Have you ever noticed two of your blog posts competing for the same keyword in Google search? It might seem like a good thing at first, you have more chances to rank, right? But in reality, this can hurt your SEO.
This issue is called keyword cannibalization, and it can confuse search engines, lower your rankings, and waste your efforts.
In this post, we’ll discuss what keyword cannibalization is, why it happens, and most importantly, how you can fix it to make sure every page on your site works together, not against each other.

So, without any further ado, let’s get started.
Table Of Contents
1 What is Keyword Cannibalization?
Keyword cannibalization happens when multiple pages on your website compete for the same or very similar keywords.
Think of it like this: you run an online shoe store and have one page targeting “running shoes” and another targeting “athletic footwear.” If both pages are optimized for the same keywords, search engines won’t know which one to rank. Instead of boosting your chances, this can reduce the visibility of both pages.
To help you avoid this, our content analysis test alerts you whenever you optimize a post for a focus keyword you’ve already used on another page.
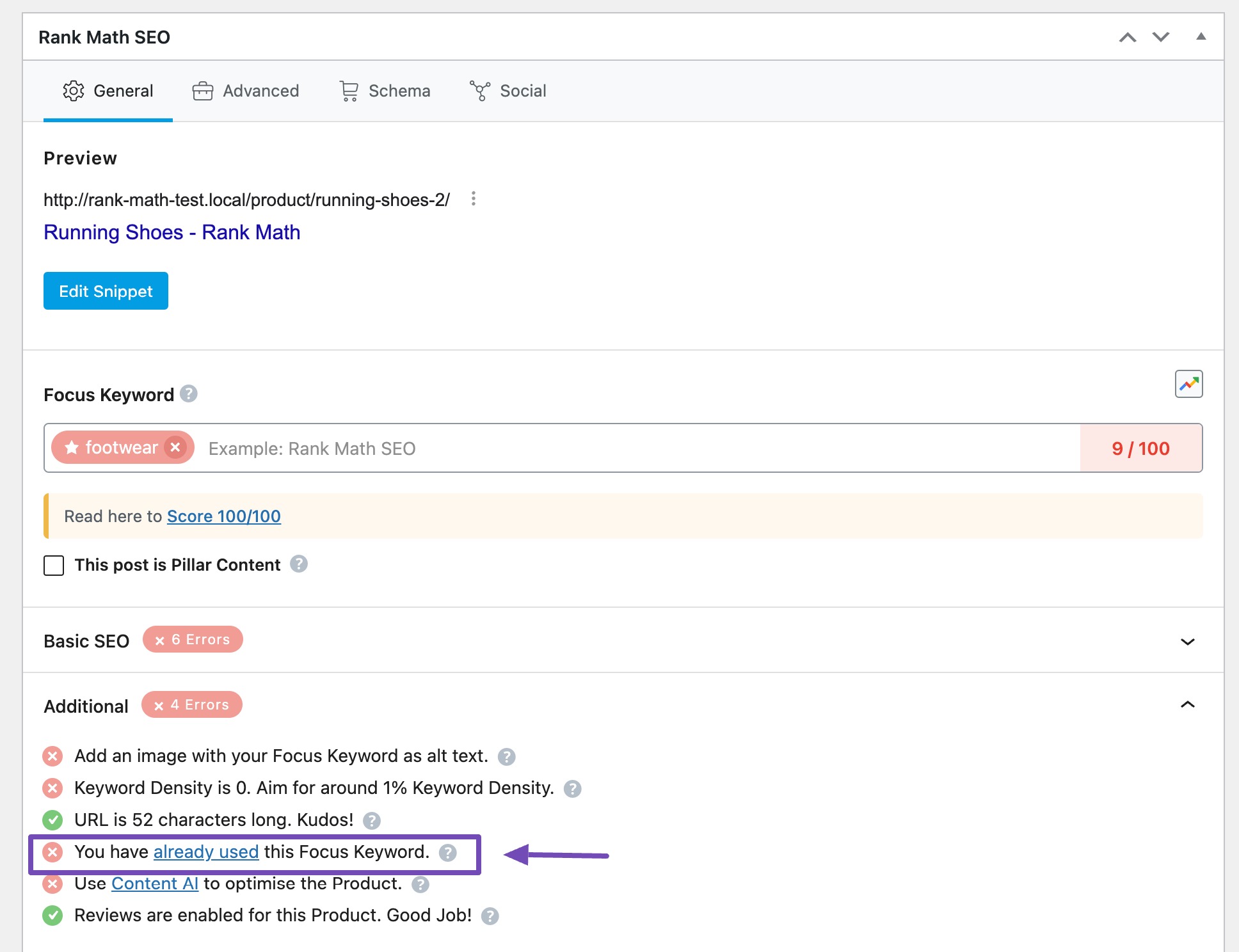
How does it occur within a website?
