Have you ever considered how search engines like Google find the perfect answers to your questions within seconds?
Behind the scenes of every search query lies a complex process known as search engine indexing, a fundamental mechanism that enables search engines to organize, analyze, and retrieve relevant content from the web.
If you’re looking to optimize your online presence, understanding search engine indexing is important.
In this post, we’ll provide you with a comprehensive understanding of search engine indexing.
So, without any further ado, let’s explore search engine indexing in detail.

Table Of Contents
1 What is Search Engine Indexing?
Search engine indexing is like creating a massive catalog or index of all the content available on the internet.
It involves systematically scanning, analyzing, and organizing web pages, documents, images, videos, and all other types of content so that search engines can quickly retrieve relevant information in response to audience queries.
The process of search engine indexing involves the following stages:
- Crawling: Search engine crawlers, also known as spiders or bots, systematically navigate the web, visiting web pages and following links to discover new content.
- Indexing: In this stage, the search engine processes and analyzes the text content along with important tags and attributes—such as
<title>tags andaltattributes for images and videos. The extracted data is then organized and stored in a structured index database. This indexing enables the search engine to quickly retrieve and deliver relevant results when users perform a search. - Ranking: Finally, search engines use complex algorithms to rank indexed pages based on relevance, authority, and user engagement, ensuring that the most relevant and useful content appears at the top of search results.
Before we discuss how search engine indexing works, let us understand the importance of indexing for search engines.
2 Importance of Search Engine Indexing
Indexing is important for search engines because it allows them to process and retrieve information efficiently from the internet.
Without indexing, search engines will struggle to deliver accurate and timely results to the audience.
By organizing and categorizing web content, indexing helps search engines deliver a better user experience by presenting the audience with relevant and useful information in response to their queries.
It also helps search engines handle complex search queries from a variety of sources, formats, and languages.
3 How Does Search Engine Indexing Work
As we’ve discussed briefly, search engines include crawling, indexing, and ranking to index a site. Let us now discuss them in detail.
3.1 Crawling
Crawling, in the context of search engines, refers to the process of systematically browsing the web to discover and retrieve web pages and other online content.
Role of Web Crawlers
Web crawlers, also known as spiders or bots (Googlebots), play an important role in the crawling process. They act as automated agents that traverse the internet, visiting web pages and collecting data to be indexed by search engines.
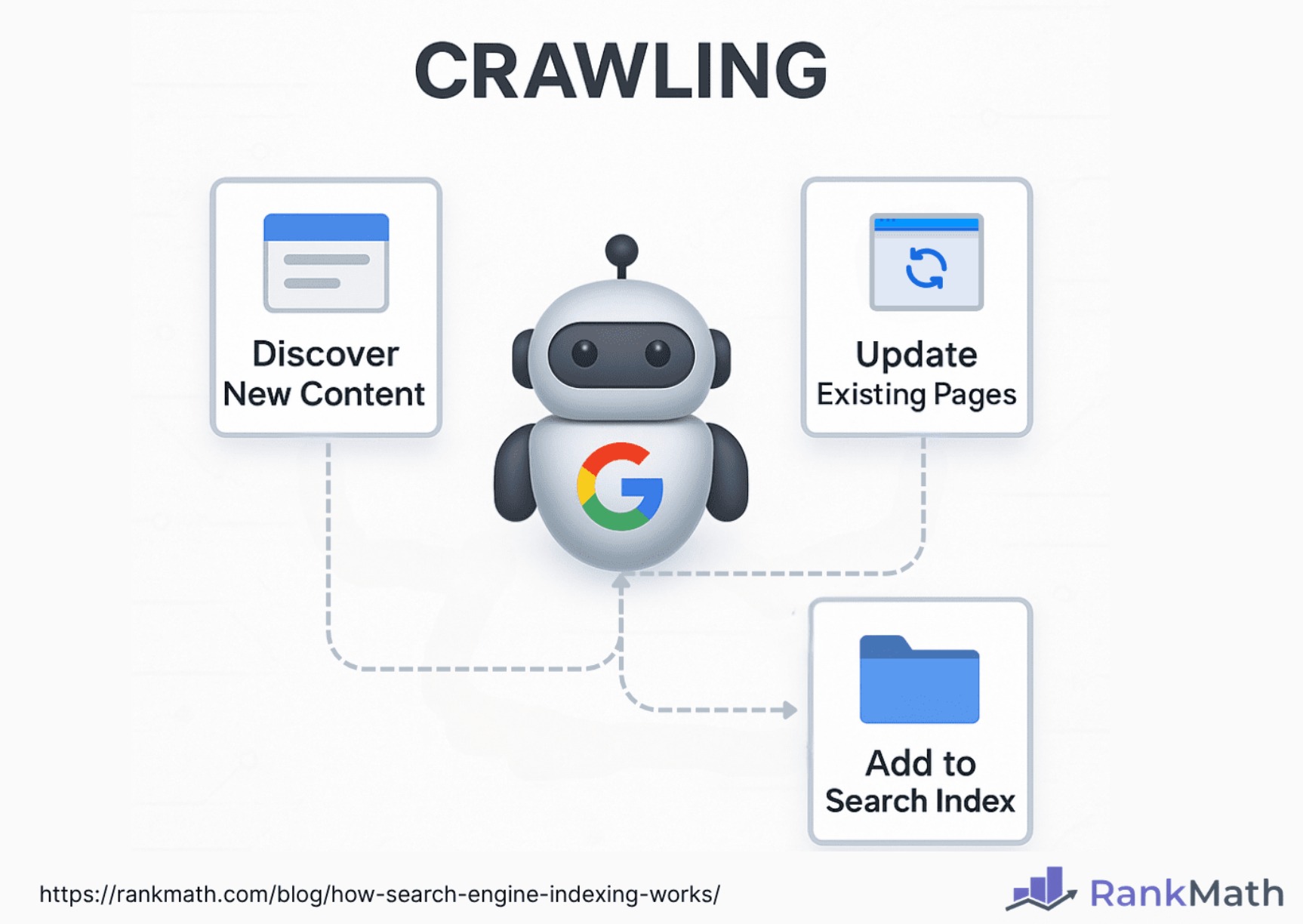
Web crawlers are responsible for discovering new content, updating existing information, and ensuring that search engine indexes are comprehensive and up to date.
Techniques Used by Web Crawlers to Navigate and Gather Data From Websites
Web crawlers use several techniques to navigate and gather data from websites:
Link Traversal (Following Links)
Think of web crawlers like people browsing the internet. They land on one page and then click links to go to other pages—just like you would.
For instance, A crawler visits your homepage. It sees a link to your blog and follows it. Then it finds links to individual blog posts and follows those too. This process helps crawlers discover more content on your site, just by following links from one page to the next.
URL Normalization (Cleaning Up Website Addresses)
Sometimes the same page can appear under slightly different web addresses (URLs). Crawlers use URL normalization to figure out which version is the main one, so they don’t waste time crawling duplicates.
- For instance:
https://example.com/pagehttps://example.com/page/https://example.com/PAGE
These all look similar but are treated as different by default. Normalization helps crawlers understand they’re really the same page.
This prevents your site’s content from being mistakenly identified as duplicate, which can harm your SEO.
Reading the Robots.txt File (Respecting Website Rules)
Before crawling a site, crawlers check for a special file called robots.txt. This file tells them what they’re allowed to look at—and what to skip.
This is helpful for protecting sensitive or unimportant areas of your site from being crawled.
HTML Parsing (Understanding the Page Content)
Once on a page, the crawler examines the HTML code, which is the underlying structure of the page, to understand its content.
- It pulls out things like:
- The page title
- Headings and paragraphs
- Images and links
- Metadata (e.g., page descriptions)
For instance, if your blog post has an <h1> headline like <h1>10 Tips for Better SEO</h1>, the crawler sees that and notes it as the main topic of your post.
This helps search engines figure out what your page is about so they can show it to the right people in search results.
How Web Crawlers Discover New Content
When the web crawlers visit a site, the first thing they look for is the robots.txt file.
Checking robots.txt file
This file instructs search engines which pages they are permitted to access and which ones to exclude.
For instance, if you go to rankmath.com/robots.txt you’ll see the site’s crawling instructions. You can do the same for most websites—just add /robots.txt to the URL. Almost every website has this file to help guide web crawlers.
