What is a Content Delivery Network?
A content delivery network, content distribution network, or CDN, is a group of servers that work together to allow visitors to access web content quickly.
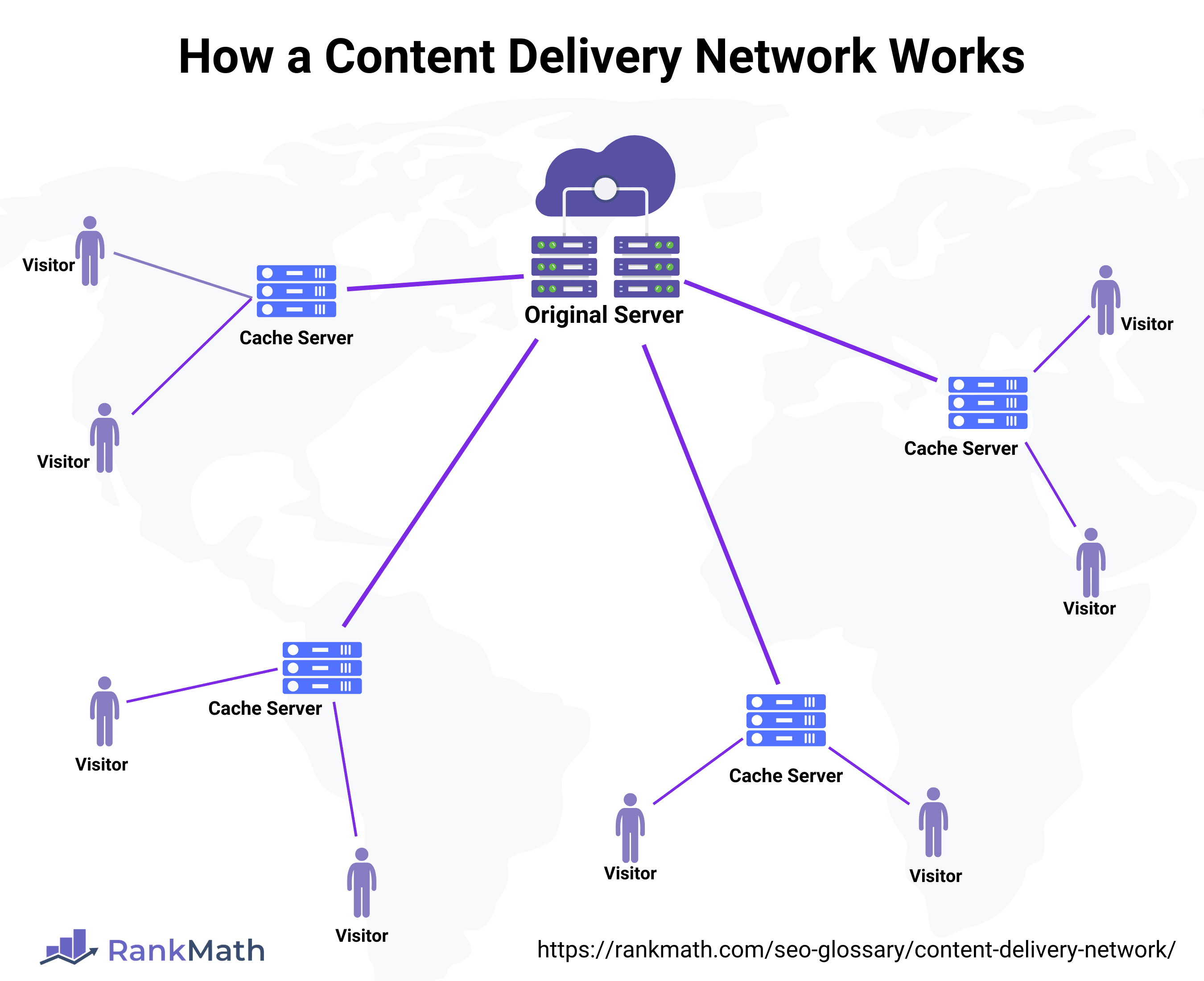
A content delivery network has servers in multiple locations worldwide. When visitors want to access content on a site that implements it, the network serves them from the server closest to them. Thus, the content delivery network helps reduce the site’s page speed.
