Are you finding that your website isn’t attracting as much traffic as you’d like?
Or perhaps you’re getting visitors, but they’re not converting into customers. Maybe you’re even struggling to rank for the keywords you know are important to your business. That’s because your site is affected by SEO issues.
Search Engine Optimization (SEO) involves enhancing the quantity and quality of your website’s traffic by boosting its visibility in search engine results.
You might wonder how to improve your SEO if you do not see the desired traffic levels.
In this post, we’ll discuss the most common SEO mistakes and provide solutions to fix them.
So, without any further ado, let’s get started.
Table Of Contents
Let us now address the common technical, on-page, content, and off-page mistakes and discuss how to fix them.
1 Common Technical SEO Mistakes & Fixes
Let’s begin with the technical SEO issues and their fixes.
1.1 Poor Crawling or Indexing
A quick way to check for these issues is to type site:yoururl.com into Google. This will show you all the pages from your website that have been indexed by the search engine.
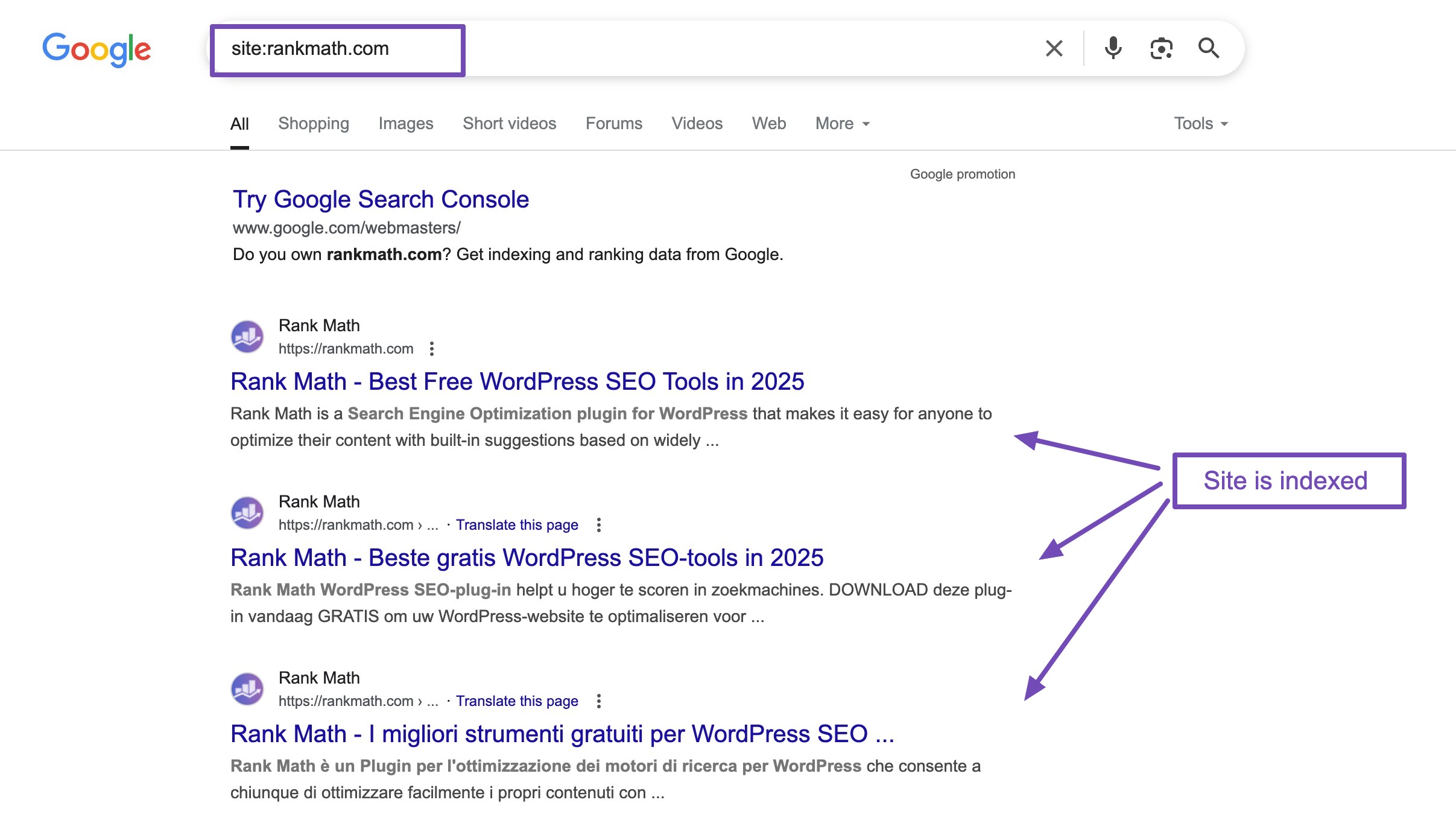
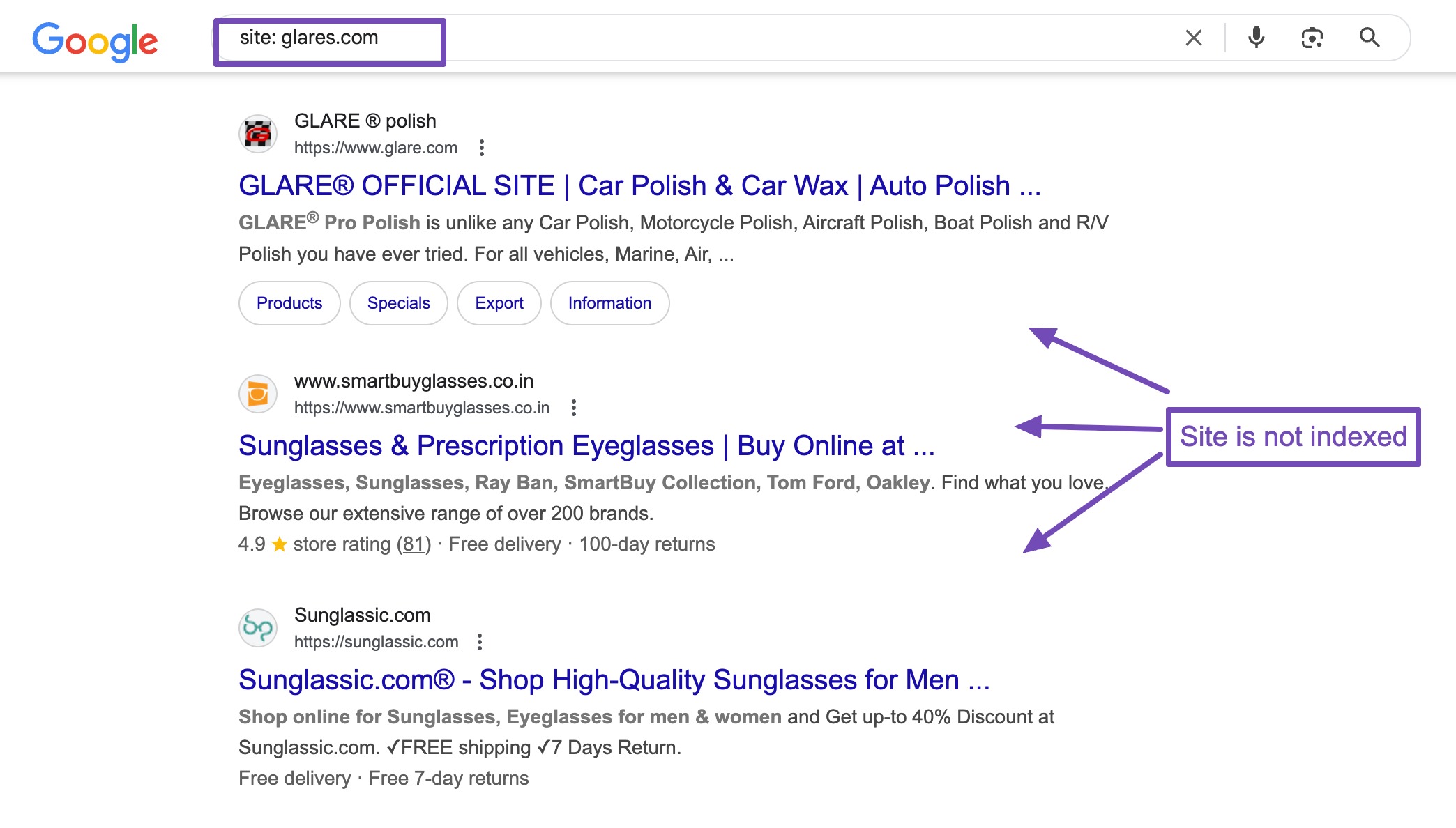
If nothing appears, there’s likely a reason you’re not receiving any traffic.
One common SEO mistake that can severely impact your website’s visibility and performance is misconfiguring the robots.txt file and the sitemap.
The robots.txt file serves as a guide for search engine crawlers, instructing them on which parts of your website they are allowed to access and index.
A misconfigured robots.txt file can unintentionally block search engines from crawling important pages, leading to poor indexing and diminished search visibility.
Similarly, a sitemap lists all the pages on your website that you want to be indexed.
If your sitemap is incomplete, outdated, or incorrectly formatted, it can cause search engines to miss key pages, resulting in an incomplete indexing of your site.
Refer to our dedicated tutorial on robtos.txt and sitemap issues and their fixes.
Fix: Ensure robots.txt File is Correctly Configured, and Submit a Sitemap to Google Search Console
Correctly Configure the Robots.txt File
Review your existing robots.txt file to identify any directives that might be blocking important pages. You can usually access this file by visiting yourdomain.com/robots.txt.
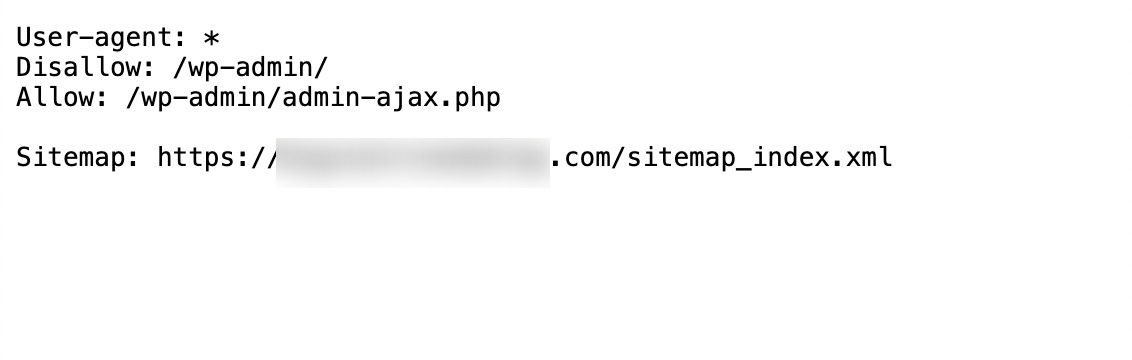
Ensure that key sections of your website, such as your main content pages, product pages, and blog posts, are not disallowed. Typically, you want to allow search engines to crawl these areas to improve their indexing.
Rank Math SEO makes it very easy to edit your robots.txt file.
To do so, navigate to Rank Math SEO → General Settings and click Edit robots.txt, as shown below.
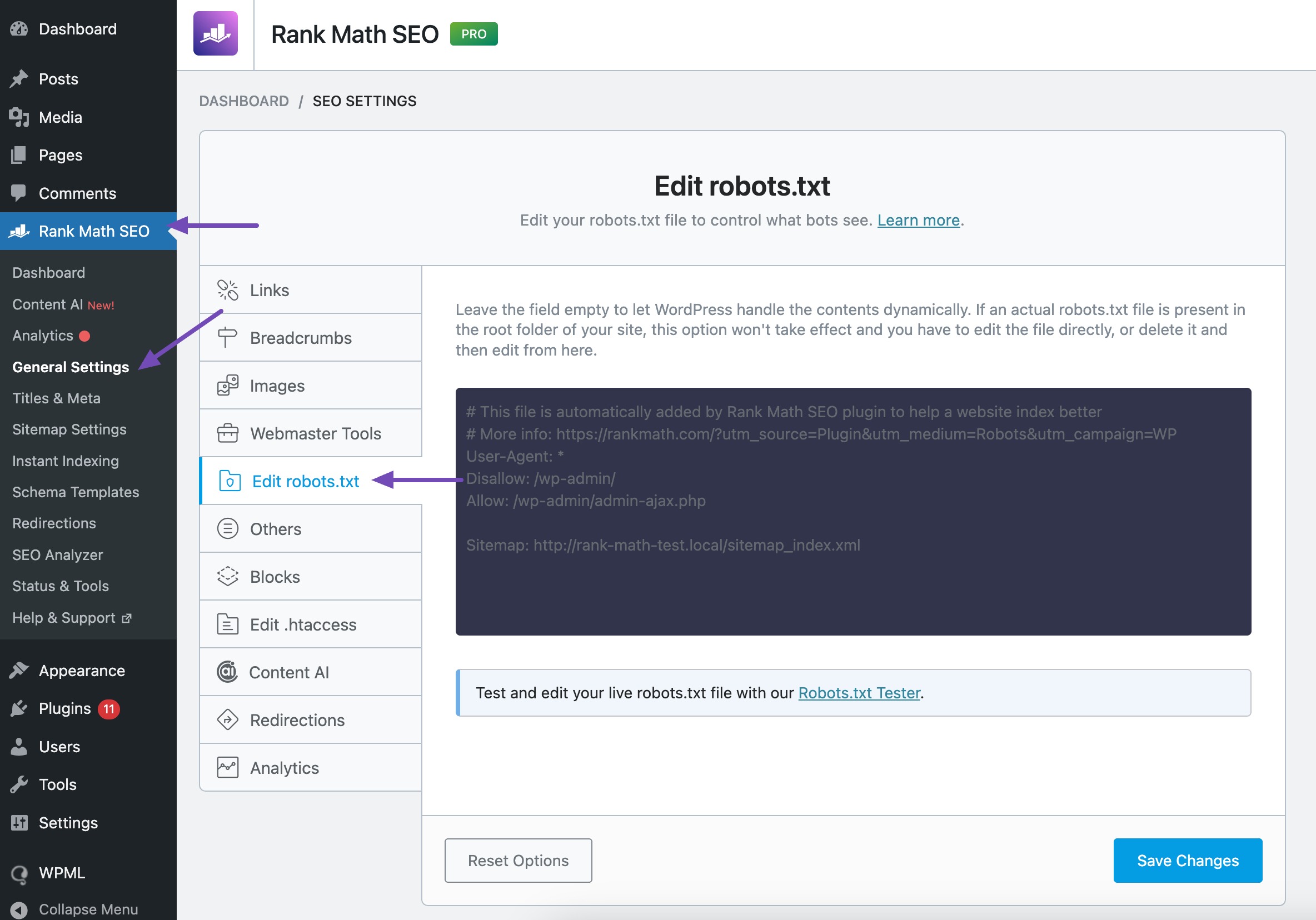
Once you’ve made the changes, save the robots.txt file.
While it’s important to allow access to essential pages, you may want to disallow search engines from crawling certain areas, such as admin pages, duplicate content pages, or sensitive information sections.
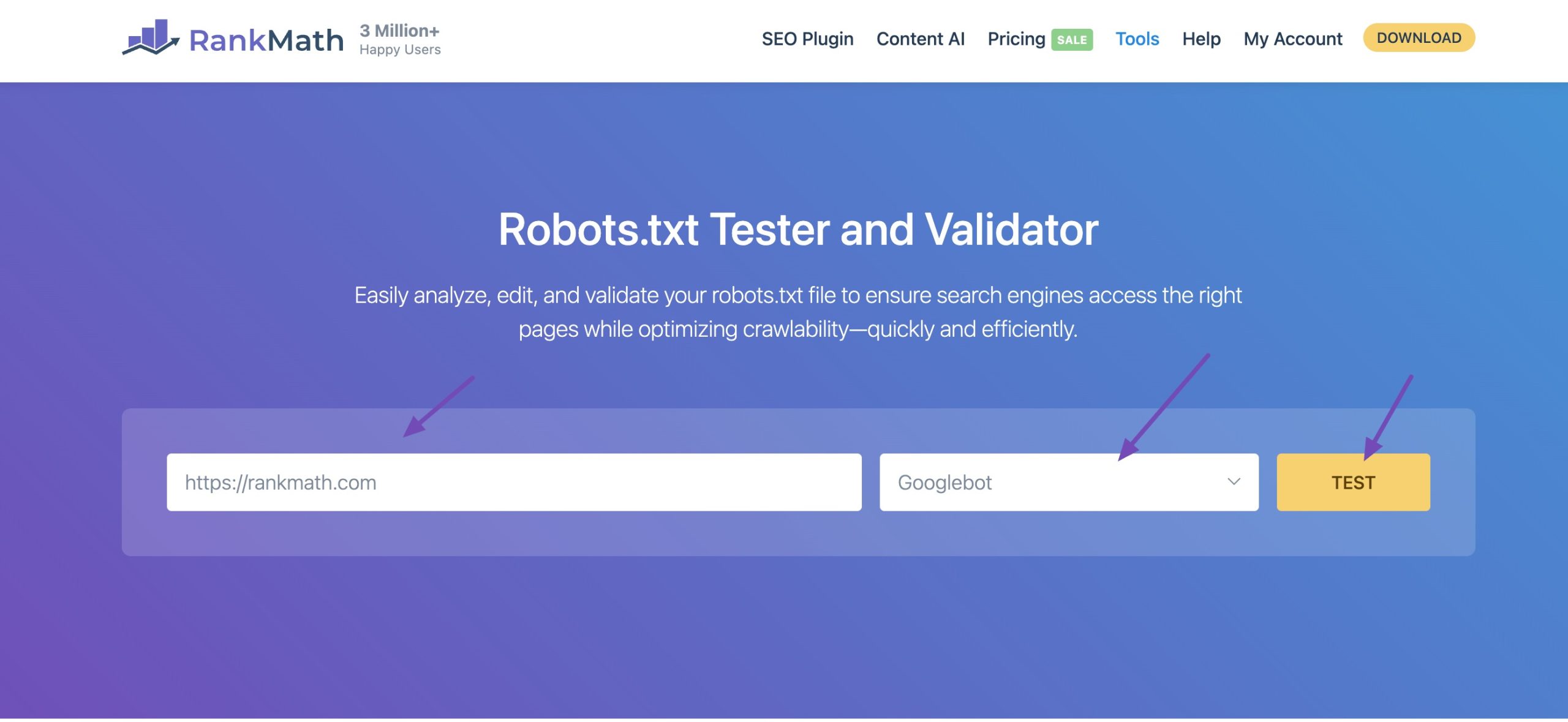
You can use a robots.txt tester tool to validate your robots.txt file and ensure there are no errors.
Simply enter your URL, choose the user agent (like Googlebot), and click TEST to verify that the file is working as expected.
Create and Submit a Sitemap
Rank Math SEO automatically submits your sitemap to Google. To do so, you have to connect Rank Math with your Google Search Console account.
To do so, navigate Rank Math SEO → Analytics → Connect Google Services (if you haven’t already).
