When you manage a website, you might wonder whether using subdomains is a good idea for SEO. Should you keep everything on one domain, or split content into subdomains for better organization?
The truth is, subdomains can help in some cases, but they also come with their own challenges. If you’re not careful, they can hurt your rankings instead of helping.
In this post, we’ll break down everything you need to know about subdomains and SEO. We’ll discuss when to use them, how to optimize the content, and tricks to help improve SEO for subdomains.
So, let’s dive in and take the mystery out of subdomain SEO!
Table Of Contents
1 What Are Subdomains?
A subdomain is a section of your main domain that works like a separate website. It appears before your main domain name in the URL.
For instance, if my main site is example.com, I can create a subdomain like blog.example.com for articles or shop.example.com for an online store.
Unlike subdirectories (like example.com/blog), subdomains are treated as separate entities by search engines. This means they can have their own content and ranking potential, but they don’t always share authority with your main site.
You can use subdomains to organize different sections of your site. For instance, you can create us.example.com for your U.S. audience and fr.example.com for your French audience. This makes it easier to deliver content aligned to each region.
Refer to our dedicated tutorial on subdomains vs subfolders to understand subdomains in more detail.
2 Why Create Subdomains for SEO?
You can use subdomains when you want to separate different parts of your website without mixing everything together. Subdomains act like their own websites, which can help in a few ways:
- Target different keywords: For example, you can create
blog.example.comto focus on blog-related terms while your main site targets product keywords. - Reach different audiences or regions: Many global brands use subdomains for language or regional content, like
us.example.comfor the U.S. andfr.example.comfor France. - Host different types of content: If you have an online course platform, a store, or a support center, putting them on separate subdomains can make navigation easier.
A well-known example is Wikipedia. It uses subdomains to serve different languages:
en.wikipedia.org– Englishes.wikipedia.org– Spanishfr.wikipedia.org– French
This approach ensures that users see content that’s most relevant to them.
3 Strategies for Optimizing SEO for Subdomains
Let us now discuss the strategies for performing SEO for subdomains.
3.1 Content Strategy
Your subdomain should have its own purpose and unique content. One of the biggest mistakes is copying content from your main site. This creates duplicate content, which confuses search engines and can hurt rankings.
To avoid this, only create a subdomain when you have enough original content for a specific audience or topic that your main domain doesn’t cover.
To keep your content unique and optimized, use tools like Google Search Console or Rank Math to check for duplicate pages.