Keyword cannibalization can occur for a few reasons:
- Overlapping Content: When different pages cover similar topics, search engines struggle to figure out which one is most relevant.
- Multiple Pages Targeting the Same Keyword: If you optimize several pages for the exact same keyword, they end up competing against each other.
- Confusing URL Structures: If your URLs are too similar, search engines may think the content is the same, causing ranking issues.
The best way to fix this is through strategic content management and SEO planning, making sure every page has a clear purpose and targets unique keywords.
2 SEO Impact of Keyword Cannibalization
Let us now discuss the SEO impact of keyword cannibalization.
2.1 Decreased Visibility in Search Engine Results
When multiple pages on your site target the same keyword, search engines get confused about which one to rank. Instead of one strong page showing up at the top, you end up with two or more weaker pages competing against each other.
The result? None of them rank as high as they could. This means your overall visibility drops, and your site is less likely to appear in top positions for the keywords you’re trying to rank for.
2.2 Dilution of Authority and Relevance
Search engines look at a page’s authority and relevance when deciding how to rank it. If you spread your content across multiple pages for the same keyword, you’re splitting that authority instead of consolidating it on one strong page.
John Mueller informs keyword cannibalization will dilute the ranking strength of your pages.
When this happens, your site struggles to establish itself as the go-to source for that topic, which can hurt your overall rankings.
2.3 Lower Click-Through Rate (CTR) & Fluctuating Rankings
Even if two of your pages manage to show up on the SERP, they’re usually in lower positions. Lower rankings often mean fewer clicks and missed traffic opportunities.
When search engines can’t decide which page is most relevant, they may keep switching between them in search results. This leads to unstable rankings and inconsistent traffic.
3 How to Find Keyword Cannibalization Issues
As mentioned before, keyword cannibalization can hurt your rankings in search engines. Hence, it’s important to find the issues as soon as possible.
3.1 Run a site: search
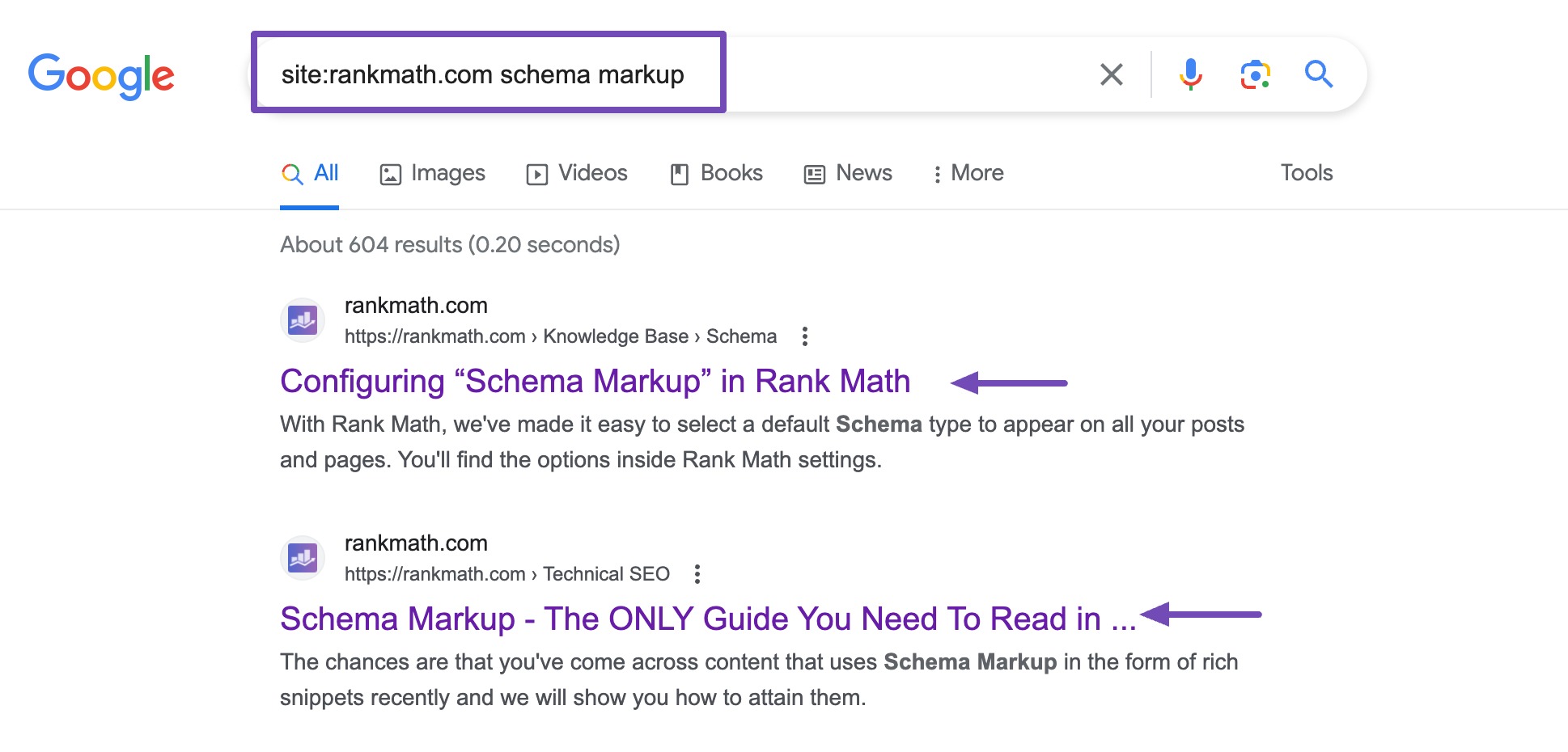
One of the easiest ways to check for keyword cannibalization is by using Google’s site: search operator.
Navigate to Google and search for site:yourwebsite.com "topic". Replace yourwebsite.com with your domain and "your topic" with the keyword you want to check. This will show you all the pages on your site that Google thinks are related to that keyword.
