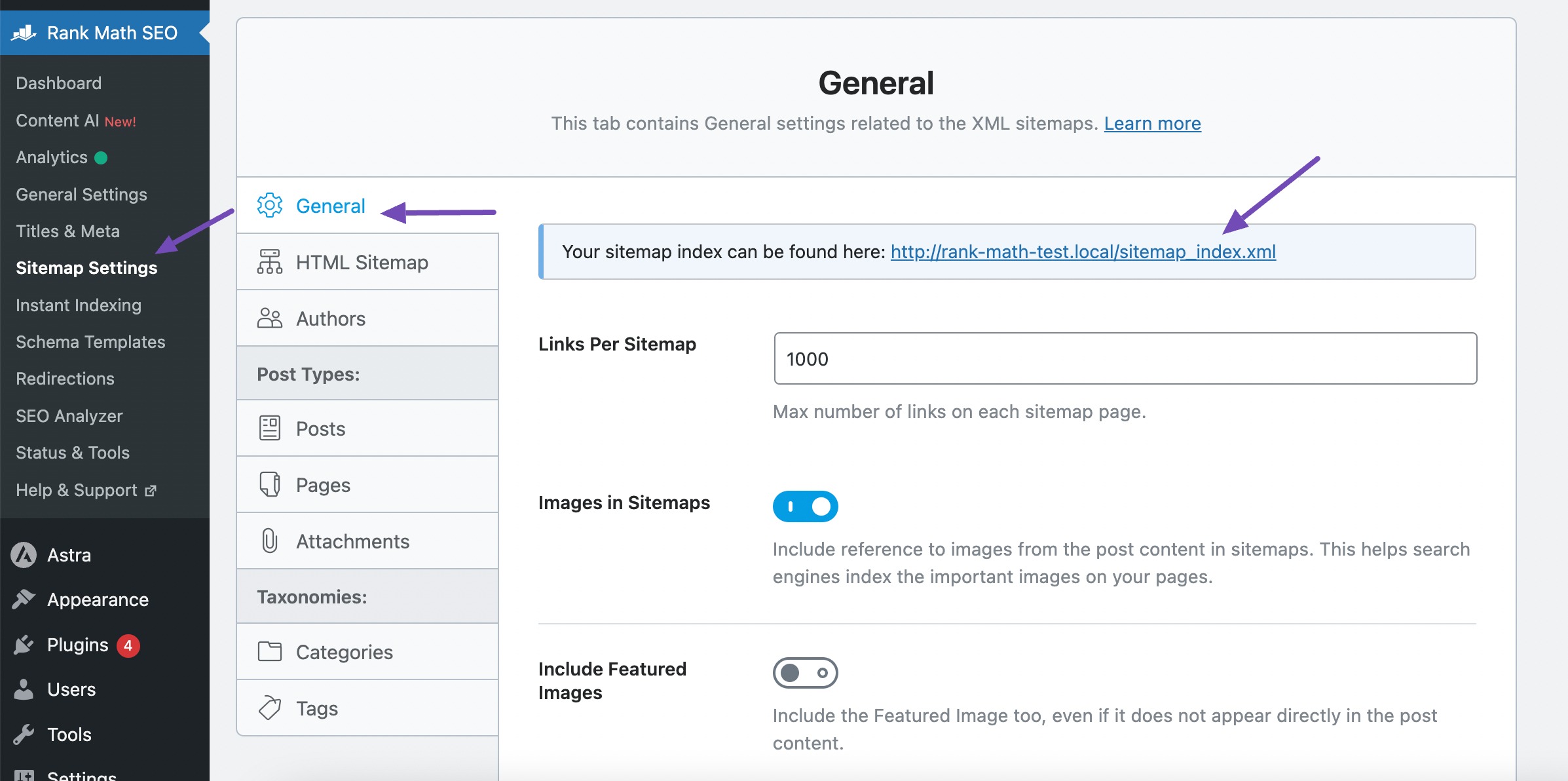
If you haven’t added your website to Google Search Console yet, you’ll need to do so first. Once logged in, select your website property from the list of properties.
In the left-hand menu, click Sitemaps under the Indexing section.
Enter the URL of your sitemap (e.g., https://example.com/sitemap_index.xml) into the provided field and click SUBMIT.