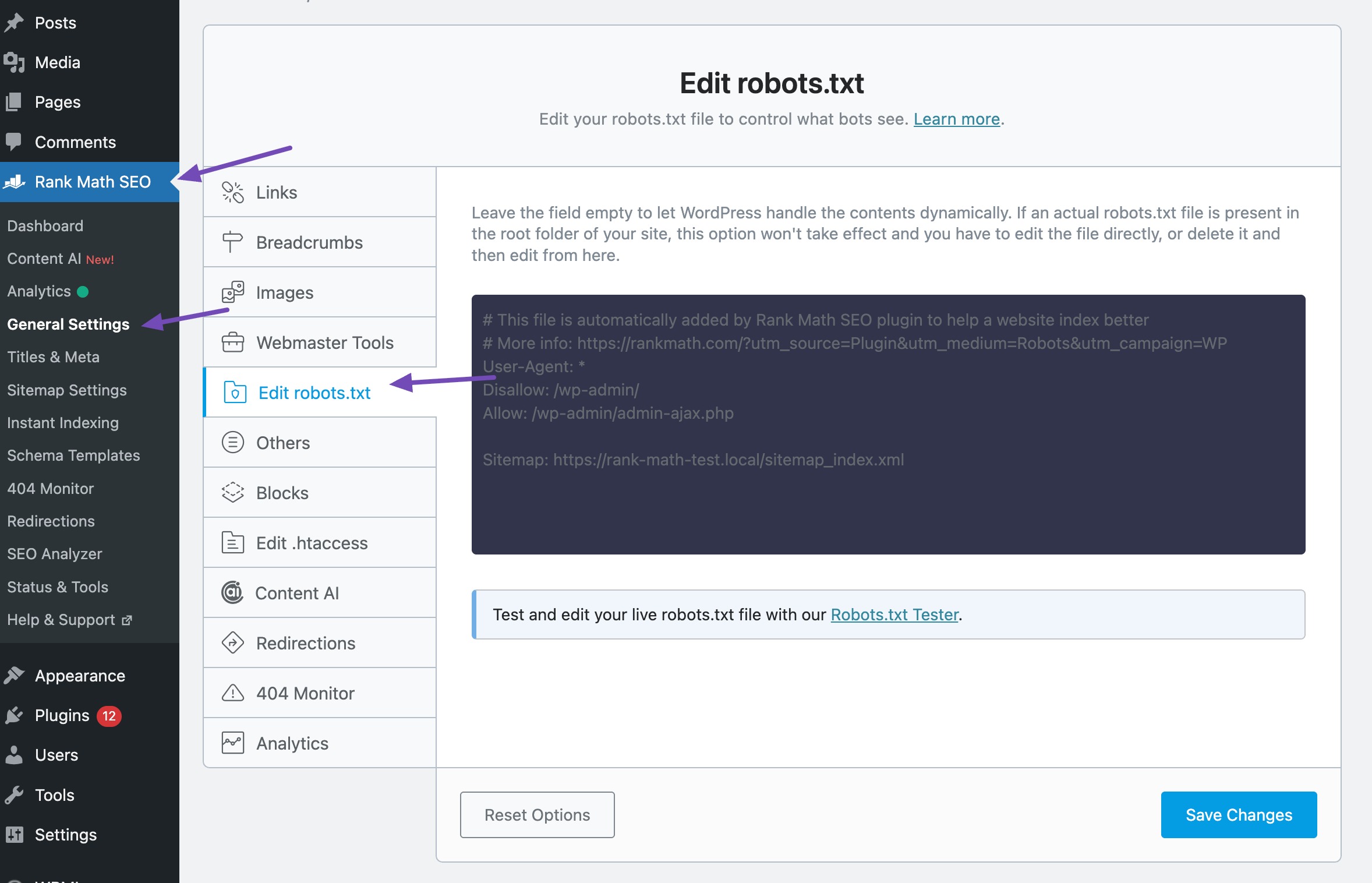
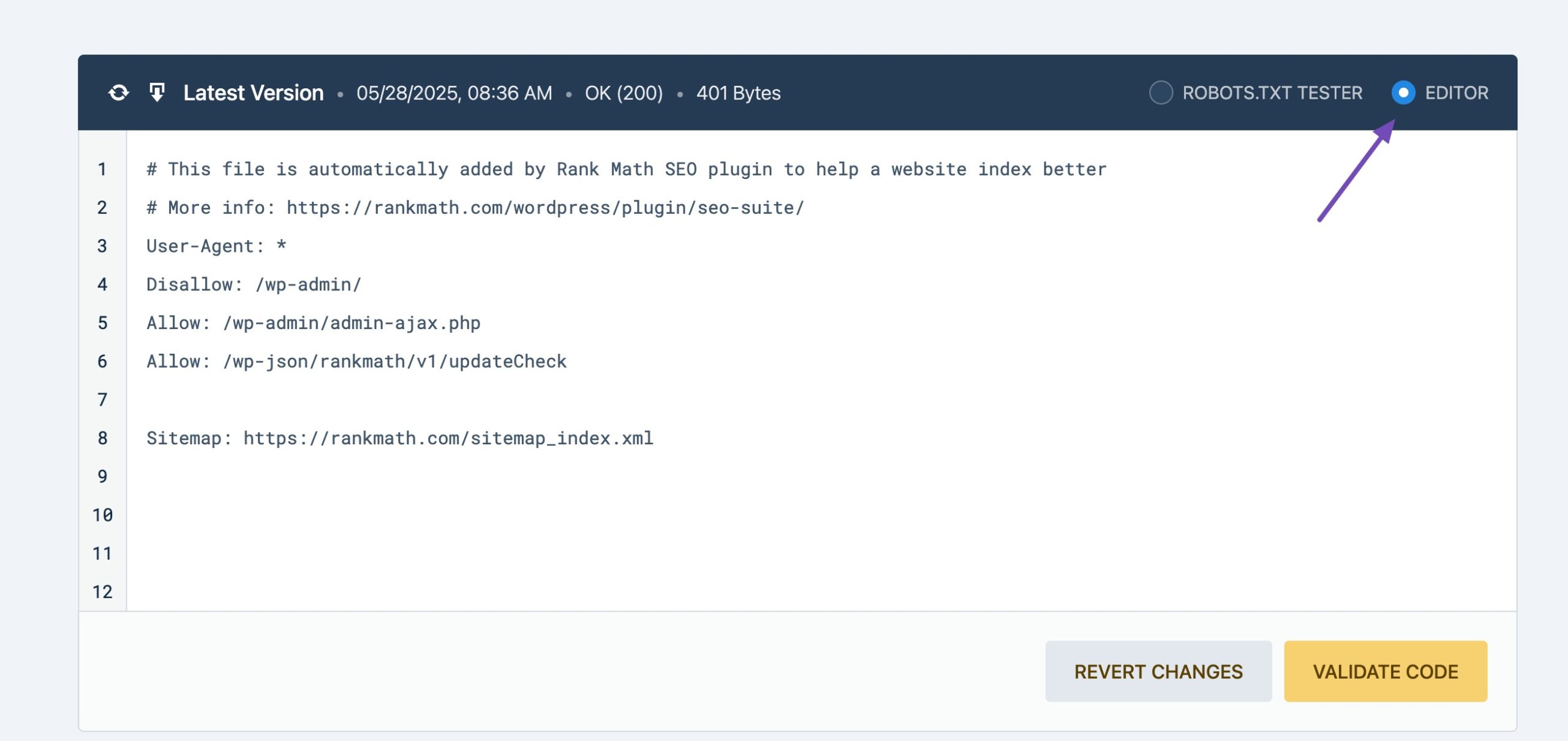
If your site doesn’t have a robots.txt file, Rank Math makes it easy to create and edit one.
To do so, navigate to General Settings in Rank Math. Click Edit robots.txt. Add rules to allow or disallow crawling of specific parts of your site.
Validating Your Robots.txt File
You can also test your file for any errors using our Robots.txt Tester and Validator. Just paste your domain URL, select a crawler, and click TEST. If there’s an issue, it will highlight the error.
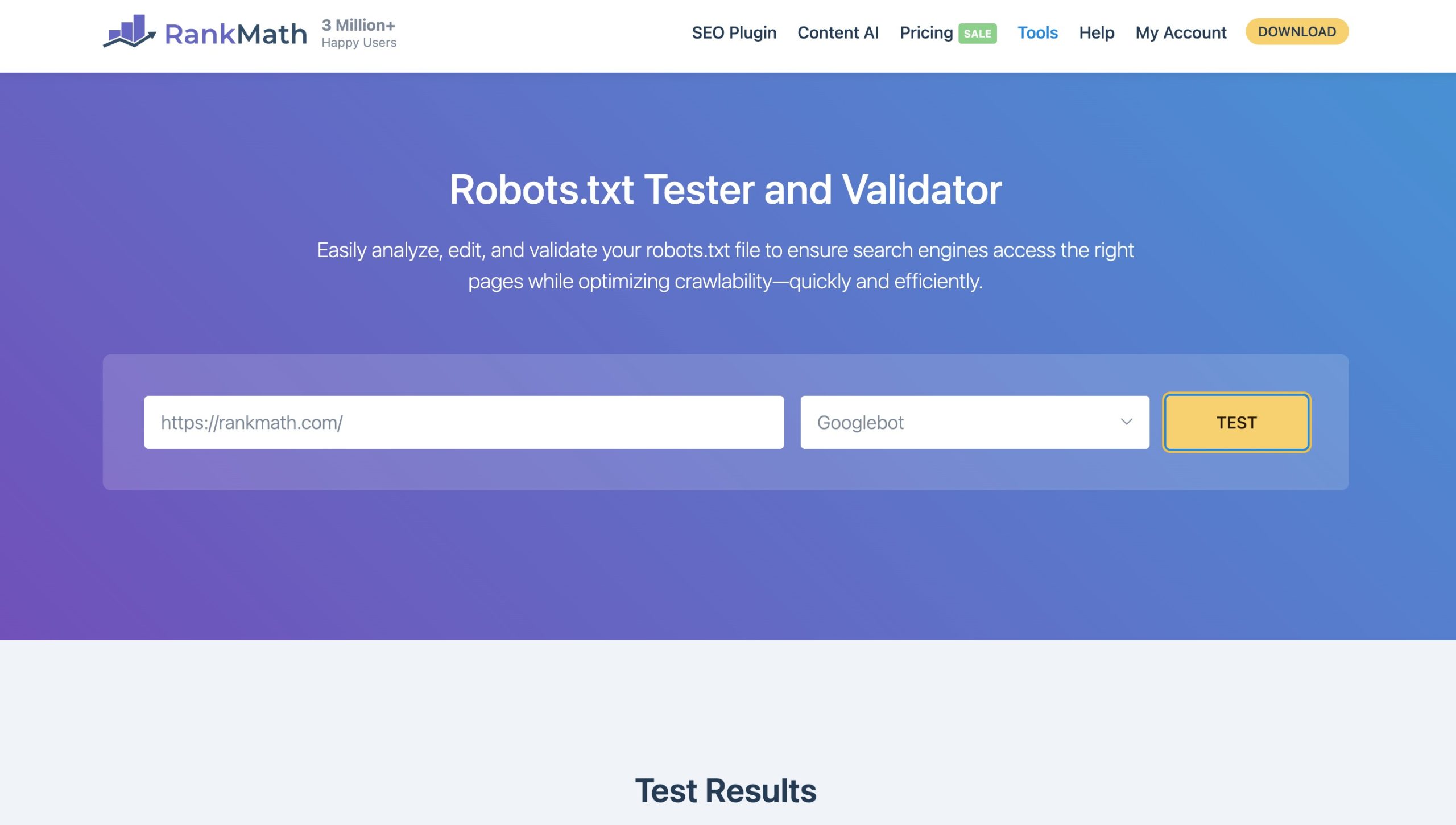
You can even switch to EDITOR mode to quickly make changes. However, note that this tool is only for validation purposes. Any changes you make here won’t update your actual robots.txt file—you’ll need to copy and paste the updated content into your live file.