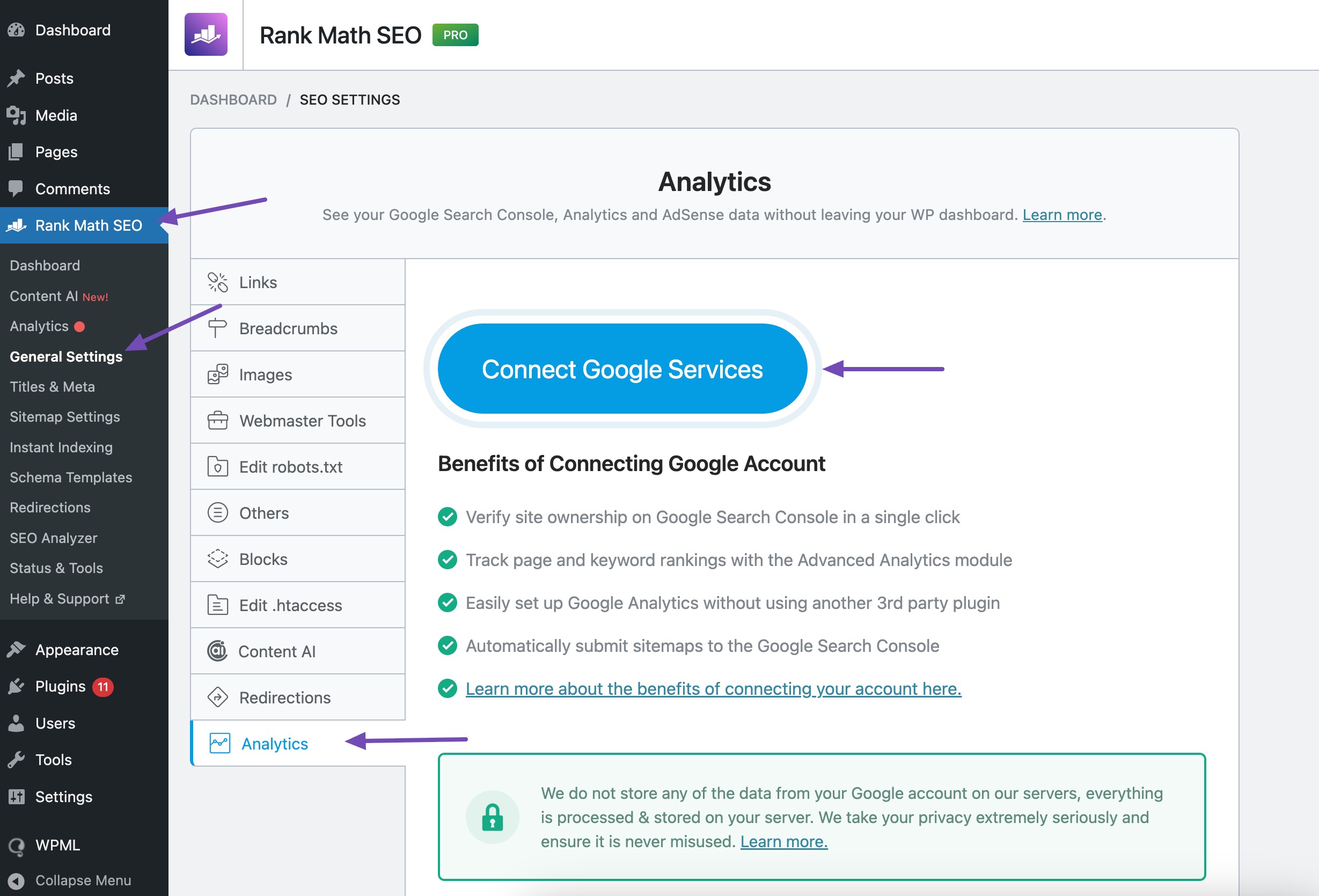
Sign in with the Google account you want to use. Grant the necessary permissions.
Once you have connected Rank Math SEO with your Google Search Console account, it automatically submits your sitemap index to Google.
Ensure your sitemap is up-to-date and includes only the pages you want search engines to index. Avoid including duplicate pages, low-quality content, or pages with no SEO value.
1.2 Unoptimized Website Structure
A poorly organized website structure can significantly hinder your SEO performance. When pages lack a clear hierarchy and logical organization, search engine crawlers struggle to index your content effectively, and users may find it difficult to navigate your site.
An unoptimized structure often features disorganized internal linking, no defined categories, and disconnected content. This can result in lower rankings on search engine results pages (SERPs), reduced crawl efficiency, and lost organic traffic opportunities.
Fix: Implement Best Practices for Website Structure
Start by building a clear, hierarchical structure for your site. Think of it like a pyramid:
Homepage → Main Categories → Subcategories or Individual Posts
For example, a recipe blog can follow this structure: Homepage → Recipes → Vegan Recipes → Chickpea Curry
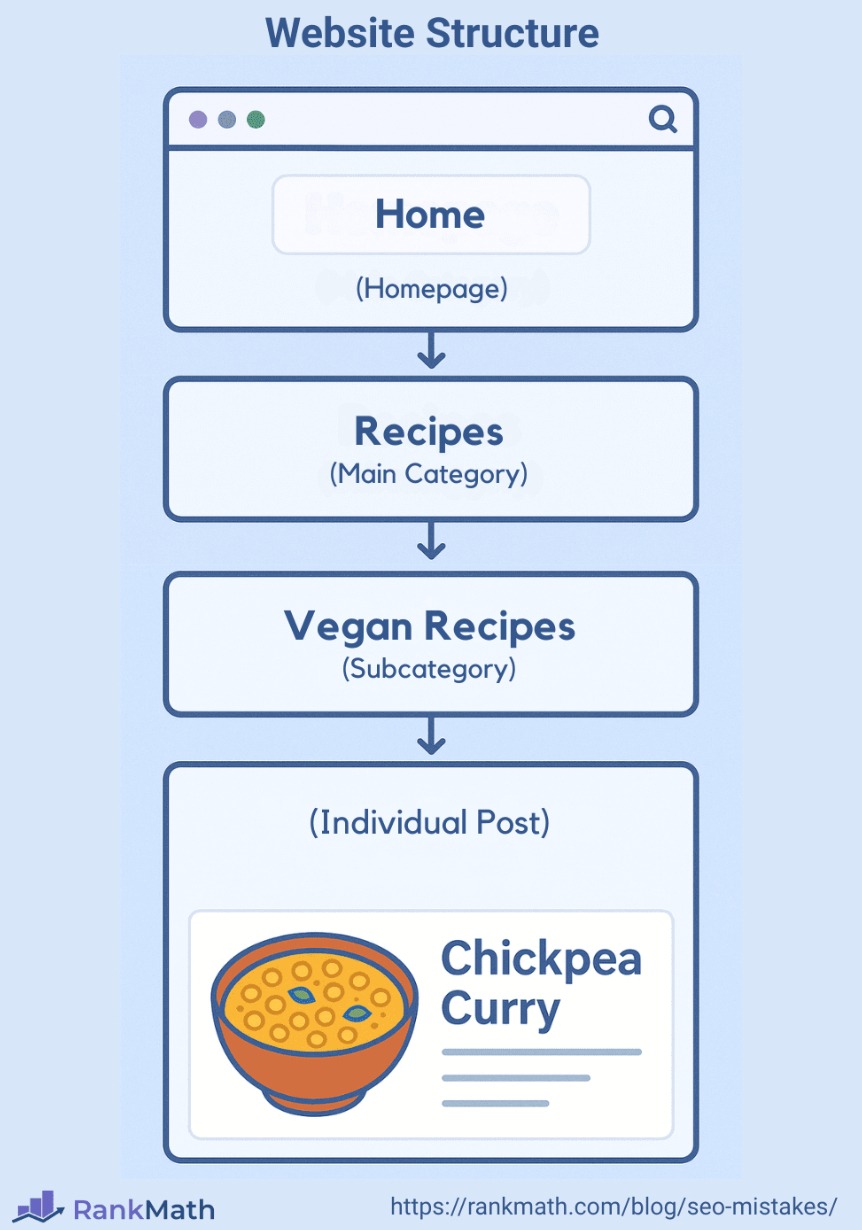
This layout helps users and search engines understand how your content is grouped and related.
Next, identify and fix orphan pages—pages that aren’t linked to from any other page on your site. These pages are invisible to both users and search engines unless directly accessed. With Rank Math PRO, you can easily find and fix them.
Once you’ve installed the PRO version of Rank Math, navigate to the posts/pages section from your WordPress dashboard to find the orphan pages. Select Orphan Posts from the drop-down menu and click on Filter as shown below.
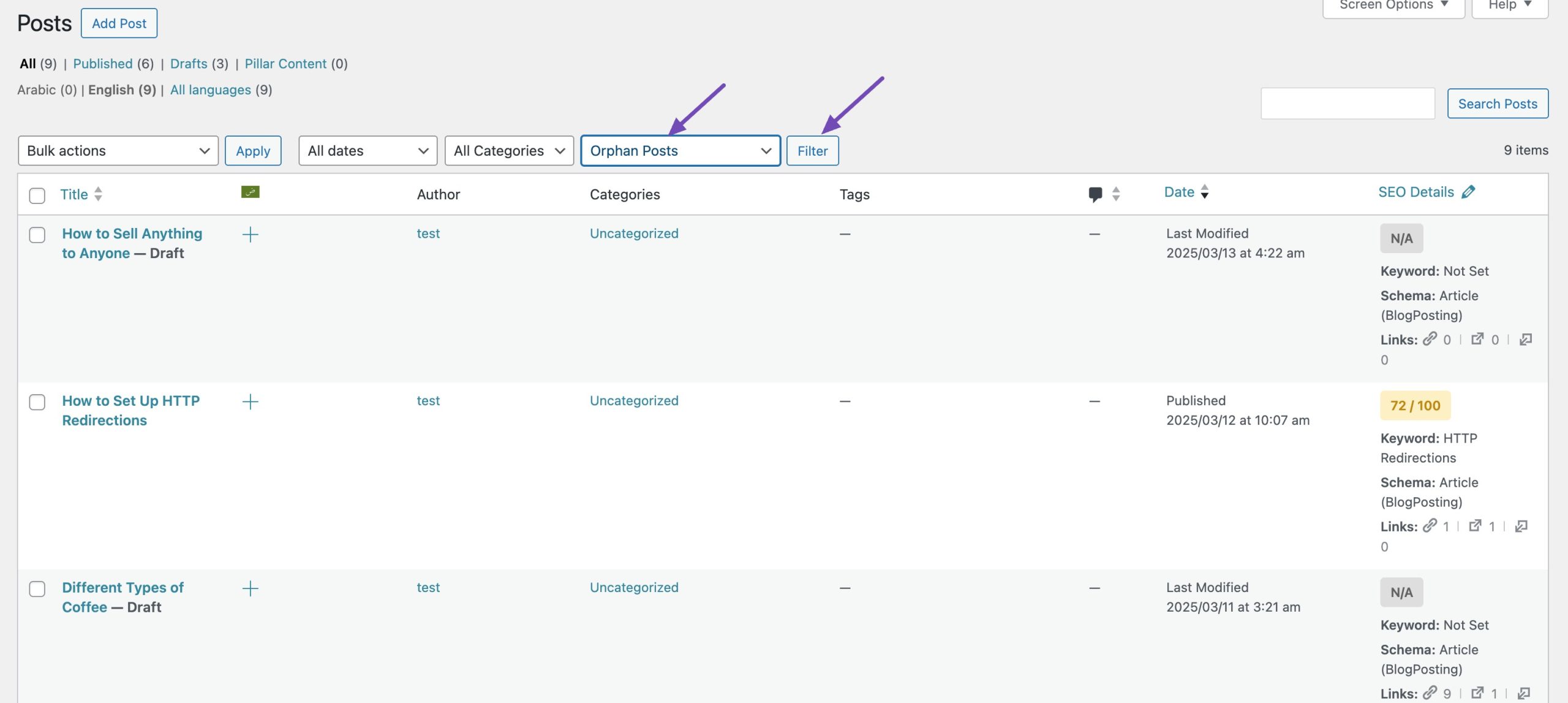
Rank Math SEO will display all the orphan posts, pages, and custom posts within seconds on your screen.
Also, with Rank Math’s AI Link Genius, you can easily identify orphan pages and add relevant internal links to them. From your WordPress dashboard, click Rank Math SEO. Once done, scroll down and enable the Link Genius module, as shown below.
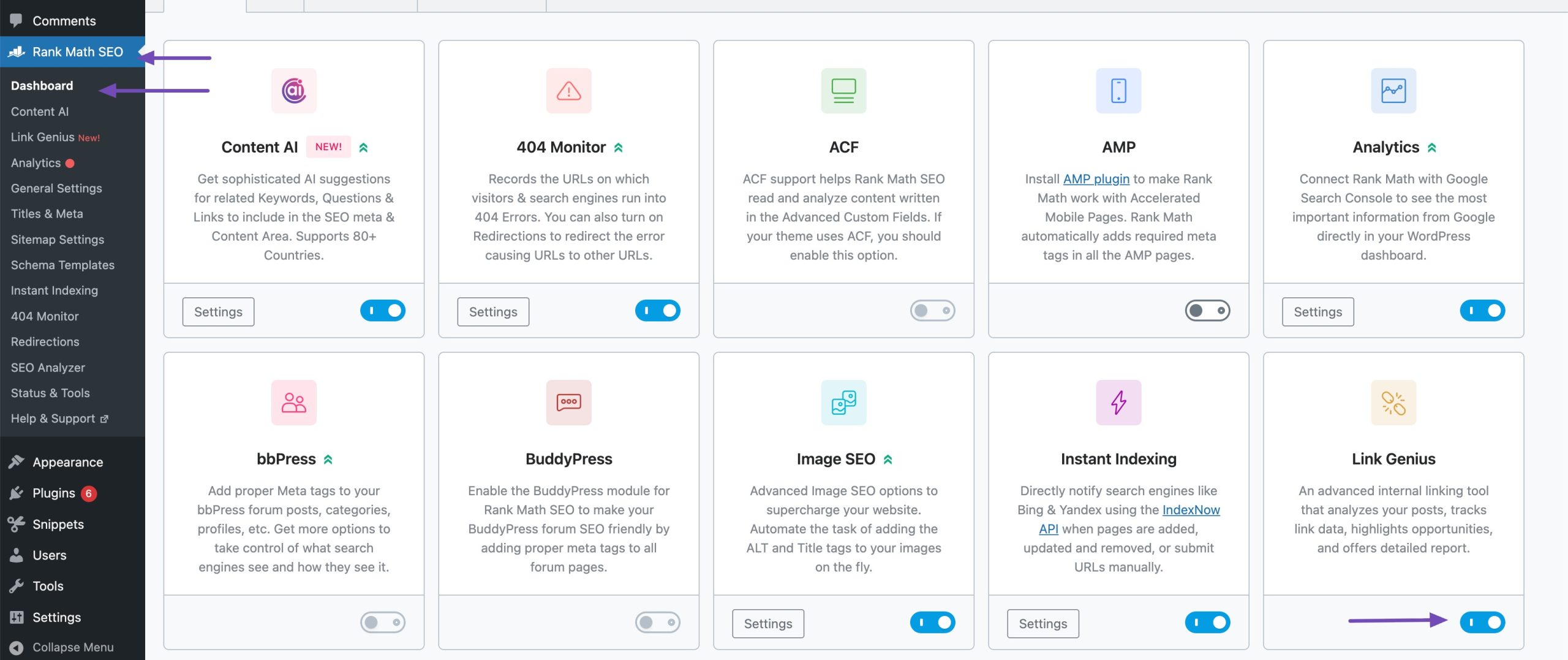
Navigate to Rank Math SEO → Links from your WordPress dashboard. Then, click Posts and click Orphan Posts. You will be presented with the orphan posts on your site.
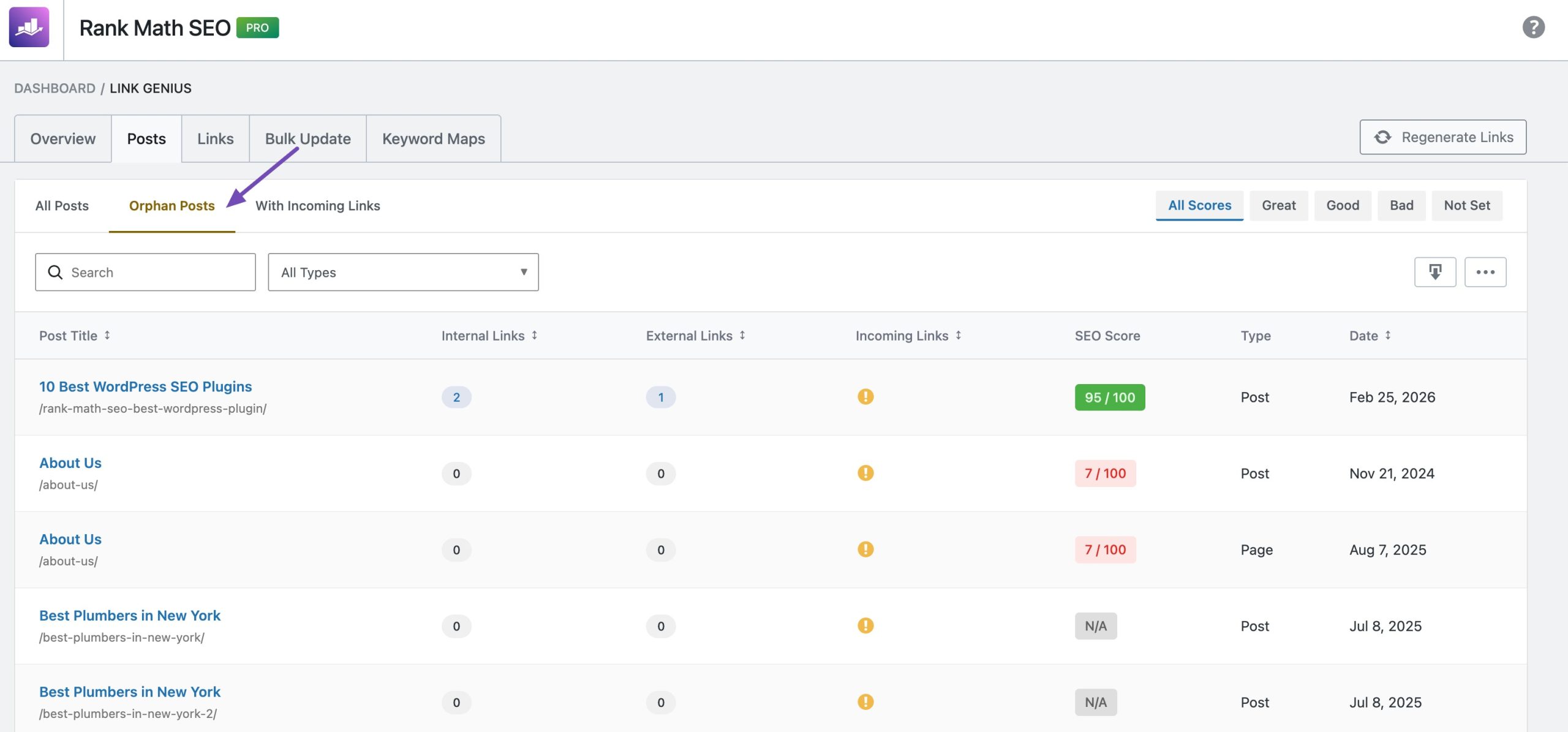
Now, click on the page you want to fix. Then click the Rank Math SEO icon. Scroll down the Rank Math SEO sidebar and click Link Opportunities. Then, click Generate.