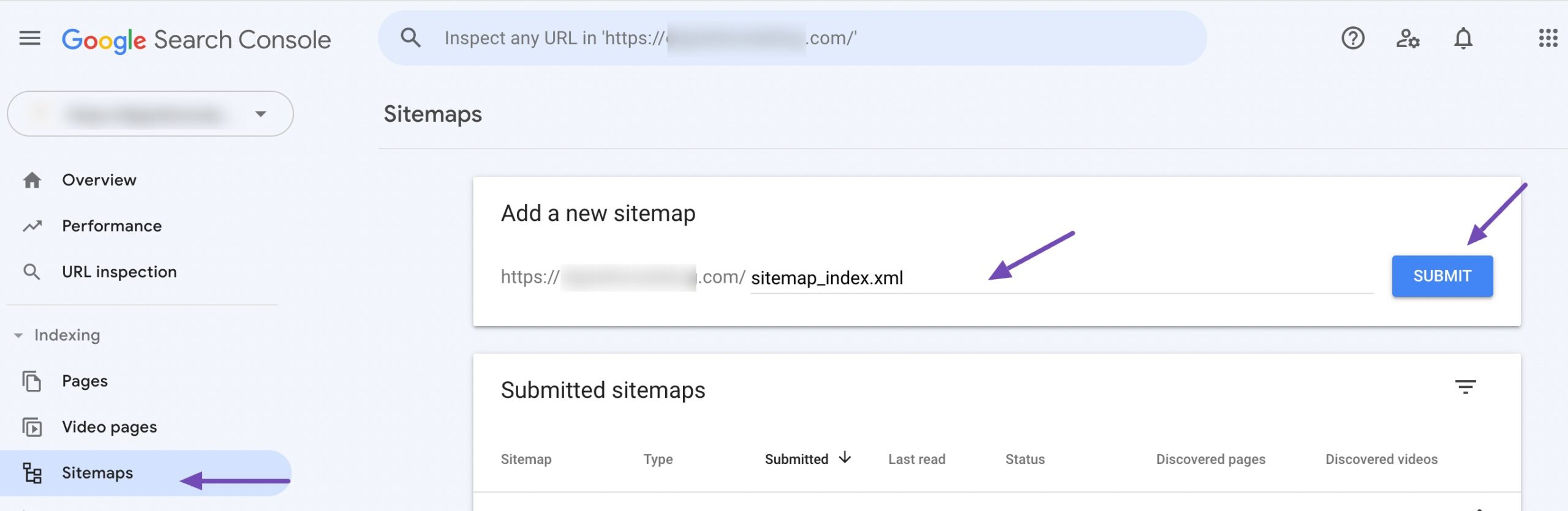
After submitting your sitemap, Google will display a message confirming the submission. It may take time for Google to process the sitemap and index your website’s pages.
If you’ve connected Rank Math to your Google Search Console account, the plugin will automatically submit your sitemap for you—no manual steps needed.
3.3 Use Instant Indexing
If you want your content to show up in search results faster, Rank Math’s Instant Indexing feature is a great tool, especially for search engines like Bing and Yandex.
To use this feature, install and activate the Instant Indexing for Google plugin on your site. Once done, navigate to Rank Math SEO → Instant Indexing → Console, add the URLs you want to index, and click the Send to API button, as shown below.
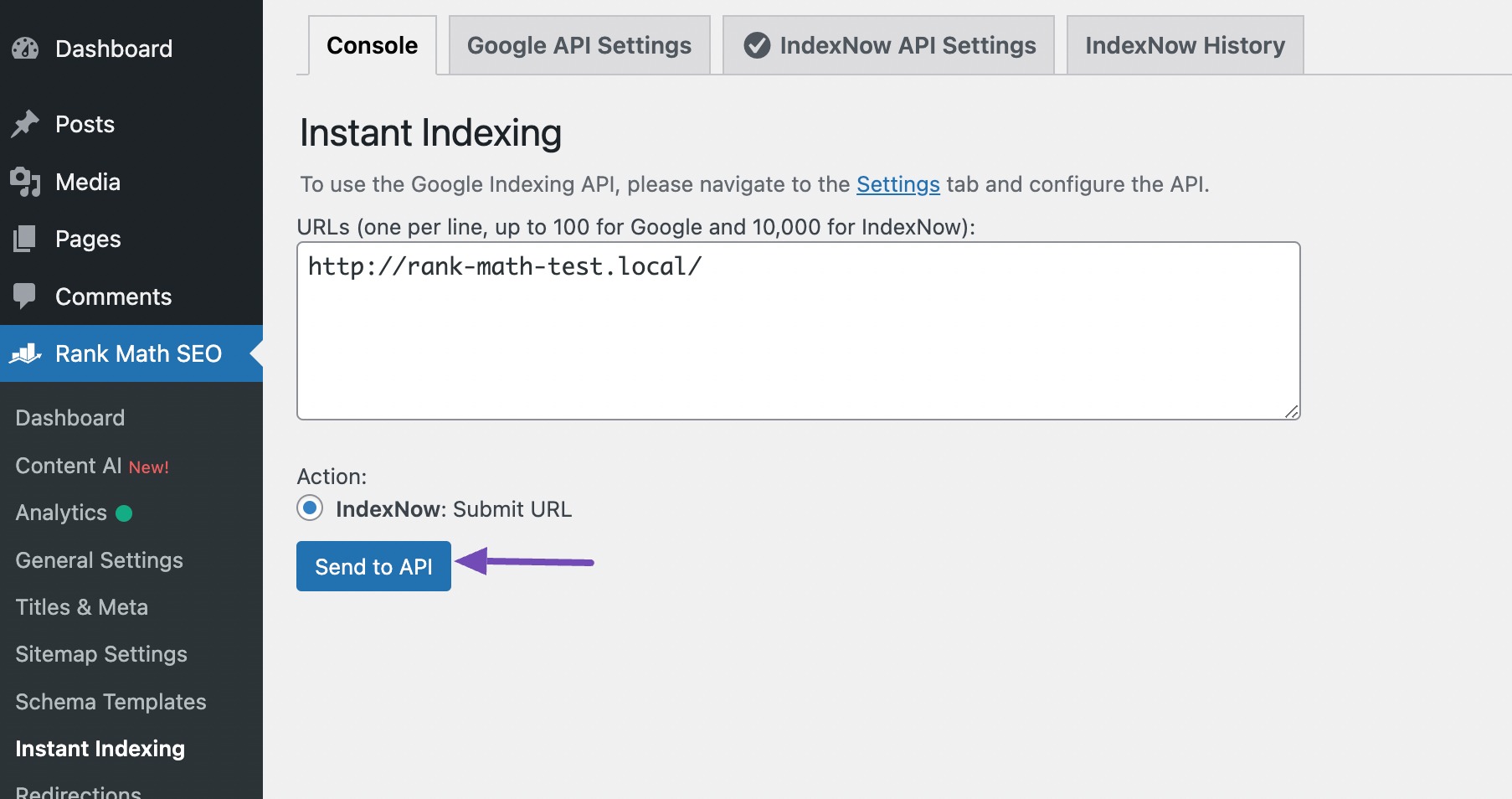
This tells the supported search engines to crawl your content immediately, instead of waiting for them to discover it on their own. You can also use IndexNow to submit your URLs to the search engines instantly.
