What is the URL Inspection Tool?
The URL inspection tool is a Google Search Console feature that provides detailed information about how Google views a specific URL on your website. It is exclusive to Google and can only be accessed by the blogger through a Google Search Console account.
The URL inspection tool allows webmasters to check the index status, identify crawling and indexing issues, and view the rendered version of their webpages. Bloggers can also use it to request that Google index their pages.
The URL Inspection tool is the search field at the top of Google Search Console. You can quickly access it by clicking on the field itself or by selecting URL Inspection, as shown below.
{Sample of the Google Search Console URL inspection tool
Importance of the URL Inspection Tool
The URL Inspection tool allows bloggers and SEO professionals to uncover detailed insights into how Google perceives specific pages on their site. For example, the tool enables bloggers to identify webpages Google has crawled, indexed, and not indexed.
The URL Inspection tool also enables bloggers to identify the issues that may prevent Google from crawling and indexing their pages. This is critical because it ensures that essential pages on your site are accessible to Google and appear correctly on Google search result pages.
How to Use the URL Inspection Tool
The URL inspection tool is intuitive and straightforward to use. To get started, log into your Google Search Console and enter the URL you want to inspect into the URL inspection tool at the top of the page. Once done, click Enter on your keyboard.
Google Search Console will return with the index status and other reports about the URL.
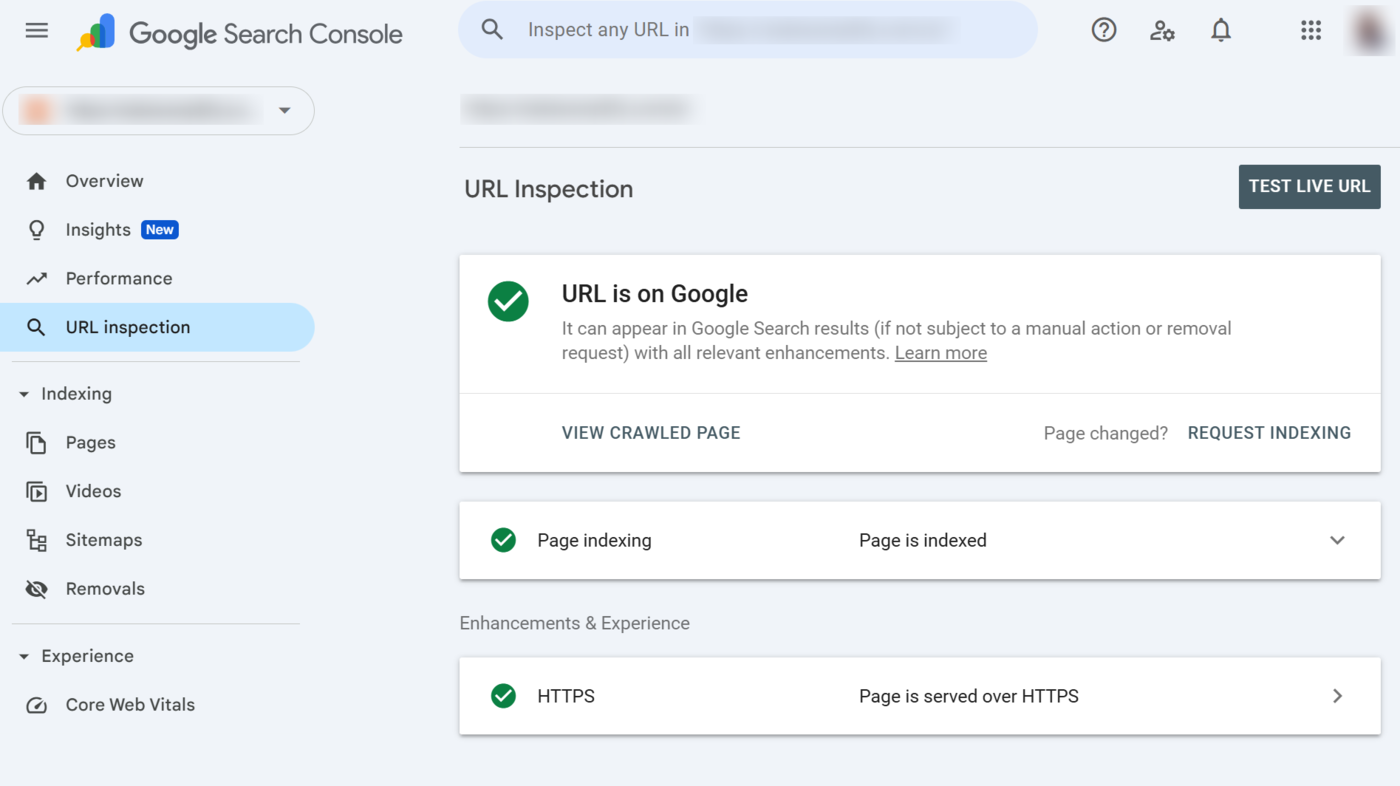
URL Inspection Tool Reports
The URL inspection tool offers multiple options and reports that allow you to perform specific actions and assess how Google perceives your pages. We will detail them below.
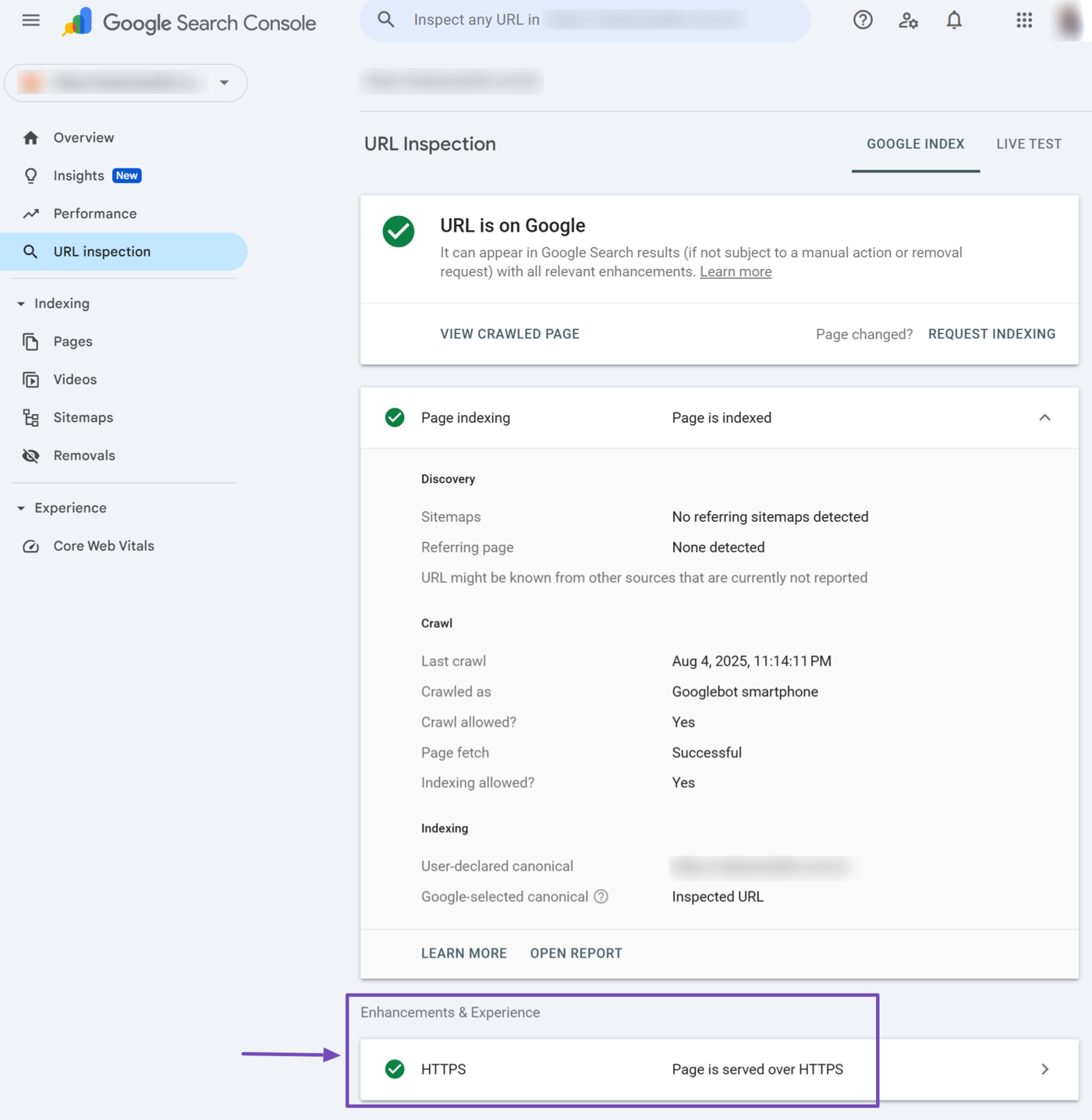
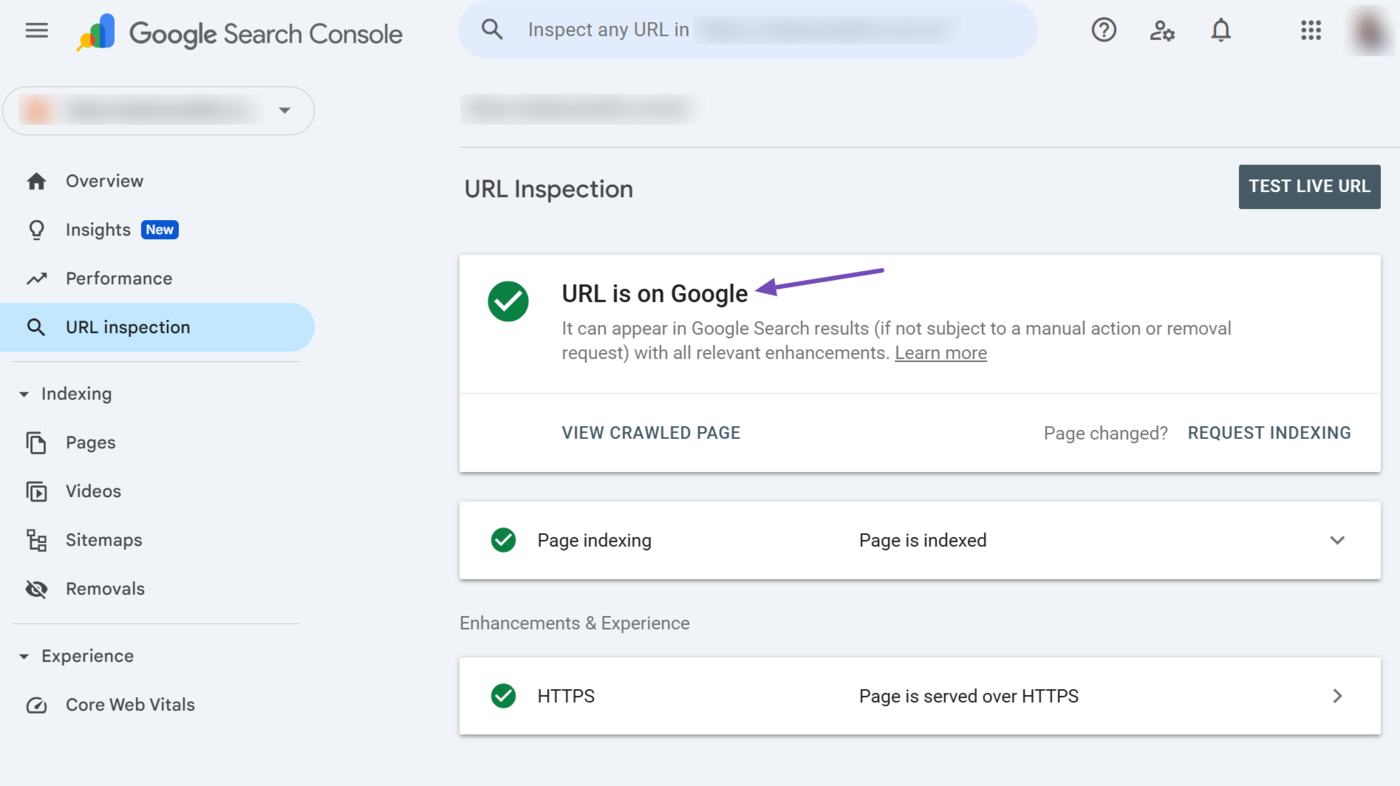
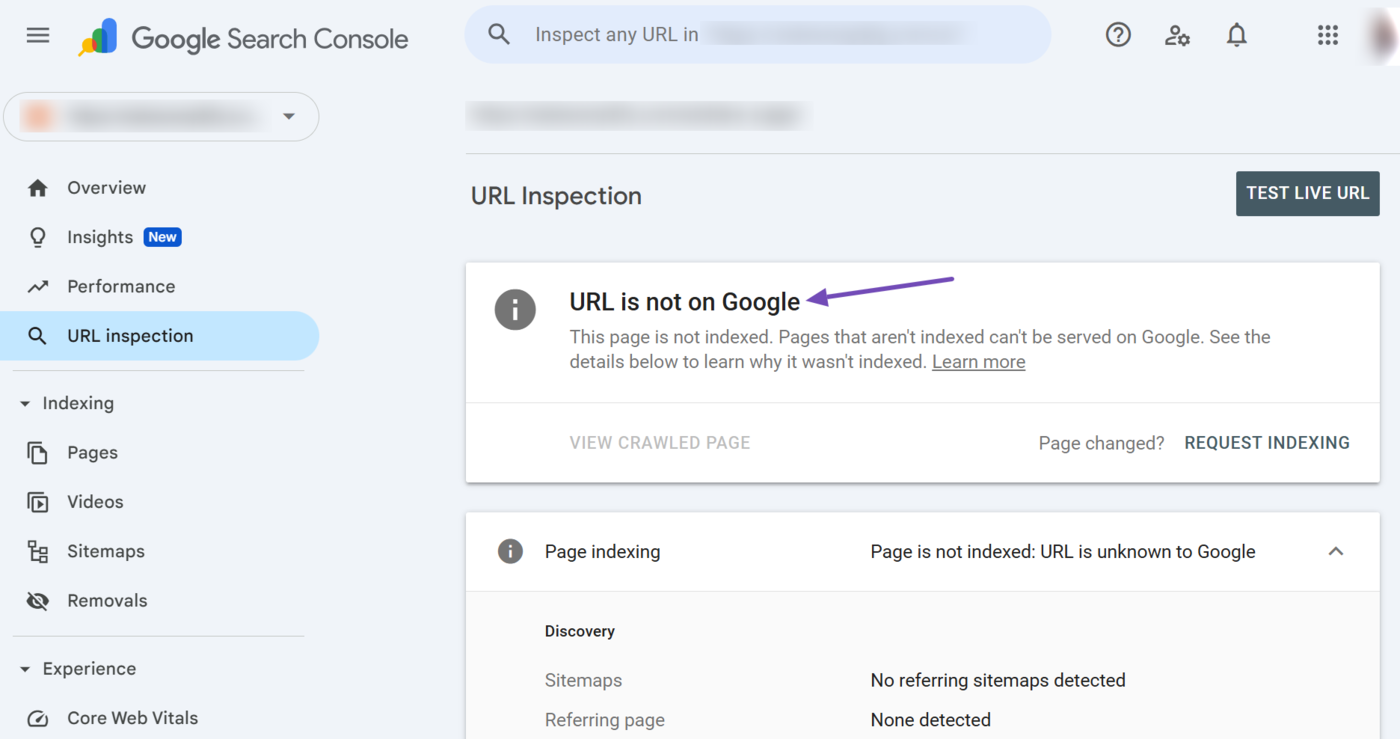
1 URL is on Google
At the top of the URL Inspection tool is the index status. It will display one of two status reports:
- URL is on Google
- URL is not on Google
URL is on Google indicates that Google has indexed the page and can display it on search results pages. This status report does not guarantee that Google will display the URL on search results pages. It only indicates that the page is eligible for display, and Google may display it.
On the other hand, the URL is not on Google status report indicates that Google has not indexed the URL and cannot display it on search results pages. This status report indicates the URL is unavailable, or Google could not crawl or index it for specific reasons.