For instance, at Rank Math SEO, we have a detailed blog post on Schema markup and a knowledge base article on the same topic. Even though they both target similar keywords, they serve different purposes—one is for in-depth learning, and the other is a quick help guide.
Because they target different search intents, Google knows which one to show for which query, so there’s no negative impact on rankings.
3.2 Use Rank Math SEO Analytics
Another way to check for keyword cannibalization is by using Rank Math’s SEO Analytics feature. It comes with an integrated Rank Tracker that gives you accurate reporting on how your pages are ranking.
To do so, navigate to Rank Math SEO → Analytics → Rank Tracker from your WordPress dashboard, as shown below.
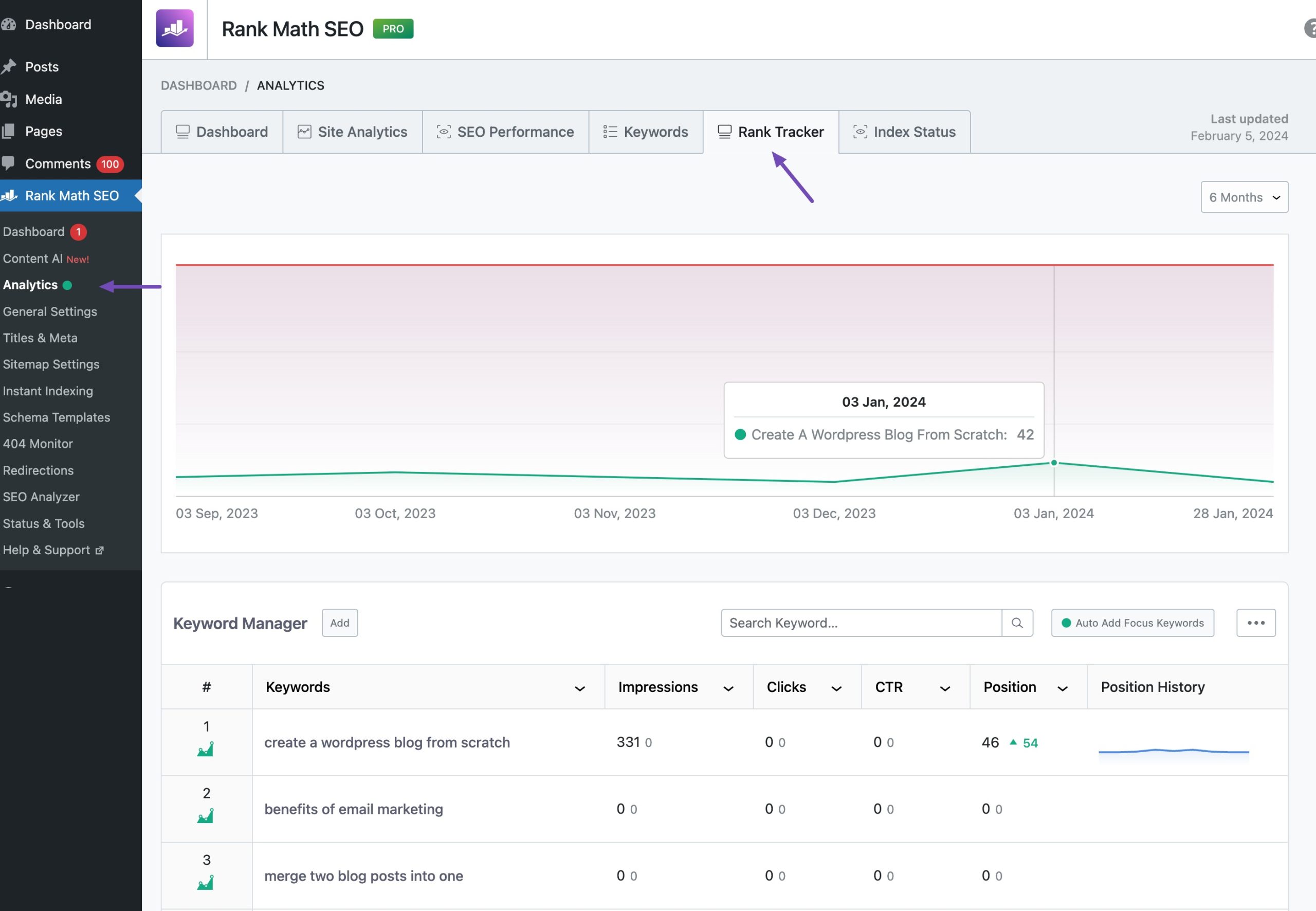
Here, you’ll get a comprehensive view of the keywords for which your content is ranking. Let’s say you check the keyword SEO tools. If the report shows that only one of your blog posts is ranking for that keyword, then there’s no keyword cannibalization issue. But if multiple pages show up for the same keyword, that’s a sign you need to take action.
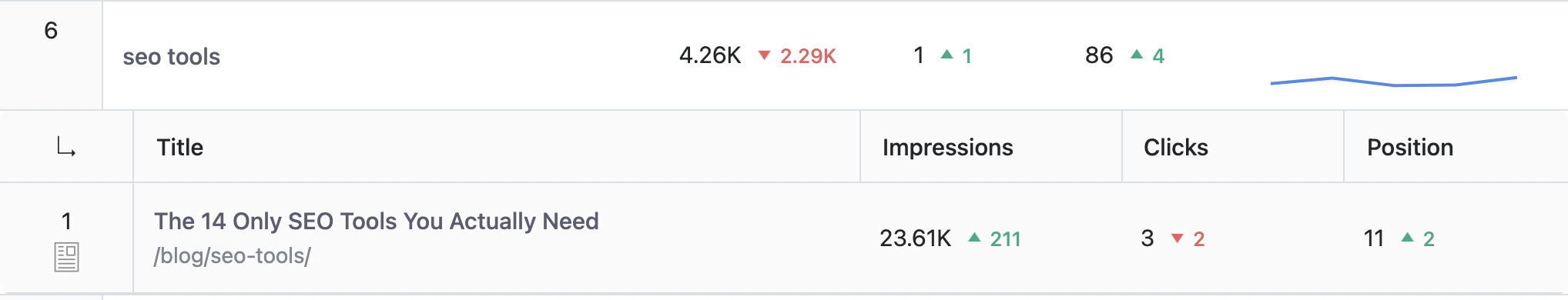
This method makes it super easy to see which pages are ranking for which keywords, without the guesswork.
Learn more about Rank Math Analytics here.
3.3 Use Google Search Console
Another simple way to find keyword cannibalization is through Google Search Console (GSC). It’s free and shows you which pages are ranking for the same keywords.