3.4 Monitor Your Indexing Status
To make sure your content is showing up in search results, it’s important to keep an eye on your site’s indexing status. This helps you identify any issues early—like pages that aren’t being indexed—and ensures your audience can actually find your content.
With Rank Math’s Index Status feature, you can easily monitor which of your pages have been indexed by search engines like Google, right from your WordPress dashboard. Simply navigate to Rank Math SEO → General Settings → Analytics from your WordPress dashboard. Then navigate to the Index Status tab, as shown below.
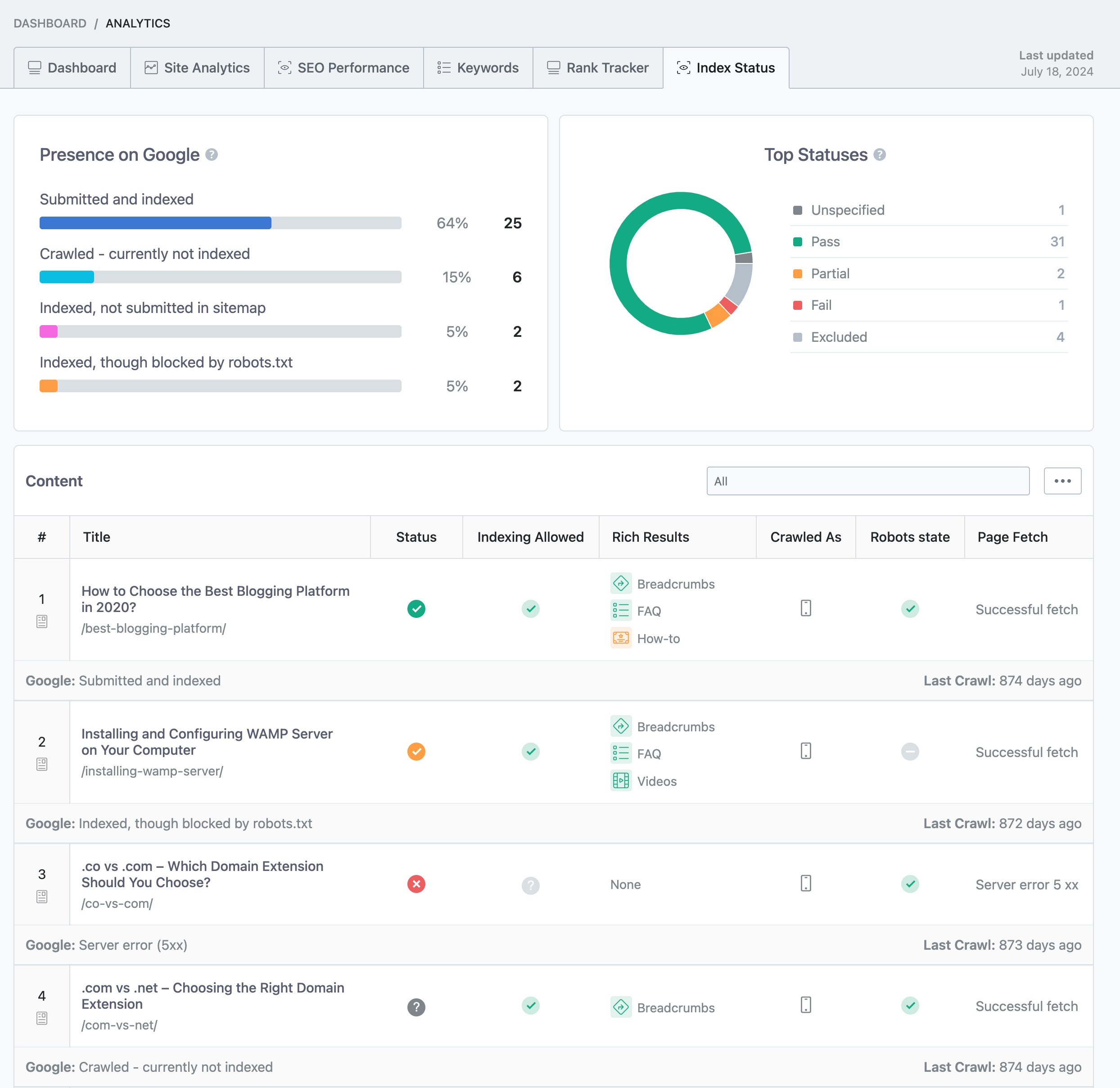
It provides you with clear insights into how well your content is being picked up and can highlight any potential problems that might be affecting your visibility.
3.5 Check robots.txt for Crawl Issues