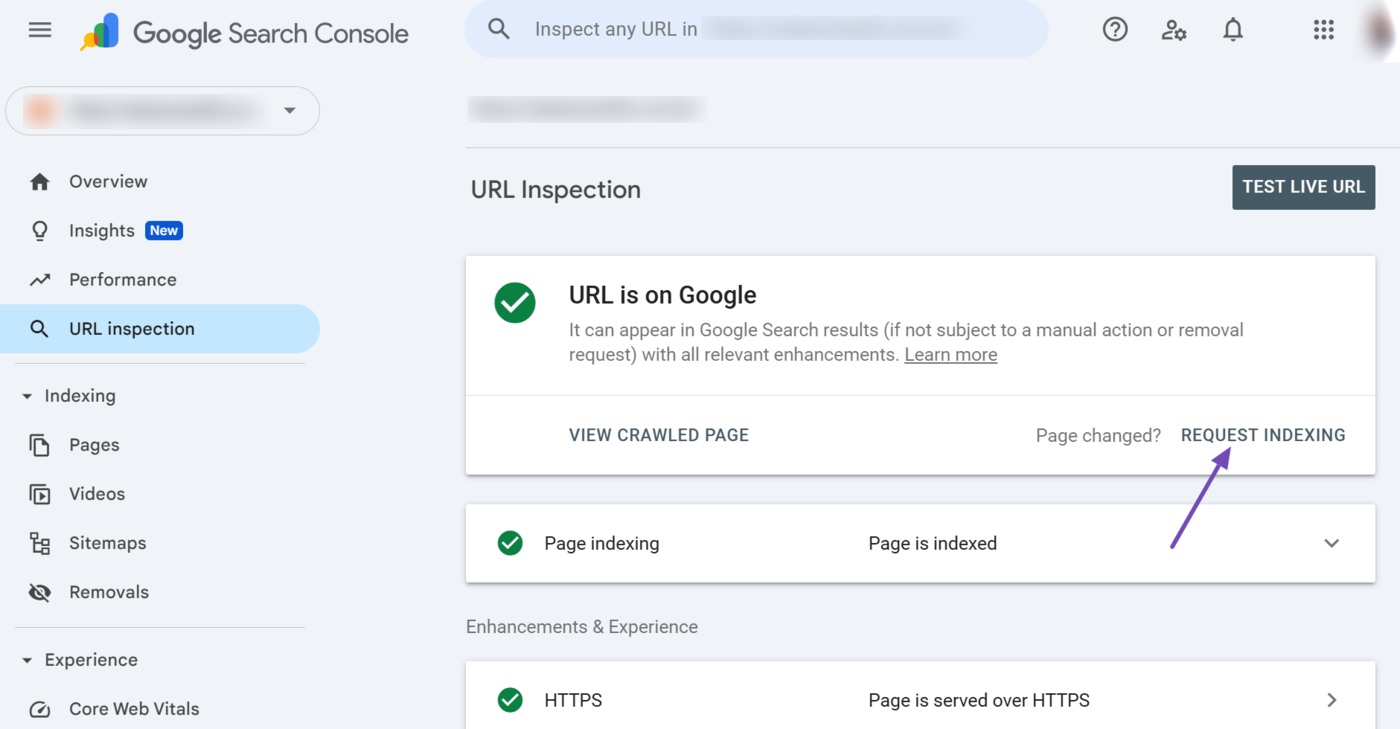
2 Request Indexing
The Request Indexing option allows you to request Google to index the webpage. This is handy if you have updated the page since Google’s last visit. However, click the option once, as clicking it multiple times will not affect how quickly Google recrawls the page.
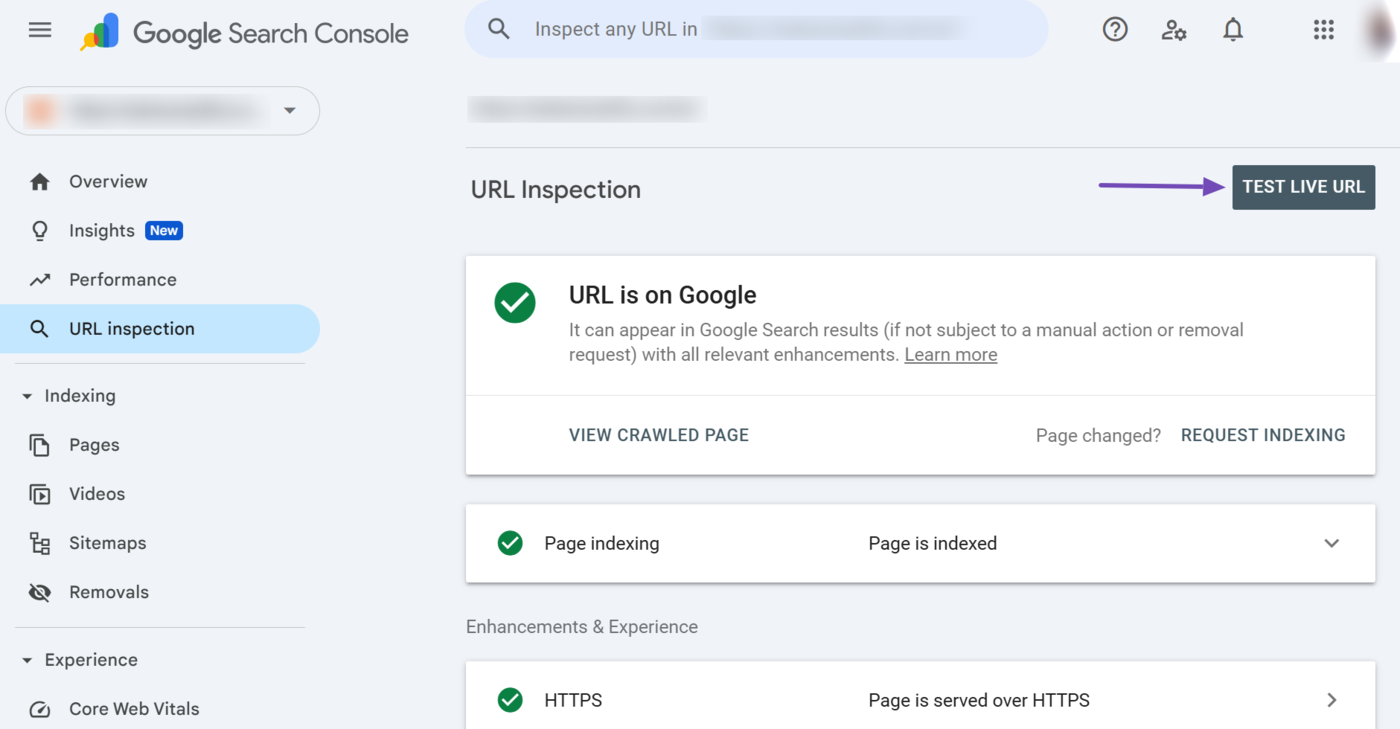
3 Test Live URL
The Test Live URL option allows you to view how the URL appears in real time rather than how it currently appears in Google’s index. This option helps identify issues on the page or test it after fixing an issue.
To test the live URL, click Test Live URL.
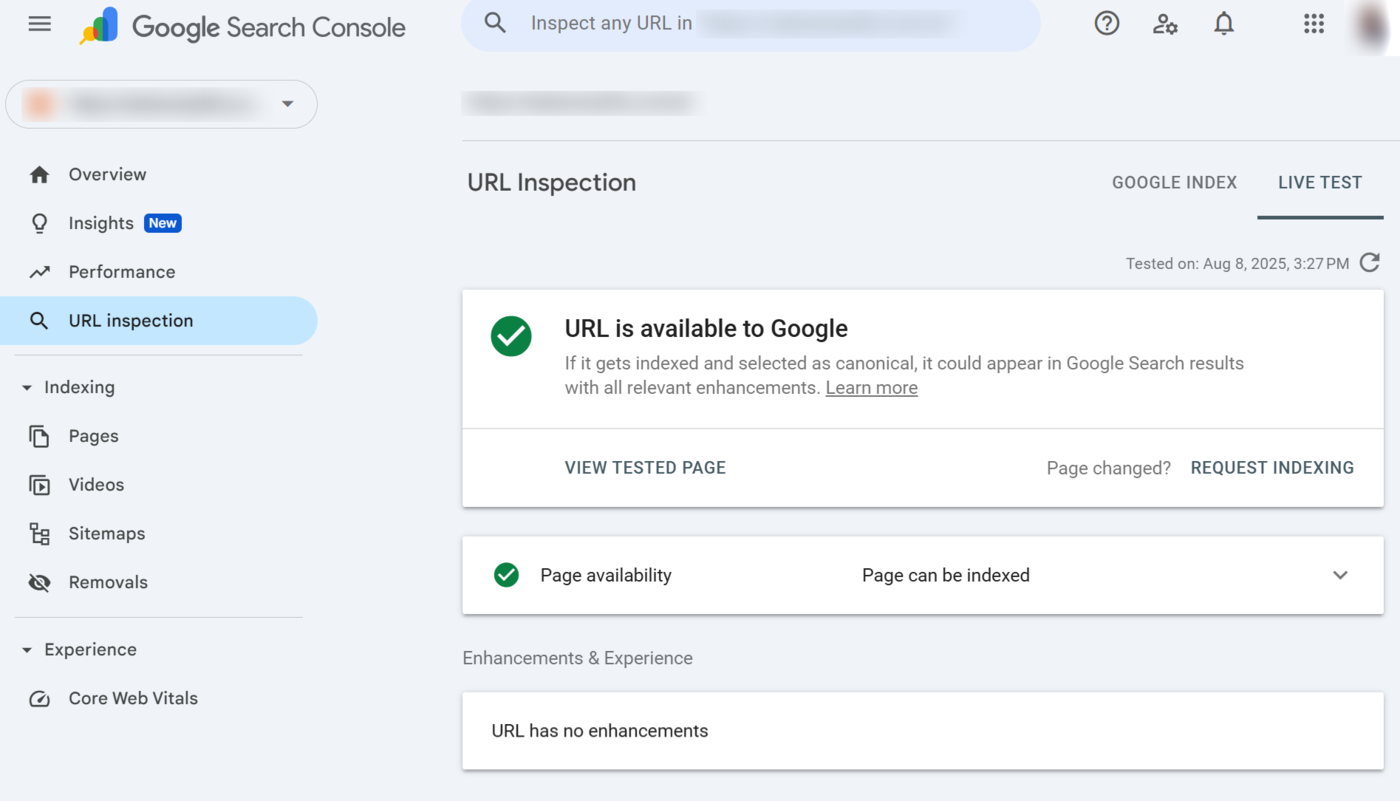
The URL Inspection tool will run a live test on the URL and return the results. Review the results to diagnose the current situation of the webpage.