Here’s how you do it:
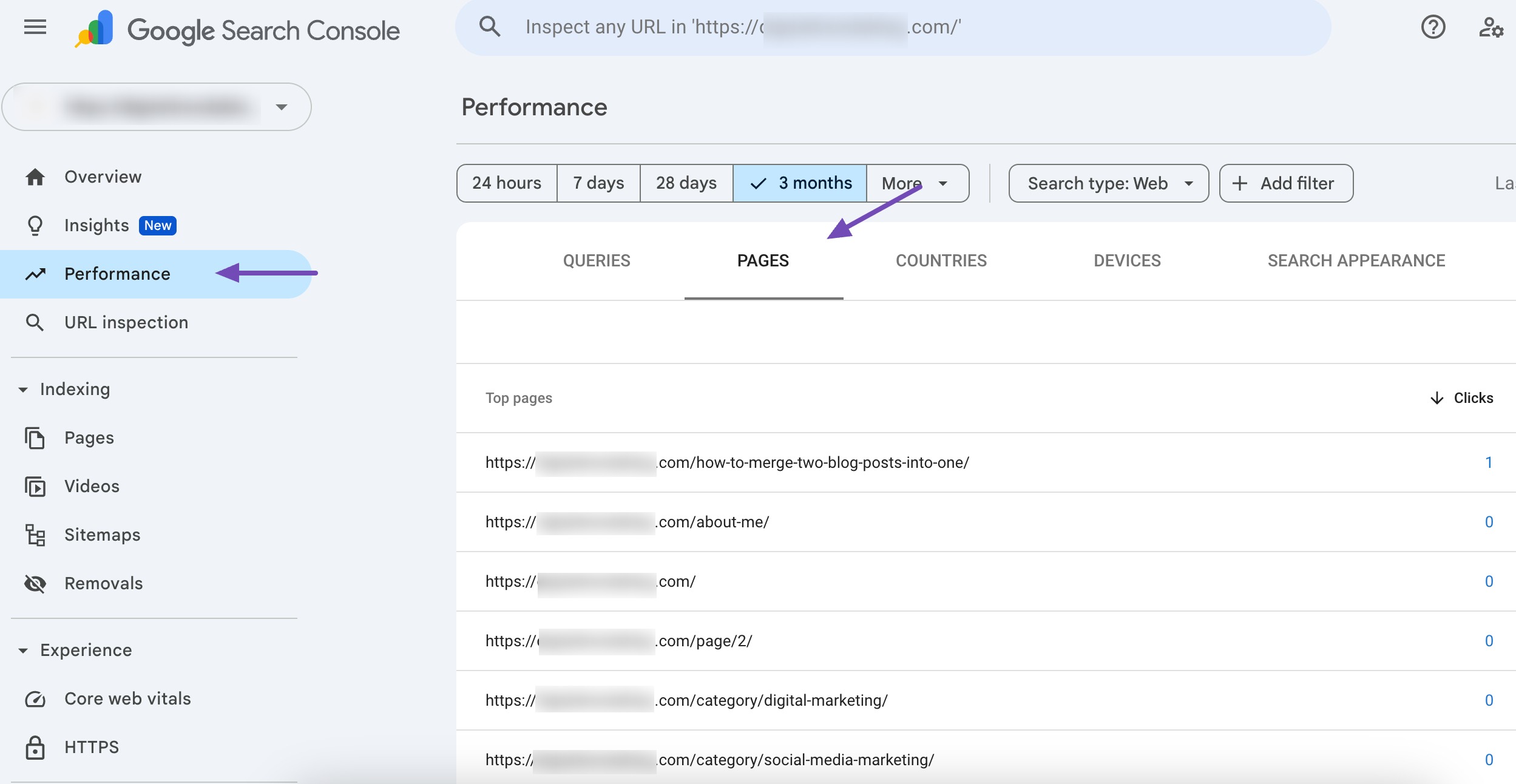
Log in to Google Search Console and select your property. Navigate to the Performance section.
Scroll down to PAGES to see which URLs are competing for the same keyword.
4 How to Fix Keyword Cannibalization Issues
Now that you know how to spot keyword cannibalization, let’s go over the best ways to fix it.
4.1 Use Redirects
One of the most effective ways to resolve cannibalization is by setting up 301 redirects from the less important pages to the main page you want to rank.