Your robots.txt file tells search engines which parts of your site they can or can’t crawl. If it’s misconfigured, it can accidentally block important content from being indexed.
Refer to our dedicated tutorial on editing robots.txt file using Rank Math.
Once you’re in the Edit robots.txt tab, review the file’s contents carefully to ensure that the directives accurately reflect your website’s intended crawling and indexing instructions.
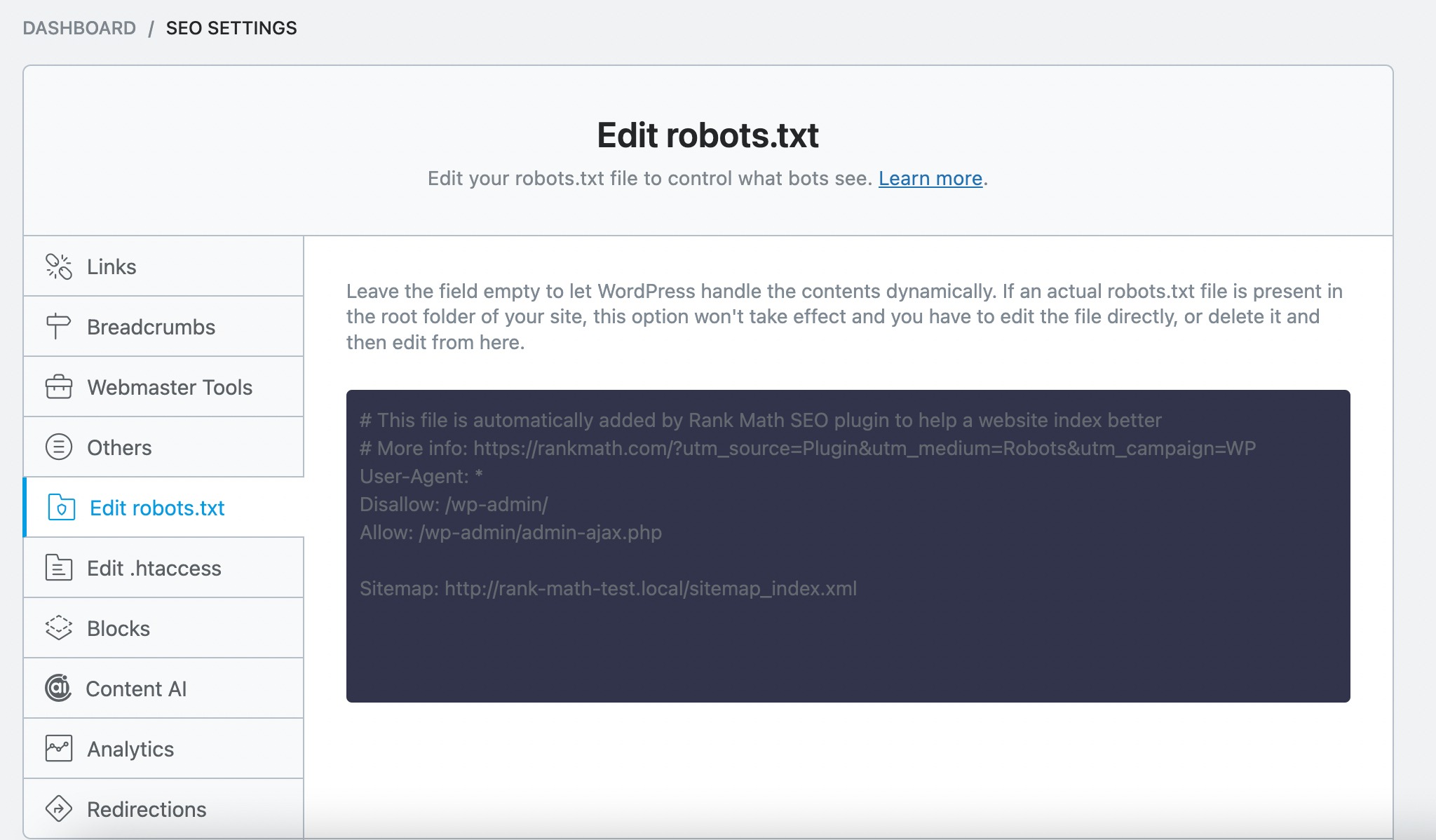
If you spot any issues, like essential pages being blocked or syntax errors, go ahead and fix them. This might mean updating or removing old Disallow rules or correcting formatting mistakes.
Once you’ve made your changes, don’t forget to save. A clean, accurate robots.txt file helps ensure search engines can properly crawl and index your site.
3.6 Make Sure There’s No Duplication of Pages
Duplicate content can confuse search engines and hurt your rankings. If Google sees multiple pages with similar content, it may not know which one to index, or might skip all of them altogether.
Here’s what you can do:
- Consolidate similar pages: If you have multiple pages that cover the same topic, consider merging them into one comprehensive page.
- Use 301 redirects: After consolidation, redirect the old or less relevant pages to the main one. This passes SEO value and avoids splitting your rankings.
- Add canonical tags: If you need to keep similar pages live (for technical or user reasons), use a canonical tag to tell search engines which version is the original and should be indexed.
3.7 Remove Unwanted Noindex Tags
A noindex tag tells search engines not to index a page, meaning it won’t appear in search results. That’s useful for pages you don’t want public, like thank-you pages or admin sections.
But if you accidentally apply a noindex tag to important content, it can seriously hurt your site’s visibility.