4 Page Indexing
The page indexing report provides insights into how Google discovered, crawled, and indexed the page. You want it to return a Page is indexed message. Click on the report to expand it.
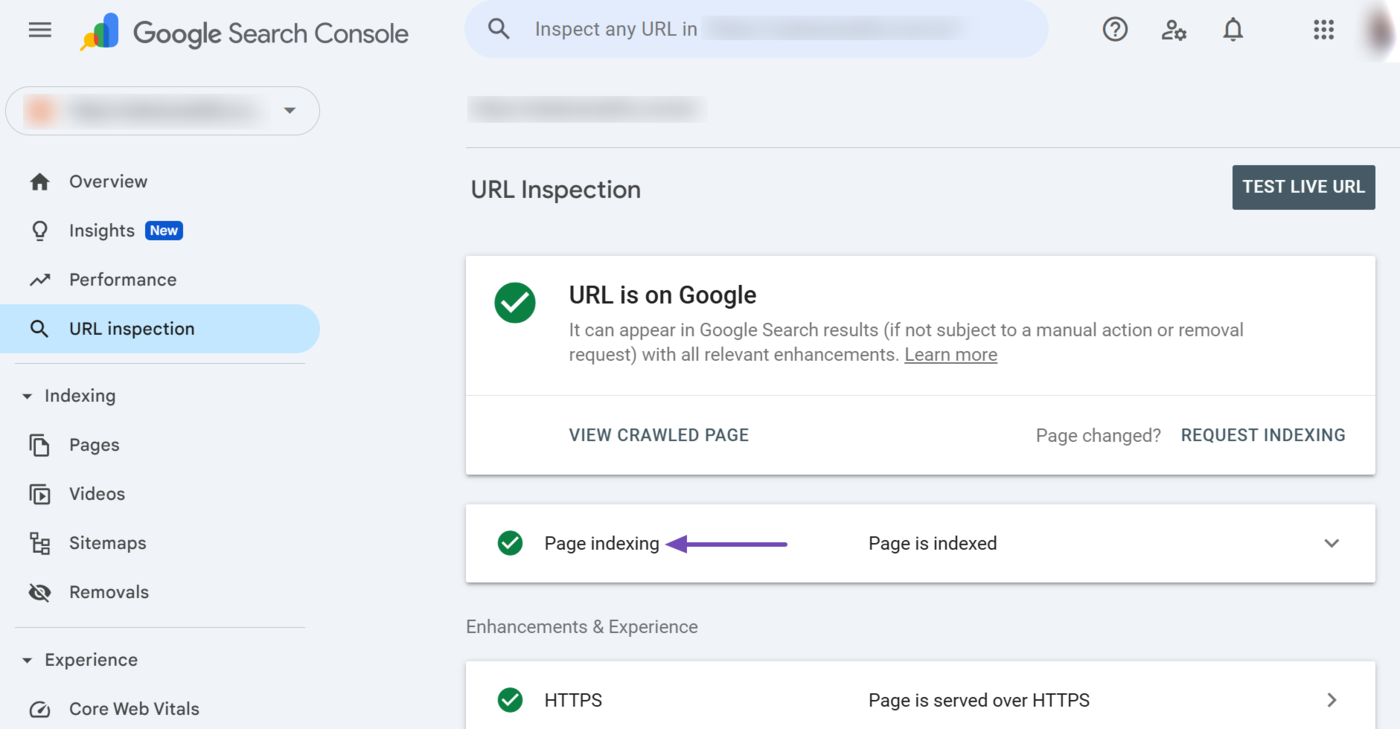
Once expanded, the page indexing report will display multiple reports, including the following:
- Sitemaps
- Referring page
- Last crawl
- Crawled as
- Crawl allowed?
- Page fetch
- Indexing allowed?
- User-declared canonical
- Google-selected canonical
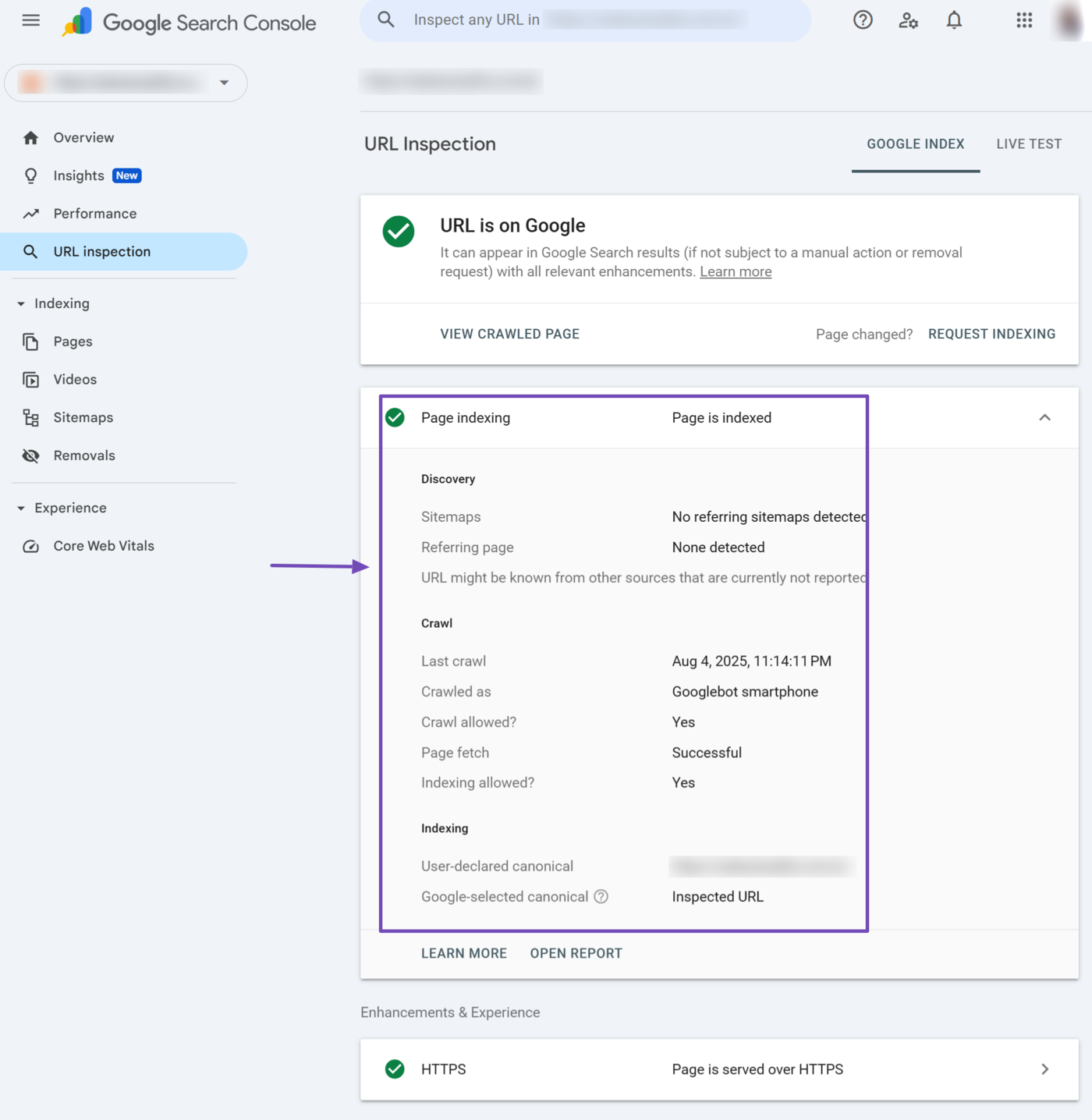
We will explain the available reports below.