Once a search engine lands on your site, it won’t stop at just one page. As it crawls, it follows internal links to discover more pages. This process continues until it crawls all available links to follow.
Pages with no internal or external links pointing to them are called orphan pages—and search engines often ignore them.
Submitting an XML Sitemap
To ensure all your pages (even orphan ones) get noticed, you should submit an XML sitemap to search engines.
As a Rank Math user:
- Enable the Sitemap module.
- Navigate to Sitemap Settings to find your sitemap index URL.
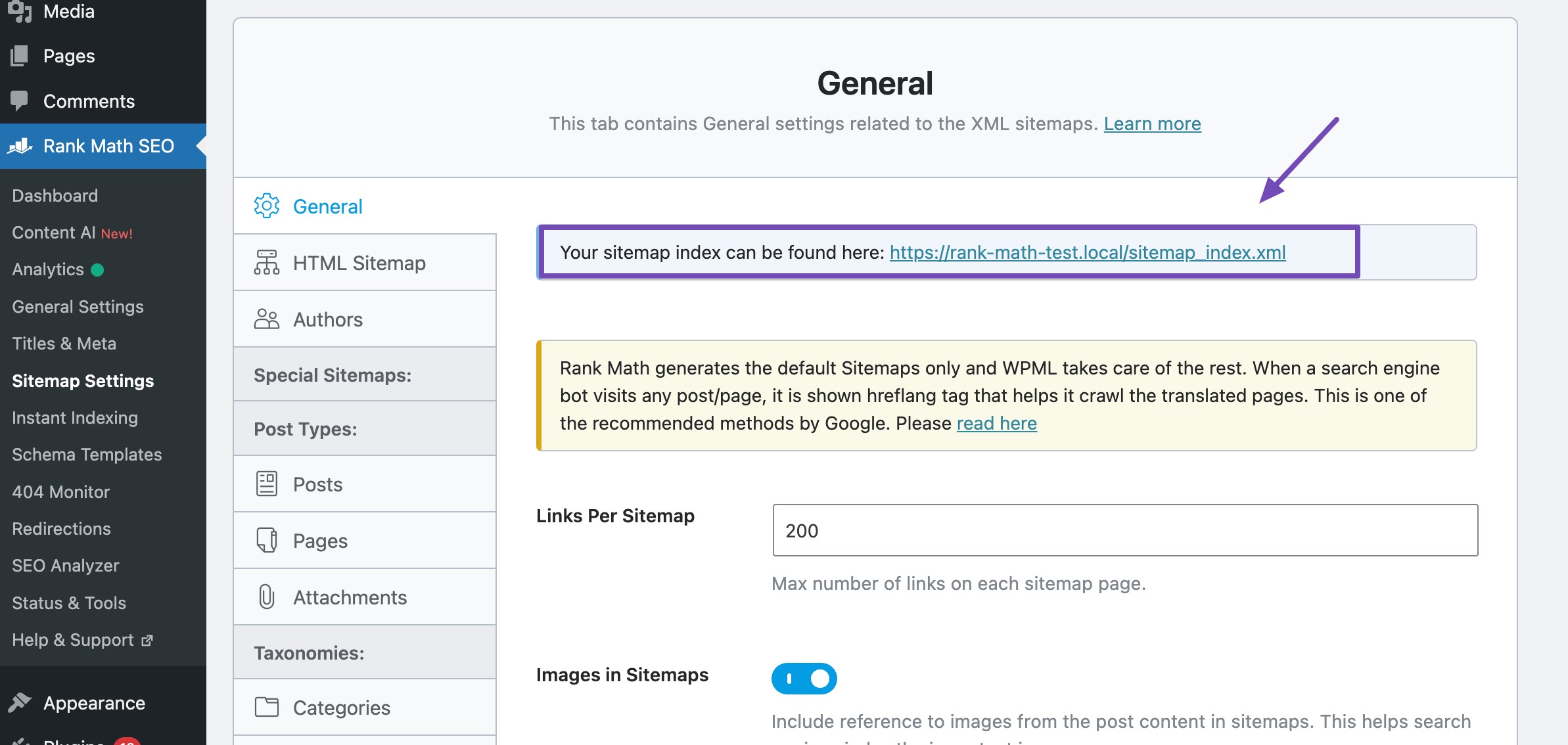
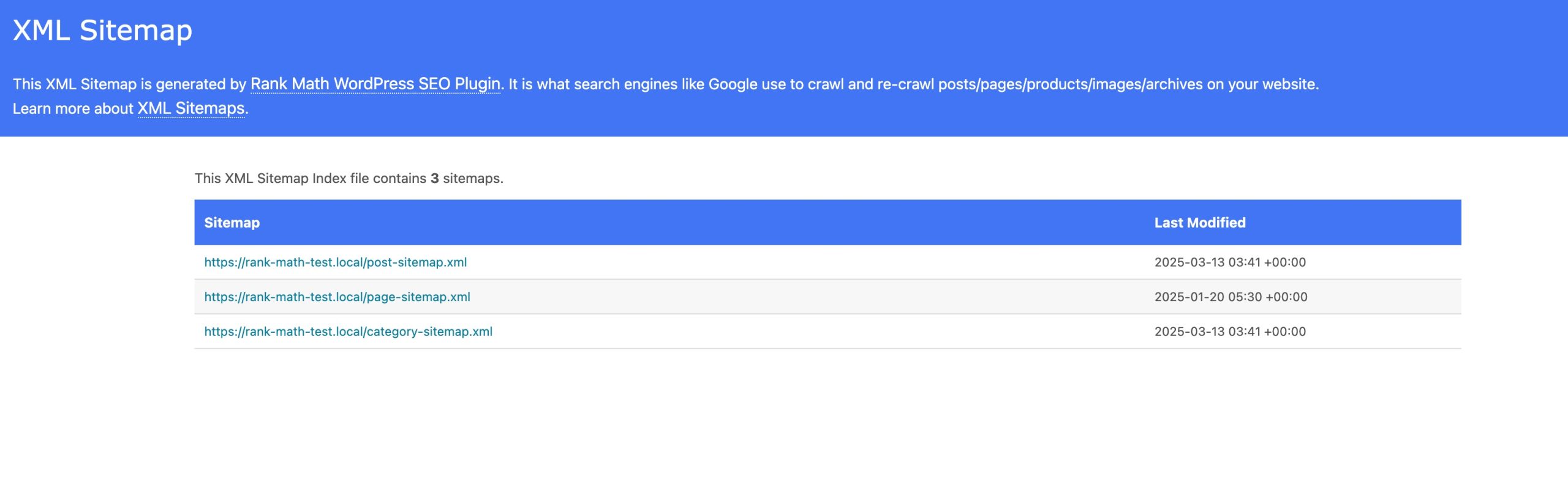
This index consolidates all your sitemaps in one place—a best practice for SEO.
If you’ve connected your site to Google Search Console through Rank Math’s Analytics tab, your sitemap will be submitted to Google automatically.
For other search engines:
- Bing: Use Bing Webmaster Tools. You can sign in with your Google account and import your sites from Google Search Console.
- Yandex and Naver: Each has its own webmaster tools for submitting sitemaps.
To get your pages crawled and indexed faster, enable Rank Math’s Instant Indexing module.
