What is a 301 Redirect?
The HTTP 301 redirect status code indicates the requested resource has been permanently moved to a new location. It is also called 301 Moved Permanently.
If you have run a site for a while, you would have knowingly or unknowingly made some changes to your URLs. For example, you may have:
- Migrated your site from
httptohttps - Changed your site’s permalink
- Changed your domain name
- Changed a page’s URL
- Deleted a page
- Moved a page
- Merged multiple pages
Depending on what has changed, visitors and search engine crawlers may encounter a 404 Not Found page or land on a different version of the page other than the one you want them to visit.
To prevent this, you can create 301 redirects. That way, visitors and search crawlers that visit the old URLs will be redirected to the new one. Search engines will also update their databases with the new URL.
The 301 Moved Permanently redirect belongs to the 3xx series of HTTP status codes.
3indicates the status code is a redirection.xxis a placeholder for two numbers that indicate the type of redirection.
In this article, we’ll cover:
How Does a 301 Redirect Work
The browser and server handle the 301 redirects without any input from your end. Here is a rundown of how it works:
- You click a hyperlink or enter a URL into your browser’s address bar
- Your browser sends an HTTP request to the server, requesting to access the resource at the URL
- The server responds with an HTTP 301 status code and includes the resource’s new URI in the response’s Location header
- Your browser makes a new request to the server, requesting to access the resource at the new location
- The server sends the resource to the browser
- The browser displays the resource to you
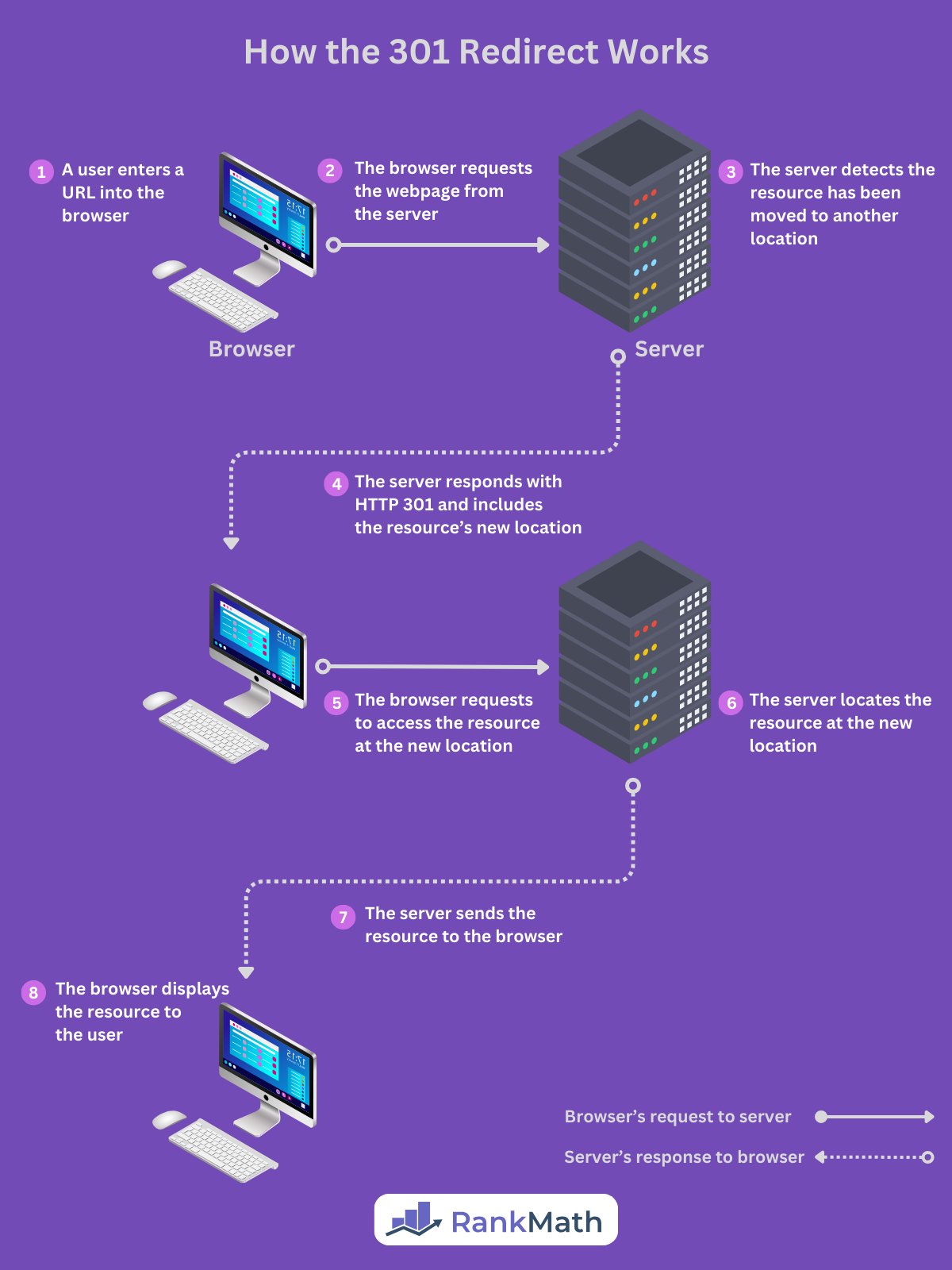
The above explanation is just a simple illustration. Browsers and servers communicate using Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP), so the requests and responses are sent in HTTP format.