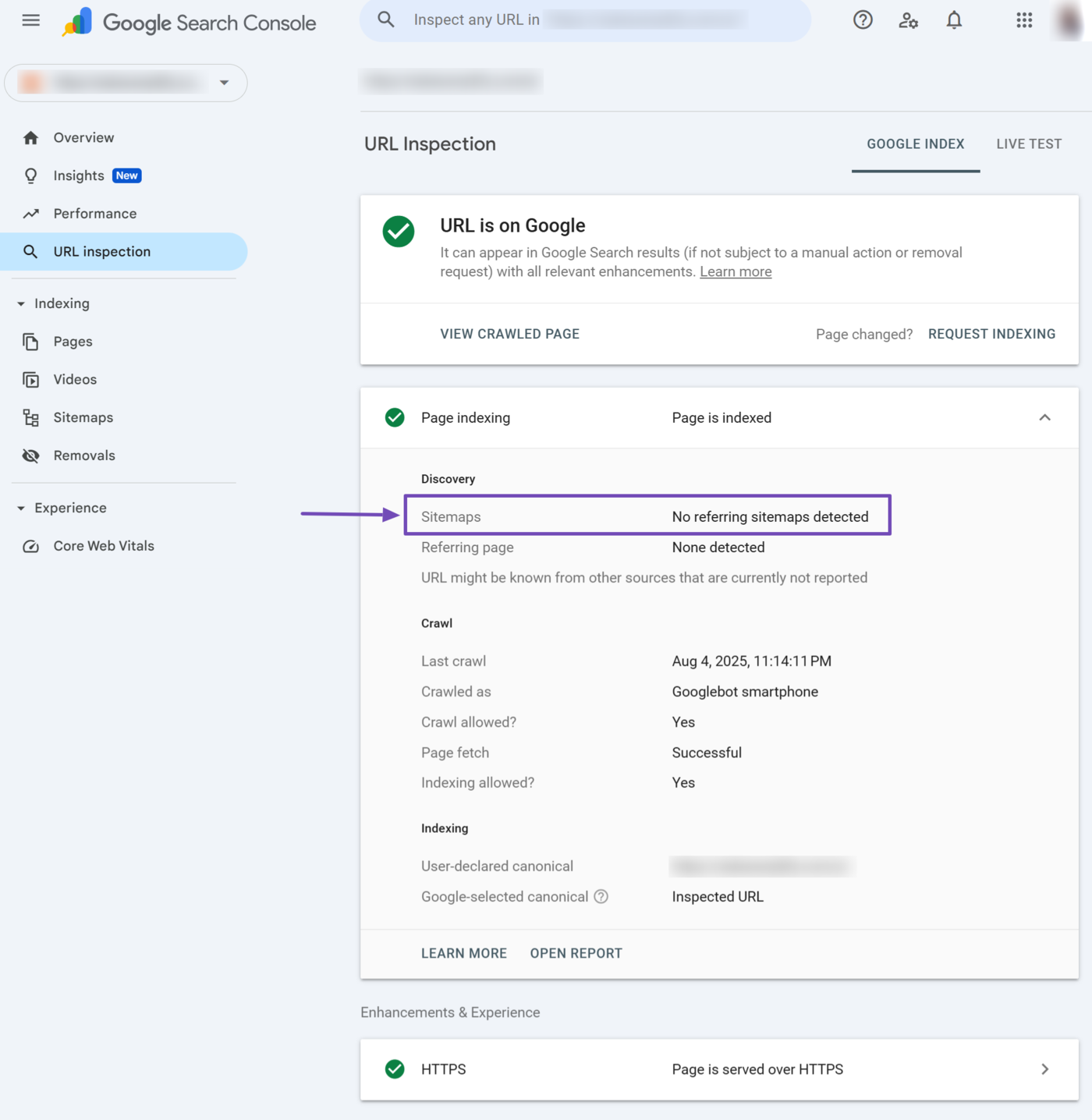
5 Sitemaps
The sitemaps section should contain the URL of your sitemap. Otherwise, it may return “Temporary processing error” or “No referring sitemap detected.”
- Temporary processing error: This indicates a temporary issue that prevents Google from retrieving data from your sitemap. You may re-inspect the URL to check if it resolves the problem.
- No referring sitemap: This indicates that Google could not identify the sitemap that contains and refers to the inspected URL.
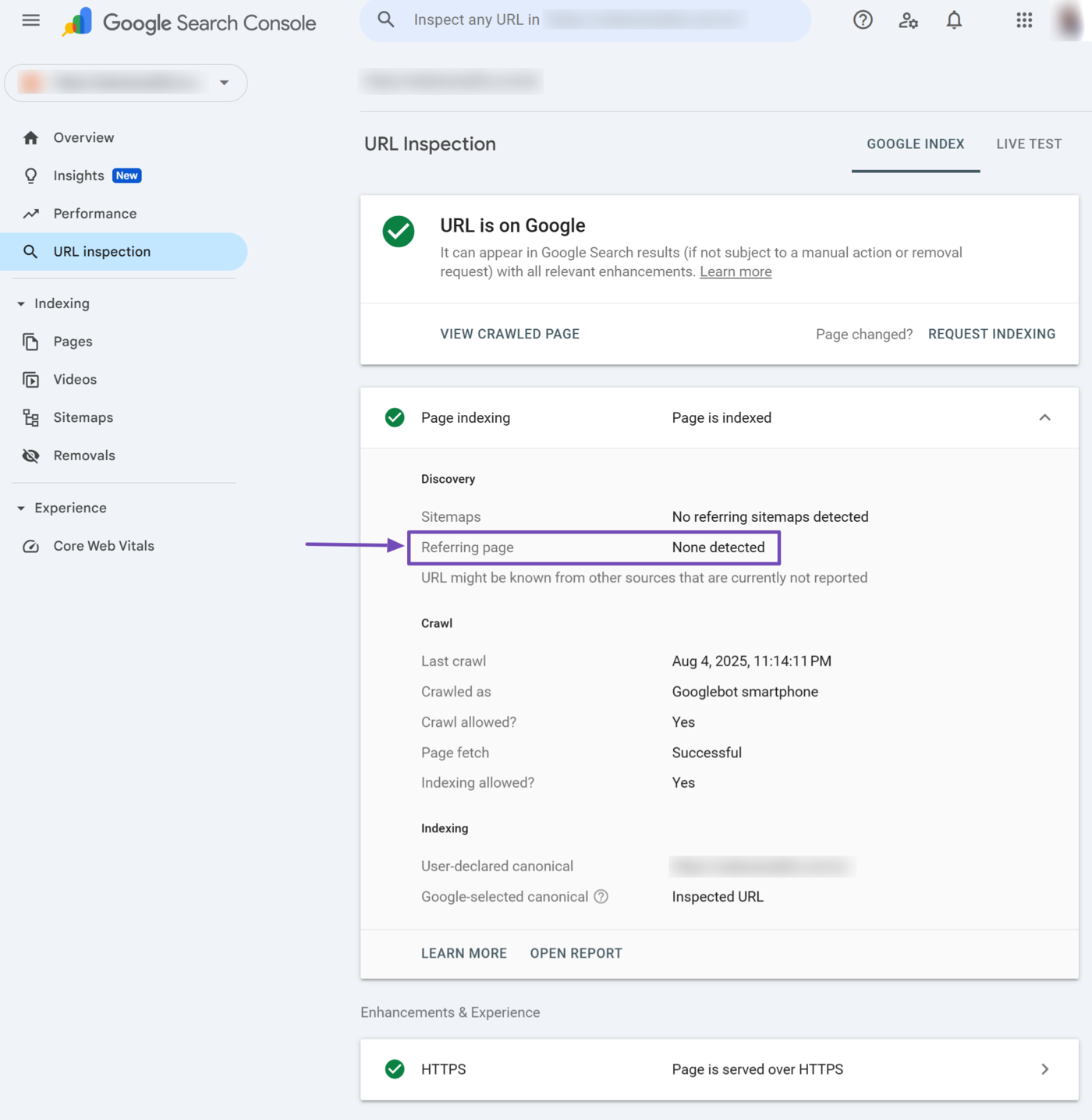
6 Referring Page
The referring page field contains the URL through which Google discovered the URL. This field may contain the inspected URL or the URL of some other page linking to it.
This field may also be blank if the referring information is not available. Optionally, it may display “URL might be known from other sources that are currently not reported” to indicate that Google discovered the URL through some other means.