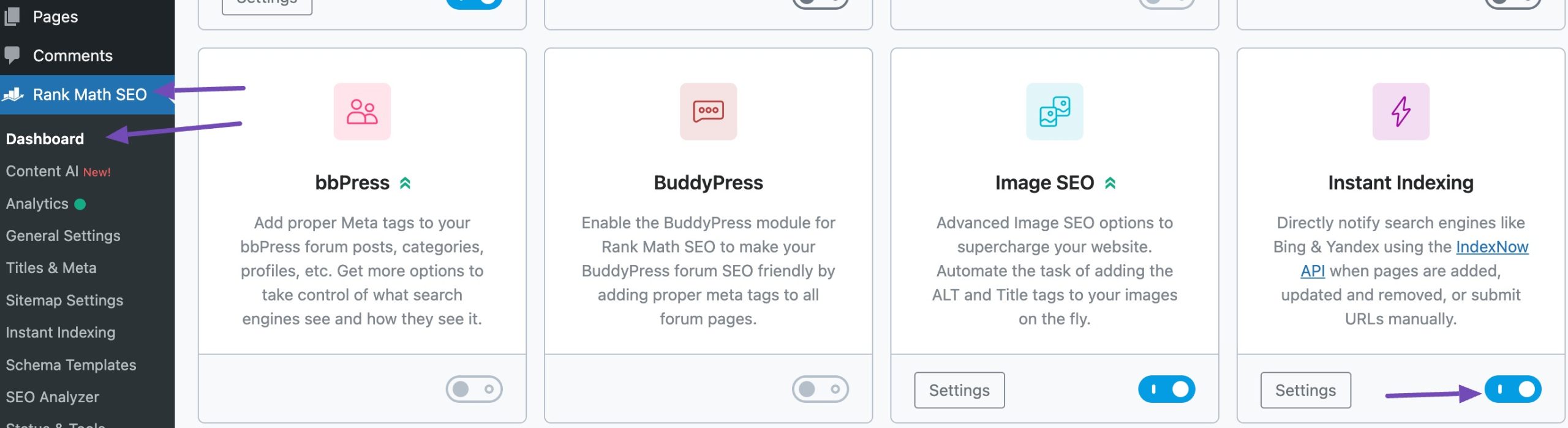
Once enabled, search engines like Bing and Yandex will be automatically notified whenever a page is created, updated, or deleted—no extra steps required. If you haven’t activated this module yet, now’s the time.
You can learn more about Sitemaps in our dedicated article, and fix the sitemap issues if you have any.
- Crawling is how search engines explore the web to discover and collect pages.
- Web crawlers (like Googlebot) move from one page to another by following links.
- They read a site’s robots.txt file first to know what pages to skip.
- URL normalization helps avoid crawling the same content multiple times under different URLs.
- HTML parsing allows crawlers to understand the structure and content of a page.
- Submitting an XML sitemap helps search engines find all your pages, including hidden or orphaned ones.
- Rank Math makes it easier to manage crawling instructions, generate sitemaps, and speed up indexing.
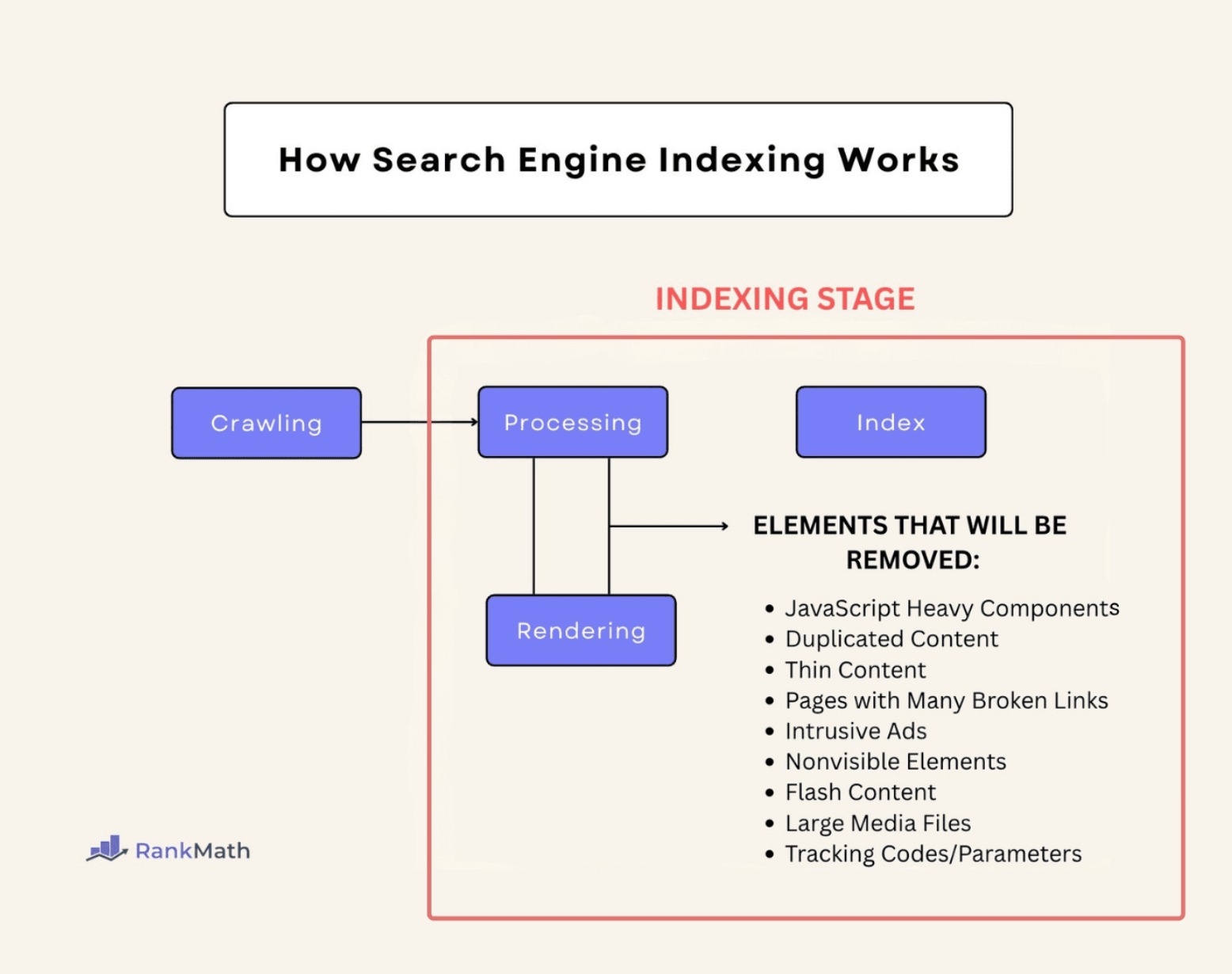
3.2 Indexing
Once search engine bots (also known as crawlers) have successfully navigated your site, they return the collected data to Google for further processing. But before your content is added to the search engine index, it goes through an important phase known as processing—a key part of the indexing stage.
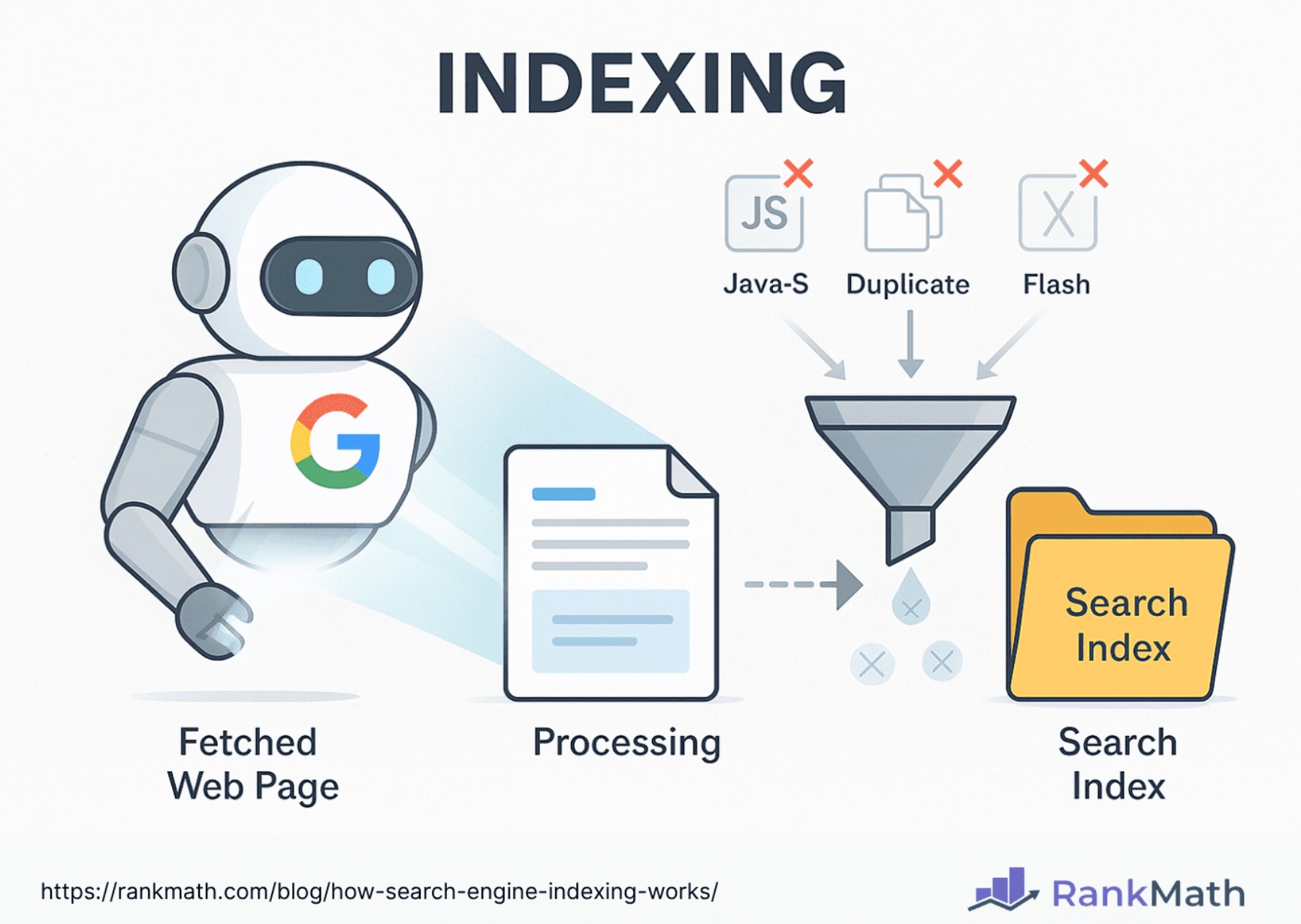
During this stage, search engines analyze your content and remove elements that don’t contribute to search relevance. These can include:
- Heavy JavaScript elements
- Duplicate or thin content
- Pages with many broken internal or external links
- Excessive or intrusive ads
- Invisible elements or Flash content
- Large media files without proper optimization
- Unnecessary tracking codes and URL parameters
This filtering helps search engines conserve resources and focus only on content that improves search results.