For example, a browser looking to access the webpage located at yourdomain.com will send the below HTTP request to a server.
GET /index.html HTTP/1.1 Host: yourdomain.com
The server will then reply with the HTTP 301 status code, indicating the page has been permanently moved. The response includes the current location of the resource.
HTTP/1.1 301 Moved Permanently Location: https://yourdomain.com/home
The browser then sends another request to the server. It will request to access https://yourdomain.com/home.
GET /index.html HTTP/1.1 Host: https://yourdomain.com/home
The server then sends the files located https://yourdomain.com/home to the browser, which then presents them to the visitor.
The 301 response code is typically invisible to the visitor. However, you can observe the redirection by monitoring changes to the URL you entered into the browser and the URL presented to you once the page is loaded.
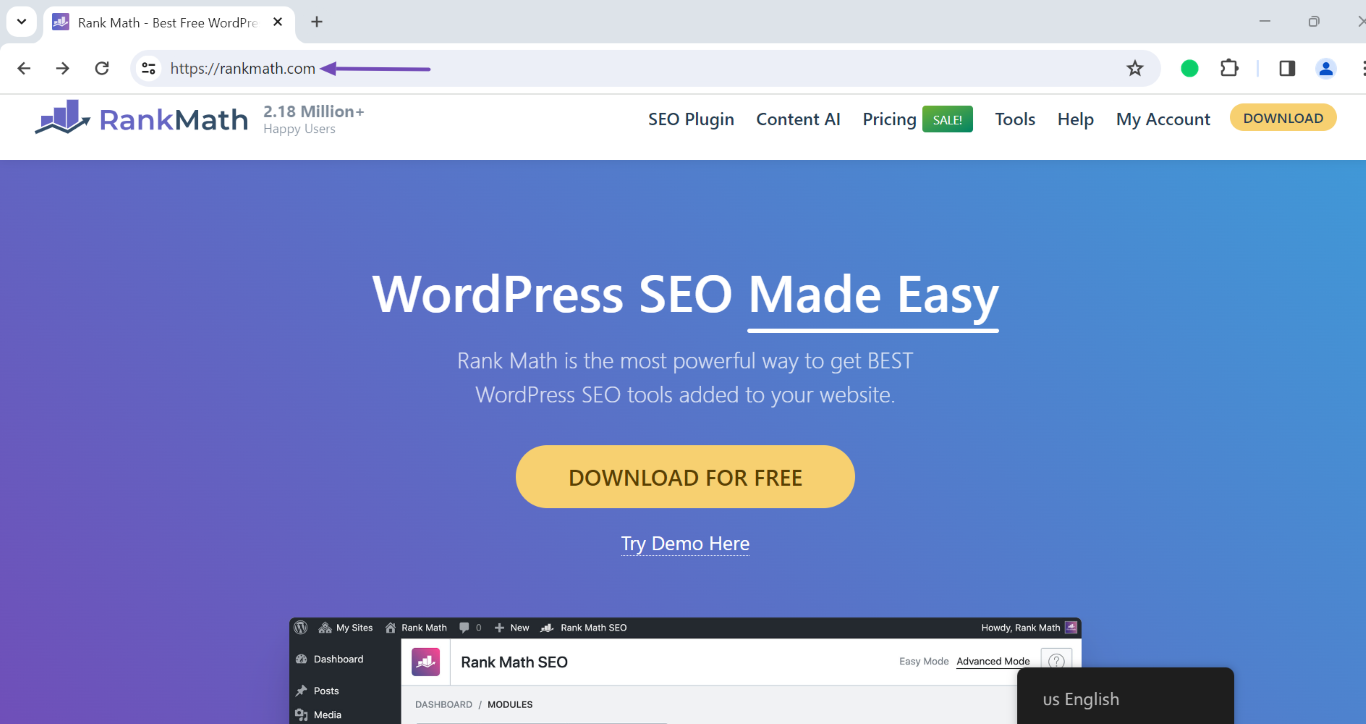
For example, when we enter the unsecured http://rankmath.com into our address bar:
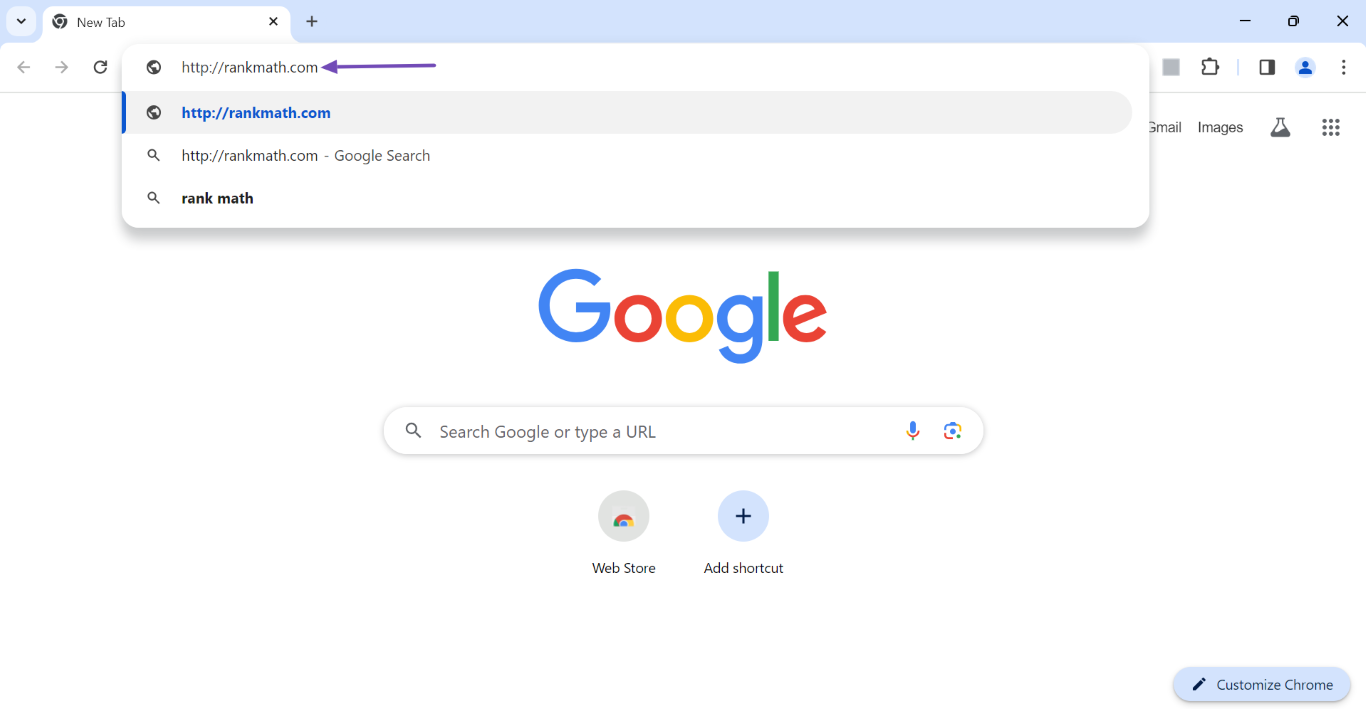
Our browser displays the secured https version of our site without any extra input from our end. This is a result of the 301 redirect that redirects visitors from the http to the https version of our site.
Why the 301 Redirect is Important
The 301 redirect provides your site with several SEO and usability benefits. This helps to ensure that your site can rank and your visitors do not encounter usability and user experience issues when using your site.
1 301 Redirects Preserve Your Link Equity and Pagerank
Google assigns a value to all webpages based on the quality and quantity of pages that link to them. This value is called PageRank, and Google uses it to determine where your content will appear in search results.