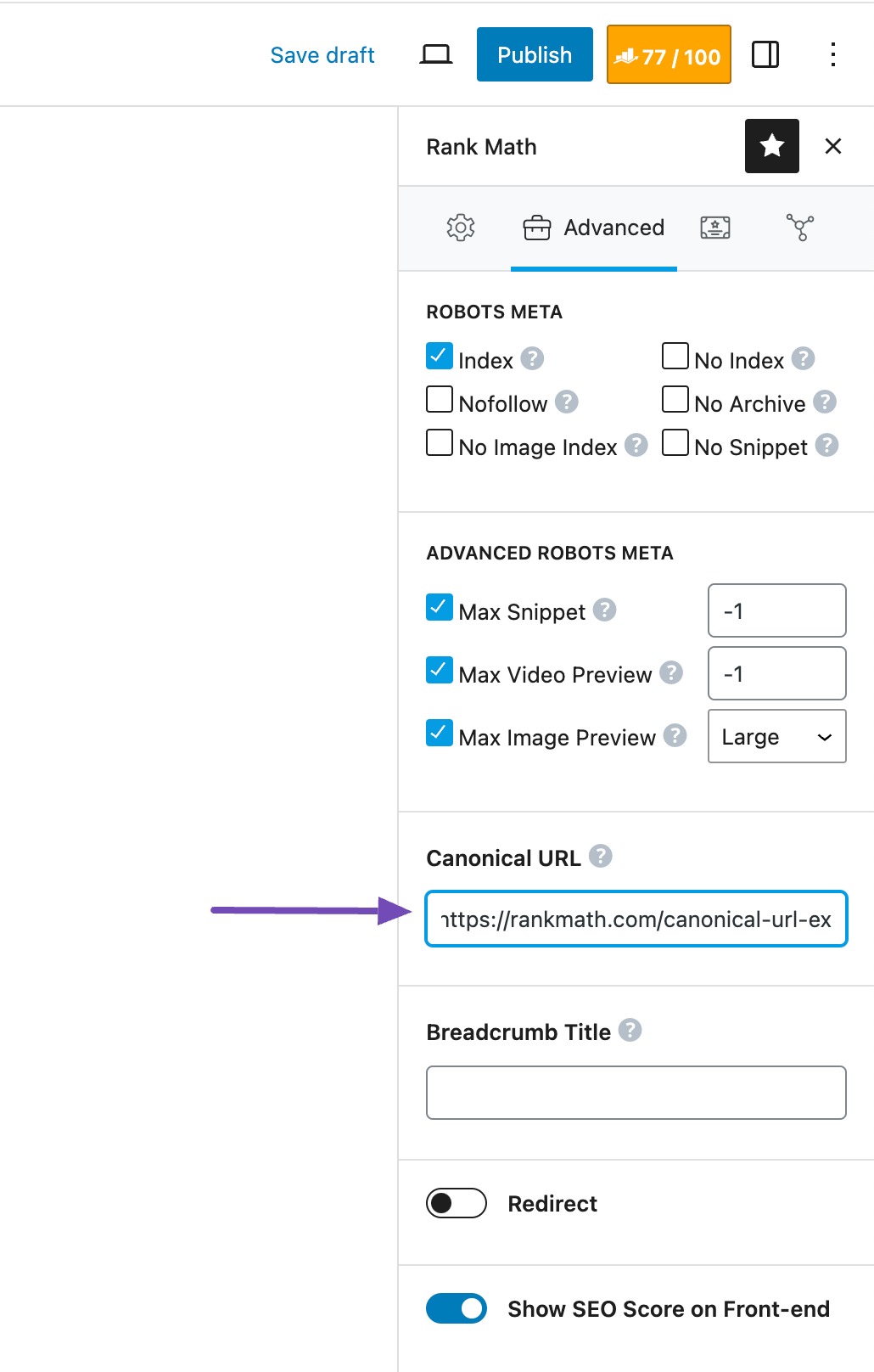
If you have regional pages with similar product descriptions, use canonical tags to tell search engines which version is the primary one. In Rank Math, you can set the canonical URL in the Advanced tab of the meta box, which makes this easy to manage.
AI tools can also make your job easier. Rank Math’s Content AI helps you find keywords, plan content, and write SEO-friendly text that stands out.
This is especially useful when you want to create content that doesn’t compete with your main site. Make sure you do keyword research specifically for each subdomain so you’re targeting terms that fit its purpose rather than overlapping with your main site.
3.2 Backlink Strategy
Backlinks are essential for subdomain SEO because they don’t automatically share authority with your main domain. Each subdomain needs its own backlink profile to rank well.

Start by getting backlinks from high-quality, relevant websites that match the purpose of your subdomain.
For instance, if you run a blog on a subdomain, reach out to industry publications, write guest posts for related blogs, or collaborate with influencers who can link to your content. If your subdomain is an online store, partner with affiliate marketers, product reviewers, or niche forums to get links pointing to your products.
Don’t overlook internal linking. Linking from your main domain to the subdomain signals to search engines that the two are connected, and it can pass some authority. For instance, you might link to a blog article on your subdomain from a popular page on your main site. You can also add relevant links from the subdomain back to the main domain to keep your structure cohesive.
If your subdomain serves a regional audience, use local SEO tactics to build backlinks. Submit your site to local business directories, reach out to regional news sites, or form partnerships with local organizations. This not only helps you earn backlinks but also improves rankings for location-based searches.
3.3 Track SEO Subdomain Performance
To track the SEO performance of your subdomains, you need to set them up separately in Google Search Console and Google Analytics. Search engines treat subdomains as separate sites, so adding them as individual properties is the only way to get accurate data.
Start by creating a new property in Google Search Console for your subdomain and verifying ownership using DNS, HTML file upload, or Google Tag Manager.
In Google Analytics, you can create a separate property for the subdomain or set up tracking so that data flows together if you want to keep a unified user journey.
If you want to make this process easier, you can use Rank Math SEO.
Once you’ve installed the plugin on your website, navigate to General Settings and the Analytics tab in Rank Math. If you haven’t connected your site to a Rank Math account, follow the steps to enable the Analytics module.
During setup, ensure all available checkboxes are selected to integrate Google Search Console and Google Analytics data.