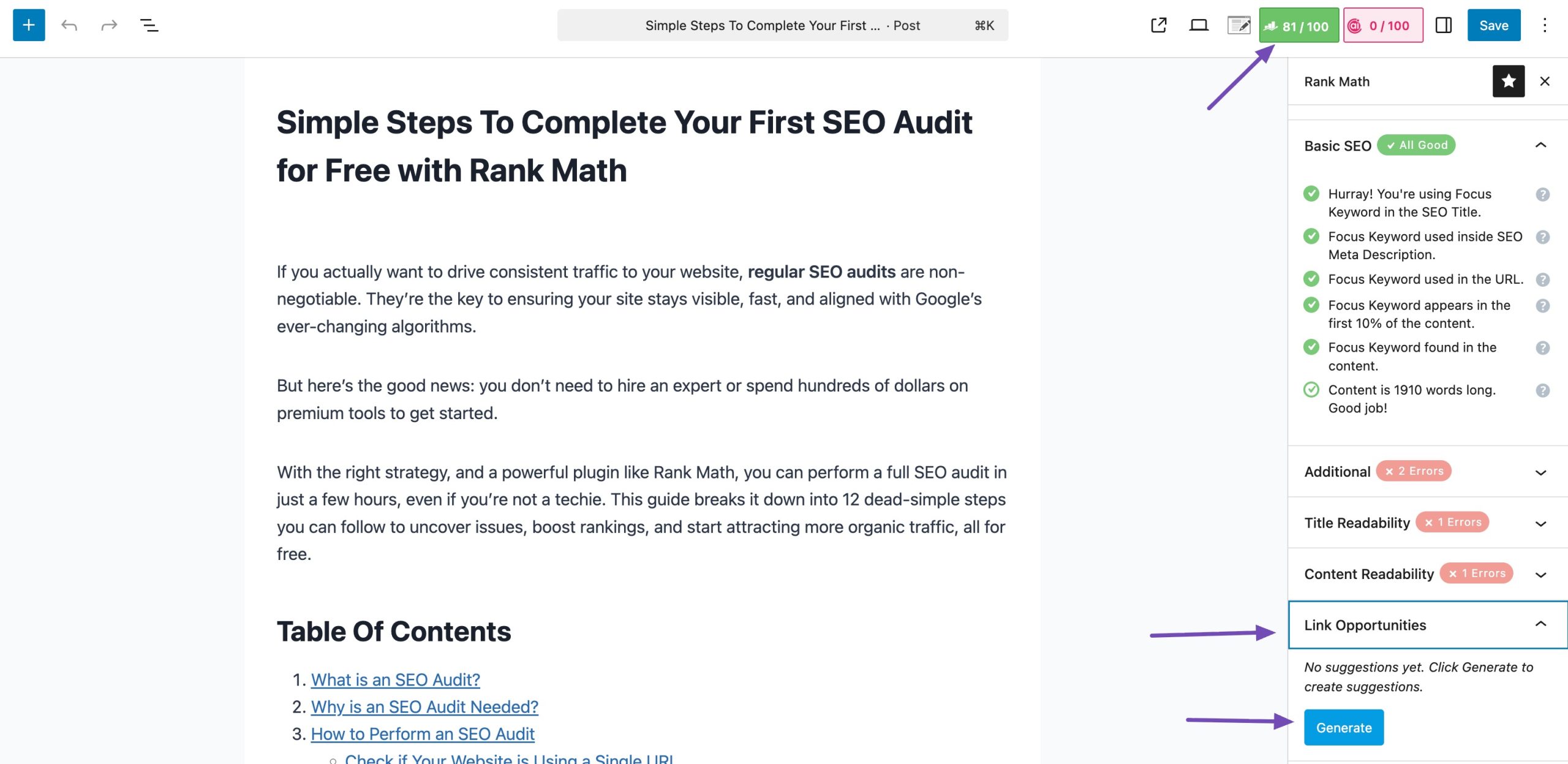
Rank Math will generate relevant internal links. Each link has two options: Copy Link URL and Insert URL.
- Copy Link URL: Copies the link to your clipboard
- Insert URL: Inserts the internal link directly into the post
Also, ensure your internal links reflect your site’s structure. Use keyword-rich anchor text and link related content wherever appropriate. Organize your categories and subcategories logically, and make sure your URLs are descriptive and SEO-friendly.
Refer to our dedicated tutorial on website structure to improve the website navigation.
1.3 Slow Page Load Times
Another SEO issue that many websites suffer from is slow page load times.
Slow page load times are a critical SEO issue that negatively affects both user experience and search engine rankings. Search engines like Google prioritize fast, responsive websites, and slow-loading pages can lead to reduced visibility and organic traffic.
When pages take too long to load, visitors are more likely to leave your site before engaging with your content. This increased bounce rate signals to search engines that the user experience is poor.
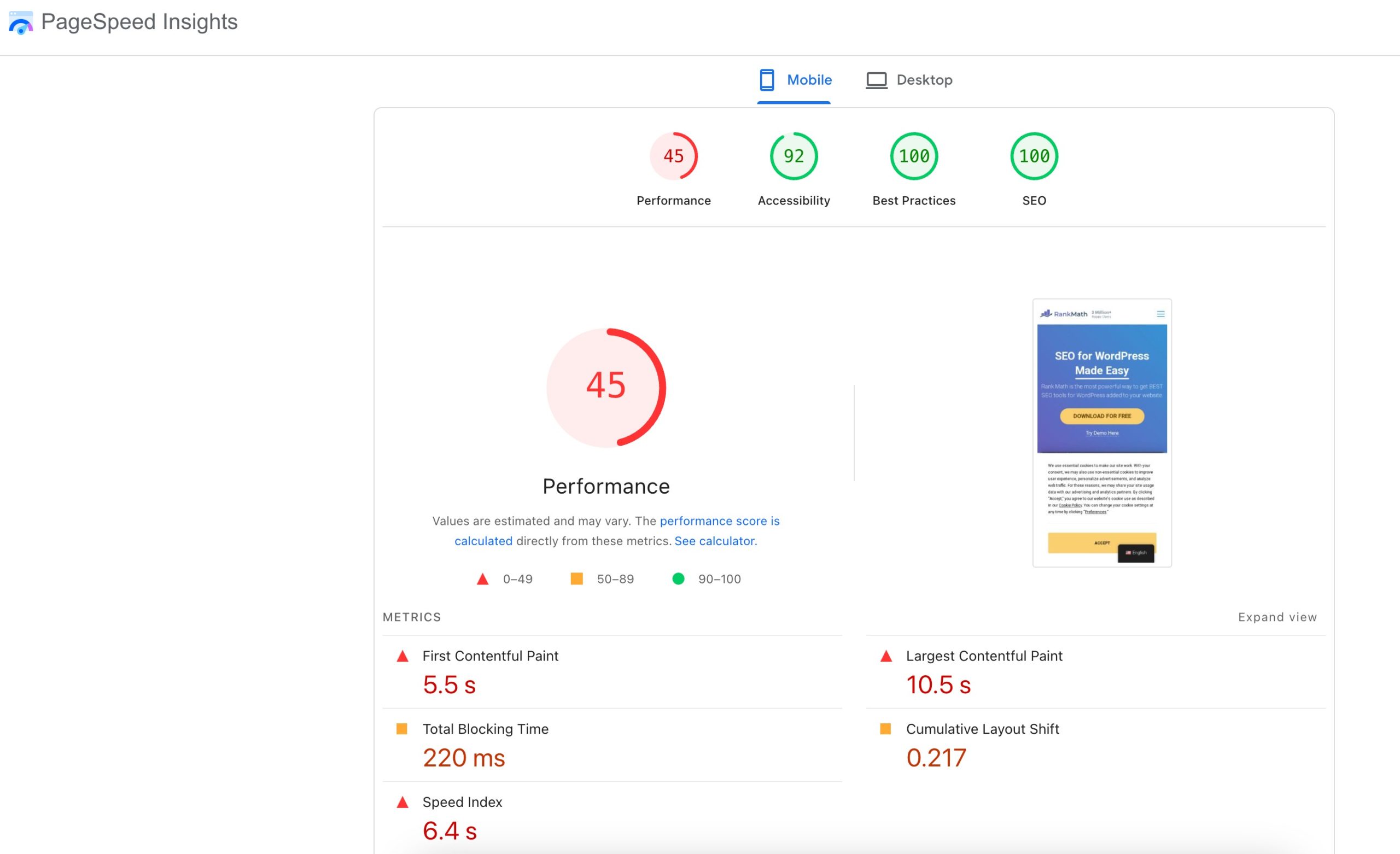
Key performance metrics, such as Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) and Total Blocking Time (TBT), help identify where performance is lagging.
To identify slow page load times, you can use Google PageSpeed Insights, enter your URL, and run the analysis. The tool will highlight performance scores and key metrics like Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) and Total Blocking Time (TBT) to show where your page is slowing down, along with recommendations for improvement.
Fix: Optimize Images, Leverage Browser Caching, and Use a Content Delivery Network (CDN)
To address slow page load times and improve both user experience and SEO, consider implementing the following solutions.
Optimize Images
Compressed images load faster and use less bandwidth. Use tools such as TinyPNG to reduce images’ file sizes without sacrificing quality. You can also consider using the Imagify plugin, which helps you to optimize your images effortlessly.
Use appropriate image formats for different types of images. For instance, JPEG is generally better for photographs, while PNG is preferable for images with transparency.
Add alt tags to your images. Alt text (alternative text) helps search engines understand what your images are about. It’s essential for image SEO and also improves accessibility for users relying on screen readers.
Fortunately, Rank Math SEO allows you to automatically add missing alt attributes to images using dynamic variables, such as the image file name, which should be manually set to something descriptive and relevant. Ensure that you’ve enabled the Image SEO module from your WordPress dashboard.
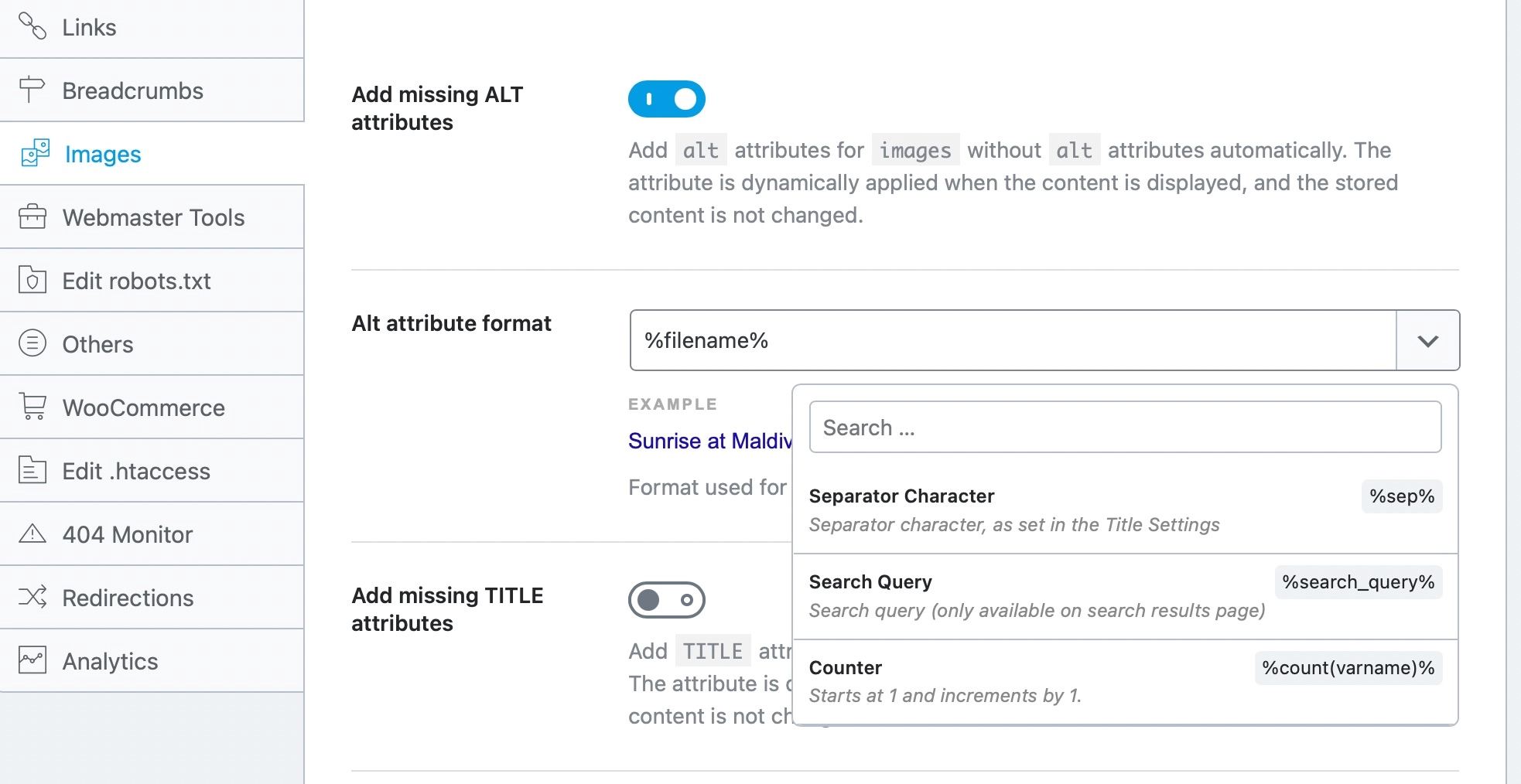
And, Rank Math SEO changes the image alt text value on the frontend of your website (i.e. without changing the value that’s stored) so that if at a later date you wish to alter the alt text again and set something manually, this can be done.
You can also use our Content AI to generate alt text for your images in WordPress. When you upload an image to your Media Library, simply click the Generate Alt button next to the Alt Text field, and the AI will generate an alt text for you, as shown below.