A 301 redirect tells search engines that the page has permanently moved and passes most of the SEO value (or link equity) to the preferred page.
Example:
If you have these URLs:
www.example.com/blog/seo-tipswww.example.com/articles/seo-strategies
You can redirect both to:
www.example.com/blog/ultimate-seo-guide
This way, instead of splitting ranking signals between multiple pages, you consolidate everything into one strong page.

After setting up the redirects, monitor the performance of your main page to make sure rankings and traffic improve.
Learn how to set up redirections in Rank Math to create redirections easily.
4.2 Use Canonical Tags
If you have multiple pages that are very similar or nearly identical, using canonical tags is a great solution.
A canonical tag tells search engines which page is the primary version you want to rank. You simply add it to the <head> section of the duplicate or similar pages, pointing to your preferred page.
For instance:<link rel="canonical" href="https://www.example.com/preferred-page" />
You can easily set a canonical URL in Rank Math. To do so, navigate to the Advanced tab of Rank Math in your post/page editor. If you’re unable to find the Advanced tab, please enable the advanced mode from WordPress Dashboard → Rank Math SEO → Dashboard.
Under the Advanced tab, you can change the Canonical URL field to point to the primary version of your content.
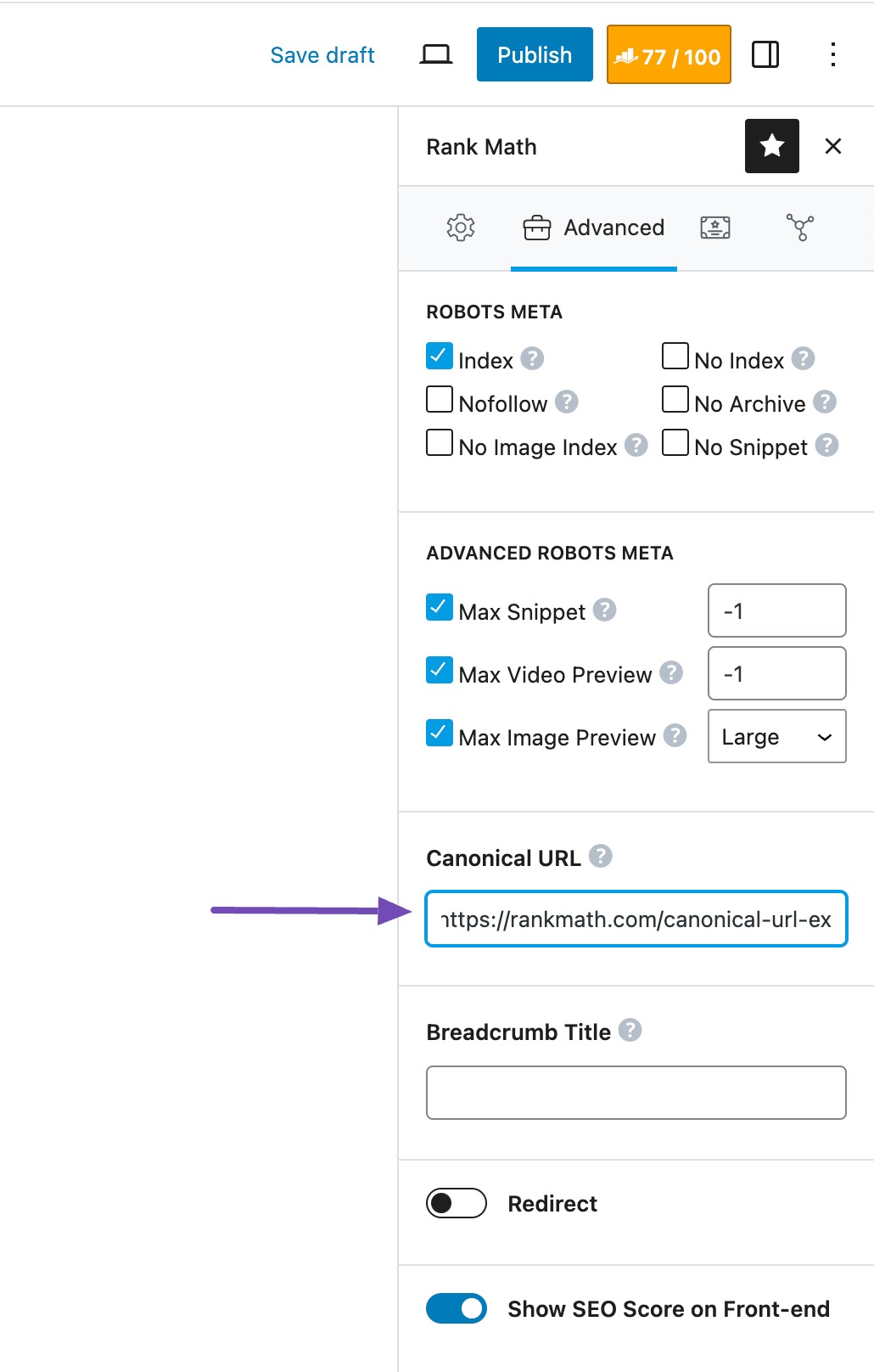
This signals to Google that the page you specified is the main version, so it consolidates your ranking power instead of splitting it across multiple URLs.