If your website has thousands of pages, search engines may not crawl and process everything due to a crawl budget—a limit to how many pages bots can crawl. If your pages are bloated with non-essential elements, even important content may get skipped during processing.
To ensure your pages get processed and indexed properly, it’s essential to optimize for speed and user experience.
Identifying Pages Disregarded During Processing
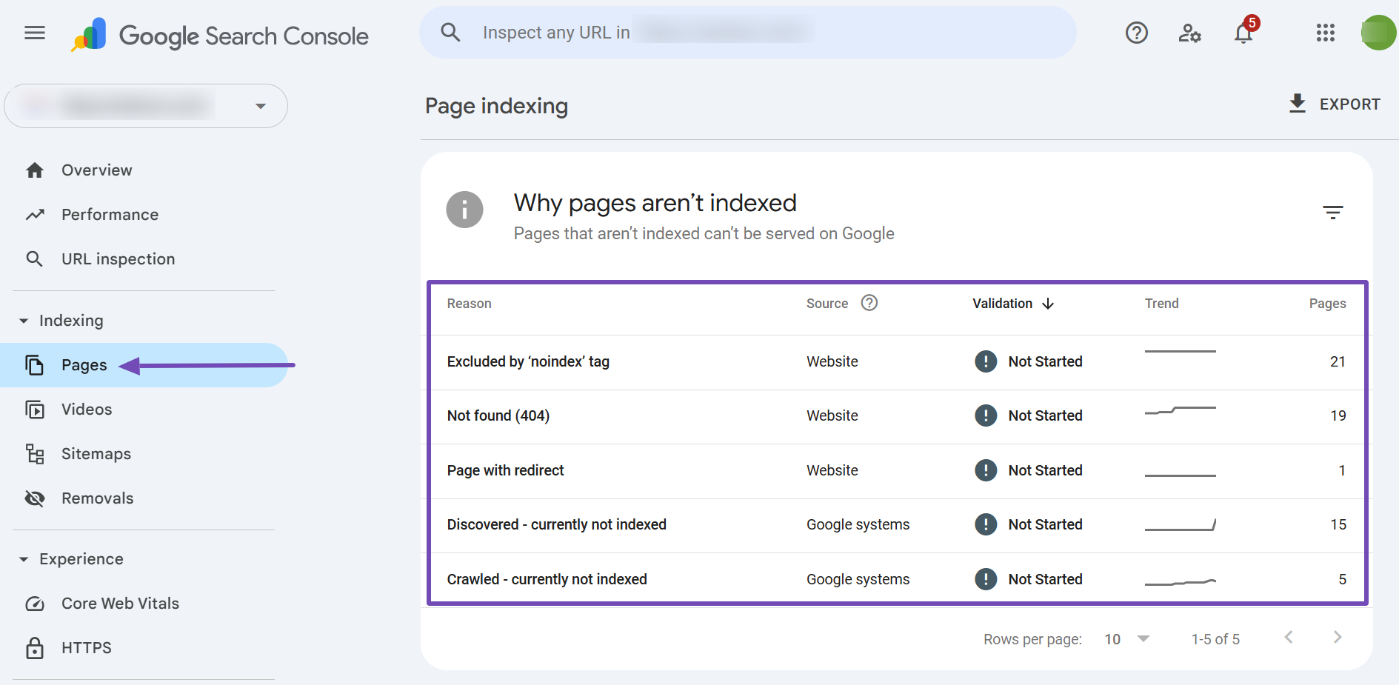
You can identify pages that were excluded during processing using Google Search Console. To do so, navigate to Indexing → Pages and review the listed issues to see how many pages are affected. Click on a specific issue to view all the impacted pages.
If you’re a Rank Math PRO user, you can get even more detailed insights. Navigate to Analytics module → Index Status tab. The Index Status tab prioritizes fetching high-traffic pages before other pages.
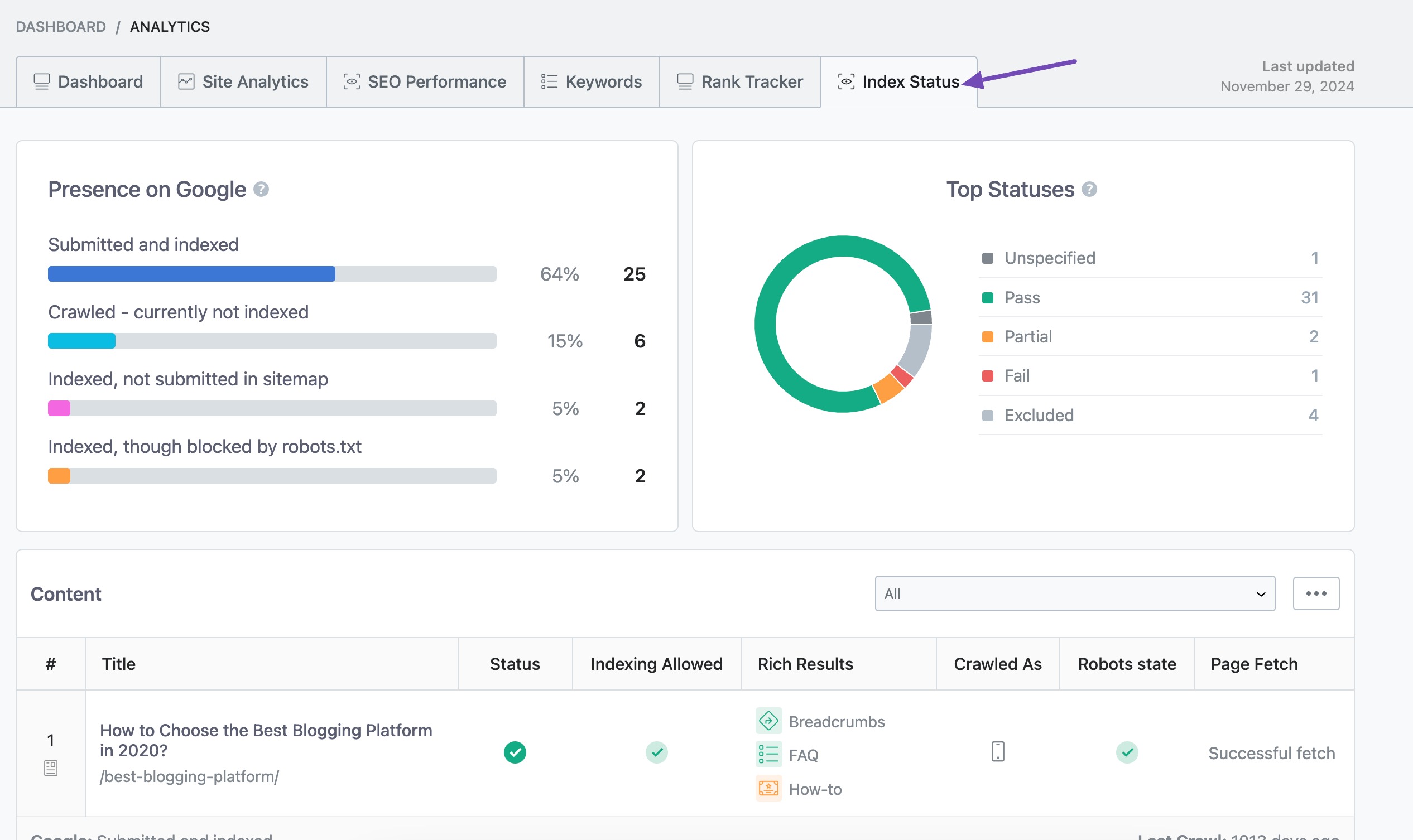
View and sort through the issues. Click on a page to see detailed indexing information.