Pages also pass link equity when they link to your pages. Typically, the more high-quality links you get, the more link equity you receive and the higher your PageRank.
Moving your pages to a new URL will cause you to lose the link equity and PageRank associated with the previous page. However, with a 301 redirect, you can pass your link equity and PageRank to the new URL.
2 301 Redirects Help Google Determine Your Canonical URL
Most webpages can be accessed through multiple URLs. For example, yourdomain.com and www.yourdomain.com typically lead to the homepage of the same site.
Google identifies these pages as duplicates and selects one of them as canonical, that is, the main version of the page.
Google uses several methods to determine which page is canonical. However, Google considers the 301 redirect a strong signal that you want it to consider the URL you are redirecting to as canonical.
3 301 Redirects Improve the User Experience for Your Visitors
When you move your pages without setting up a 301 redirect, your visitors will encounter 404 pages whenever they visit the old URLs. That will lead to a negative user experience and cause your visitors to click the back button or navigate to other content.
Setting up 301 redirects prevents this and ensures your visitors can access your content even after changing the URL.
4 301 Redirects Help Preserve Your Backlinks
Many sites run SEO audits periodically, and one of the things they look out for is broken external links. These are links that originate from their site and point to nonexistent resources on other sites.
If you receive links from other sites and then delete the linked resource without setting up a 301 redirection, those links would lead to 404 pages. The linking site may discover these broken links during the SEO audit and replace them with links to other sites, including your competitors.
To prevent that, you should set up 301 redirects that redirect your backlinks to the new URL. That way, the linking site is less likely to remove your URLs.
Google’s Recommendation on Using the 301 Redirect Code
Since you want to rank on Google, you should pay attention to what Google says about using 301 redirects on your site. Consider these recommendations as best practices. That is, the things you should do to get the most out of your 301 redirects.
1 Only Use 301 Redirects if You Will Not Return to the Old URL
Google recommends using 301 redirects when you are sure you will never return to the URL you are redirecting from. If you intend to return to the old URL in the future, consider using a temporary redirect like 302 Found instead.
2 Use Meta Refresh When You Cannot Set Up a 301 Redirect
Google recommends you set up your permanent redirections using the 301 redirect. When you cannot set a 301 redirect, say because you cannot access your server, Google recommends using the meta redirect instead.
Ensure that you set the meta redirect to zero seconds as Google treats meta redirects set to zero as permanent redirects. For example:
<meta http-equiv="refresh" content="0; url=https://yourdomain.com/home">
In the above code:
http-equiv="refresh"tells the browser to redirect to the new pagecontent="0tells the browser to redirect to the new page after zero secondsurl=https://yourdomain.com/home"tells the browser to redirect to https://yourdomain.com/home
3 Redirect Your Old Pages to the Corresponding New Page
When you change your site’s URL, Google recommends redirecting your old pages to the corresponding page on the new URL.
For example, if you moved from yourdomain.com to example.com, you should redirect the homepage from yourdomain.com to example.com. Similarly, you should redirect a page like yourdomain.com/what-is-yoga to its new location at example.com.
4 Avoid Long Redirect Chains
Google recommends avoiding redirect chains wherever possible.
A redirect chain occurs when there are multiple redirects between the initial URL and the final URL. For example, URL A redirects to URL B, which in turn redirects to URL C, and then finally to URL D.