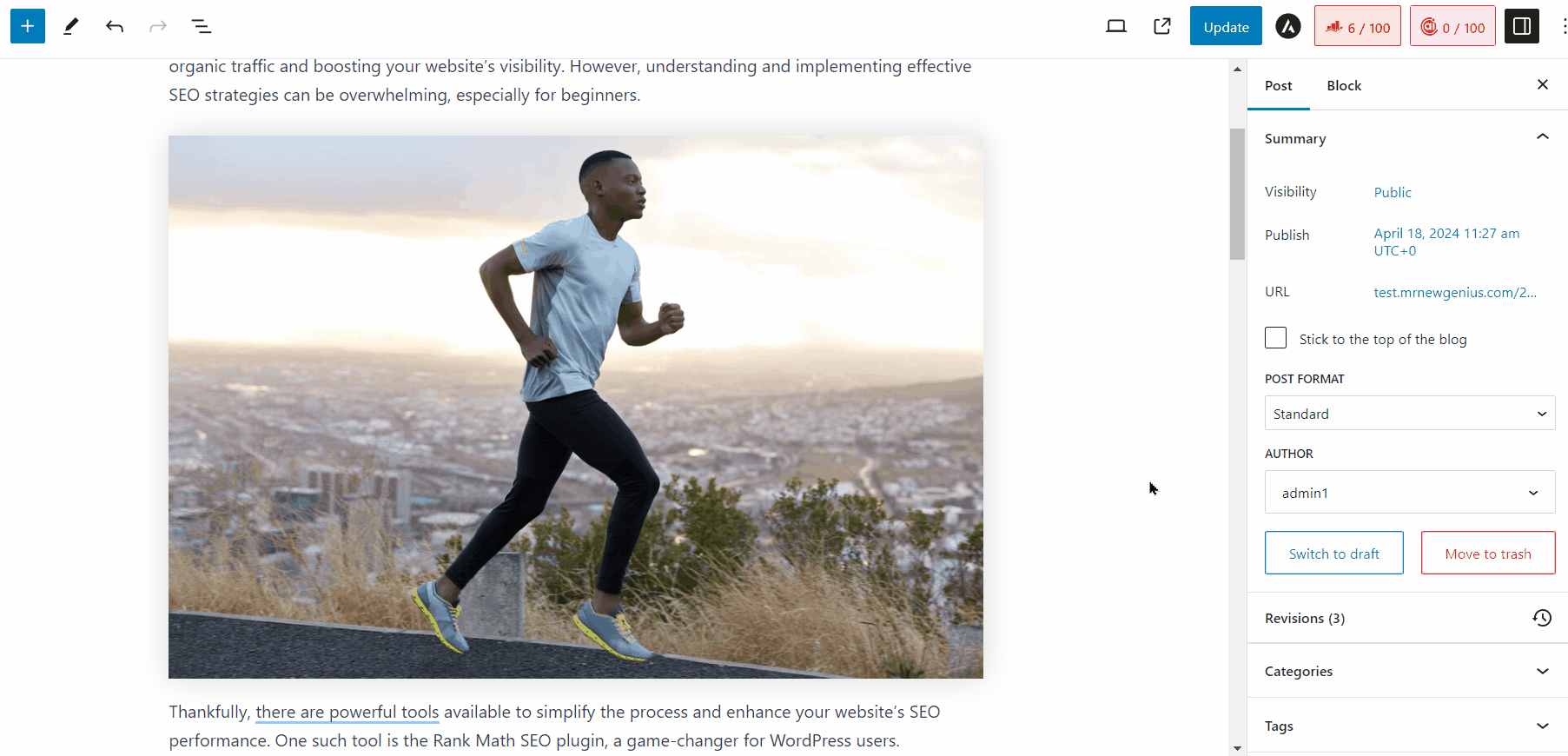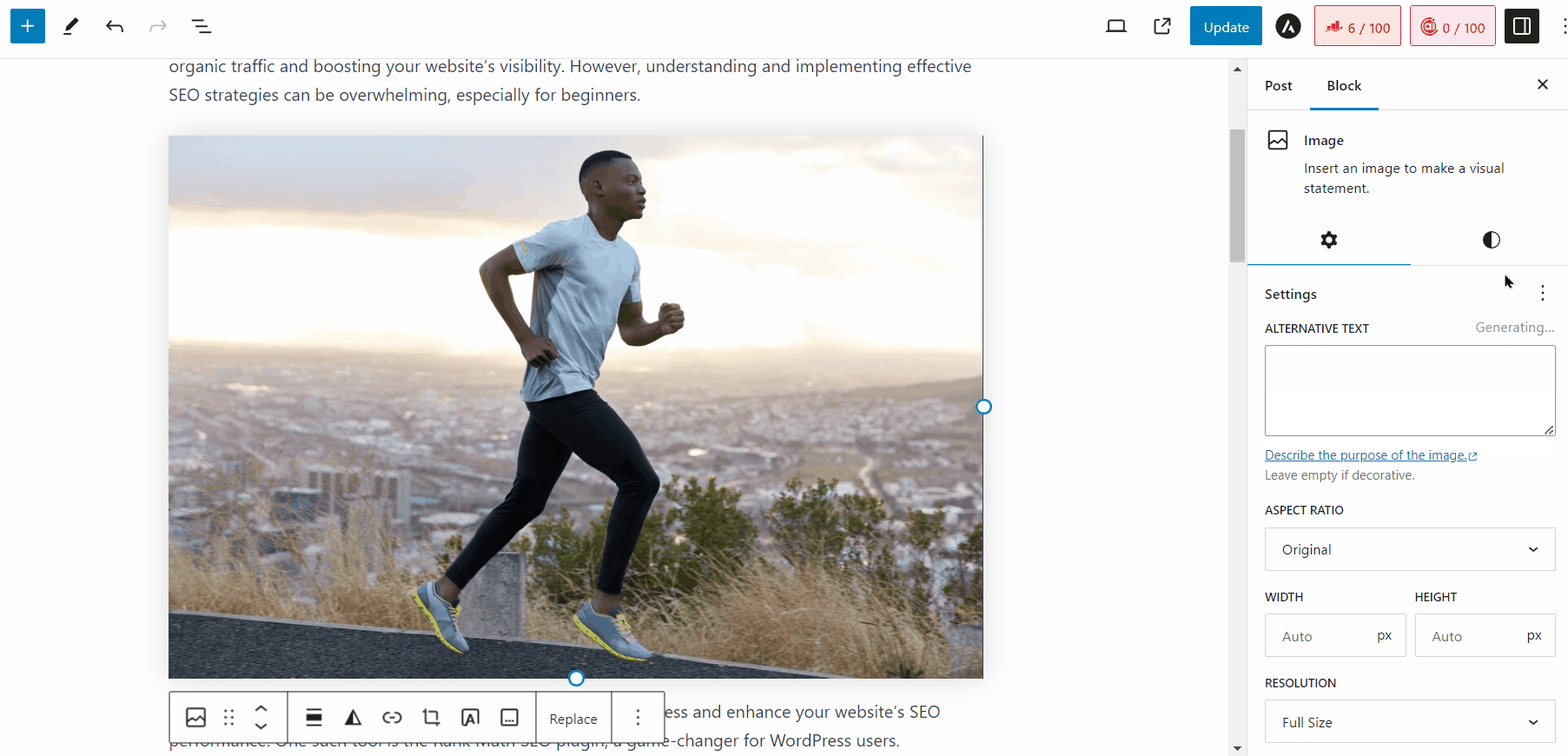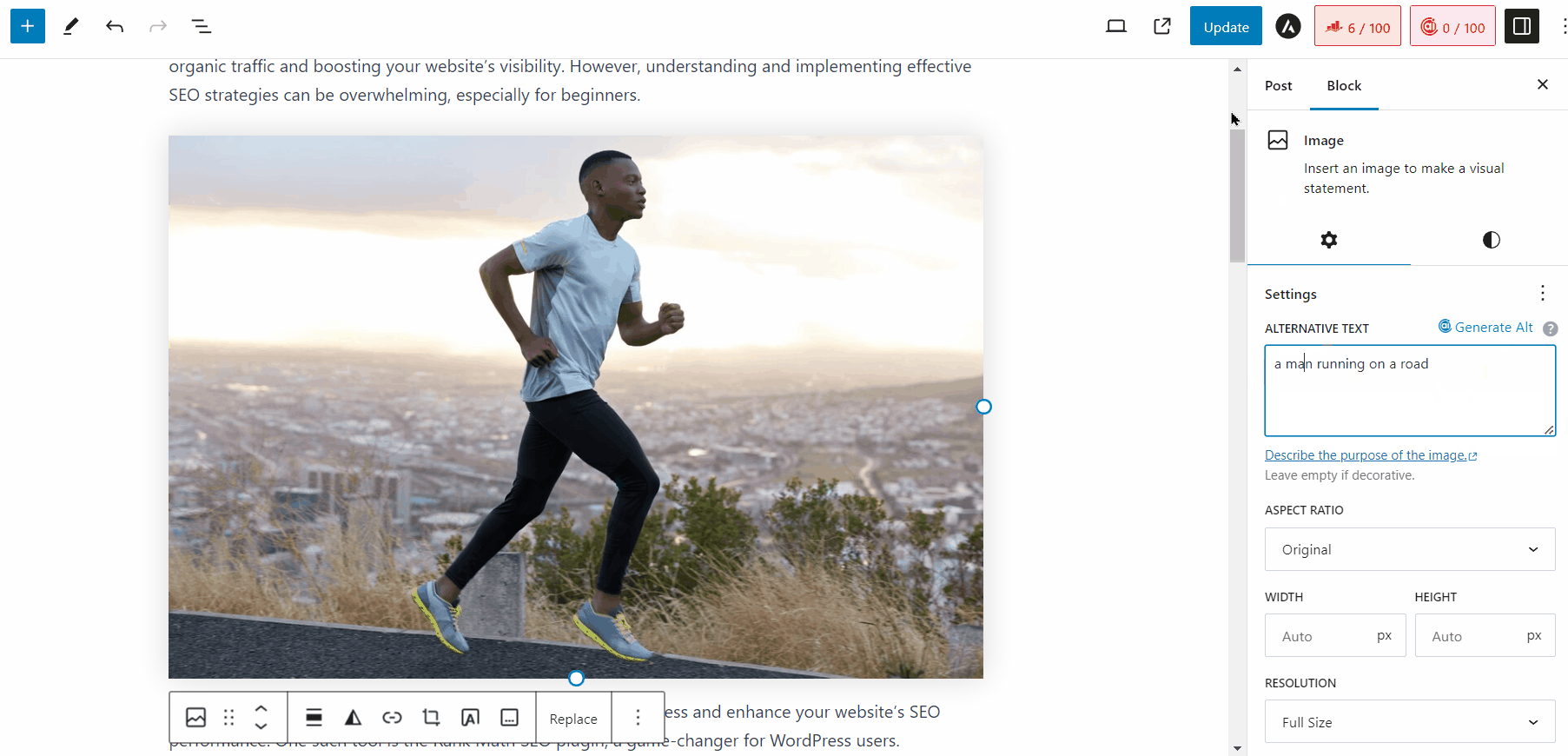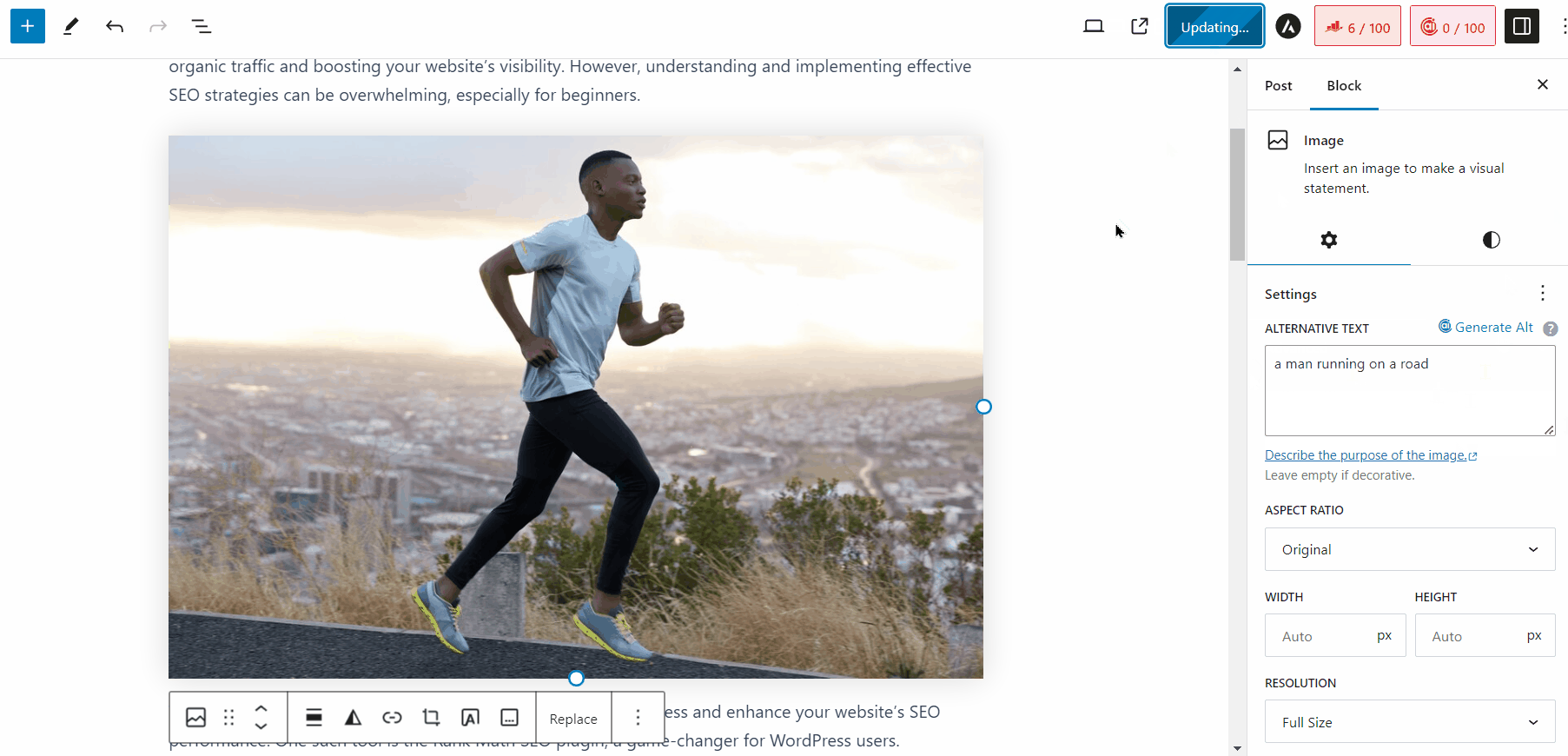
You can also refer to our image SEO guide, which covers the various ways to optimize images for search.
Leverage Browser Caching
Browser caching helps speed up your website by storing frequently used resources (like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript files) in the visitor’s browser. This way, returning users don’t have to download the same files every time they visit your site.
To enable browser caching, configure your server to set expiration dates for various file types. This tells the browser how long to keep these files before checking for updates. You can also use cache-control headers to define how long browsers and other intermediaries (like CDNs) should store your content.
If you’re using WordPress, installing a caching plugin makes this process much easier. Tools like WP Rocket and W3 Total Cache offer advanced caching features and customization options.
It’s no surprise that 56% of respondents from our survey are using WP Rocket. With WP Rocket, enabling browser caching is effortless—just install and activate the plugin. It automatically handles page caching and other performance optimizations for you.
Use a Content Delivery Network (CDN)
A Content Delivery Network (CDN) improves your website’s speed by distributing its static content, such as images, CSS, and JavaScript files, across a network of servers located around the world. When someone visits your site, the CDN delivers the content from the server closest to them, reducing latency and load times.
We recommend using RocketCDN, a premium CDN that seamlessly integrates with WP Rocket for easy setup and optimal performance.
By offloading static files to the CDN, you lighten the load on your main server and ensure faster content delivery to users, no matter where they are.
Refer to our dedicated tutorial on speed optimization to improve your website’s load times.
1.4 Broken Links and 404 Errors
Broken links and 404 errors are common SEO mistakes that significantly impact your website’s performance.
Broken links occur when a URL points to a page that no longer exists, leading the audience to a 404 error page.
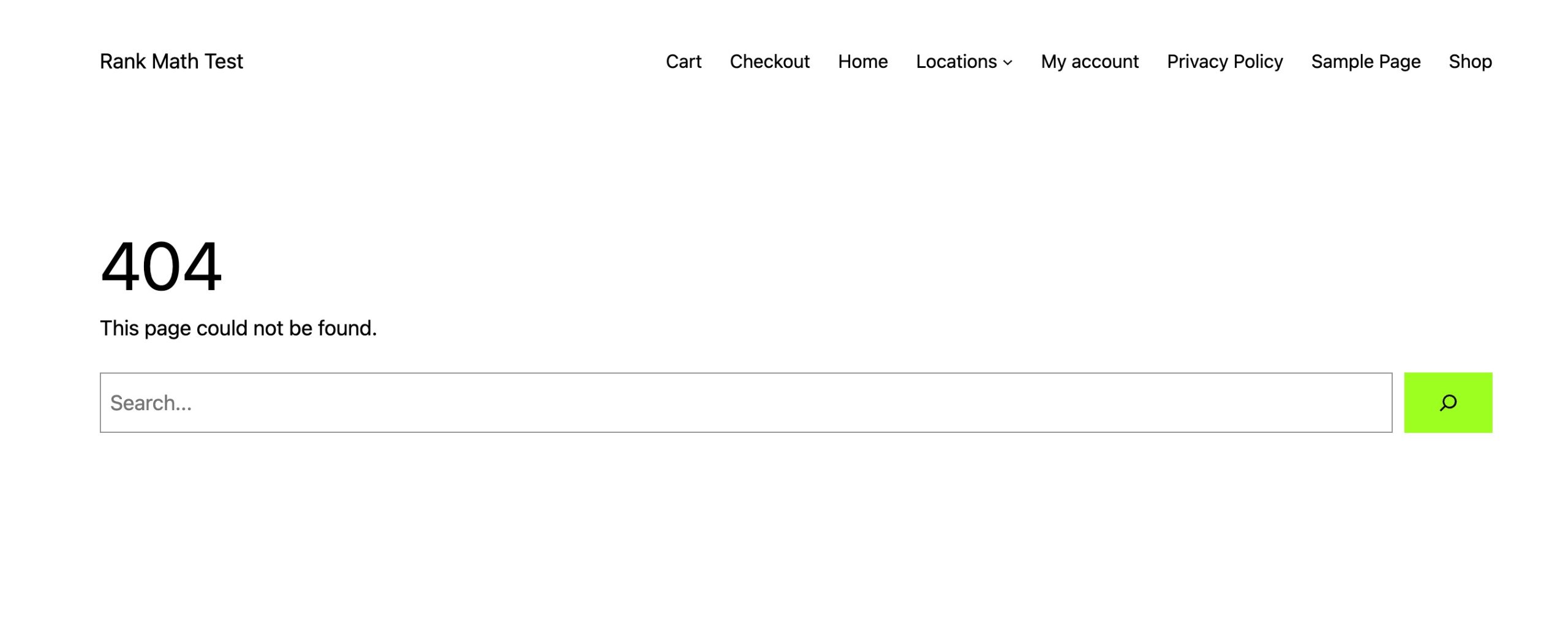
This not only frustrates users but also increases bounce rates, signalling poor user experience to search engines.
In the AI Link Genius, click Rank Math SEO → Links, as shown below. Then, click Links again. You will be presented with the status of your links. Click Broken. This report shows the internal and external broken links on your site. To view the internal broken links alone, click Internal, and to click the external broken links alone, click External.
Additionally, broken links can disrupt the flow of link equity, negatively affecting your site’s ability to rank in search engine results.
Fix: Regularly Audit the Site for Broken Links and Set Up 301 Redirects Where Necessary
Use tools like Google Search Console to scan your website for broken links. These tools can identify URLs that return 404 errors or other status codes indicating issues.
In Google Search Console, navigate to the Pages section and check the box for Not indexed to view pages that aren’t indexed.
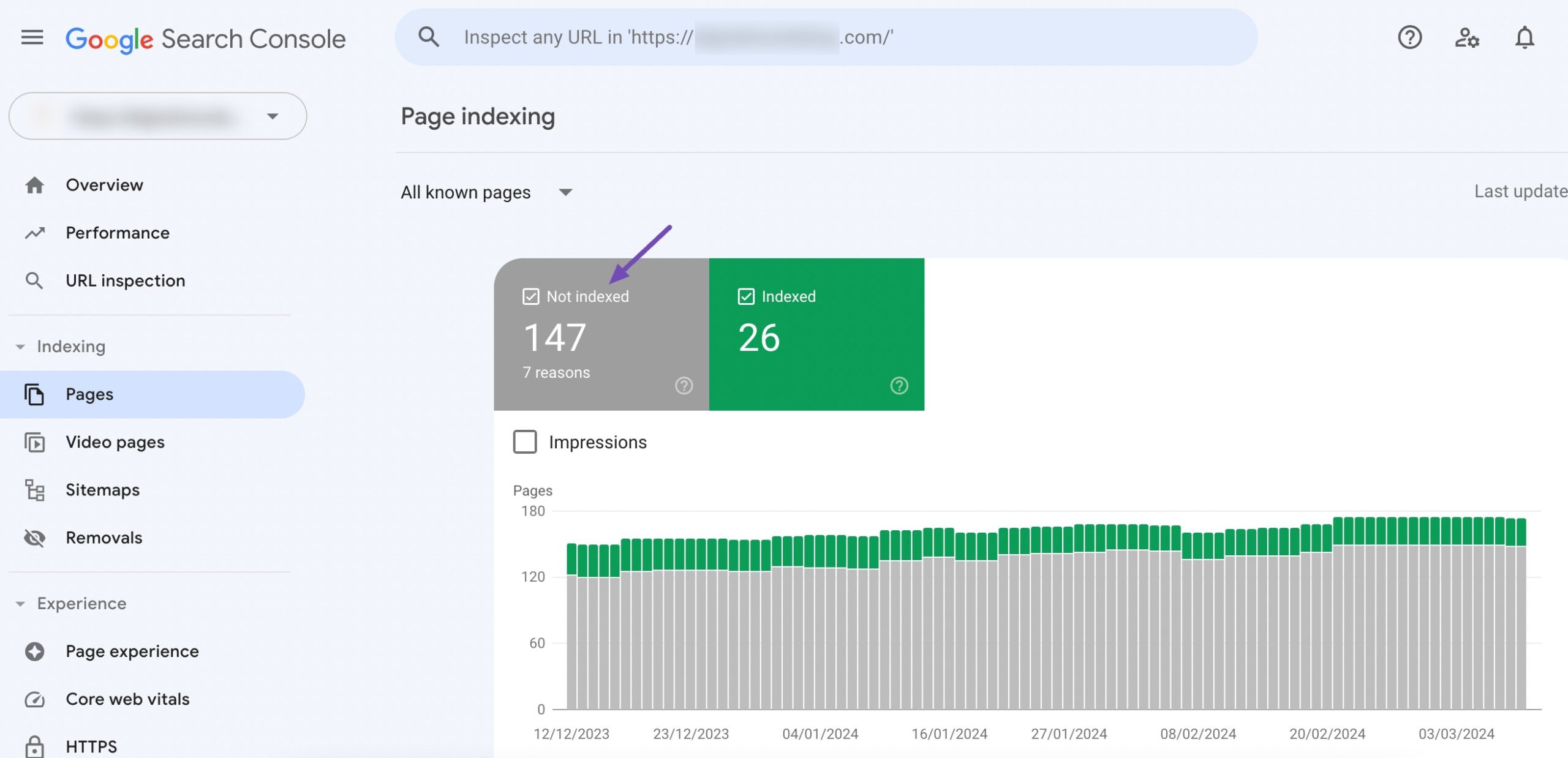
Scroll to the Why pages aren’t indexed section and look for Not found (404). Click it to see a list of broken links causing 404 errors, helping you identify and fix these issues.