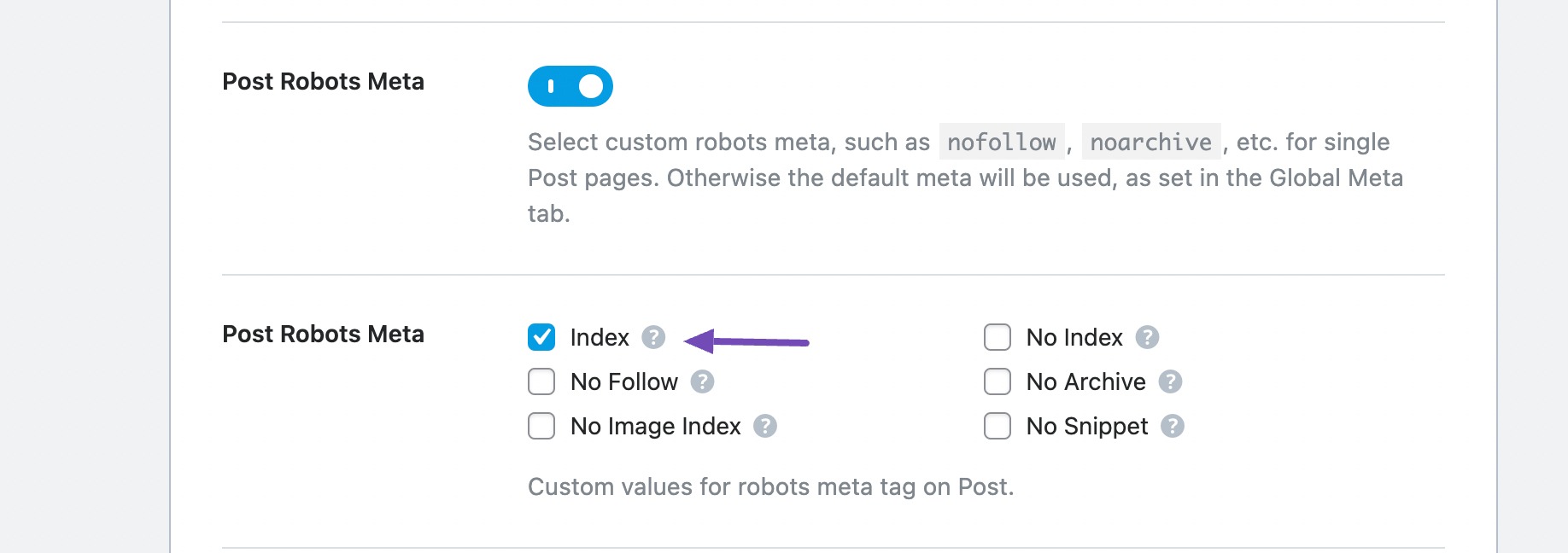
If you’re using Rank Math, navigate to Titles & Meta → Global Meta settings and ensure the Robots Meta is set to Index.

Similarly, check for the Post/Page Robots Meta.
You can also check an individual page/post by navigating to the Advanced tab in the Rank Math SEO meta box. Ensure that the ROBOTS META is set to Index, as shown below.
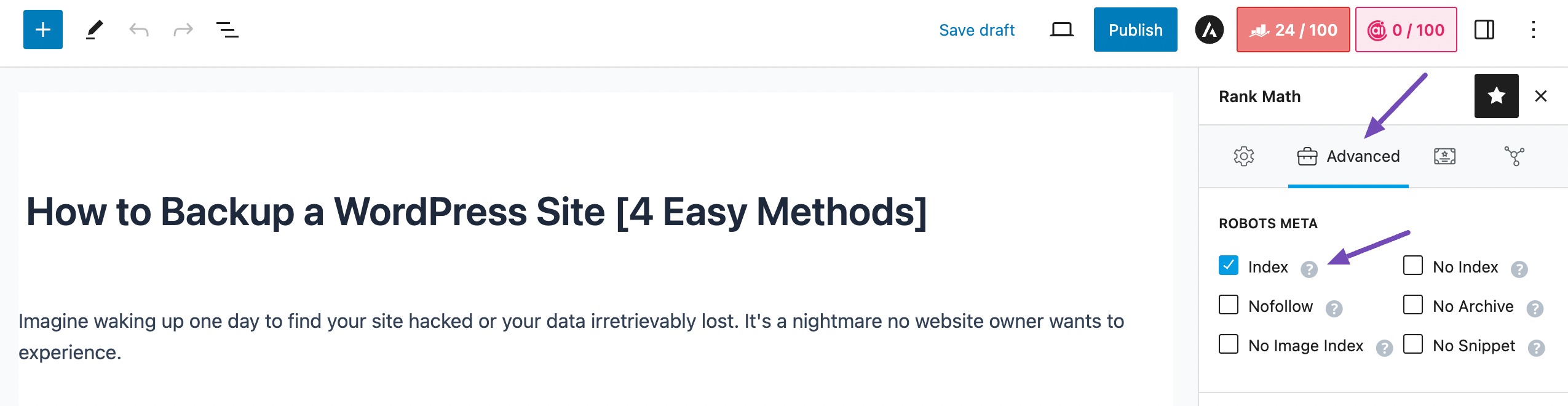
A quick scan through these settings can prevent major indexing issues and keep your pages visible in search results.
3.8 Check for Nofollow Internal Links
A “nofollow” link is an HTML attribute that tells search engine crawlers not to follow the link to its destination.
While it’s common to use nofollow attributes for external links, applying them to internal links may inadvertently affect the indexing and ranking of important pages on your website.
You can verify nofollow links in the same manner as you check the noindex tag with Rank Math.