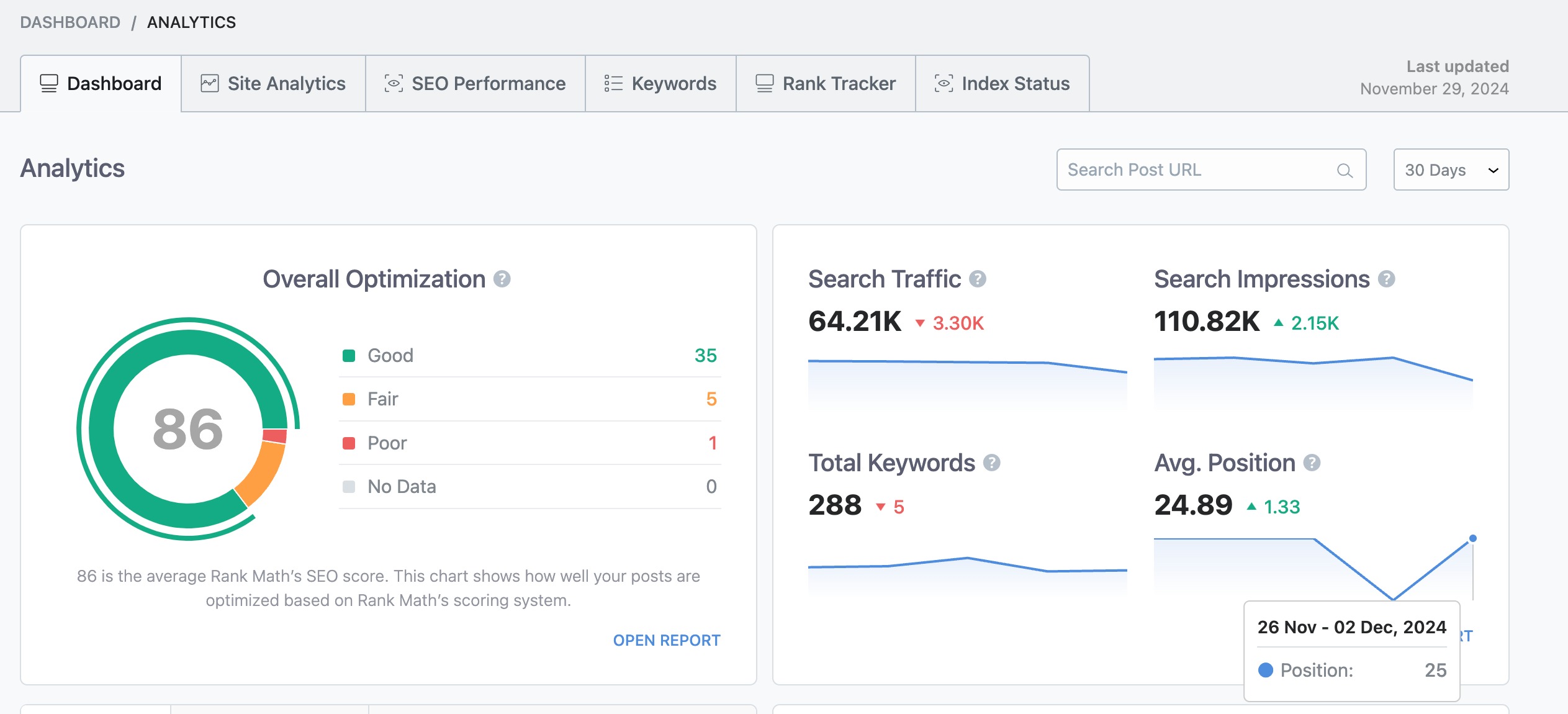
Rank Math automatically pulls data from Google Search Console and Google Analytics, storing it directly on your server for privacy and security. This eliminates any concerns about external storage or third-party data access.
You can view and analyze important performance metrics for your subdomains right from your WordPress dashboard without switching between tools.
3.4 Maintain Consistent Branding & User Experience
Your subdomains should look and feel like your main site. Keep the same logo, colour scheme, fonts, and navigation structure across all of them. This consistency builds trust and strengthens your brand identity.
For example, Amazon uses multiple subdomains, such as music.amazon.com for Amazon Music and aws.amazon.com for Amazon Web Services. Even though these serve completely different purposes, they share a similar design language, colour palette, and branding elements. This consistency makes users feel like they’re still within Amazon’s site, which improves trust and navigation.
Make sure your URLs follow a clear, structured format so users recognize your brand. Also, keep your tone and messaging consistent across all subdomains for a seamless communication style.
Finally, don’t forget about mobile responsiveness. Every subdomain should load and function well on any device to give users a smooth browsing experience.
4 Frequently Asked Questions
Do subdomains hurt SEO?
No, subdomains don’t automatically hurt SEO. However, search engines treat them as separate sites, so you need unique content, proper optimization, and backlinks for each subdomain to rank well.
How many subdomains can I have?
There’s no strict limit, but avoid creating too many subdomains without a clear purpose. Each one needs its own SEO strategy, content, and backlink profile.
Will my subdomain compete with my main site?
Not necessarily. Subdomains are treated as separate websites by search engines, so direct competition is rare if you target different keywords and topics. However, if both your main site and subdomain use the same keywords and similar content, they can compete in search results. To avoid this, make sure each subdomain has unique content and focuses on a different intent or audience.
Can I rank a subdomain independently?
Yes, you can. Since subdomains are considered separate entities, each one can build its own SEO strategy, authority, and backlinks to rank independently in search results. This is why many businesses use subdomains for blogs, e-commerce stores, or regional content. Just remember that ranking a subdomain requires the same effort as ranking a standalone website.
5 Conclusion
Managing SEO for subdomains takes extra effort, but when done right, it can boost your visibility and improve the user experience.
Make sure each subdomain has unique, optimized content, builds its own backlink profile, and is properly tracked in Google Search Console and Google Analytics.
Consistency matters too. Keep your branding, design, and navigation uniform across all subdomains so visitors feel like they’re on the same site.
If you treat each subdomain like its own site while still connecting it to your main domain, you’ll create a strong SEO foundation that helps every part of your website rank better.
If you like this post, let us know by Tweeting @rankmathseo.