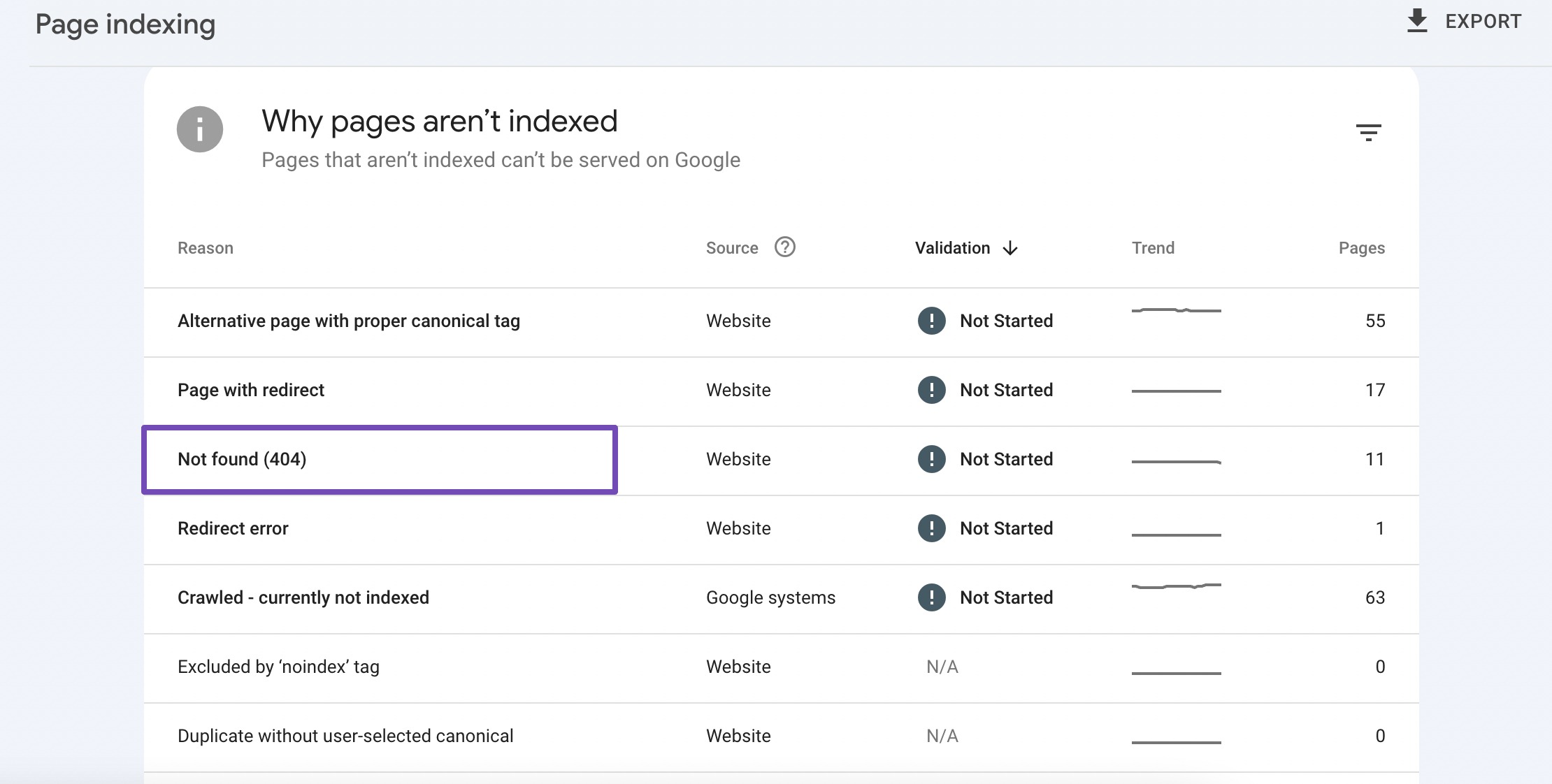
You can also use Rank Math SEO to monitor the 404 errors on your site.
To do so, navigate to Rank Math SEO → Dashboard → Modules, switch to Advanced Mode, and enable both the 404 Monitor and Redirections modules.
Next, go to Rank Math SEO → 404 Monitor to view a log of all 404 errors on your site. To fix a broken link, hover over it and click Redirect, or select multiple URLs to apply a bulk redirect.
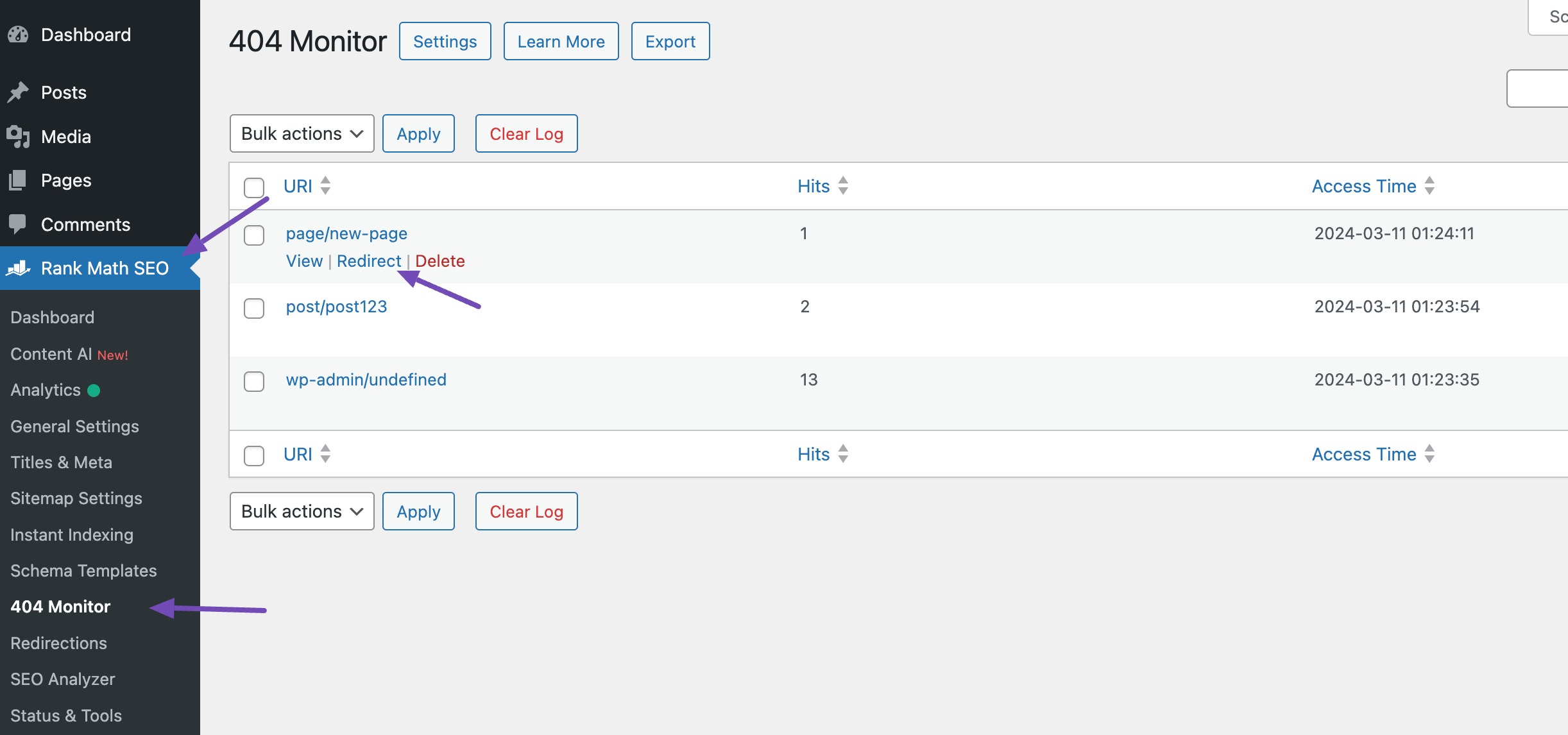
You’ll be taken to the Redirections page. Enter the destination URL, keep the redirection type as 301 (Permanent Move), and configure optional settings like activation time or category. Then click Add Redirection.
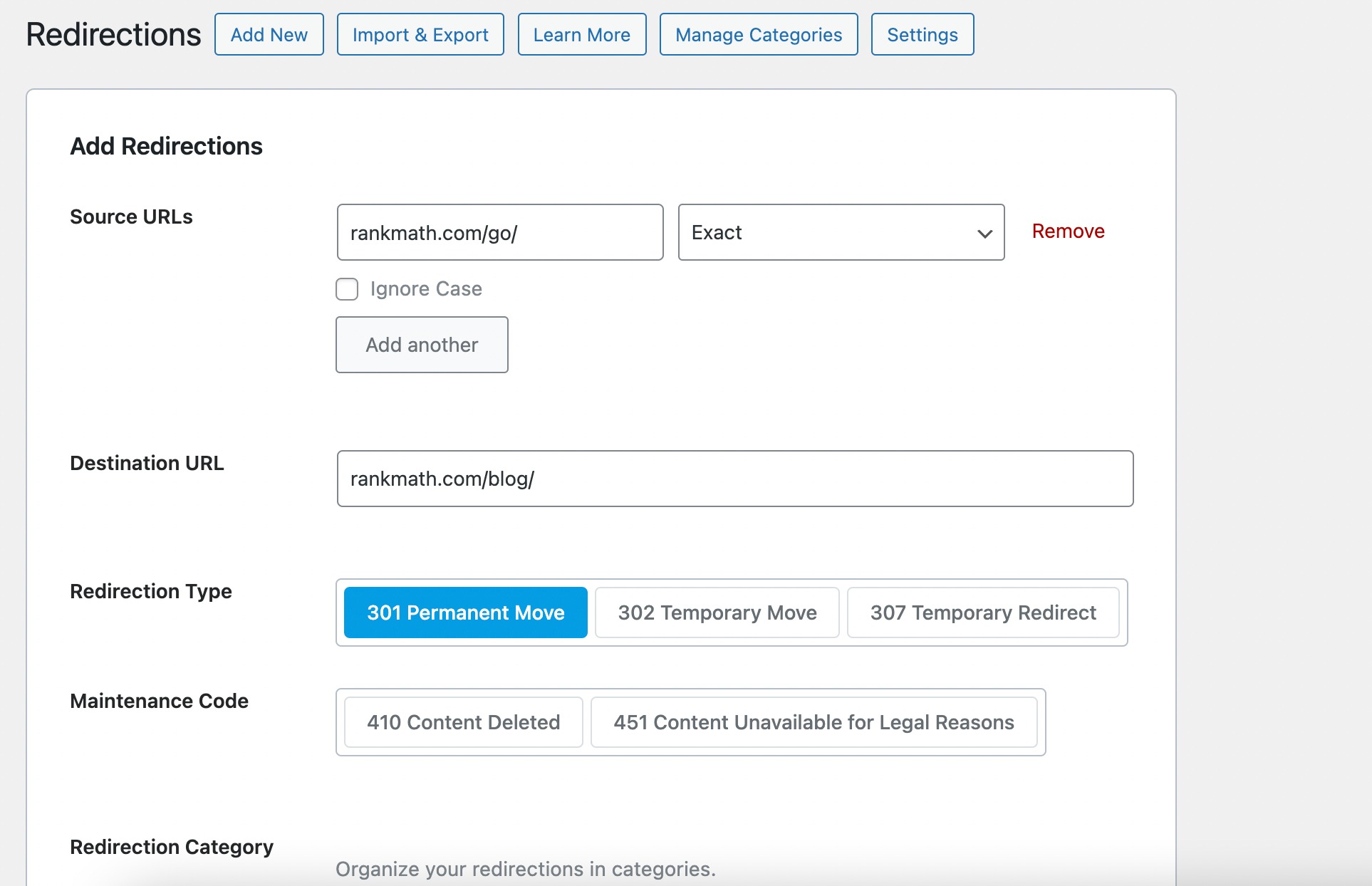
To view and manage existing redirects, go to Rank Math SEO → Redirections.
Alternatively, you can choose to delete broken links, update the URLs, or resolve the root cause of the errors.
Set up regular, automated audits to monitor your site for broken links continuously. This approach helps catch and resolve issues promptly, maintaining a smooth user experience.
After setting up 301 redirects, update any internal links on your site that pointed to the old URLs. This ensures that the audience and crawlers directly access the correct pages without relying on redirects.
If possible, reach out to the owners of sites that link to your broken pages and request an update to the new URL. This step enhances the user experience and maintains the value of inbound links.
Refer to our dedicated tutorial on finding and fixing broken links in WordPress.
1.5 Ignoring Mobile Optimization
One significant SEO mistake is ignoring mobile optimization.
As more audiences access the internet via mobile devices, having a website that isn’t mobile-friendly can severely impact user experience and SEO performance.
A site that doesn’t adapt to different screen sizes can lead to poor navigation, slow load times, and overall frustrating user experiences.
Moreover, search engines like Google prioritize mobile-friendly websites.
Why is Mobile Important?
A mobile-friendly website isn’t just a nice-to-have—it’s essential. Here’s why your mobile presence is important to your business:
- Mobile-friendly sites rank higher in Google search results.
- More than half of all searches on Google.com come from mobile devices.
- The majority of traffic for many advertisers comes from mobile users.
- Visitors are 5x more likely to leave if your site isn’t mobile-friendly.
Your audience is on mobile. Make sure your website is ready for them.
Fix: Implement Responsive Design and Test Mobile Usability
Nothing frustrates mobile users more than a non-responsive website. For instance, the below screenshot shows a non-responsive website where important information is buried in layouts designed only for desktops. This kind of poor experience can cause visitors to bounce almost instantly.

Design your website with mobile users in mind first, then progressively enhance the experience for larger screens. This approach ensures that mobile usability is prioritized.
Use CSS media queries to create flexible grid layouts that adapt to different screen sizes. This ensures that your content looks good and functions well on any device.
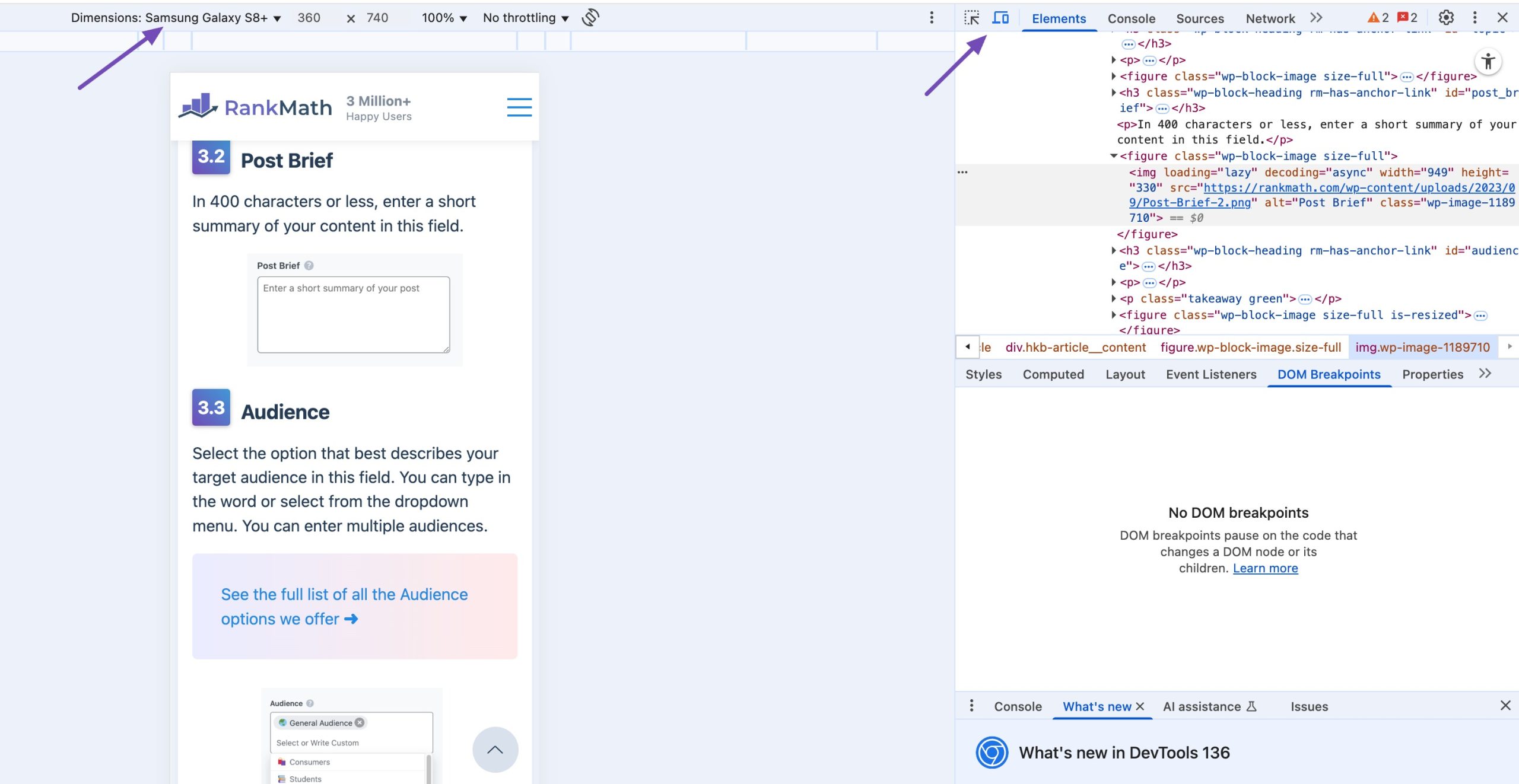
Make sure images and fonts scale appropriately for various screen sizes. To check this, navigate to your post or page, right-click on it, and select Inspect. Click on the Toggle Device Toolbar and then select the device to browse your page.
1.6 Lack of Schema Markup
The lack of Schema markup is a significant SEO issue. It deprives search engines of valuable context about a website’s content, resulting in less visibility and fewer opportunities for rich snippets in search engine results pages (SERPs).
Schema Markup, or structured data, provides search engines with additional information about webpage content. This enhances their understanding and enables rich snippets like star ratings, product prices, and event details.
Fix: Add Schema Markup
You can fix this SEO issue using Rank Math SEO and utilize the built-in Schema Markup feature within the plugin.
Rank Math SEO offers a user-friendly interface for implementing structured data across various types of content, including articles, products, events, recipes, and more.
Refer to our dedicated tutorial on Schema markup and implement Schema Markup at the click of a few buttons.
Just for a quick run-through, ensure the Schema module is enabled in Rank Math SEO, as shown below.