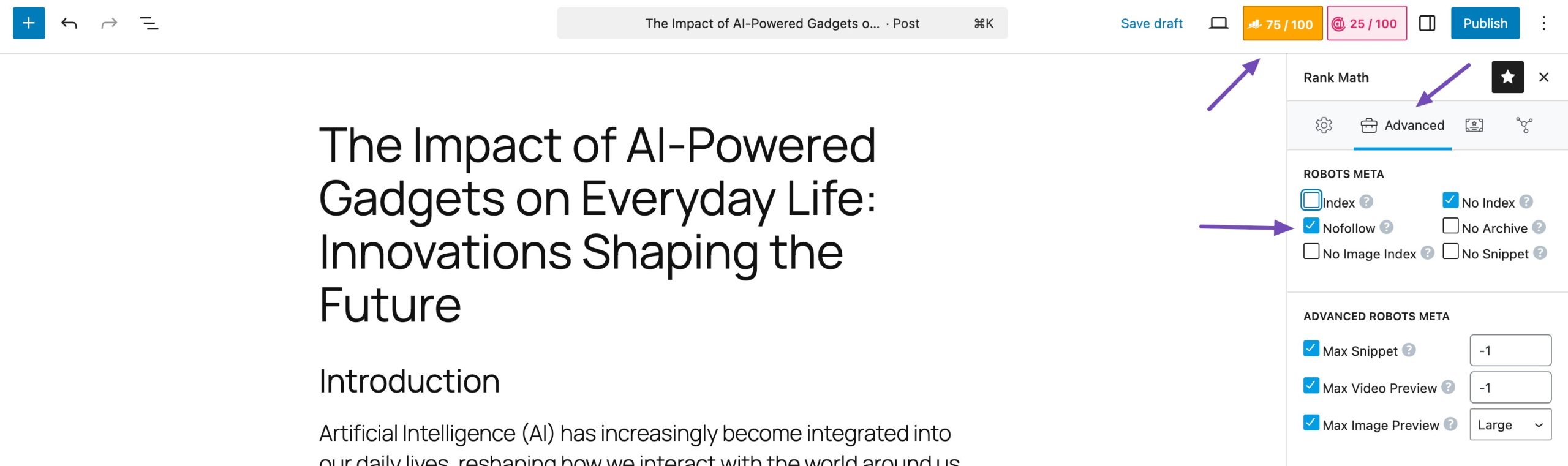
Doing so will help Google index your site and ensure that your valuable content receives the visibility it deserves in search engine results pages.
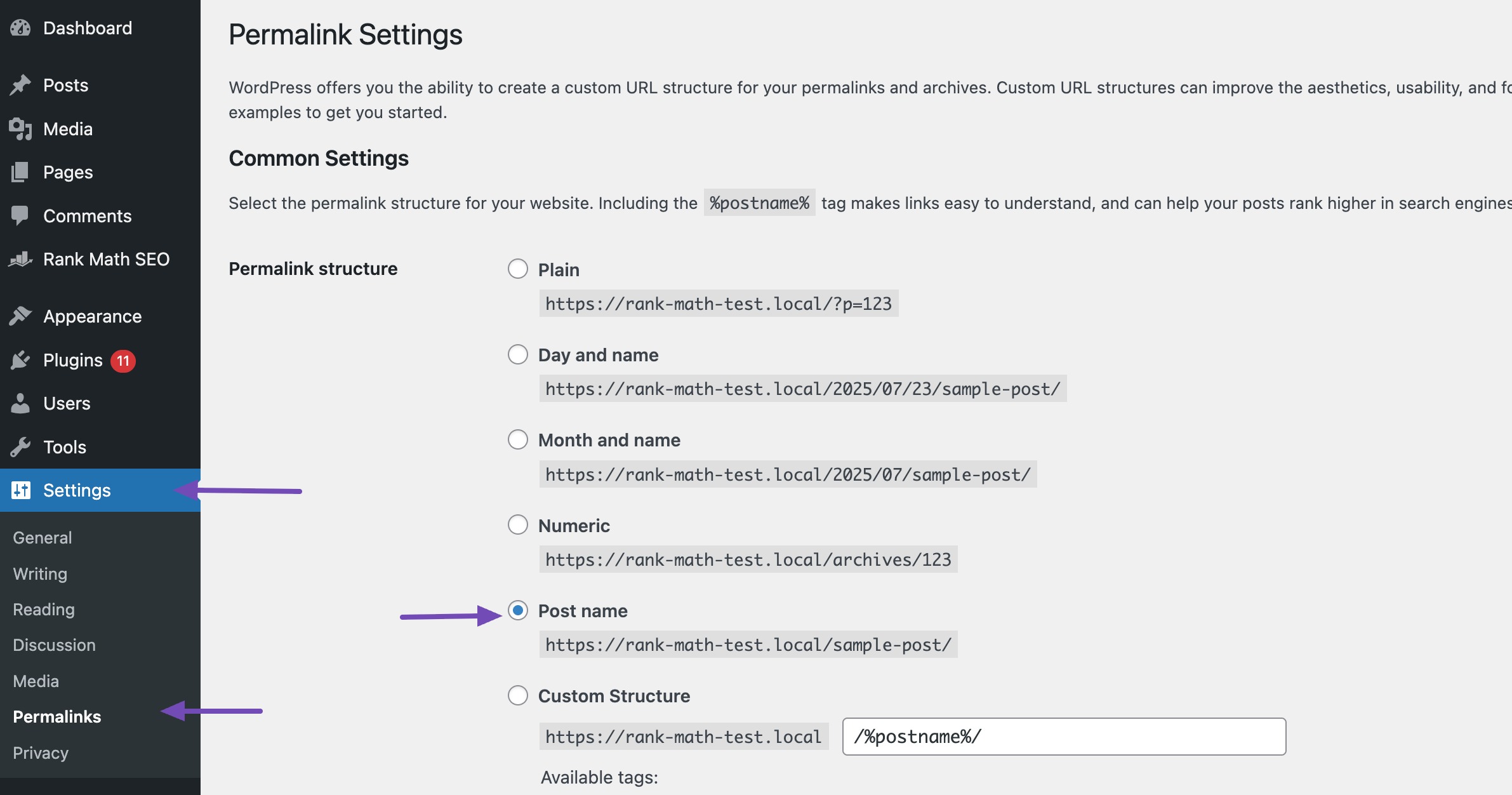
3.9 Use Clean, SEO-Friendly URLs
Clean permalink structures make it easy for Google to understand what your page is about. Avoid generic URLs with random characters or numbers (like example.com/?p=123).
Instead, use descriptive URLs that include relevant keywords like example.com/seo-basics/. This improves not only indexing clarity but also click-through rates from search results.
If you’re using WordPress, navigate to Settings → Permalinks and choose a structure Post name to keep things simple and SEO-friendly.
Refer to our dedicated tutorial to create SEO-friendly URLs for your site.
3.10 Build Powerful Internal Links
Internal links are important in helping Google discover content on your website as it navigates from link to link.
However, if a page on your website lacks internal links, Google may struggle to explore other content on your site, which can delay indexing your site’s additional pages.
To solve this, consider including internal links strategically within your content to guide Google to relevant areas of your website.
But what exactly constitutes a powerful internal link?
For instance, if your website features pages that attract the most traffic and rank well on Google, offering valuable content to the audience. By internally linking from these high-traffic posts to other pages on your site, you establish robust internal links that enhance navigation and indexing efficiency.
You can track the internal links using Rank Math’s link counter.
3.11 Build High-Quality Backlinks
Backlinks, links from other websites pointing to your site, are like votes of confidence in the eyes of search engines. When authoritative sites link to your content, it signals that your site is trustworthy and valuable.