Refer to our dedicated tutorial to learn more about canonical URLs in detail.
4.3 Optimize Anchor Text
Your internal links play a big role in how search engines understand your site. If you use the same anchor text for different pages, Google might assume those pages are about the exact same topic, which can lead to keyword cannibalization.
To fix this, make sure your anchor text is specific and contextually relevant to the page you’re linking to. Instead of using the same keyword over and over, vary the wording to match the page’s unique focus.
For instance:
- If you have two pages, one about SEO tips and another about SEO strategies, don’t use SEO tips as the anchor text for both.
- For the SEO tips page, link with practical SEO tips for beginners.
- For the SEO strategies page, use advanced SEO strategies to boost rankings.
This helps Google understand the difference between your pages and reduces the risk of them competing for the same keyword.
4.4 Content Differentiation
If you have multiple pages targeting similar keywords, you need to make each page unique. This is called content differentiation. Instead of writing two articles that cover the exact same topic in the same way, give each page a distinct focus so Google understands they serve different purposes.
Example:
Let’s say you run a digital marketing blog and have two articles:
- Article 1: SEO Tips for Beginners
- Article 2: Advanced SEO Strategies for Experienced Marketers
If both articles just list generic SEO tips, they’ll compete with each other. Instead, differentiate them like this:
- In Article 1, focus on easy, beginner-friendly tips like keyword research basics and meta tag optimization.
- In Article 2, cover complex strategies like schema markup, advanced link building, and technical SEO.
By making each article unique and targeting a different audience segment, you reduce keyword cannibalization and improve your chances of ranking both pages.
4.5 Target Different Search Intent
Another way to prevent keyword cannibalization is to make sure each page on your site targets a different search intent. Even if two pages use similar keywords, they can rank for different queries if their purpose is different.
Example:
Let’s say you want to rank for the keyword SEO tools. You can create two pages:
- Page 1 (Informational Intent): What Are SEO Tools and Why Are They Important? – This page explains what SEO tools are, their benefits, and how they work.
- Page 2 (Transactional/Commercial Intent): 10 Best SEO Tools to Boost Your Rankings [Comparison Guide] – This page reviews and compares tools, helping users decide which one to buy.
Both pages include the keyword SEO tools, but one targets people learning about SEO tools, while the other targets people ready to choose or buy a tool. By focusing on different intents, you avoid cannibalization and serve users at different stages of their journey.
Rank Math’s Search Intent feature helps you understand what your audience is looking for based on the keyword. In your post/page editor, navigate to the Focus Keyword field in the General tab of the Rank Math meta box.