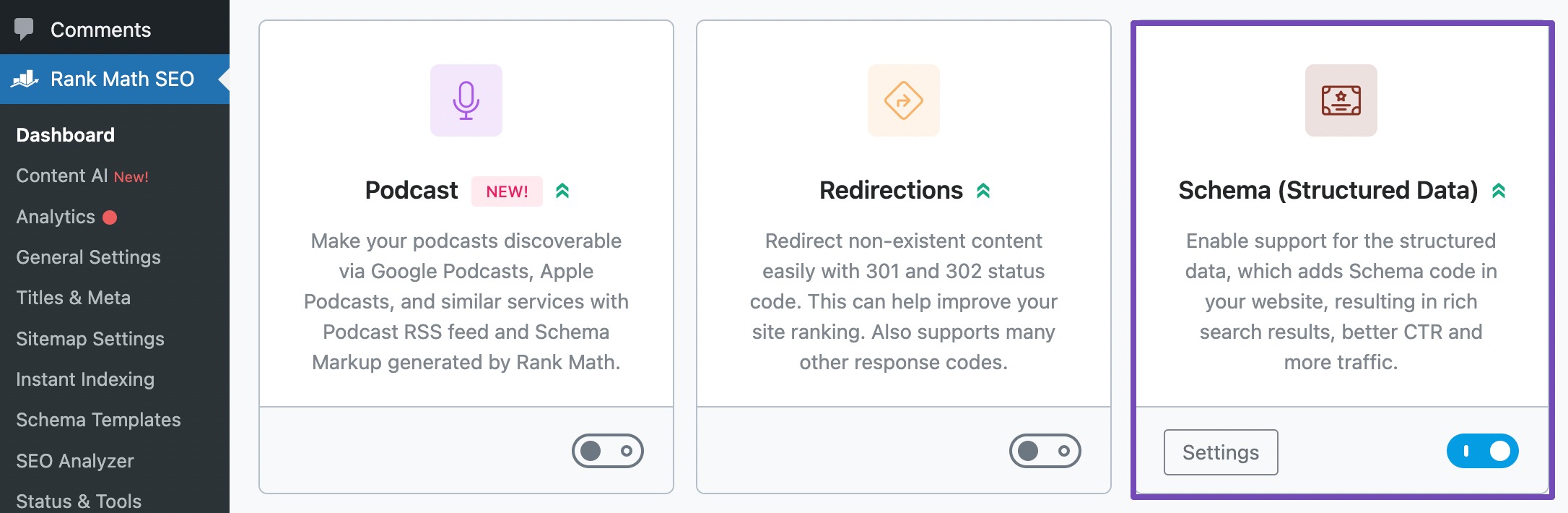
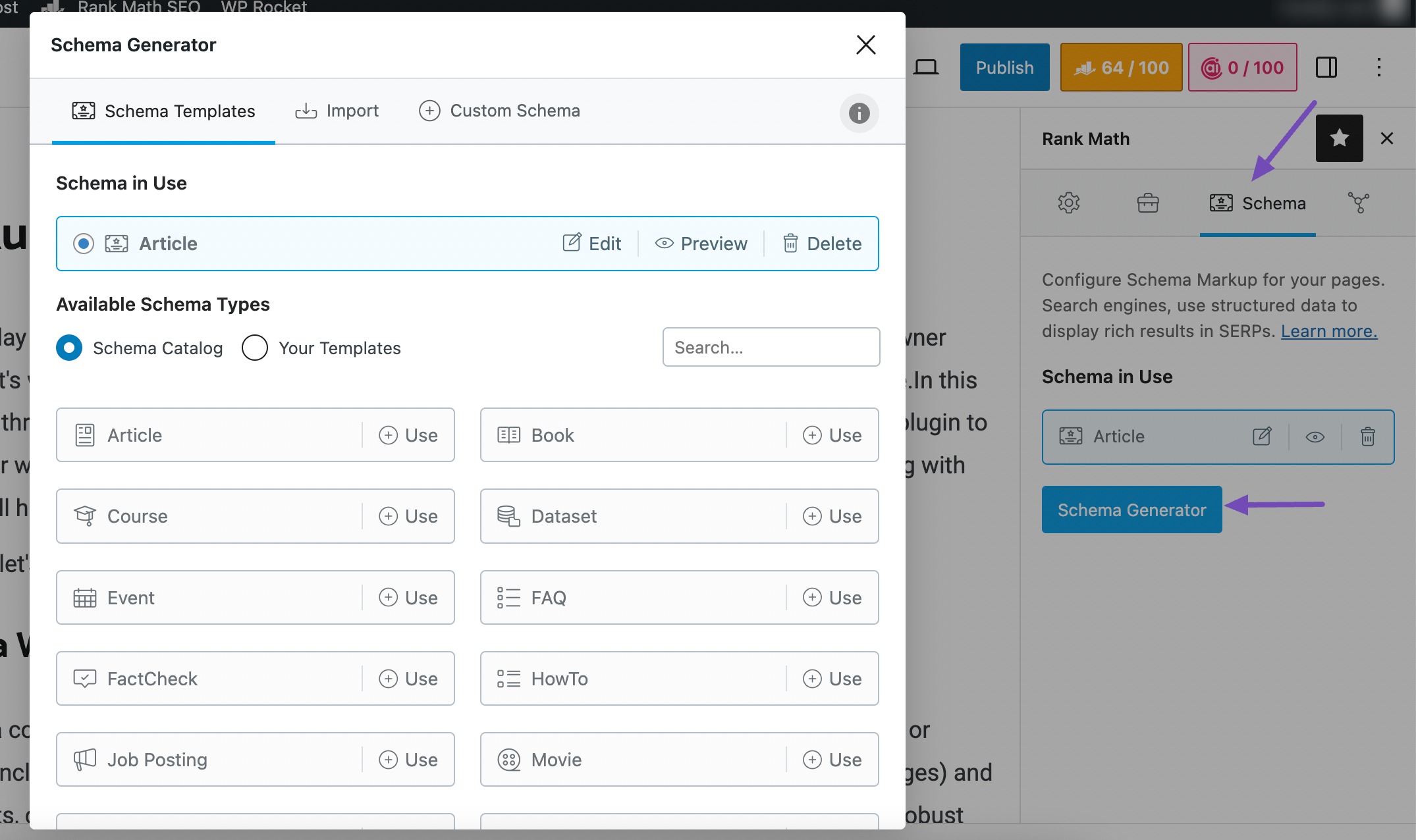
Access the Schema section in Rank Math’s settings to configure Schema settings for different types of content. You can then customize Schema markup according to your website’s needs and content types.
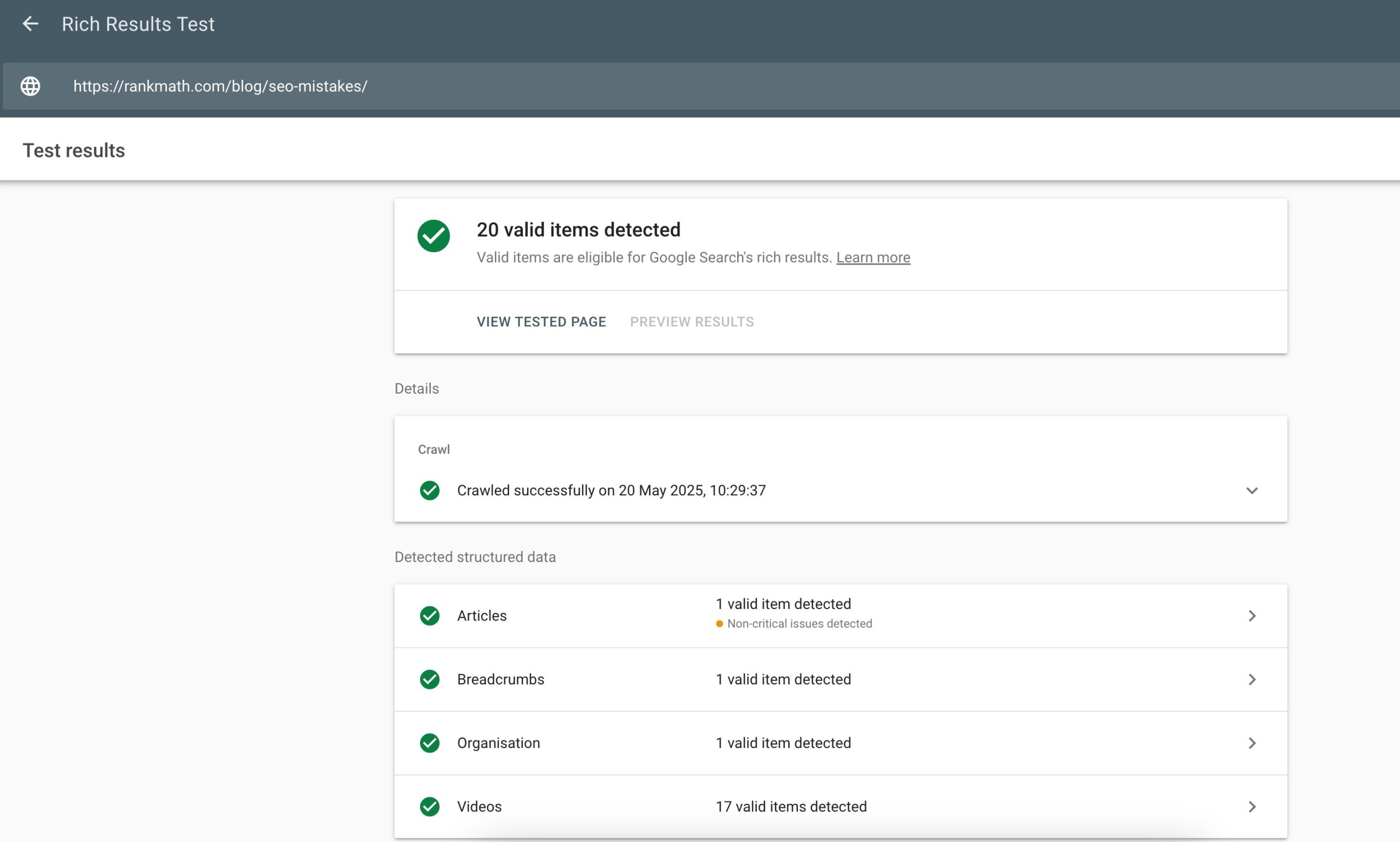
After implementing Schema markup, use Google’s Rich Results Test to validate the structured data and ensure that it meets Google’s guidelines.
2 Common On-Page SEO Mistakes & Fixes
Let us now discuss the common on-page SEO mistakes.
2.1 Poor Keyword Research
One of the most common on-page SEO mistakes is targeting the wrong keywords.
This can occur when keywords are chosen without thorough research, leading to a focus on terms that are either too competitive, too vague, or irrelevant to the target audience.
Targeting the wrong keywords can result in low search engine rankings, reduced traffic, and minimal engagement from visitors who do not find the content relevant to their needs.
Additionally, it can lead to wasted effort on content creation and optimization that does not yield the desired SEO results.
Fix: Use Tools to Find Relevant Keywords With the Right Balance of Competition and Search Volume
Start with broad terms related to your business, products, or services. These are your seed keywords that will form the basis of your research.
Use keyword research tools like Google Keyword Planner, Semrush, Ahrefs, etc, to expand your list of potential keywords. These tools provide data on related keywords, search volume, and competition levels.
To use Google Keyword Planner for keyword research, start by signing into your Google Ads account and navigating to the Tools menu.
Under the Planning section, click on Keyword Planner.
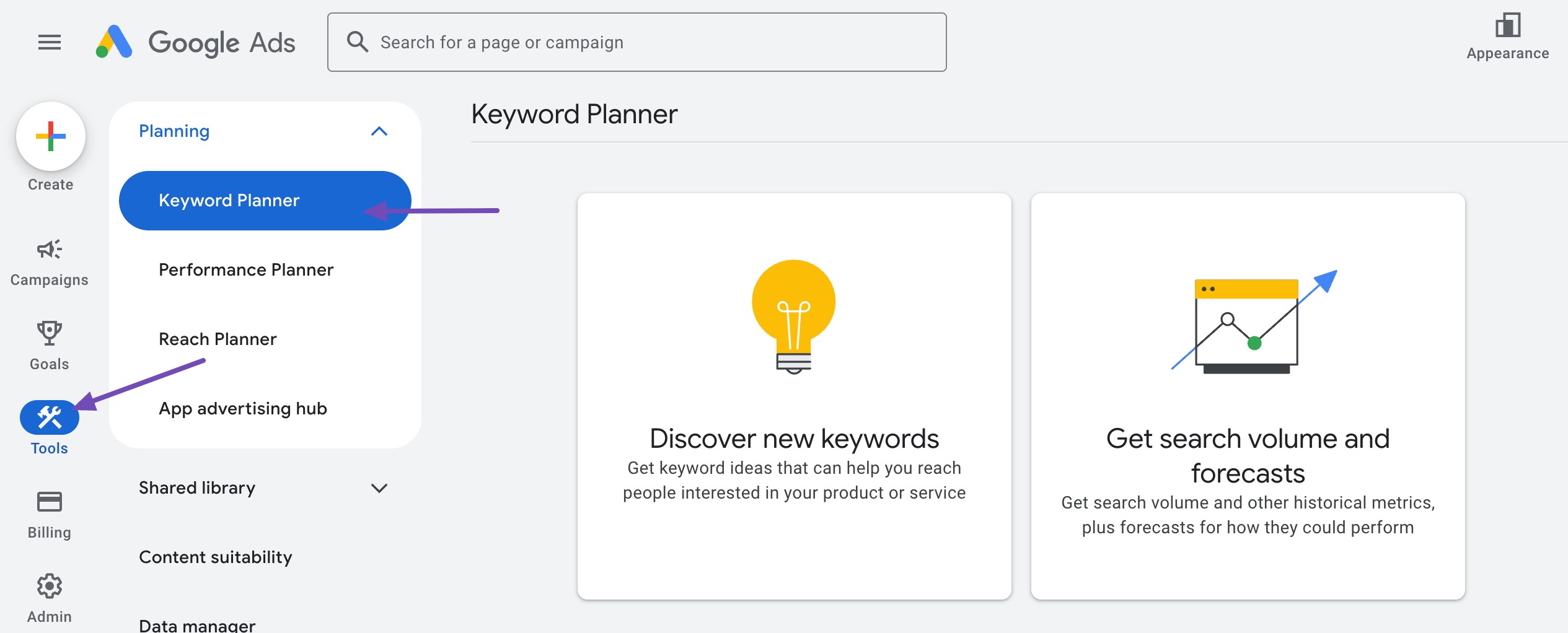
Choose Discover new keywords and enter words or phrases related to your business, or input your website URL to get keyword ideas.
The tool will generate a list of keyword suggestions along with important metrics like search volume, competition level, and top-of-page bid estimates.
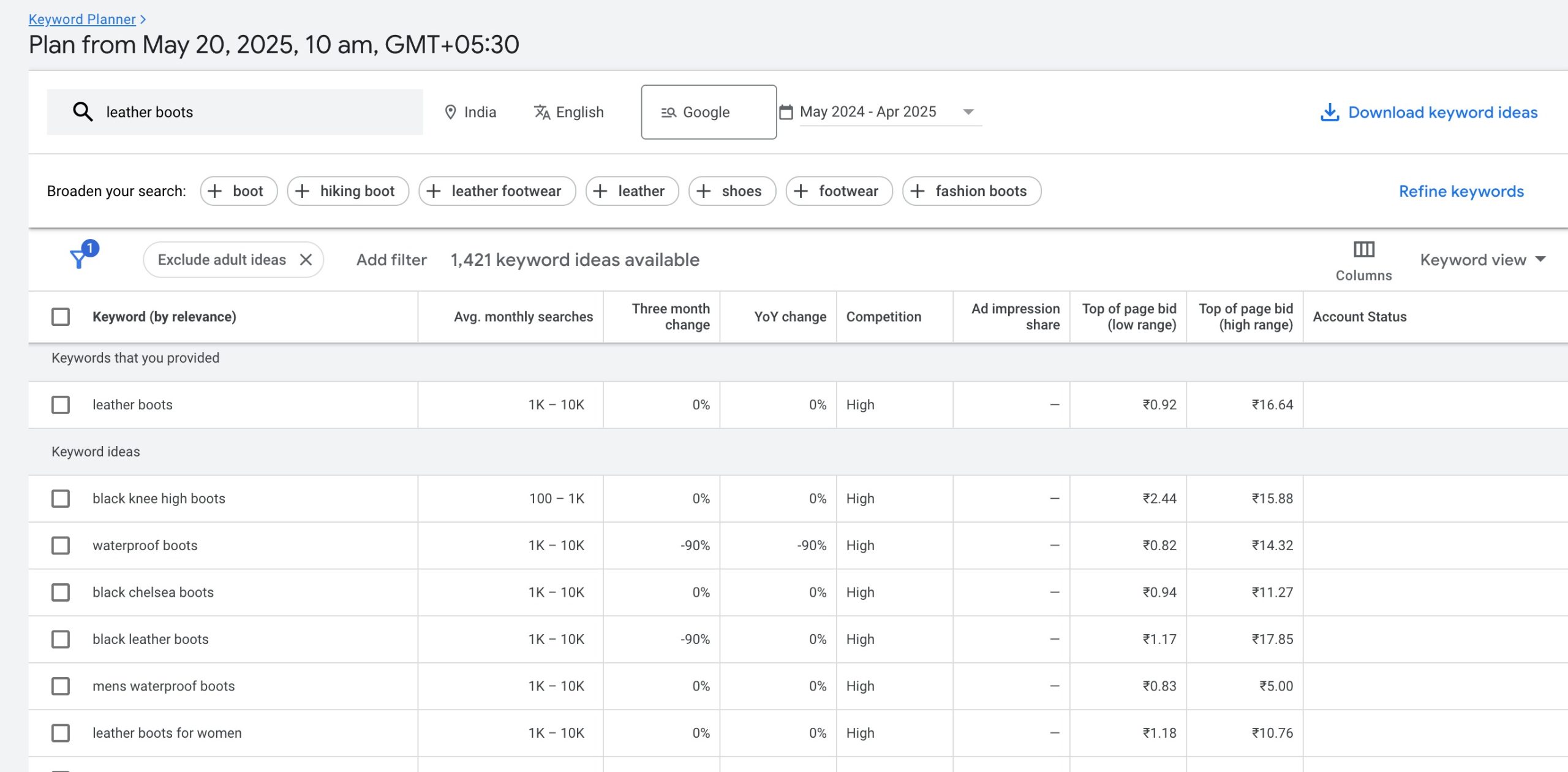
You can filter the results by location, language, or date range. Focus on keywords with a good balance of high search volume and low-to-medium competition.
Export or save your selected keywords for use in your SEO or content strategy.
Consider targeting long-tail keywords, which are longer and more specific phrases. They typically have lower competition and higher conversion rates because they match user intent more closely.
Incorporate your chosen keywords naturally into your content, including titles, headings, meta descriptions, and body text. Avoid keyword stuffing, as it can harm readability and SEO.
Refer to our dedicated tutorial on choosing the right keywords and avoiding poor keyword research.
2.2 Keyword Stuffing
Keyword stuffing is a common SEO mistake that involves overloading a webpage with keywords or phrases in an attempt to manipulate a site’s ranking in search engine results.
This practice can make the content sound unnatural and significantly detract from the user experience.
Fix: Focus on Natural Keyword Integration and Prioritize User Experience
Prioritize creating content that reads naturally and provides value to your audience. Add keywords in a way that fits into the text without disrupting the flow or readability.
Instead of repeatedly using the same keyword, use synonyms and related phrases. This approach helps to maintain a natural tone and avoids redundancy while still signaling relevance to search engines.
Strategically place keywords in important areas such as titles, headings, meta descriptions, and the first paragraph of your content. Ensure they are relevant to the context of the content.
You can also use Rank Math’s Research feature by entering your focus keyword in the FOCUS KEYWORD field and clicking the Research button.
Rank Math SEO will request our AI server to analyze the keyword, and in a few moments, you’ll find the expected word count and the expected number of times the keyword can be used in the content inside your Content AI panel.
AI isn’t just helping teams create more — it’s helping them create better. According to our survey, 27% of users say enhanced keyword targeting and placement is one of the top ways AI is improving content optimization.
