What is DNS (Domain Name System)?
The DNS (Domain Name System) is the system for converting domain names into IP addresses.
An IP (Internet Protocol) address is a set of numbers, letters, and symbols used to identify a computer on the internet. For example, 192.158.1.38 (an IPv4 IP address) and 2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334 (an IPv6 IP address).
Every website has an IP address. However, it would be difficult or even impossible to remember the IP addresses of even our favorite websites. So, domain names were invented.
However, machines do not understand domain names. So, the domain name system is used to convert the domain name we understand into the IP addresses machines understand.
How the Domain Name System Works
The domain name system relies on multiple servers to convert a human-readable domain name into a computer-readable IP address. These servers are collectively called nameservers. They include the:
- Root nameserver
- Top-level domain (TLD) nameserver
- Authoritative nameserver
However, your browser does not communicate directly with these nameservers. Instead, it communicates with a DNS resolver (Domain Name System resolver), which acts as the middleman between your browser and the nameservers.
How a Domain Name System Lookup Works
The domain name system lookup begins with a user entering a domain name into their browser and terminates with the DNS resolver returning the IP address of the domain name. We will now explain it below.
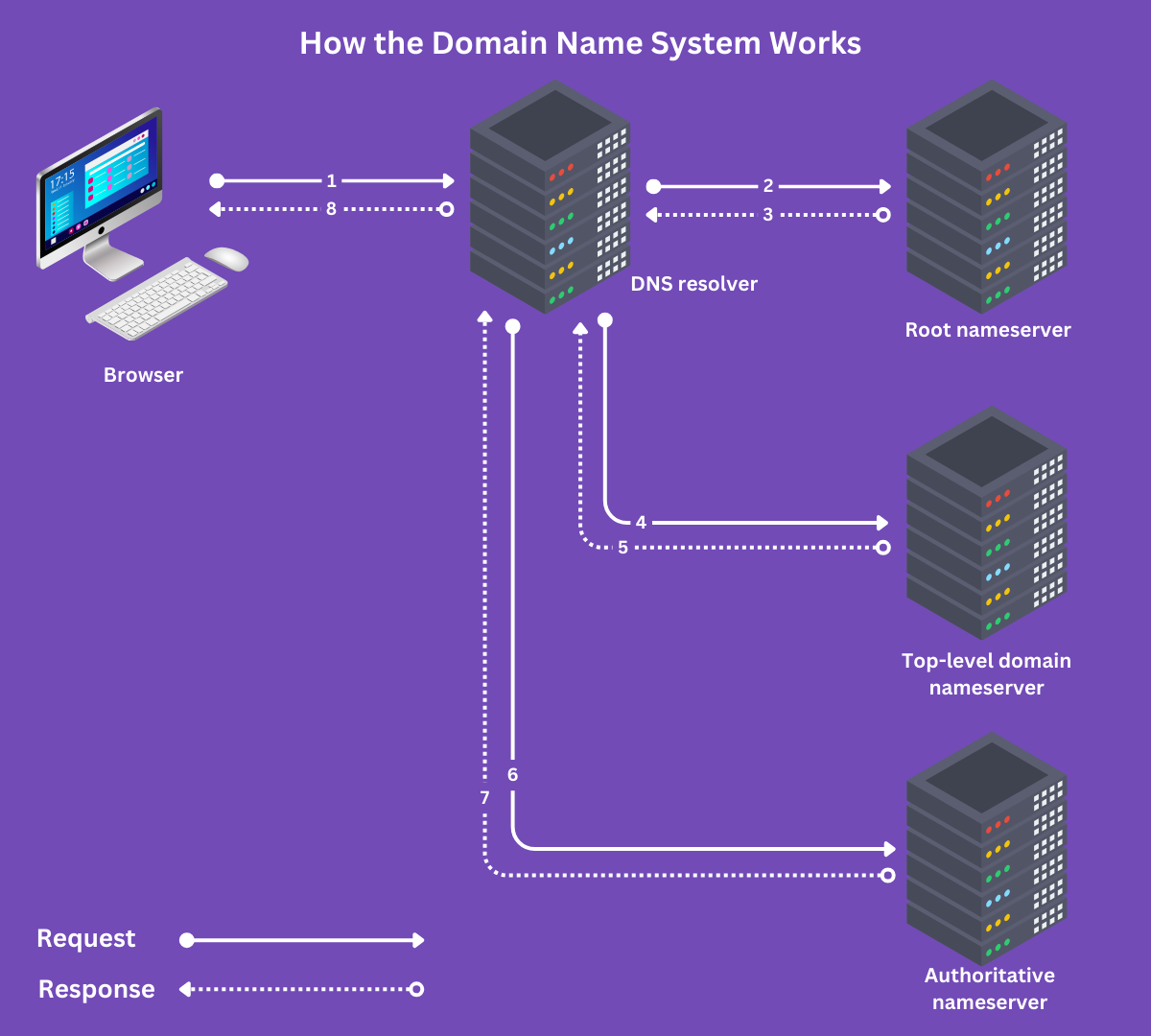
1 User Input
The domain name system lookup begins with the visitor entering a domain name into their browser. For this example, let us assume the visitor entered yourdomain.com.
2 DNS Resolver Query
The browser sends a request to the DNS resolver. The resolver is responsible for finding the IP address associated with the domain name and returning it to the browser. It is usually provided by the visitor’s Internet Service Provider (ISP).
3 Root Nameserver Query
The DNS resolver then queries the root nameserver for the details of the top-level domain nameserver associated with yourdomain.com. The root nameserver, in return, responds with the top-level domain nameserver for .com domains.
4 Top-Level Domain Nameserver Query
The DNS resolver then queries the .com top-level domain nameserver. The top-level domain nameserver replies with the IP address of the authoritative nameserver for yourdomain.com.
5 Authoritative Nameserver Query
The authoritative nameserver knows the IP address of the web server hosting the site at yourdomain.com. So, the DNS resolver will query it for this IP address.
The authoritative nameserver will then reply with the IP address of yourdomain.com. The DNS resolver then sends this IP address back to the browser and caches it in case it needs to look up the site again in the future.
The domain name system lookup is complete at this point. The browser will then make an HTTP or HTTPS request to the web server hosting the content located at the IP address. The web server will return with the content, which will then be presented to the visitor.