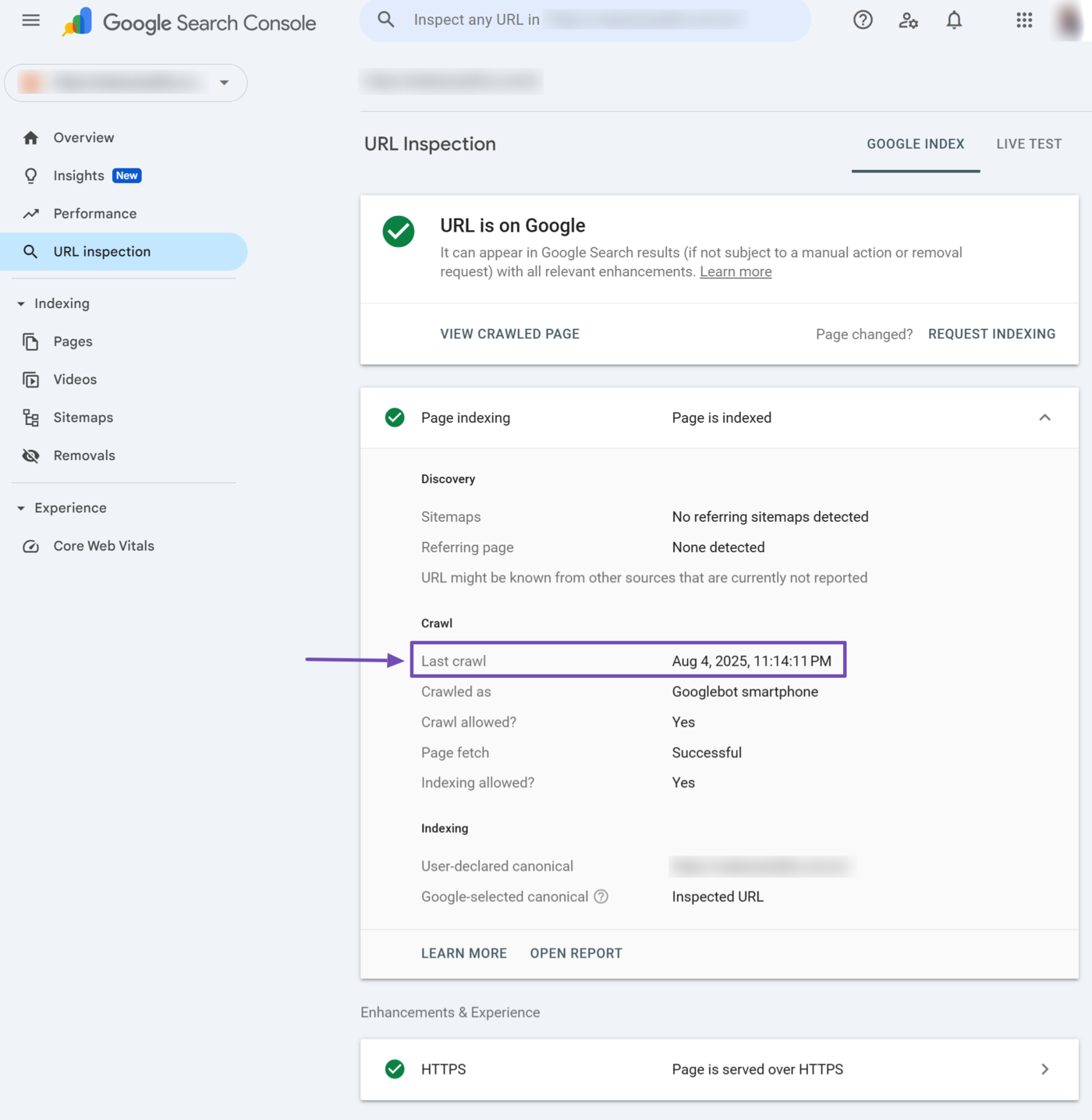
7 Last Crawl
The last crawl field specifies the date and time Google last crawled the inspected URL.
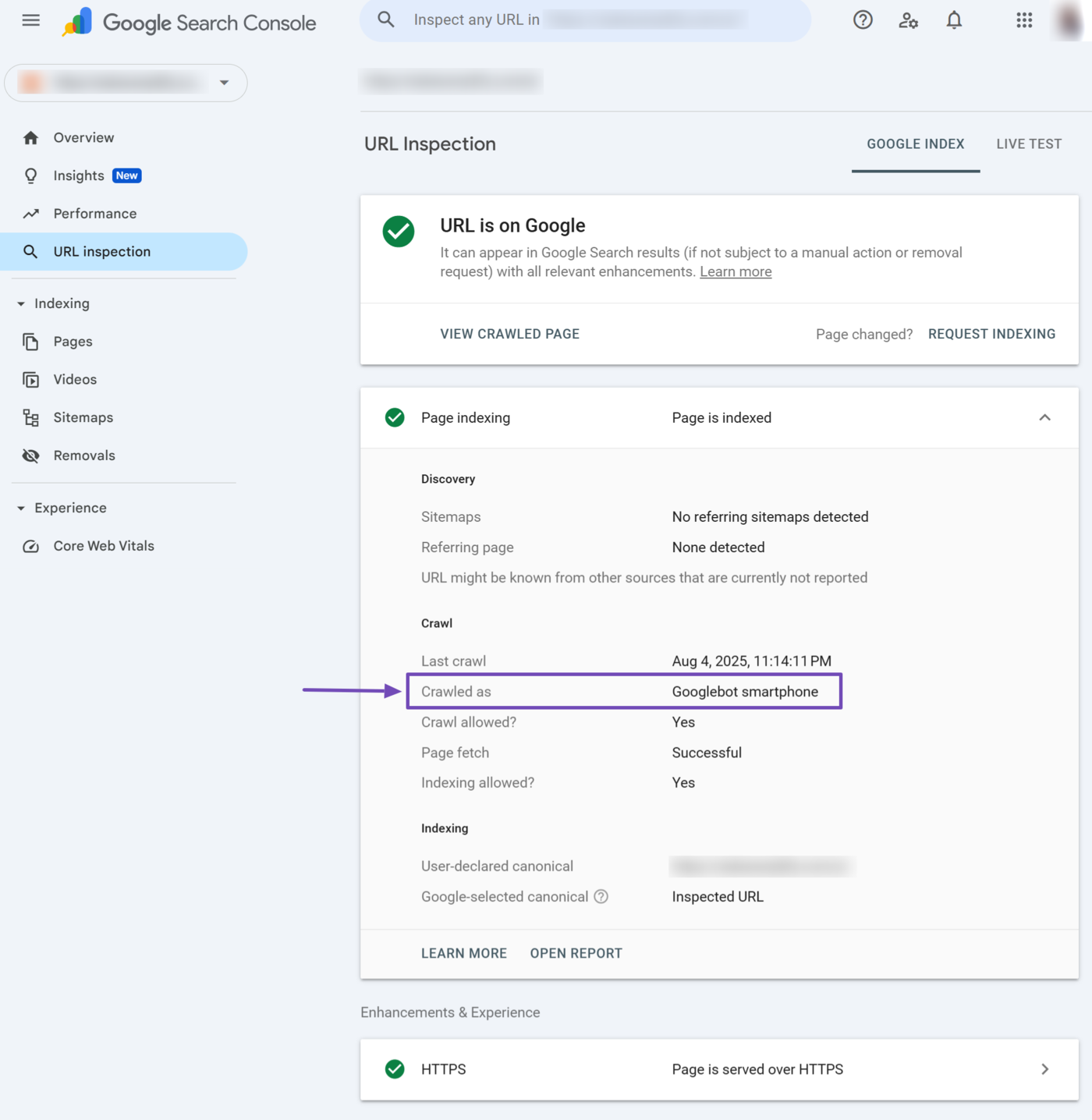
8 Crawled As
The crawled as field specifies the crawler Google used to crawl the URL. The crawler could be “Googlebot desktop” or “Googlebot smartphone.”