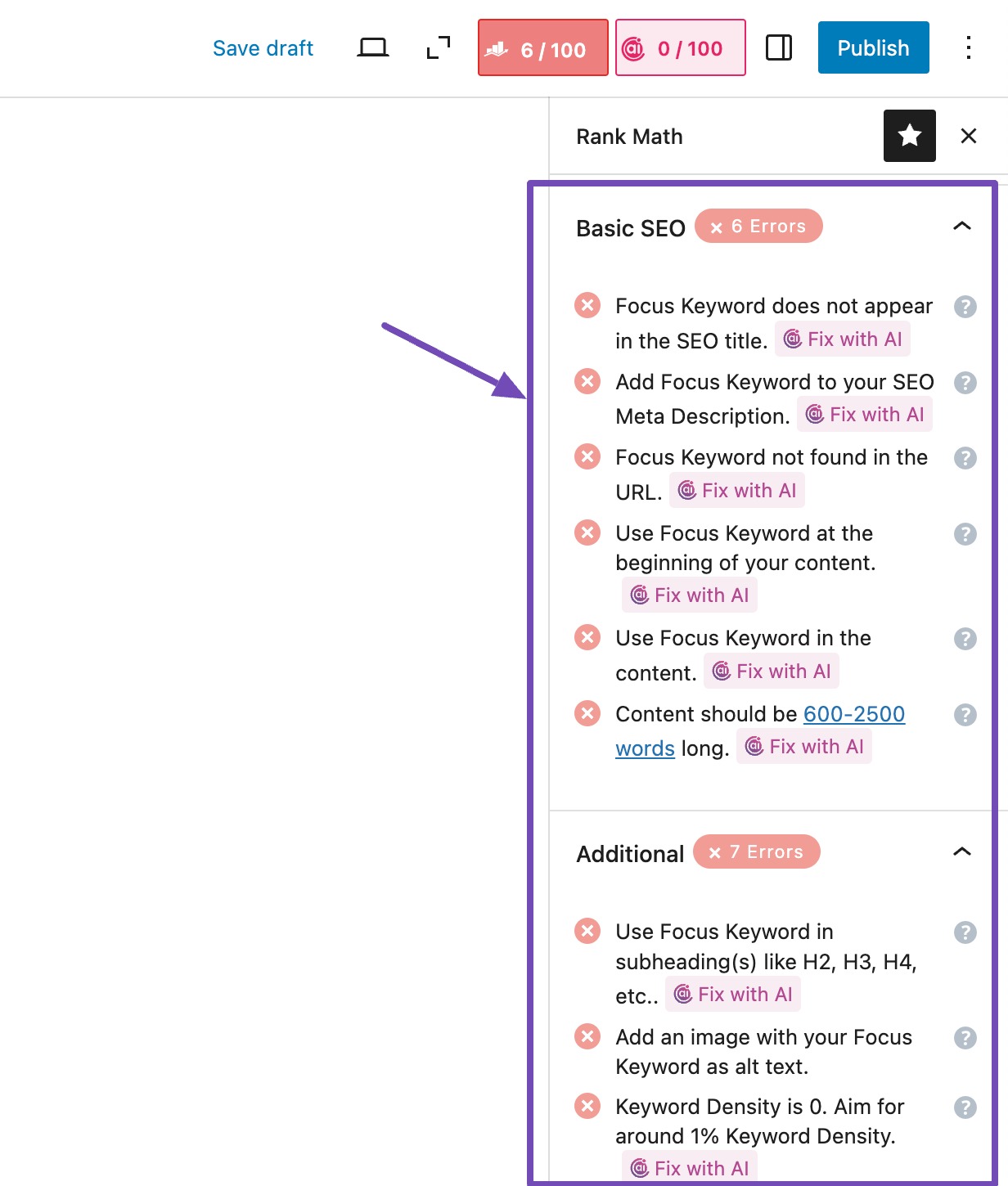
With Rank Math’s Content AI, you can review the SEO tests, and you can fix any failed tests by clicking the Fix with AI button. This button, powered by Content AI, allows you to resolve failed SEO tests automatically.
Quality content naturally attracts more traffic and engagement, which is beneficial for SEO. Hence, focus on creating high-quality content that answers users’ questions and meets their needs.
Review your content regularly for keyword stuffing and make necessary edits. Remove unnecessary repetitions and ensure the content maintains its natural flow.
2.3 Duplicate Content
Duplicate content refers to blocks of content that appear in more than one location on the internet. This can occur within a single website or across multiple domains.
When search engines encounter duplicate content, they may struggle to determine which version is the most relevant and authoritative, leading to potential issues with indexing and ranking.
Having duplicate content on your website is a common SEO mistake that can dilute your site’s visibility in search results, as search engines may prioritize one version over the others.
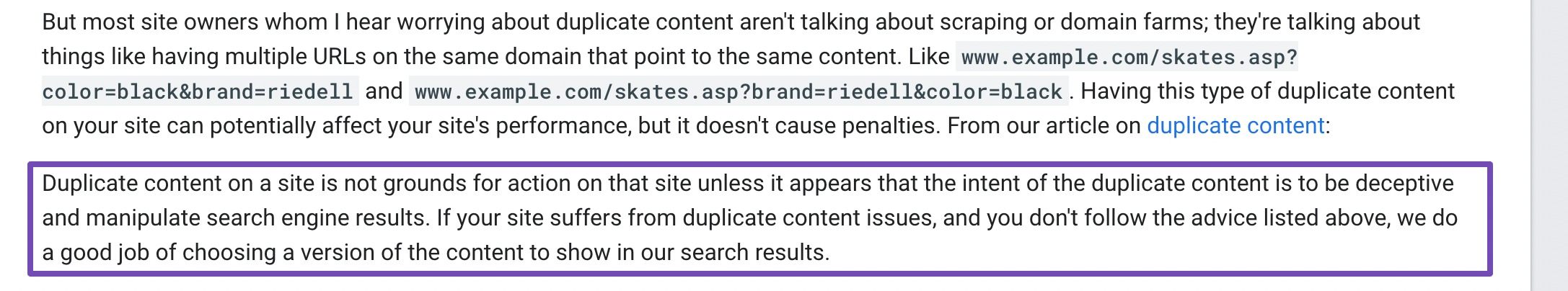
To check for potential duplicate content on your site, you can use a simple and effective method:
- Use the “site:” search operator in Google (e.g.,
site:yourdomain.com keyword) to find all indexed pages related to a specific keyword. If multiple pages are targeting the same keyword with similar content, you may have a duplicate content issue. - Copy and paste a sentence or paragraph from your content into Google search using quotation marks (e.g.,
"exact phrase here"). This can help identify duplicate content both on your own site and on external sites that may have copied your content.
Fix: Use Canonical Tags and Create Unique Content for Each Page
Determine the primary or preferred version of the content that you want search engines to index and rank.
Use canonical tags (rel=”canonical”) in the HTML code of duplicate pages to indicate the preferred version. This tag informs search engines that the content of the duplicate pages should be attributed to the canonical URL.
You can easily set canonical tags using Rank Math SEO.
To do so, start by editing the post or page containing the duplicate content.
Once inside the editor, navigate to the Advanced tab in the Rank Math SEO meta box. If you don’t see this tab, enable the Advanced Mode by navigating to Rank Math SEO → Dashboard in your WordPress admin area.
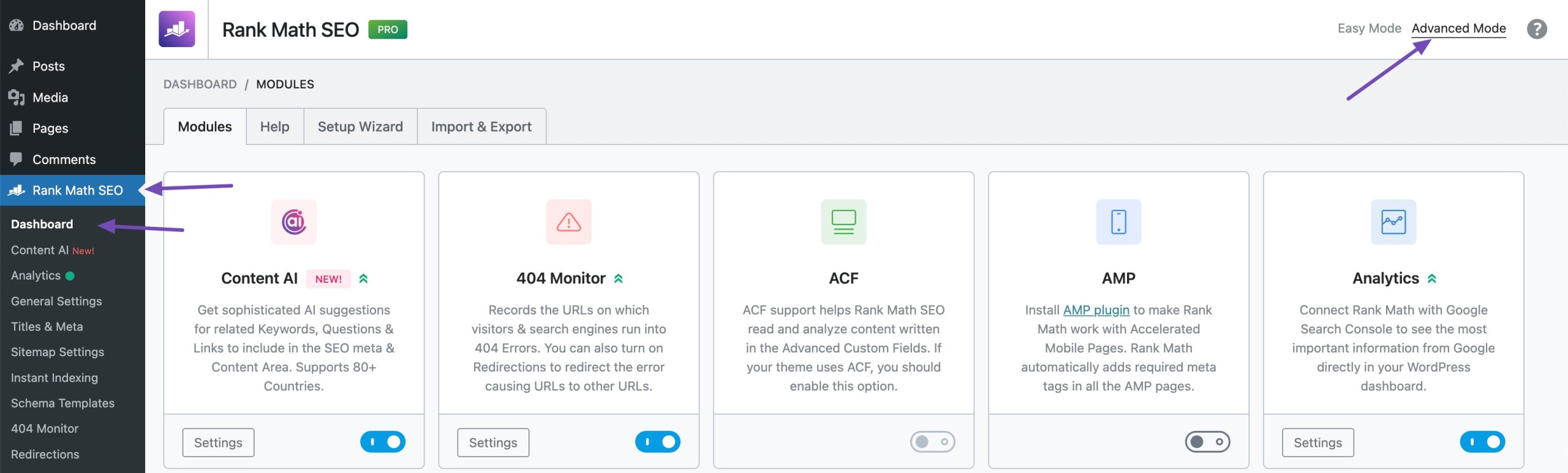
In the Advanced tab of Rank Math SEO meta box, locate the Canonical URL field and enter the URL of the original content. This signals to search engines which version of the content should be indexed. After updating the canonical URL, simply click Save or Publish to save your changes.
If you have multiple pages with similar content, consider consolidating them into a single, comprehensive page to avoid duplication and strengthen your site’s authority.
Regularly review and update your website’s content to ensure it remains relevant, accurate, and valuable to your audience. Refreshing content can help prevent it from becoming stale and reduce the likelihood of duplication.
2.4 Missing or Unoptimized Meta Tags
Meta tags, such as title tags and meta descriptions, are essential in informing search engines about web pages’ content and influencing users’ click-through rates.
Here’s what the meta title and description look like in SERPs.

Unoptimized or missing meta tags are another common SEO issue that can significantly impact a website’s performance in search engine results pages (SERPs).
Unoptimized meta tags may:
- Lack relevant keywords
- Be too generic or vague
- Misrepresent the content of the page
- Be too short or exceed character limits, leading to truncation in SERPs
Rank Math’s SEO Analyzer scans your website thoroughly and helps you identify areas where your website excels and where it needs improvement.
Navigate to Rank Math SEO → SEO Analyzer from your WordPress dashboard. This feature will scan your website and flag issues like missing title tags, or overly short/long meta content.
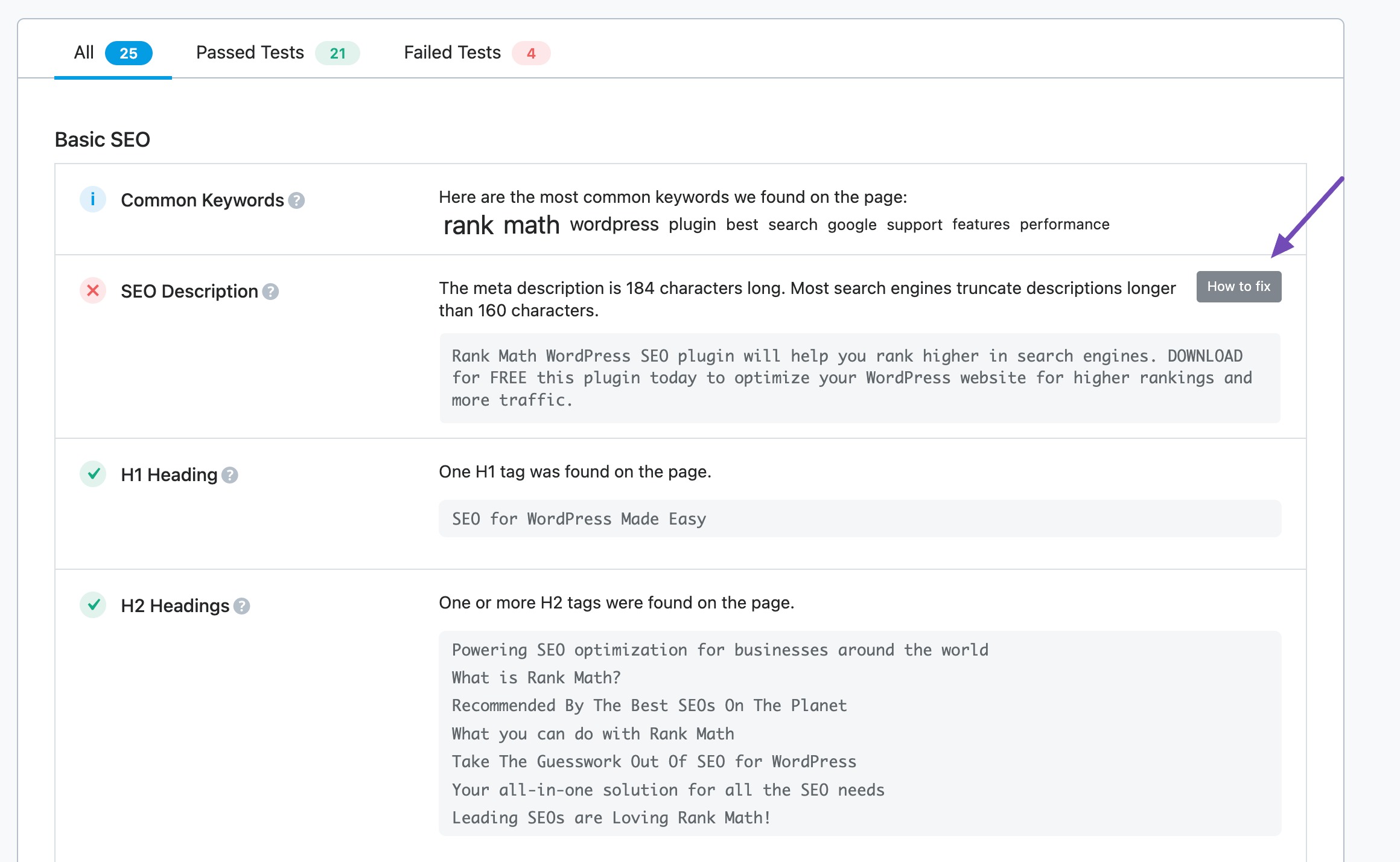
Fix: Write Unique, Descriptive, and Keyword-Rich Meta Titles and Descriptions for Each Page
Conduct a thorough audit of your website’s meta tags using SEO tools or manually inspecting individual web pages.
Look for title tags and meta descriptions that are either missing, duplicated across multiple pages, too short, too long, or not optimized for relevant keywords.
To avoid common SEO issues with your page’s title tag and meta description, you should:
- Include the target keyword.
- Ensure they are unique to each page.
- Provide a concise summary of what the audience can anticipate finding on the page.
- Make sure they align with the intent behind the target keyword.
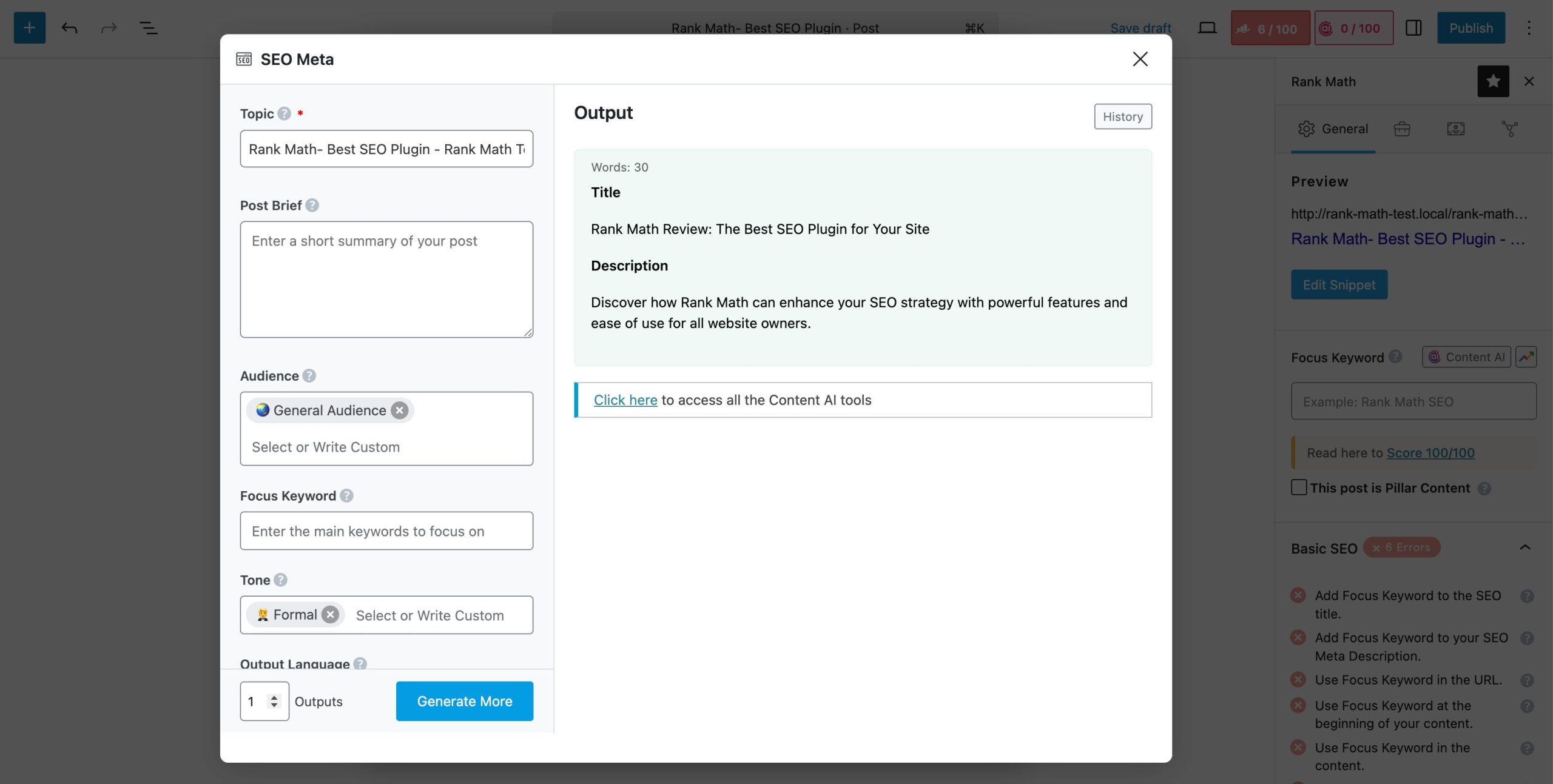
You can use Rank Math’s SEO Meta Content AI tool to add meta titles and descriptions to your pages.
Note: You must enable the Content AI module from Rank Math’s dashboard in order to use its features.
To do so, navigate to the post or page you want to add the SEO meta. Once done, click the Rank Math SEO icon at the top-right corner of the screen.
Next, click Edit Snippet, as shown below.
In the Preview Snippet Editor, click Generate With AI.
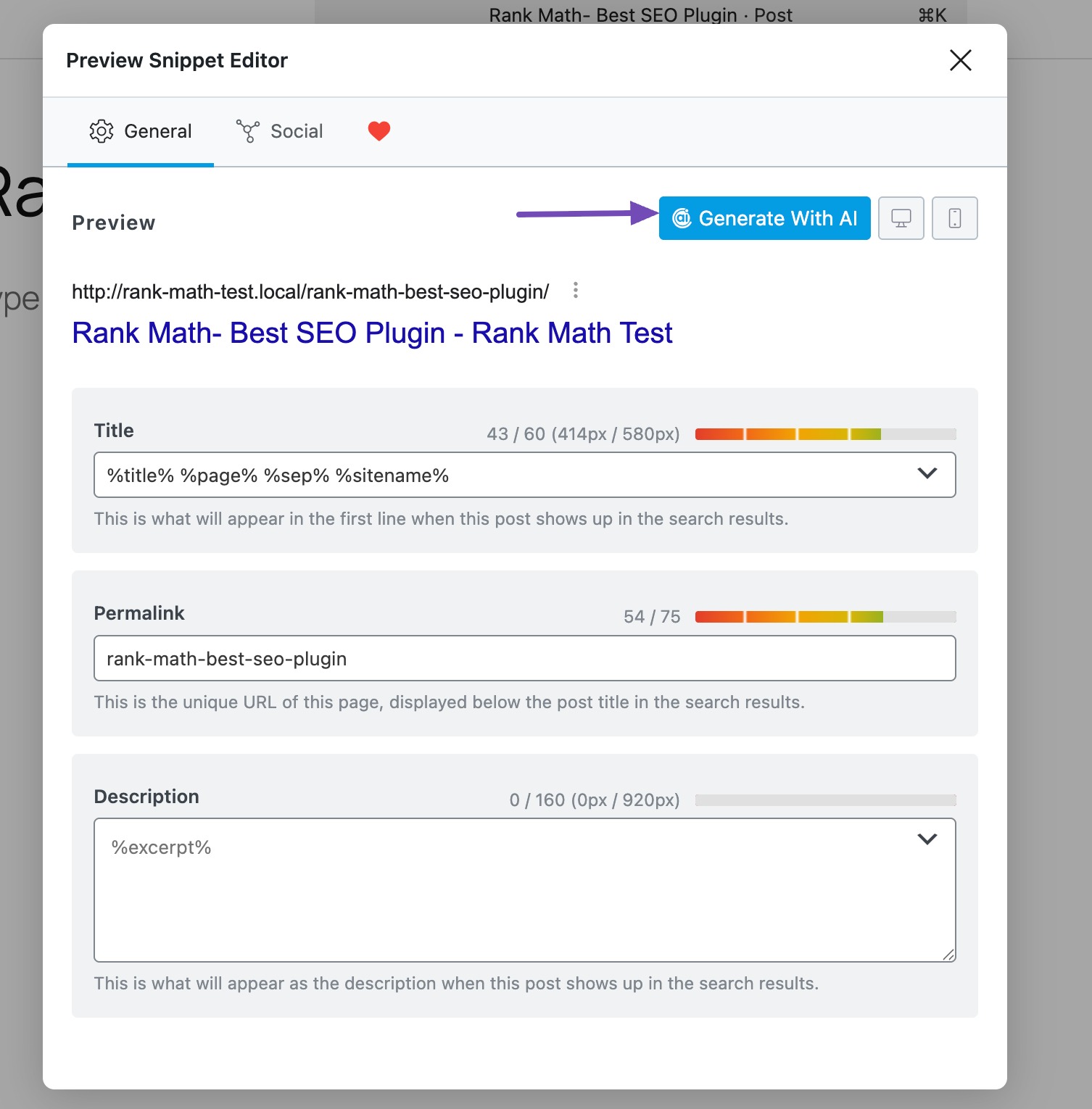
The tool will automatically generate the SEO meta tags for your post.