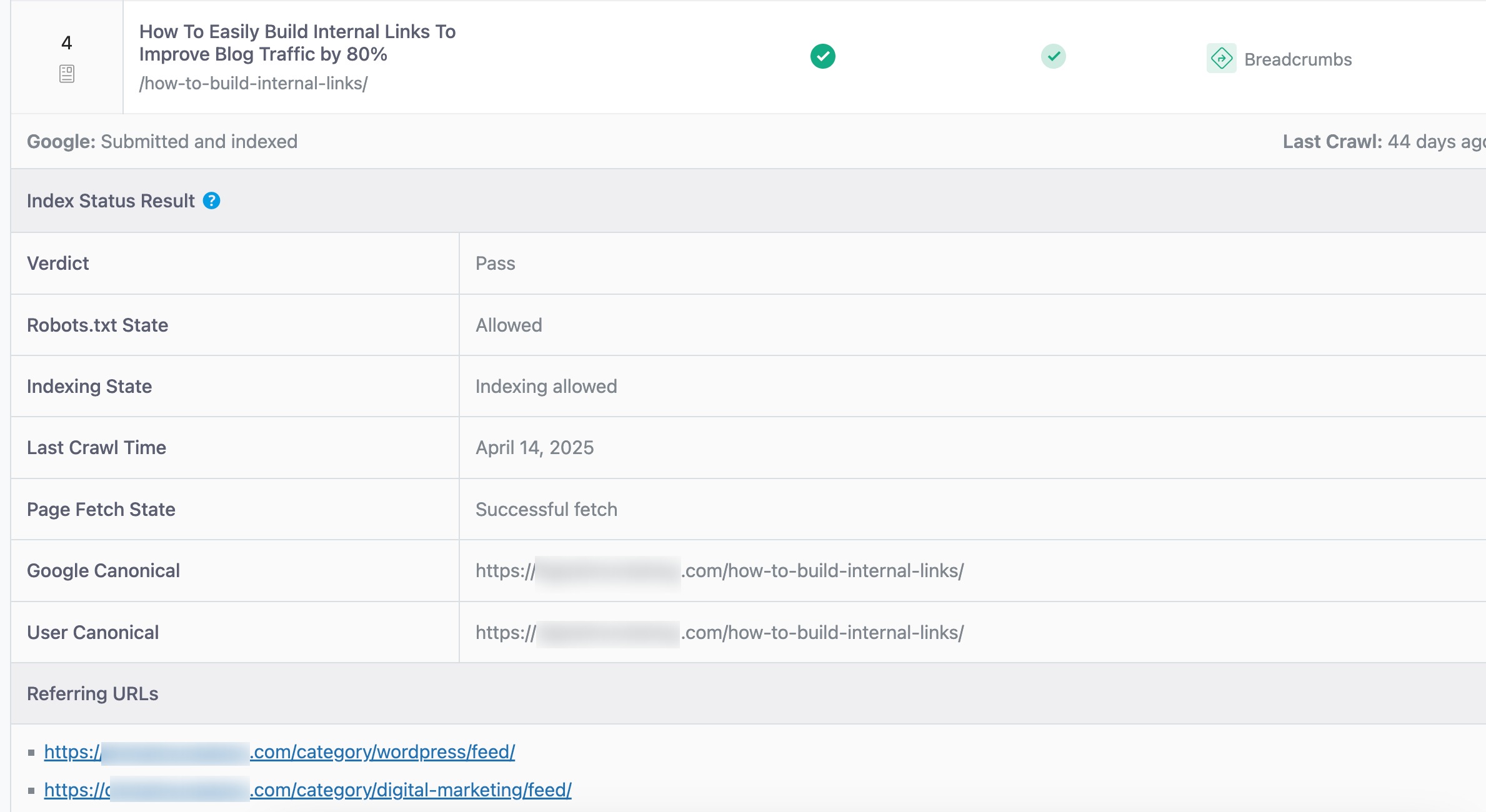
Even if you’ve used a robots.txt directive to block search engines from crawling a page, that page might still get indexed—especially if other websites are linking to it. In short, blocking crawling doesn’t always prevent indexing.
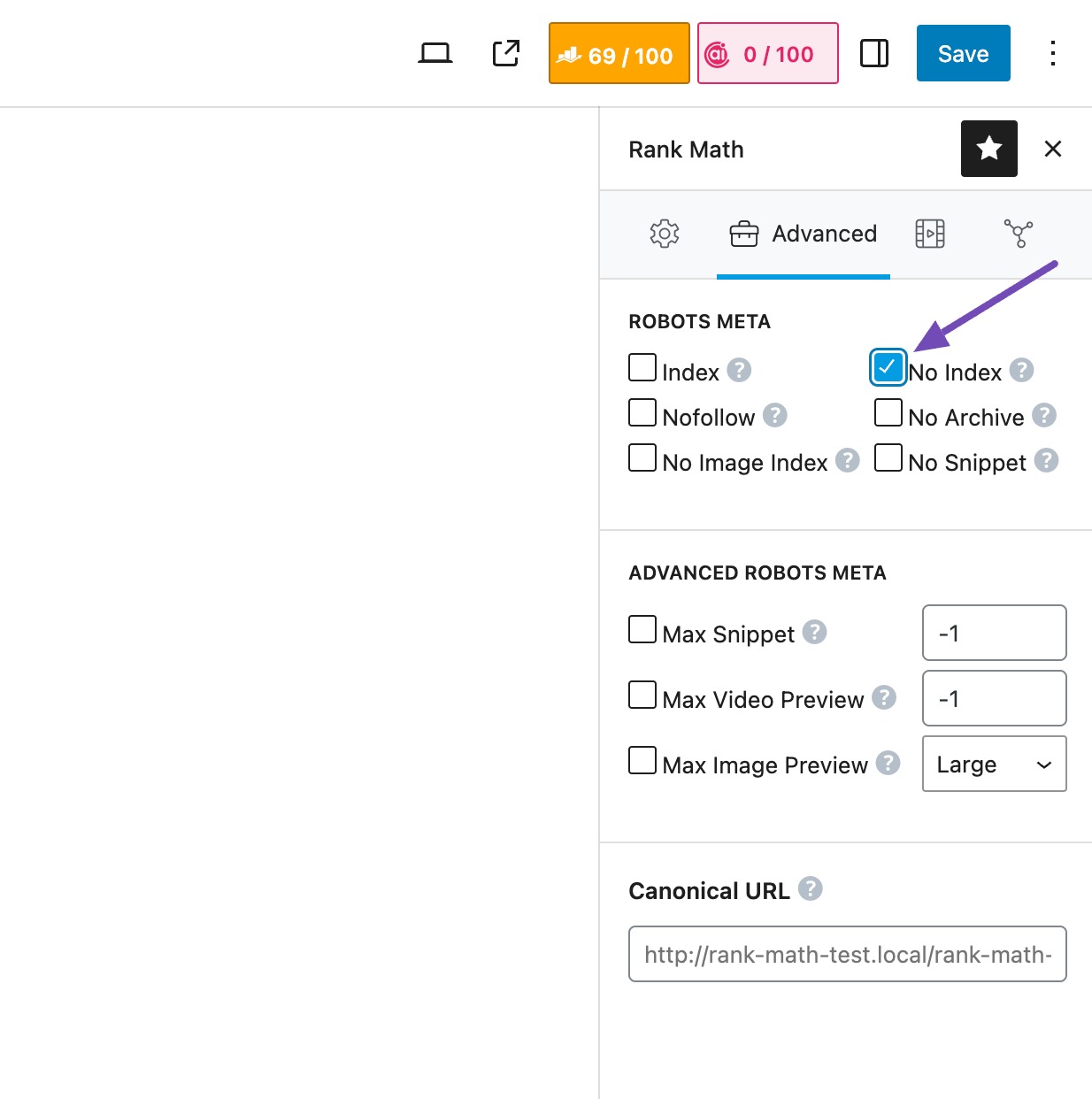
To stop a page from being indexed, the most effective method is to add a noindex meta tag.
If you want to prevent a specific page from being indexed, you can use Rank Math to do this easily. Just navigate to the page, go to the Rank Math tab, and under the Advanced options, set the ROBOTS META to noindex, then Save the page.
Once pages pass the processing stage, they move into the final indexing phase. But not all pages are treated equally.
Search engines use complex ranking algorithms to determine the relevance and importance of indexed pages.
These algorithms consider various factors, such as the presence of search terms in the content, the quality and authority of the website, user engagement metrics, and contextual relevance.
Google prioritizes:
- Mobile-friendly pages — Install a mobile-optimized theme if you’re using WordPress.
- High-quality, original content — Content that offers real value to users.
How to Create Content That Gets Indexed First
If you want your content to be prioritized for indexing, it’s essential to focus on creating high-quality, well-structured content.
AI tools have made it easier to improve crawlability and indexing. Over 50% of users say AI helps with
crawlability and indexing analysis, as well as error detection and resolution.
Tools like the Blog Post Wizard make this process incredibly efficient.
First, you can generate a blog idea by entering your niche or a brief description of your topic. If you already have a topic in mind, you can simply skip this step.