How a Content Delivery Network Works
Let us assume that you want to access our homepage at rankmath.com. Usually, your browser should connect directly to our server. However, this may take some time, depending on how far away you are from it.
If our server were in the United States, a person from the United States or Canada would connect to it faster than someone in the United Kingdom or India.
This is where the content delivery network comes in. If we use one, it will store (cache) copies of our site on its servers in various locations worldwide. Then, when you try accessing our site, it will serve our cached pages from the server closest to you.
For example, if the content delivery network has servers in the United Kingdom and the United States, it would serve American and Canadian visitors from its United States server and the United Kingdom and Indian visitors from its United Kingdom servers.
Importance of a Content Delivery Network
Content delivery networks (CDNs) reduce latency and accelerate page load times, ensuring visitors can access webpages quicker than usual.
Latency is the time it takes for data to be transmitted between two networks. When you try to access our site, latency is the total time it takes your browser to communicate with our server and for our server to return the requested services to your browser.
The farther our server is from you, the longer the latency and the longer you will wait to receive our content.
The page load time, for its part, is a combination of the latency and every other time it takes the content to display on your browser. A high latency will lead to a high page load time. This will, in turn, hurt your user experience as visitors will wait longer to access your content.
However, a content delivery network significantly reduces this by serving the webpage from the server closest to the visitor. This server, called the edge server, helps reduce latency, page load time, and bounce rate and improves user experience, engagement, and conversion rates.
Content delivery networks also help to improve your security and reduce your downtime. Since your content is spread across multiple servers, visitors can still access your site even when your server is down.
Content delivery networks also typically offer advanced security features, such as SSL/TLS encryption and Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) protection. These help to protect your site and visitors and reduce the impact of malicious attacks aimed at the site.
Limitations of a Content Delivery Network
While content delivery networks offer multiple benefits to sites that use them, they may also severely affect the site’s usability, user experience, and revenue.
1 Inconsistent Content
Content delivery networks cache content on edge servers. While this allows them to present content to visitors quickly, it may also lead to issues when the cache on the edge servers is not cleared or updated frequently.
This may cause visitors to view different content depending on the edge server that provided their content. Sometimes, the edge servers may not even be updated, causing them to return content different from that of the origin server.
2 Dynamic Content Latency
While content delivery networks excel at delivering static content quickly, they can introduce latency when it comes to dynamic content since dynamic requests often need to be routed back to the origin server.
This can slow response times, especially if the server is far from the visitor. It may also result in a less responsive experience for users dealing with real-time data or engaging in transactions.
3 Troubleshooting Issues
Content delivery networks can complicate the troubleshooting process when issues arise. This happens because it can be challenging to pinpoint the source of a problem, especially since content delivery networks serve content from multiple edge servers rather than a single origin server.
This complexity may lead to longer resolution times as technical teams may need to investigate multiple servers instead of one. The technical team may also spend considerable time and resources communicating with the content delivery network provider.
4 Misconfigured Settings
Content delivery networks can be complex to configure and manage. This can lead to errors, including misconfigured settings, which can impact the site’s security and performance.
For example, incorrect caching rules may cause the network to serve outdated content. Flawed SSL settings could expose the site to security risks. All of these will have a considerable effect on the site’s usability and user experience.
5 Less Control Over Uptime
Sites that use content delivery networks are vulnerable to security and performance issues affecting the network. This means a site may experience downtime, even when there is no issue from its end.
For example, a site can experience downtime when the content delivery network is attacked or experiences an outage or technical issue. This can be challenging for bloggers as resolving such issues is out of their control and reliant on the content delivery network.
So, a blogger would have to wait for the network to resolve the issue before they can get online again.