These links don’t just boost your credibility; they also help with indexing. When a well-established site links to you, search engine bots are more likely to follow that link and discover new pages on your website.
The more high-quality backlinks you earn, the easier it becomes for your content to get indexed and rank well.
Refer to our link-building tutorial and explore the simplest link-building methods.
4 Frequently Asked Questions
How long does it typically take for Google to index a new website?
Google’s indexing process varies, but new websites can be indexed within a few days to weeks.
Why is it essential to ensure crawlability for website indexing?
Ensuring crawlability means ensuring search engine bots can access and navigate your site easily. It’s important for indexing because if search engines can’t crawl your site, they can’t index its content.
Is it necessary to regularly update website content for indexing purposes?
Yes, regularly updating and refreshing content signals to search engines that your site is active and relevant, potentially leading to more frequent indexing and higher rankings.
What should I do if my website’s indexing suddenly drops?
If your website’s indexing drops suddenly, investigate potential issues such as crawl errors, duplicate content, or manual penalties. Addressing these issues promptly can help restore indexing and rankings.
5 Conclusion
If you want Google to index your site quickly, you need to take action, not just wait around. By following the tips we covered in this post, you can make it easier for Google to discover and index your content fast.
Indexing is the first step toward showing up in search results. So keep an eye on your site’s visibility, stay on top of technical issues, and make sure your content is both crawlable and valuable.
The more signals you send to Google, the faster your site will get noticed.
If you like this post, let us know by Tweeting @rankmathseo.