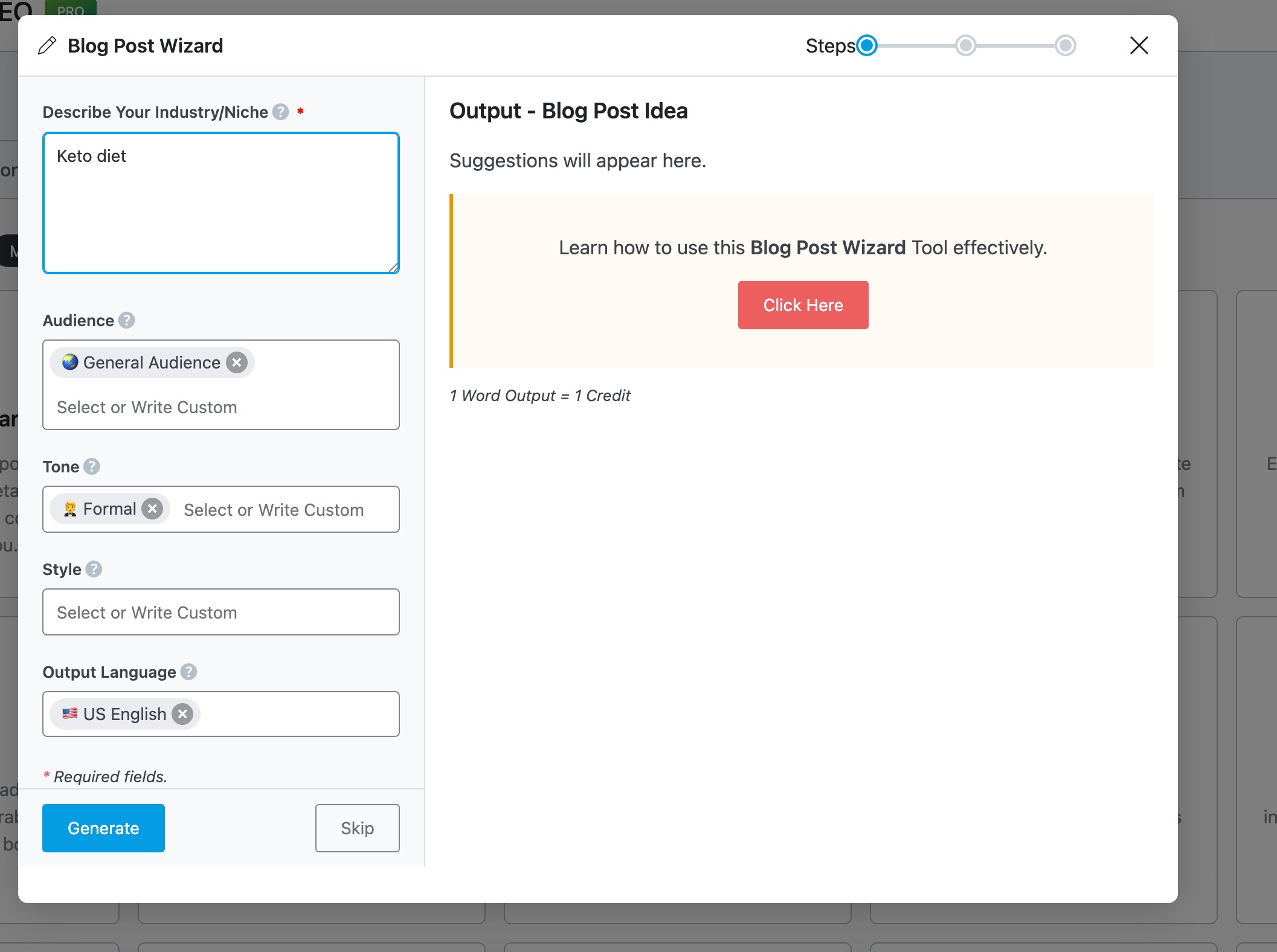
Next, you’ll move on to creating a blog post outline. Here, enter your topic, either add your own main points or let the AI suggest them, choose your target audience (with customizable options), select the tone of the article (such as formal or conversational), pick a writing style (like a tutorial), and choose your preferred language from over 28 available options.
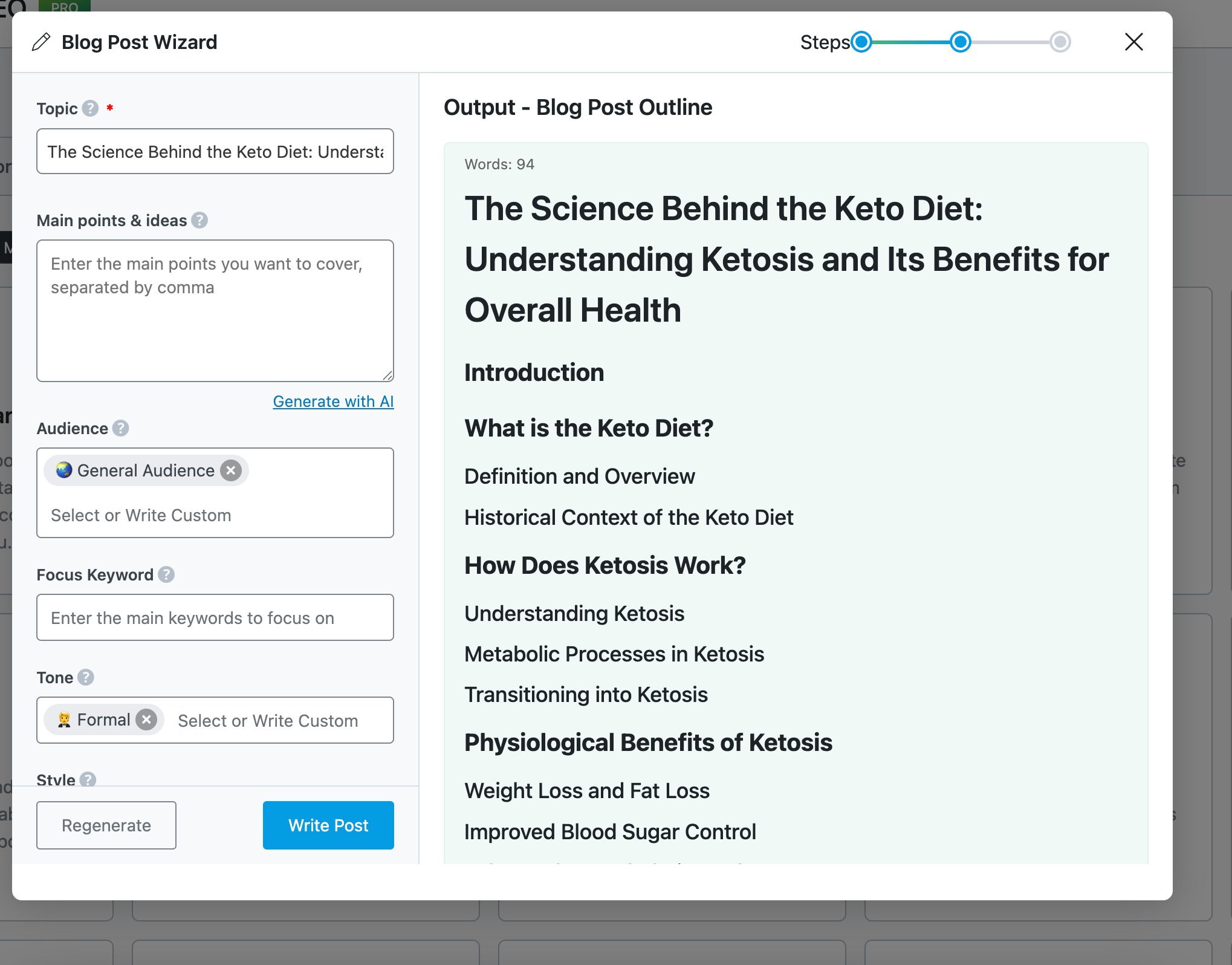
Once your outline is ready, click on Write Post, and Content AI will generate a complete article for you. Typically, it creates a well-structured post that includes an engaging introduction, a clear conclusion, key points throughout, and even an FAQ section. If the result meets your expectations, you can click Create New Post to publish it directly.
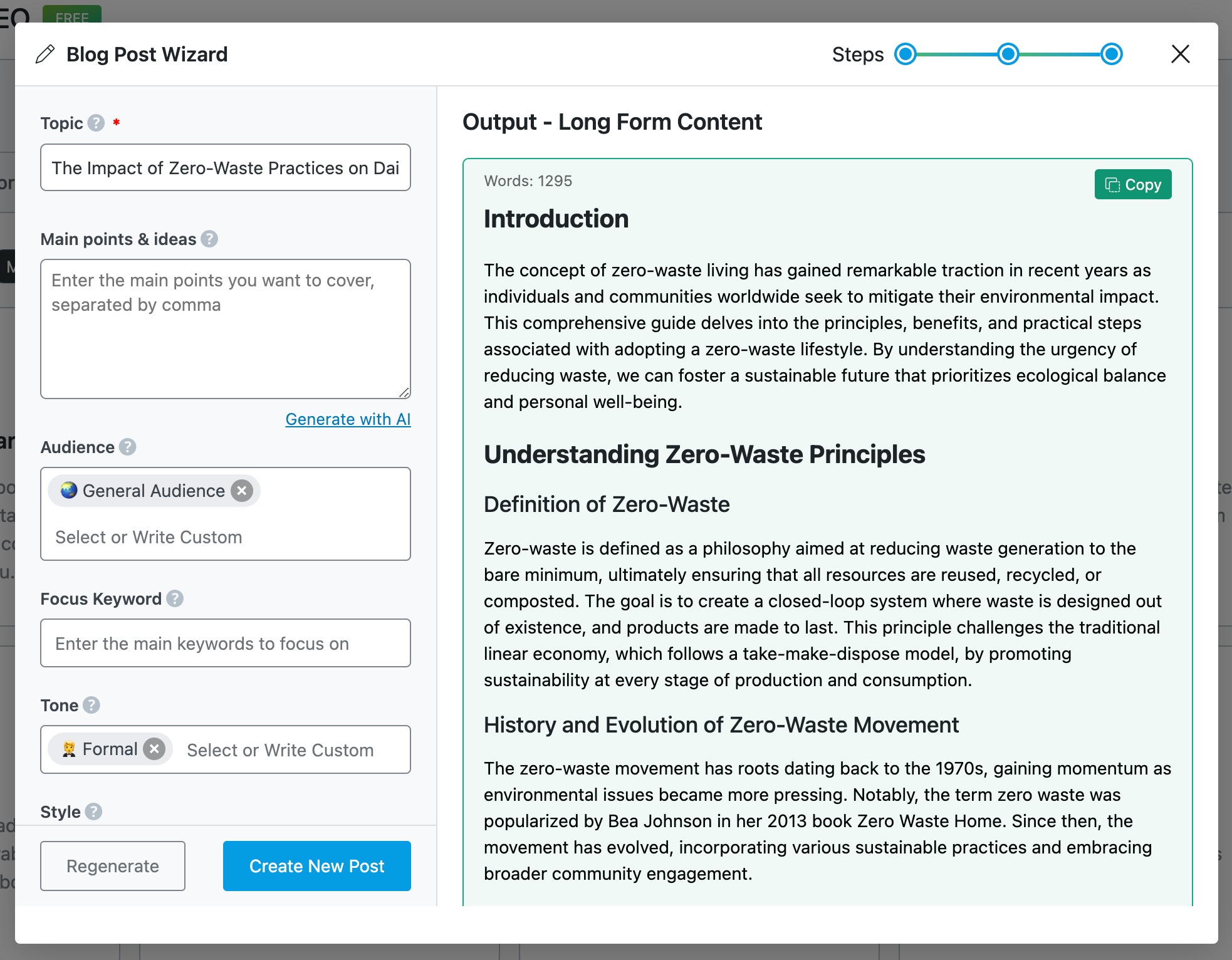
At this stage, review the content, fact-check it, and include your personal insights or expertise. Always remember: the AI-generated article is a first draft, not the final version. By combining efficiency with quality, this process helps ensure your content is optimized and ready to be indexed quickly.