- Googlebot desktop: The Googlebot crawler that imitates a desktop
- Googlebot smartphone: The Googlebot crawler that imitates a smartphone
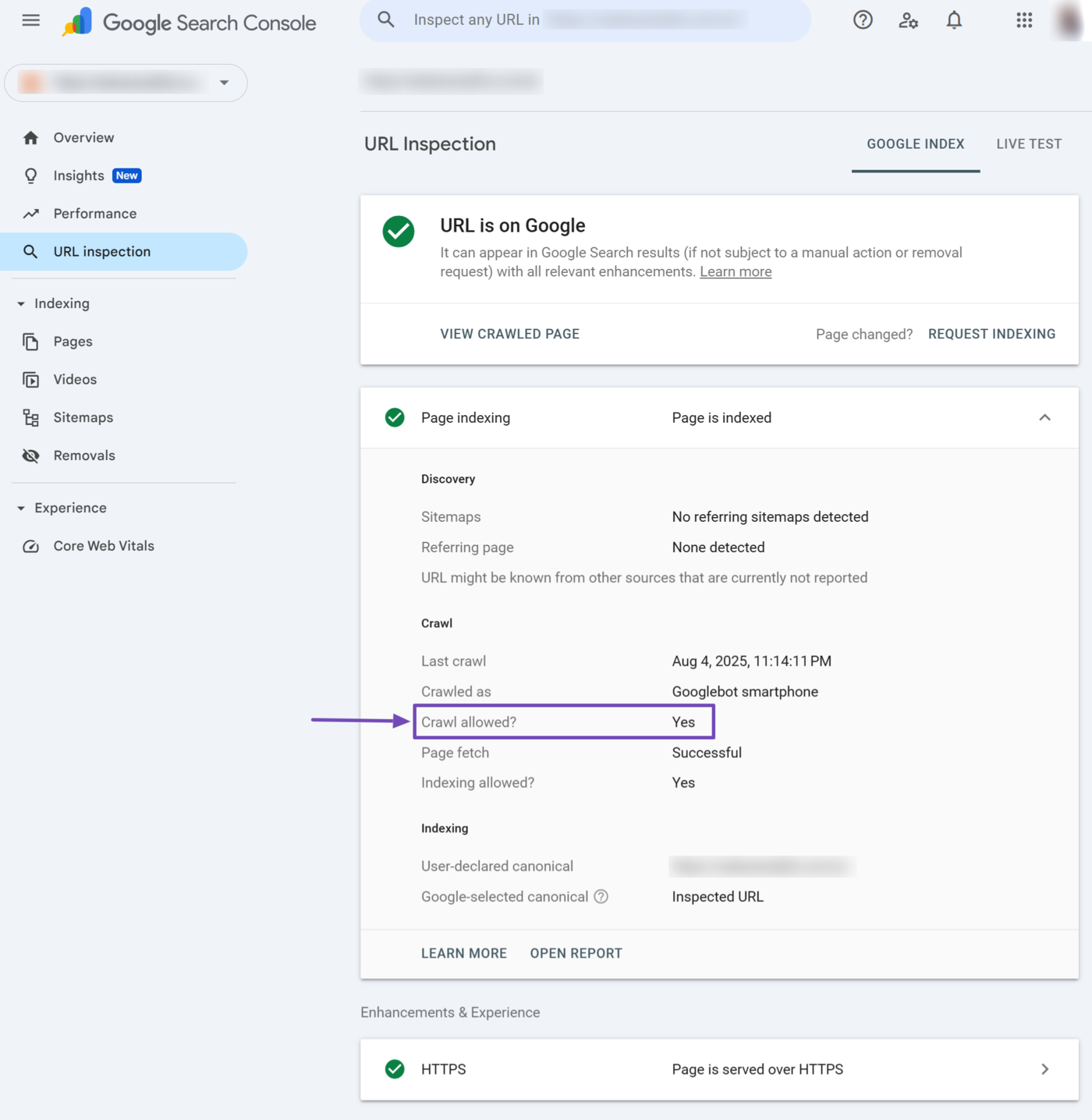
9 Crawl Allowed?
The crawl allowed field specifies whether you allow or block Google from crawling the page. It would return a Yes if you allow Google to crawl the page.
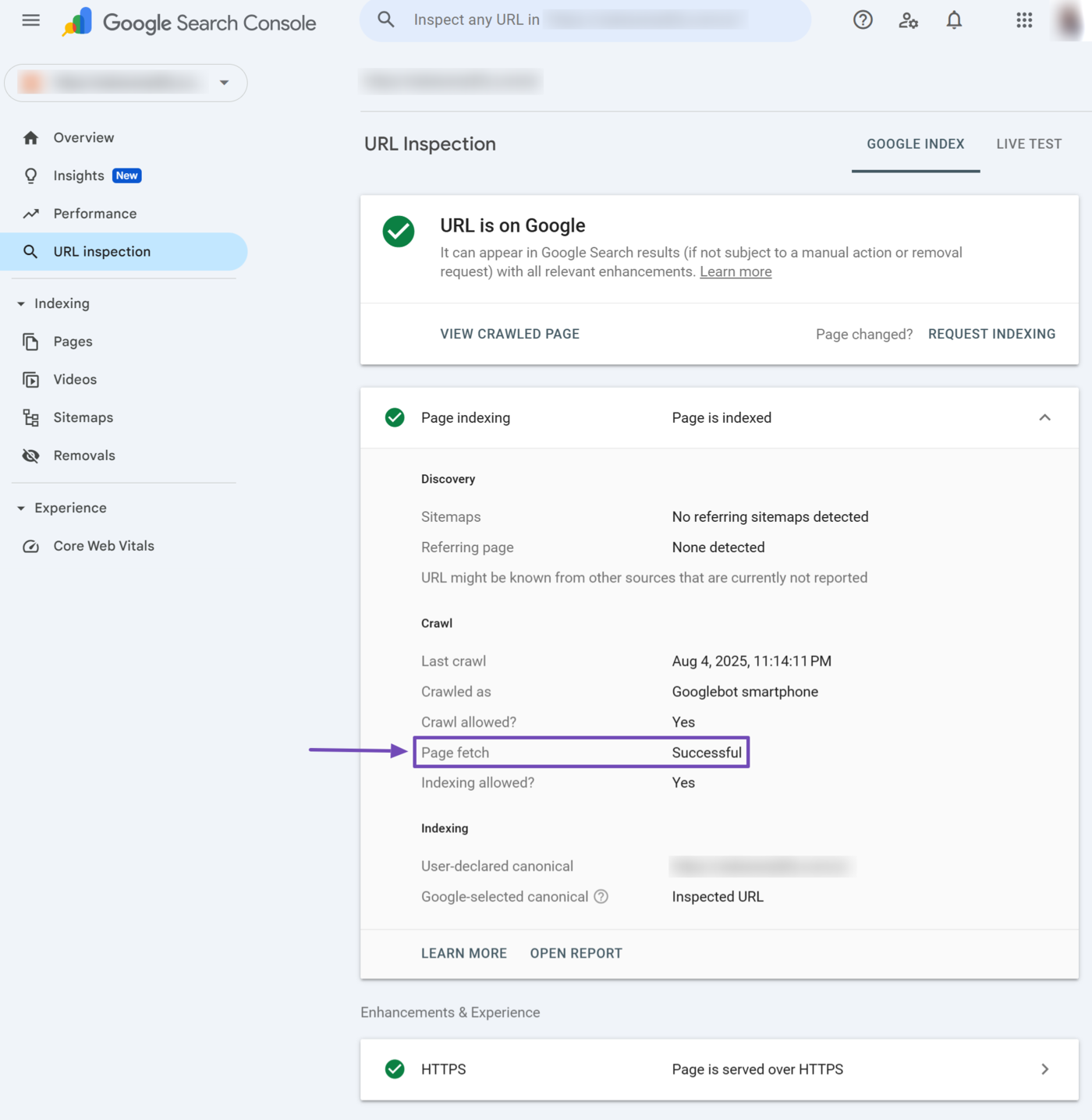
10 Page Fetch
The page fetch field specifies whether Google can access the webpage. Google cannot index the page if it cannot fetch it. This field could return:
- Successful: Google was able to fetch the page
- Failed: Google cannot fetch the page, and will include why Google could not fetch the page
- N/A: Google cannot fetch the page for some unidentified reason
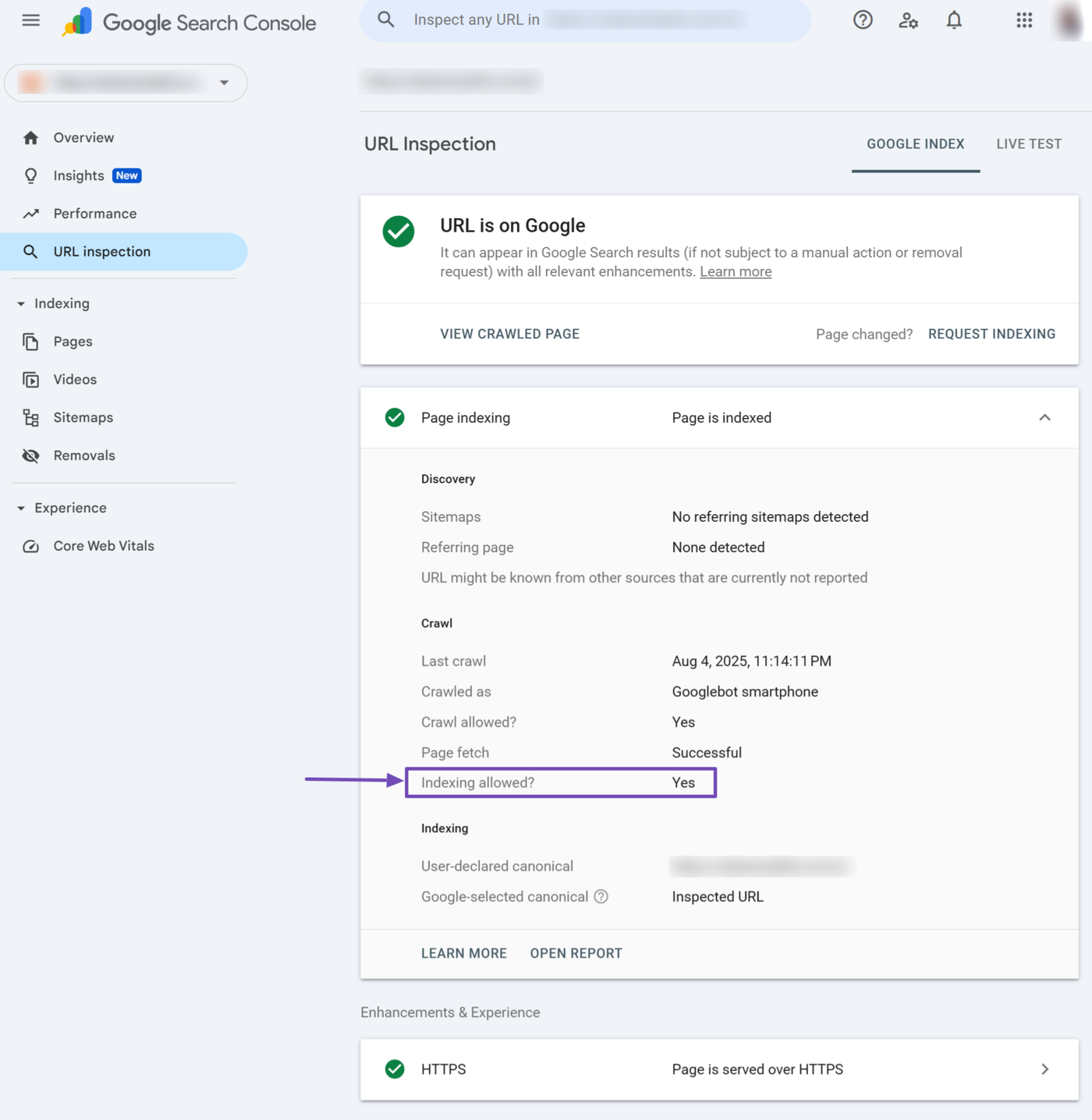
11 Indexing Allowed?
The indexing allowed field indicates whether you allow Google to index the page. It will return Yes if you allow indexing. Otherwise, it will return the reason Google could not index the page. Unindexed pages cannot appear on Google results pages.