Refer to our dedicated tutorial on on-page SEO to optimize your web pages effectively
3 Common Content Mistakes & Fixes
Let us now discuss the common content mistakes and how to fix them.
3.1 Low-Quality Content
Publishing thin, uninformative content is a significant SEO mistake.
This type of content typically lacks depth, detail, and relevance, providing little value to readers.
As mentioned before, search engines prioritize high-quality content that answers user queries comprehensively. Thin content can result in low engagement, high bounce rates, and poor search engine rankings.
Fix: Create High-Quality, Informative, and Engaging Content That Provides Value to the Reader
Before writing, identify the search intent behind the keywords you’re targeting—are users looking for information, trying to make a purchase, or comparing options?
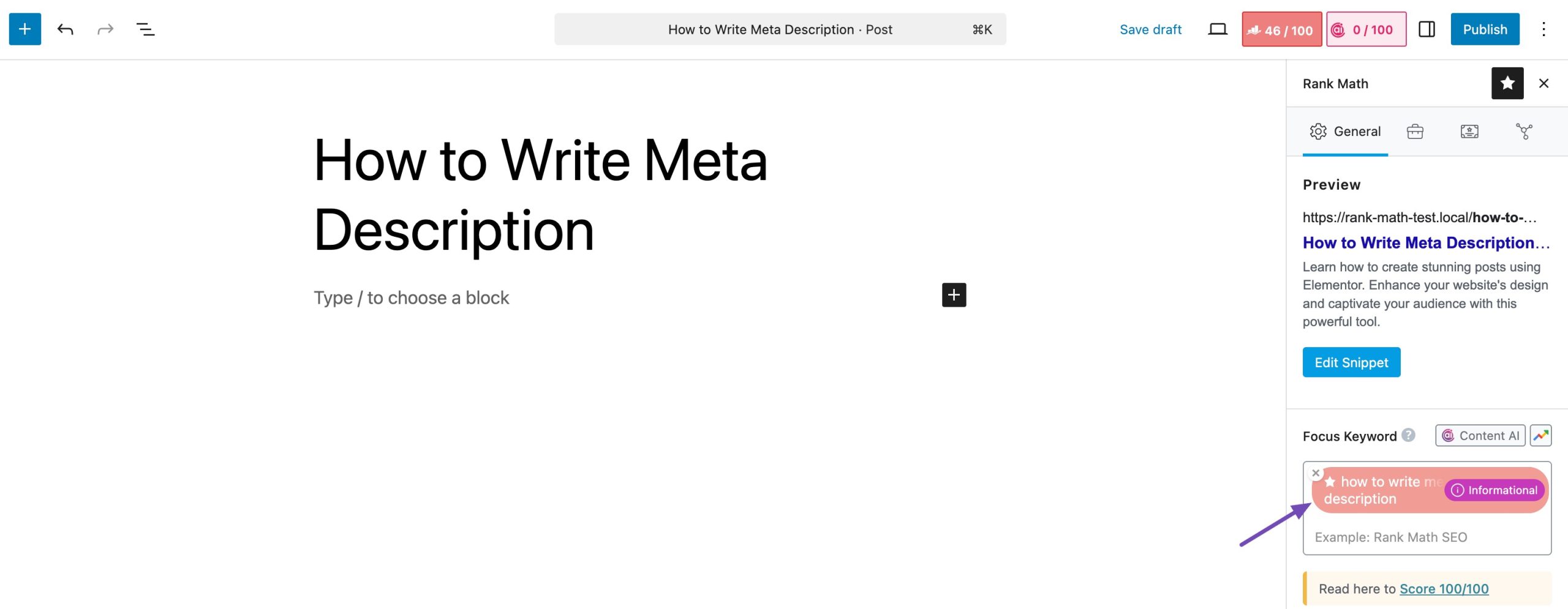
Rank Math’s Search Intent feature helps you understand what your audience is looking for based on the keyword. In your post/page editor, navigate to the Focus Keyword field in the General tab of the Rank Math meta box.
Enter a keyword, and you’ll notice an icon next to it. Hover over this icon and click on the Show Intent label. Rank Math will analyze and display the detected search intent next to the keyword field, helping you quickly determine whether your content aligns with what users are looking for.
Your content should also be well-researched and trustworthy. Use reliable sources and fact-check your information to ensure it’s accurate and up-to-date. Cover topics thoroughly—don’t just scratch the surface. Add real-life examples, how-to steps, and actionable advice that readers can implement immediately.
To make your content more engaging and easier to understand, incorporate visual elements like images, infographics, videos, and charts. These elements help break up long blocks of text and make complex ideas more digestible.
Originality is key. Avoid duplicating or rewriting existing content without adding your own insight. Share your personal experiences, case studies, or expert opinions to provide a fresh perspective that sets your content apart.
You can also use our Content AI to create high-quality content for your audience.
3.2 Neglecting Content Updates
Failing to update old content is another common SEO mistake leading to outdated information, diminishing your site’s value for the audience and search engines.
As industries develop and new information becomes available, content can become obsolete, leading to decreased relevance and lower search engine rankings.
Regularly updating content ensures that it remains accurate, useful, and aligned with current trends and information.
Fix: Regularly Review and Update Existing Content to Keep It Relevant and Accurate
Maintain an inventory of your site’s content and schedule regular audits to identify outdated or underperforming content.
Use tools like Google Analytics to track content performance and identify pages that need updates. Navigate to the Reports →Engagement → Pages and screens tab in your Google Analytics account.
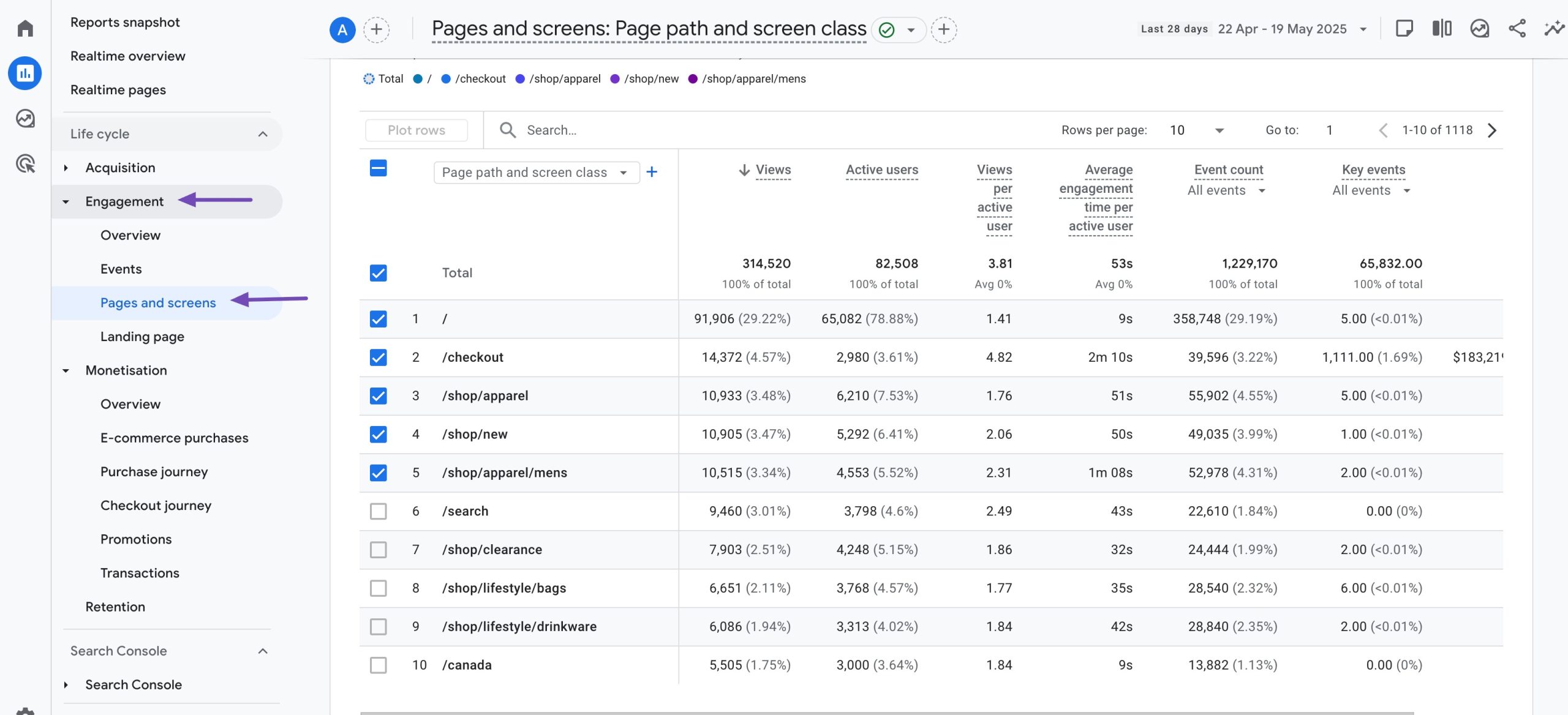
If you notice any pages with Average engagement time far below the average, you might have to update the article or page to reflect the correct information.
Update facts, statistics, and other time-sensitive information to ensure accuracy. Enhance outdated content by adding new insights, details, and visuals.
Re-evaluate and update keywords, meta tags, and internal links to align with current SEO best practices.
3.3 Not Using Header Tags Properly
Improper use of header tags (H1, H2, etc.) is a common SEO issue that can negatively impact both readability and SEO.
Header tags are essential for structuring content, making it easier for audiences to read and for search engines to understand the hierarchy and relevance of information.
Using too many H1 tags, skipping levels, or not using header tags at all can confuse readers and search engines, leading to a poor user experience and lower rankings.
Fix: Structure Content with Clear, Hierarchical Header Tags to Improve Readability and SEO
Ensure that header tags follow a logical order (H1 followed by H2, then H3, etc.) to create a clear structure.

- H1 Tag: Use only one H1 tag per page for the main title. It should clearly indicate the page’s primary topic.
- H2 Tags: Use H2 tags for major sections within the content, breaking down the main topic into subtopics.
- H3 and Lower Tags: Use H3, H4, and other lower-level tags for subsections within the H2 sections, maintaining a clear, logical hierarchy.
Write descriptive and keyword-rich headers that provide an accurate summary of the content in each section.
Well-structured headers make it easier for the audience to scan and find the necessary information, enhancing the user experience.
4 Common Off-Page SEO Mistakes & Fixes
Let us now discuss the off-page SEO mistakes and how to fix them.
4.1 Poor Backlink Strategy
External links can be valuable for SEO when used correctly, but improper linking practices can do more harm than good.
One common mistake is linking to low-quality or irrelevant websites, which can reduce your site’s credibility in the eyes of search engines. Even worse is participating in link farms — networks of websites created solely for the purpose of link exchange.
These links often lack context, relevance, and authority, and search engines like Google consider them manipulative. To maintain trust and SEO value, always link to authoritative, relevant sources that enhance the user experience and provide genuine value.
Fix: Focus on Earning High-Quality Backlinks from Reputable Sources
Start by creating high-quality content that others naturally want to reference. This can include in-depth blog posts, infographics, original research, case studies, and data-driven reports. The more value your content offers, the more likely others will link to it organically.
You can also write guest posts for established blogs and websites in your niche. This not only earns you valuable backlinks but also helps you build credibility and position yourself as an expert in your field.
Outreach is key—connect with bloggers, influencers, and webmasters in your industry. Build relationships and politely request backlinks to relevant content you’ve created. Personalized outreach often results in higher-quality link placements than bulk link requests.
To further enhance your strategy, use our Content AI tool. Within the Content AI dashboard, scroll to the section labeled Links. This section provides a curated list of authoritative and relevant external links based on your target keyword, helping you identify potential sites for outreach or reference.
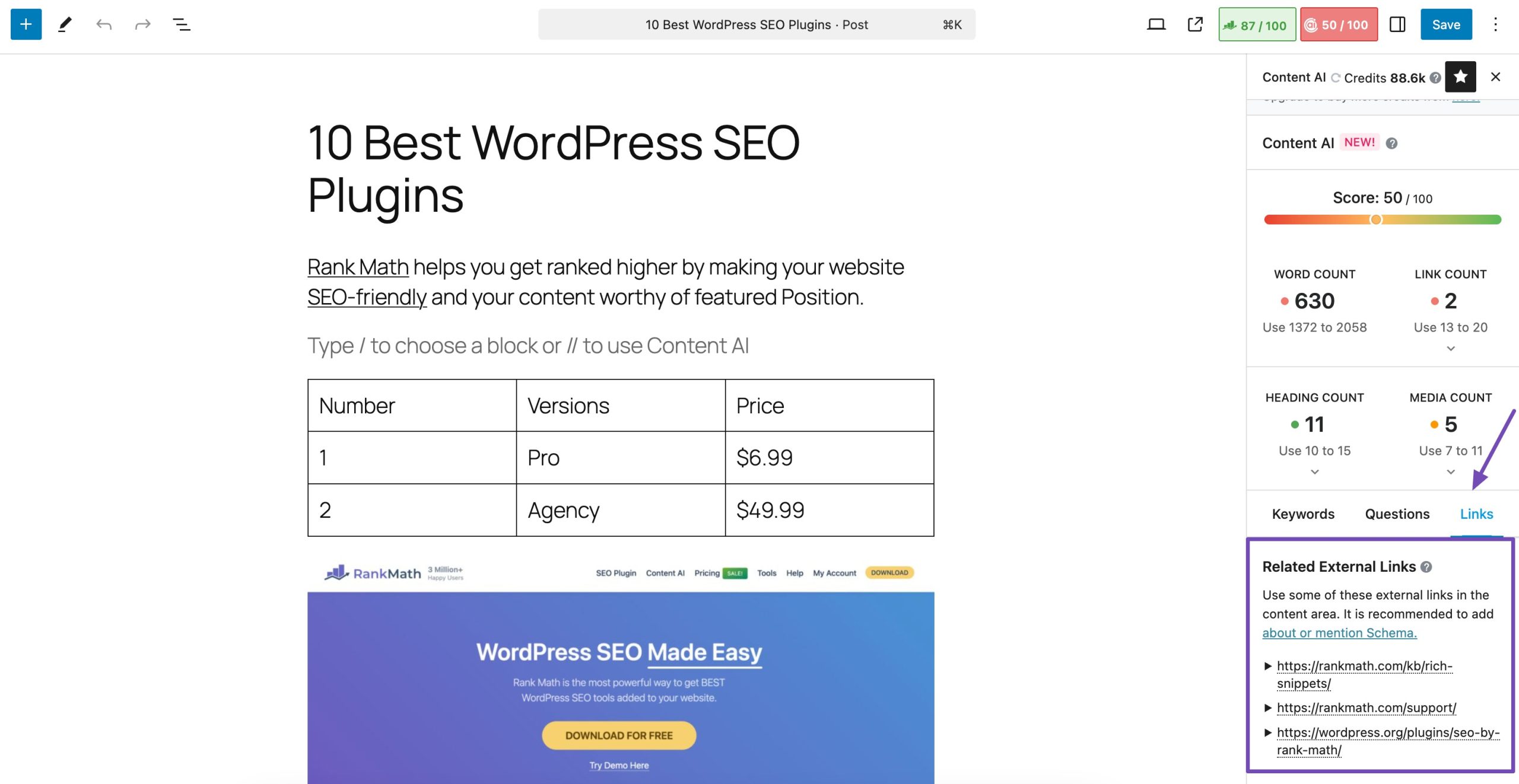
Refer to our dedicated link-building tutorial and earn links to your website.
4.2 No Local SEO Citations
One of the most common off-page SEO mistakes for local businesses is inconsistent or missing NAP (Name, Address, Phone number) information across online directories and business listings.
When your NAP details vary—even slightly—across platforms like Google Business Profile, Yelp, Bing Places, or local directories, search engines get confused about your business’s legitimacy. This inconsistency can lead to lower local rankings and less visibility in “near me” or map-based searches.
Fix: Ensure Consistent and Accurate Citations
To build trust with search engines and improve local SEO, start with Google Business Profile, Yelp, Facebook, Bing Places, Apple Maps, and move on to niche or industry-specific directories (e.g., TripAdvisor for tourism, Healthgrades for medical).
Your business name, address, and phone number should appear exactly the same across all listings, down to abbreviations (e.g., “St.” vs. “Street”) and phone formats.
If you change your address or phone number, update it across all platforms simultaneously.
Refer to our dedicated tutorial on off-page SEO and implement the insights and strategies to fix any off-page SEO issues.
4.3 Not Leveraging Social Signals
Many businesses underestimate the power of social media in their SEO strategy, assuming that since social signals (likes, shares, comments) aren’t direct Google ranking factors, they don’t matter. But that’s a mistake.
Ignoring your social presence means you’re missing out on valuable visibility, engagement, and link-building opportunities. Without active sharing, your content reaches fewer people, limiting the chances of it being referenced or linked to by others.
Fix: Use Social Media to Amplify Your Content
Share your content regularly on platforms like LinkedIn, X (formerly Twitter), Facebook, Instagram, Pinterest, and Threads, depending on your audience. Use engaging visuals, captions, and hashtags to improve reach.
Encourage likes, shares, and comments to boost organic engagement. Include social sharing buttons on your website and blog.
Collaborate with influencers or niche communities to boost the reach and credibility of your content on social media.
5 Conclusion
Addressing the common SEO issues is necessary to improve your website’s visibility and attract more organic traffic.
By implementing fixes such as optimizing meta tags, resolving broken links, and improving website performance, you can enhance user experience and boost your rankings in search engine results.
Remember to regularly monitor and update your SEO strategies to adapt to changes in search engine algorithms and user behavior.
If you like this post, let us know by Tweeting @rankmathseo.