Dealing with Duplicate Content
If you have multiple pages with similar content, even if the wording on these pages differs, search engines may still consider them duplicates because the topic is essentially the same. In such cases, search engines will usually choose one page to index and ignore the other—or in rare cases, index neither.
To avoid this, you need to clearly tell search engines which version of the page you want to be indexed. You do this using a canonical tag.
To do so, navigate to the page. In the Rank Math tab, go to the Advanced options, and locate the Canonical URL field.
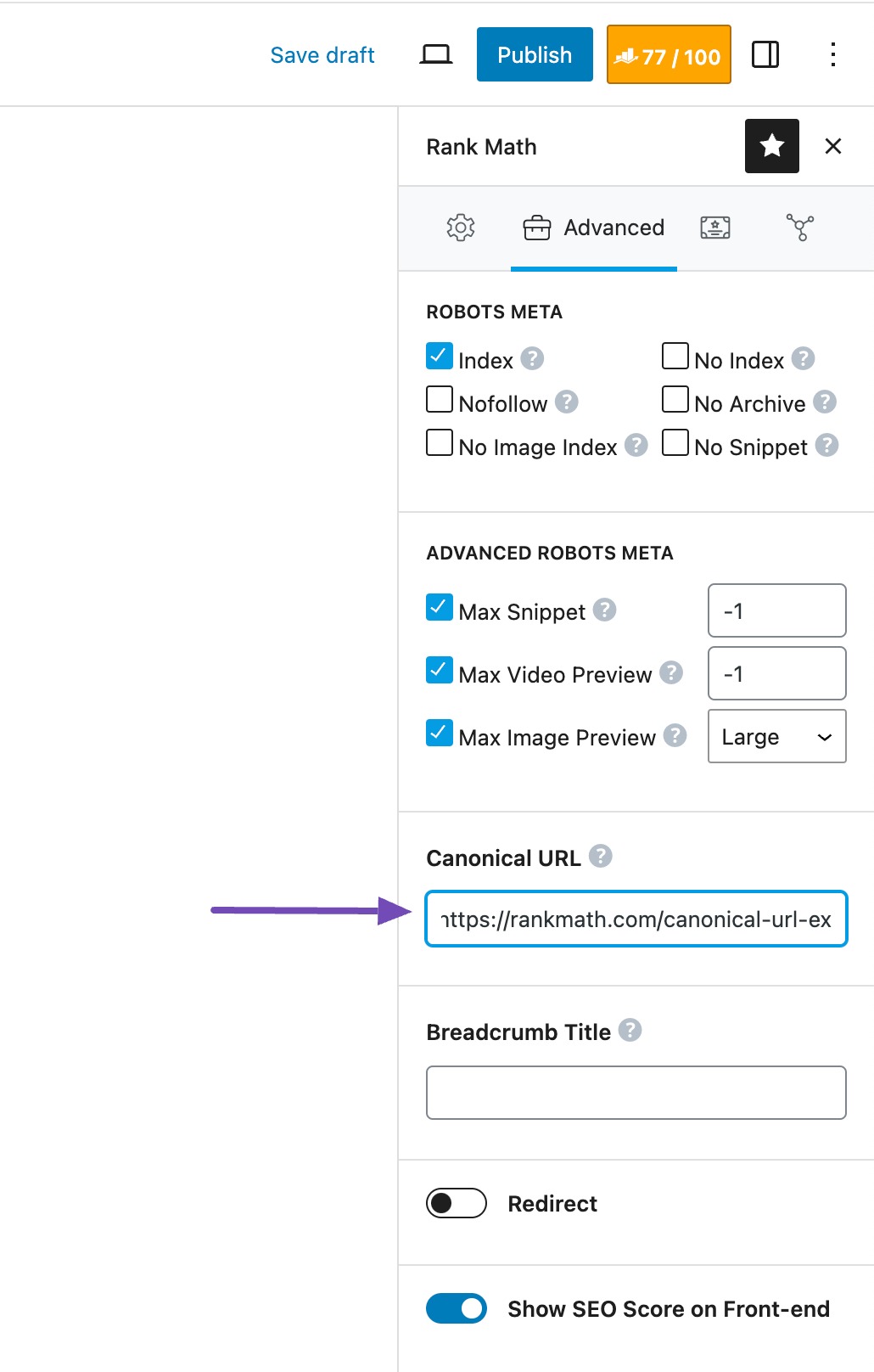
By default, every page is self-canonicalized. To change that, copy the URL of the page you want indexed, and paste it into the Canonical URL field of the duplicate page. This tells search engines to ignore the current page and index the preferred one instead.
- Indexing starts after crawling, where search engines filter out low-quality or irrelevant elements (like duplicate content, broken links, or bloated media).
- Optimizing site speed, content quality, and user experience helps ensure more pages get indexed.
- Use Google Search Console and Rank Math PRO to identify pages excluded from indexing and fix issues.
- Blocking crawling via
robots.txtdoesn’t prevent indexing—use noindex tags to control what gets indexed. - Canonical tags help avoid duplicate content issues by signaling your preferred page version.
- Tools like Rank Math’s Blog Post Wizard and Content AI streamline the creation of well-structured, index-ready content.
3.3 Ranking
Once the pages have been crawled and indexed, it’s time to rank them.
Search engines utilize various algorithms, like PageRank, to determine rankings, which evaluate the quality and quantity of incoming links to a page.

Several factors influence the ranking of web pages. Relevance to the search query is important, with pages containing content closely matching the user’s intent typically receiving higher rankings.
Authority plays a significant role, considering factors like the credibility of the website, quality of content, and the number of reputable sites linking to it.
User engagement metrics such as click-through rates, bounce rates, and time spent on a page also influence rankings, reflecting user satisfaction and interest in the content.
- Ranking happens after indexing, where search engines determine the order of pages in search results.
- Relevance to the user’s query is important—content that aligns with search intent ranks higher.
- Authority matters—strong, credible sites with high-quality content and backlinks tend to rank better.
- User engagement signals (like CTR, bounce rate, and time on page) help search engines understand content usefulness and impact rankings.
4 Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between crawling and indexing?
Crawling involves discovering and fetching web pages, while indexing involves analyzing and storing information from those pages in a searchable database.
What is the impact of page load speed on indexing?
Faster-loading pages are prioritized by search engines during indexing, as they provide a better user experience and are more likely to be ranked higher in search results.
How can you improve your website’s visibility in search engine results?
You can improve the visibility in search engine results by creating high-quality, relevant content, optimizing the websites for mobile-friendliness and speed, earning reputable backlinks from authoritative sources, and adhering to best practices for search engine optimization (SEO).
How often are search engine indexes updated?
Search engine indexes are updated continuously to reflect changes and updates to web content, with the frequency of updates varying depending on factors such as the popularity and importance of the website.
What common mistakes can prevent a web page from getting indexed?
Common mistakes that can prevent a web page from getting indexed include blocking search engine crawlers with robots.txt files, using meta robots tags to prevent indexing, and having crawl errors, such as broken links or server errors.
5 Conclusion
Search engine indexing plays an important role in how websites are discovered and ranked by search engines.
By crawling and analyzing web pages, search engines create an organized index of information to deliver relevant and accurate search results to your audience.
Understanding the process of search engine indexing can help you optimize your pages for better visibility and higher rankings.
So, next time you search for something online, remember that there is a complex system of indexing behind the scenes, ensuring that you find the most relevant results in seconds.
Happy searching!
If you like this post, let us know by Tweeting @rankmathseo.