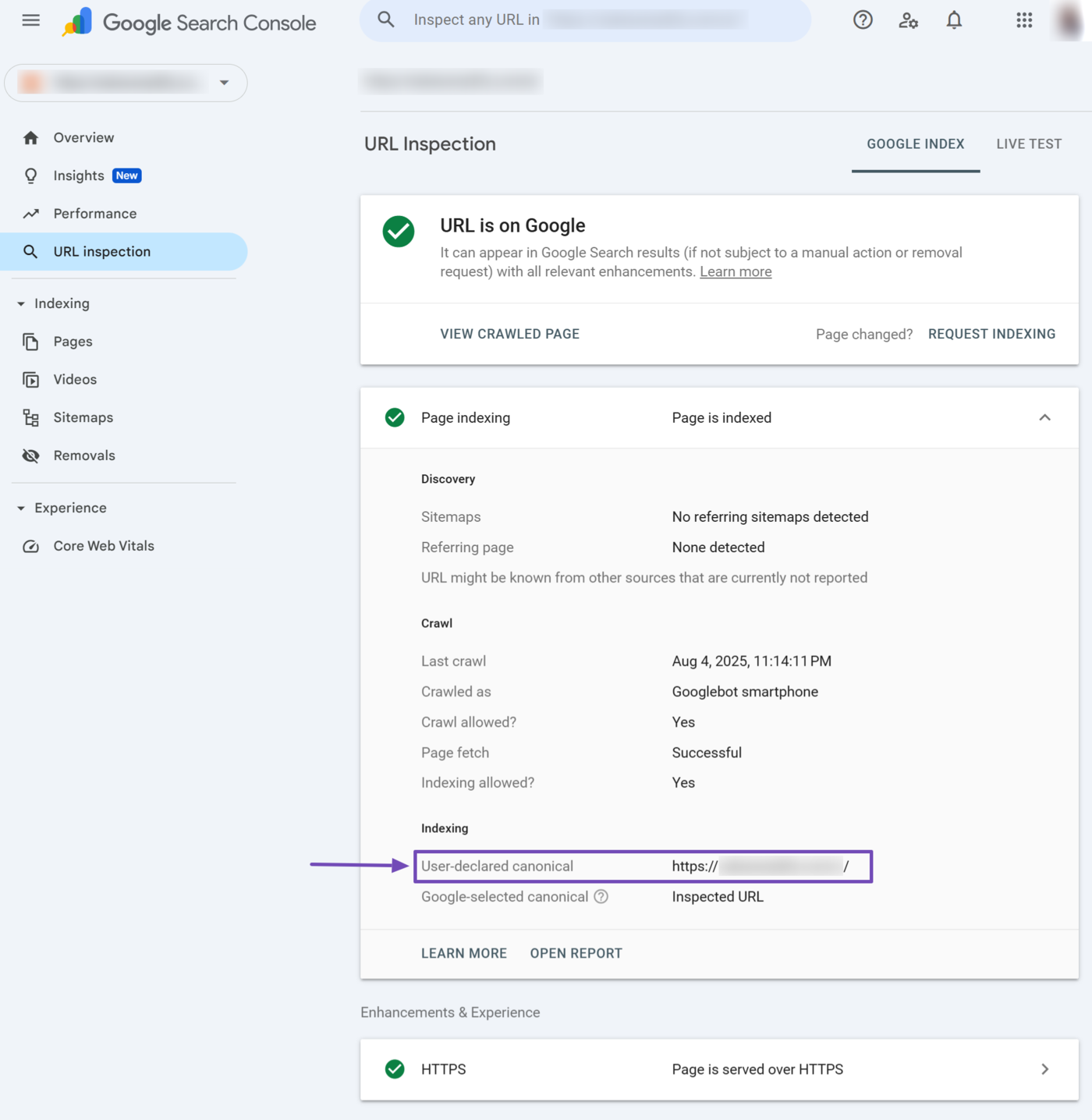
12 User-Declared Canonical
The user-declared canonical field indicates the canonical URL you declared for the URL. The canonical URL indicates the main URL among a group of URLs that lead to the same content.
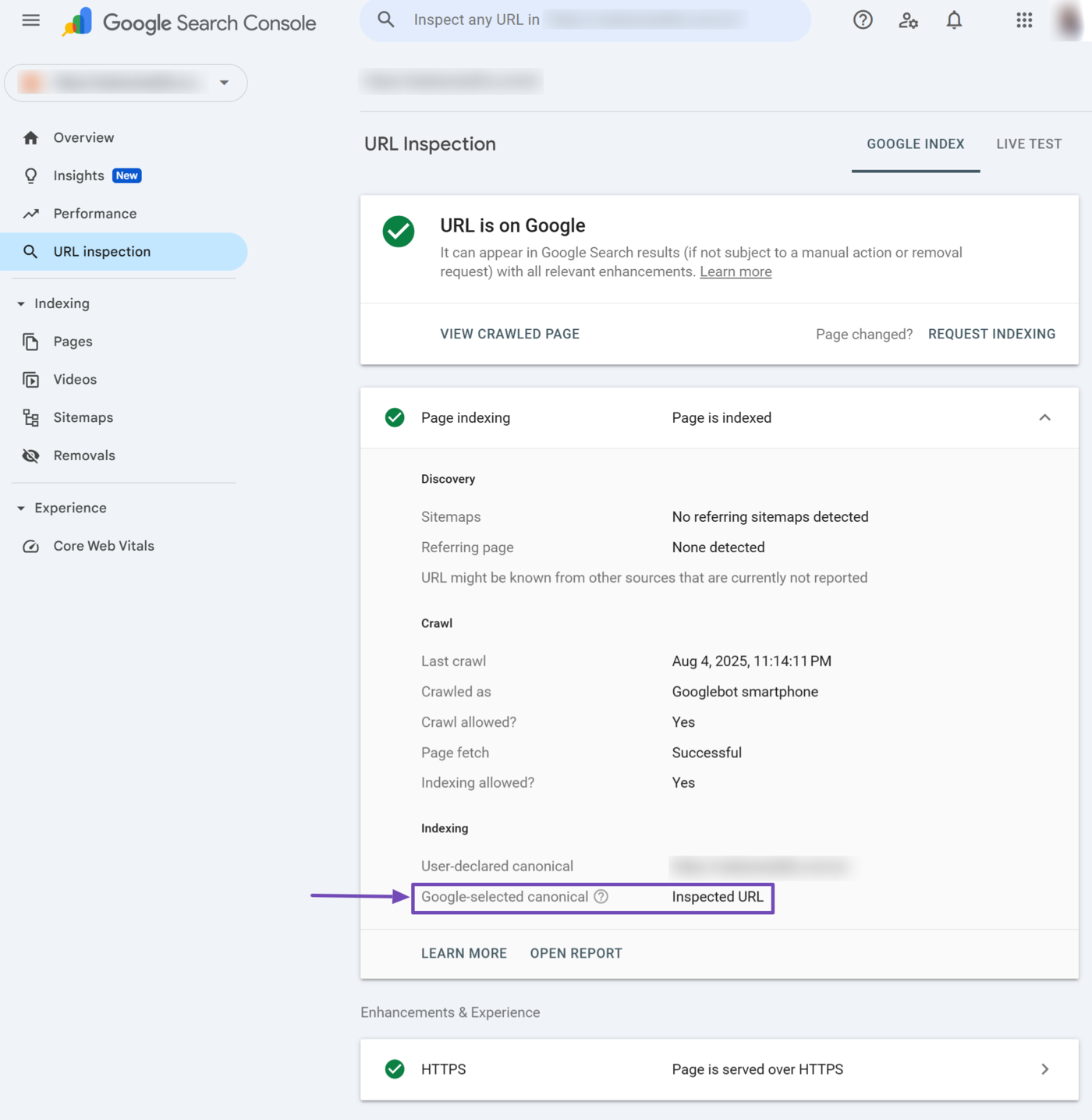
13 Google-Selected Canonical
The Google-selected canonical field specifies the URL that Google selected as canonical. If Google considers the URL you inspect as canonical, it displays Inspected URL. Otherwise, it will display the URL Google considers canonical.
This field may contain a URL from a different site under certain circumstances. This could happen if your content originally appeared on another site.
14 Experience & Enhancements
This Experience & Enhancements section outlines the enhancements made to the URL. The specific reports displayed here differ from URL to URL. For example, the inspected URL contains HTTPS.