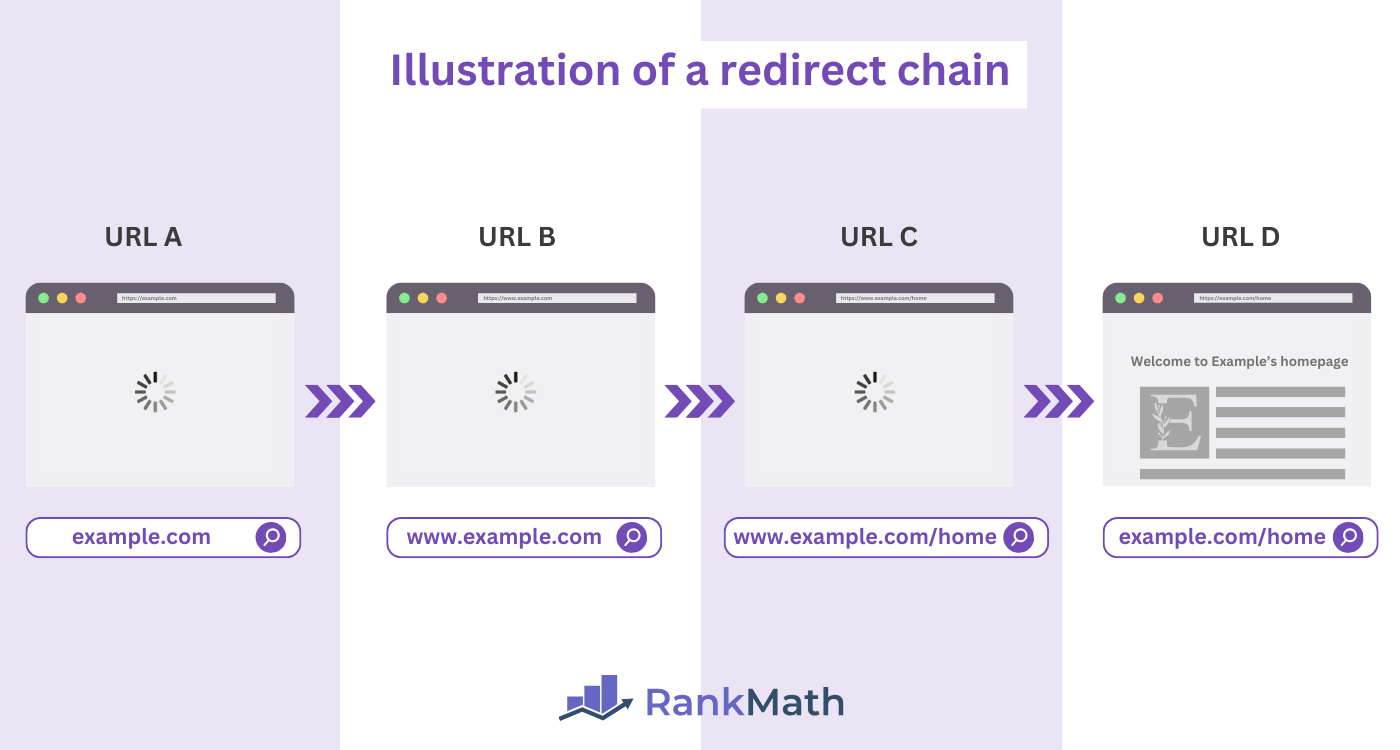
Google only follows four or five redirects (hops) before it gives up and stops following the redirect. To ensure Google follows your 301 redirects, Google recommends keeping your redirections preferably within one or two redirects, or at most, three redirects.
5 Leave the Redirections for a Year or More
If you change your domain name, for example, from yourdomain.com to example.com, Google recommends leaving the redirections in place for a year or more before abandoning the old domain or repurposing it for other purposes.
Google says this is necessary because 301 redirections happen at a page level. So, it needs to crawl each page on the old domain and follow it to its location on the new domain.
Google also needs to crawl the pages on the old domain a few times to be really sure that you have permanently moved. If Google encounters pages without 301 redirects on the old domain, it may assume you are still using the old domain.
6 Update Your Internal Links and Sitemaps
When you set up a 301 redirect on your site, Google recommends you update your internal links, sitemaps, and other links to point to the new URL.
Doing this assures Google that the content has actually moved to a new URL and makes it more likely that Google will select the new URL as the canonical URL for that resource.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What Does a 301 Redirect Do?
A 301 redirect informs the browser that the requested resource is no longer available at the specified location and has been permanently moved to another location. The server then provides the browser with the current location of the requested resource.
2. What Are 301 and 302 Redirects?
A 301 redirect indicates a resource has been permanently moved to a new location. In comparison, a 302 redirect indicates a resource has been temporarily moved to a new location. The 302 redirect indicates the resource will return to the previous URL at a later date, while the 301 redirect indicates that the resource will not return to the previous URL.
3. Is 301 Redirect Good for SEO?
The 301 redirect is good for SEO. It allows a webpage to retain its link equity, visitors, and PageRank. Google also uses the 301 redirect as a strong signal when deciding the page’s canonical URL.
4. How Do I Redirect Using the 301 Code?
You can set up 301 redirects on your server. Some Content Management Systems allow you to create 301 redirects from their settings. If you have WordPress, you can use third-party plugins to set up your redirections. You can refer to this guide on setting up 301 redirects in WordPress.