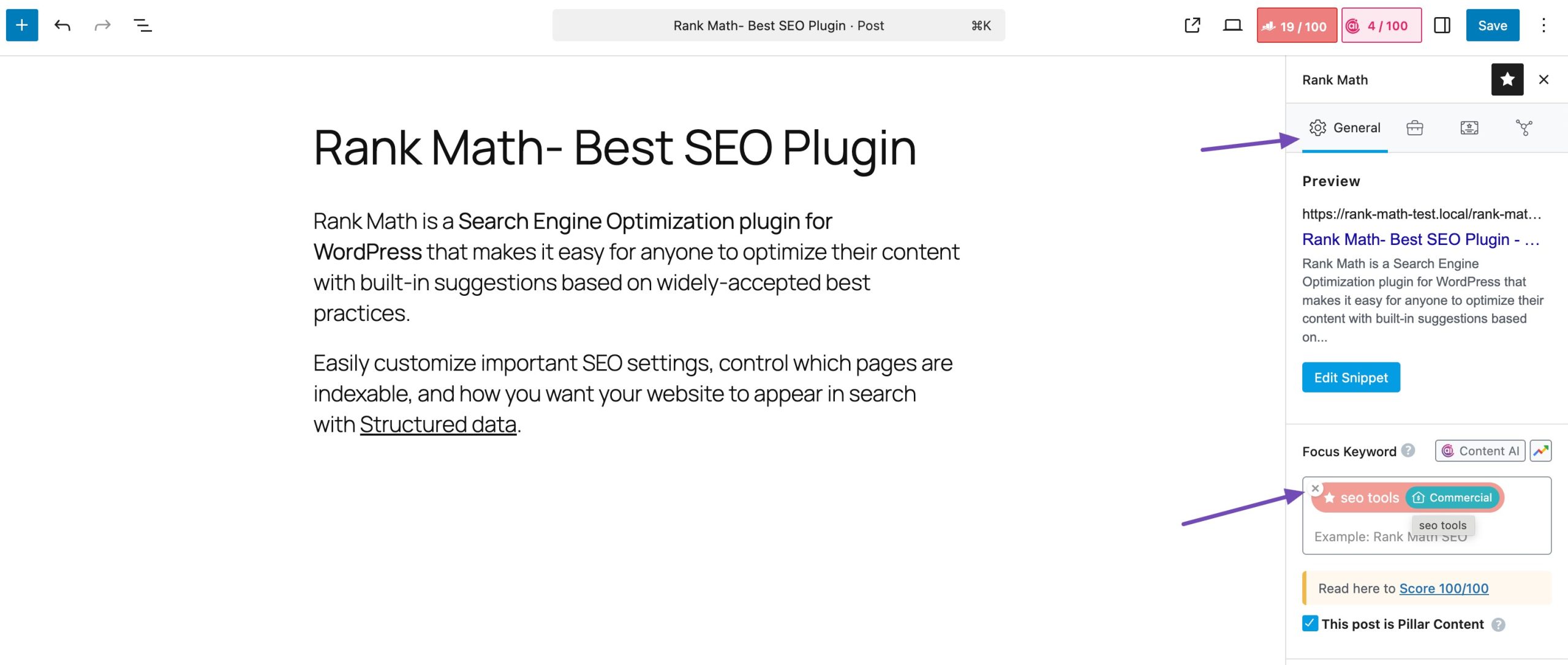
Enter a keyword, and you’ll notice an icon next to it. Hover over this icon and click on the Show Intent label. Rank Math will analyze and display the detected search intent next to the keyword field, helping you quickly determine whether your content aligns with what users are looking for.
4.6 Perform Content Audits
A content audit is an ongoing process that helps keep your SEO strategy healthy and effective. It’s not a one-time task—you should revisit your content regularly to make sure it’s still performing well and aligned with your goals.
When you conduct a content audit, ask yourself these questions:
- Is this topic still relevant to my audience?
- Is the information up to date and accurate?
- Am I targeting the right keywords for this page?
- Which topics and keywords best align with my current marketing goals?
Answering these questions will help you decide whether to update, consolidate, or remove content that no longer serves a purpose.
5 Frequently Asked Questions
How does keyword cannibalization impact SEO?
It can lead to decreased visibility, confused search engine algorithms, and a dilution of authority and relevance, negatively impacting SEO performance.
Is keyword cannibalization more common on larger websites?
Keyword cannibalization can occur on websites of any size, but larger websites with extensive content are more susceptible.
How do I measure the success of my efforts in resolving keyword cannibalization?
Monitor rankings, organic traffic, user engagement, and conversion rates for affected pages to measure the success of your keyword cannibalization strategies.
Should I consolidate all similar content into a single page?
It depends on the specific case. Consolidation is beneficial when it aligns with user intent and serves a more comprehensive purpose.
6 Conclusion
Keyword cannibalization can quietly hurt your SEO if you don’t keep it in check. The good news is that now you know exactly what it is, how to find it, and the best ways to fix it.
Take some time to audit your site, identify competing pages, and decide whether to merge, redirect, or optimize them. By making these adjustments, you’ll strengthen your rankings and make it easier for search engines and your audience to find the right content.
Start with a simple check today, and you’ll see the difference in your SEO performance.
If you like this post, let us know by Tweeting @rankmathseo.
