What Is Ranking?
Ranking refers to the position a webpage holds on search result pages for a specific keyword or query. It is also called the SEO ranking or search ranking.
For instance, the WebMD webpage below ranks in second place for the keyword “yoga poses for beginners.”
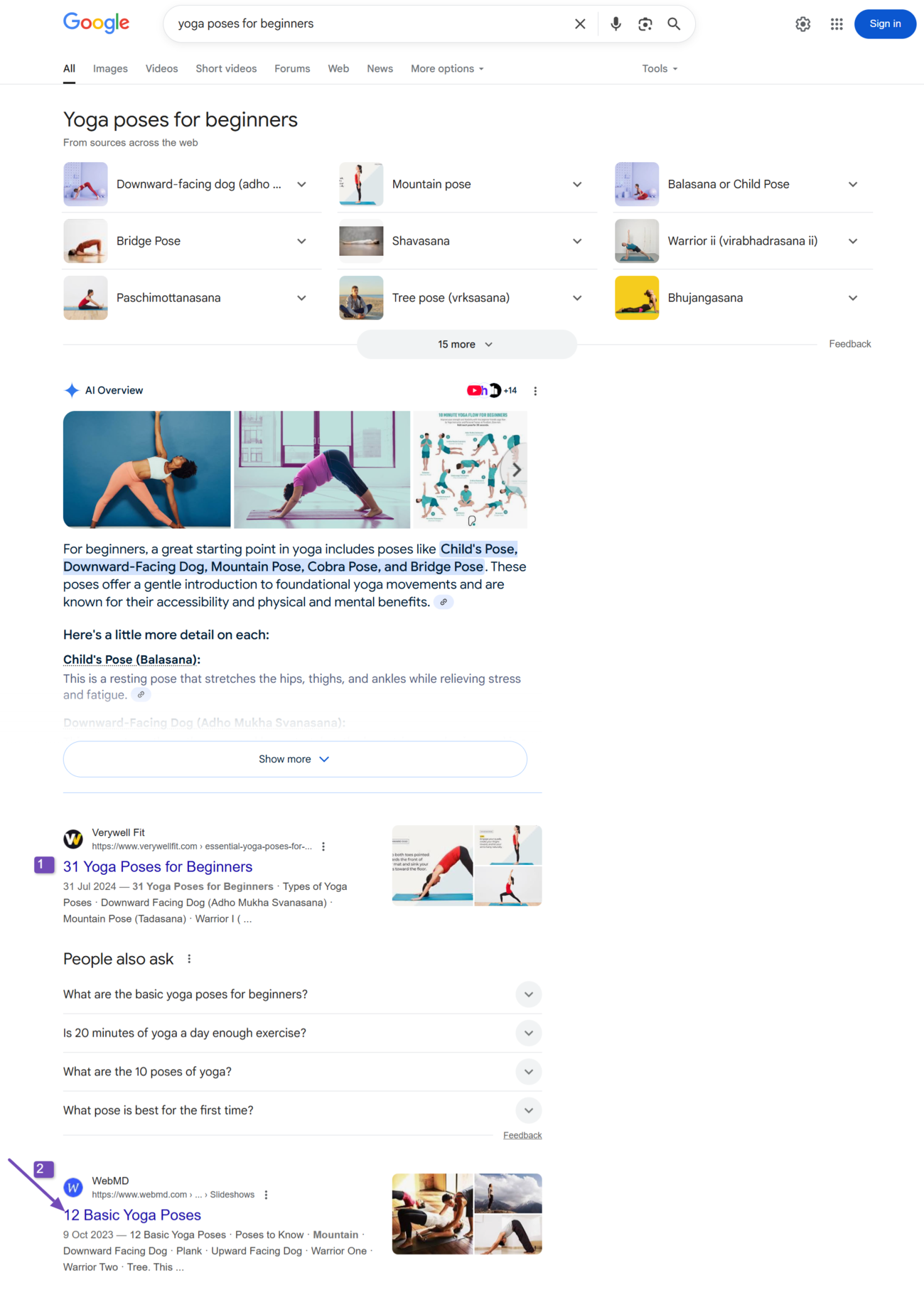
However, it ranks in fourth place for the keyword “best yoga poses.”
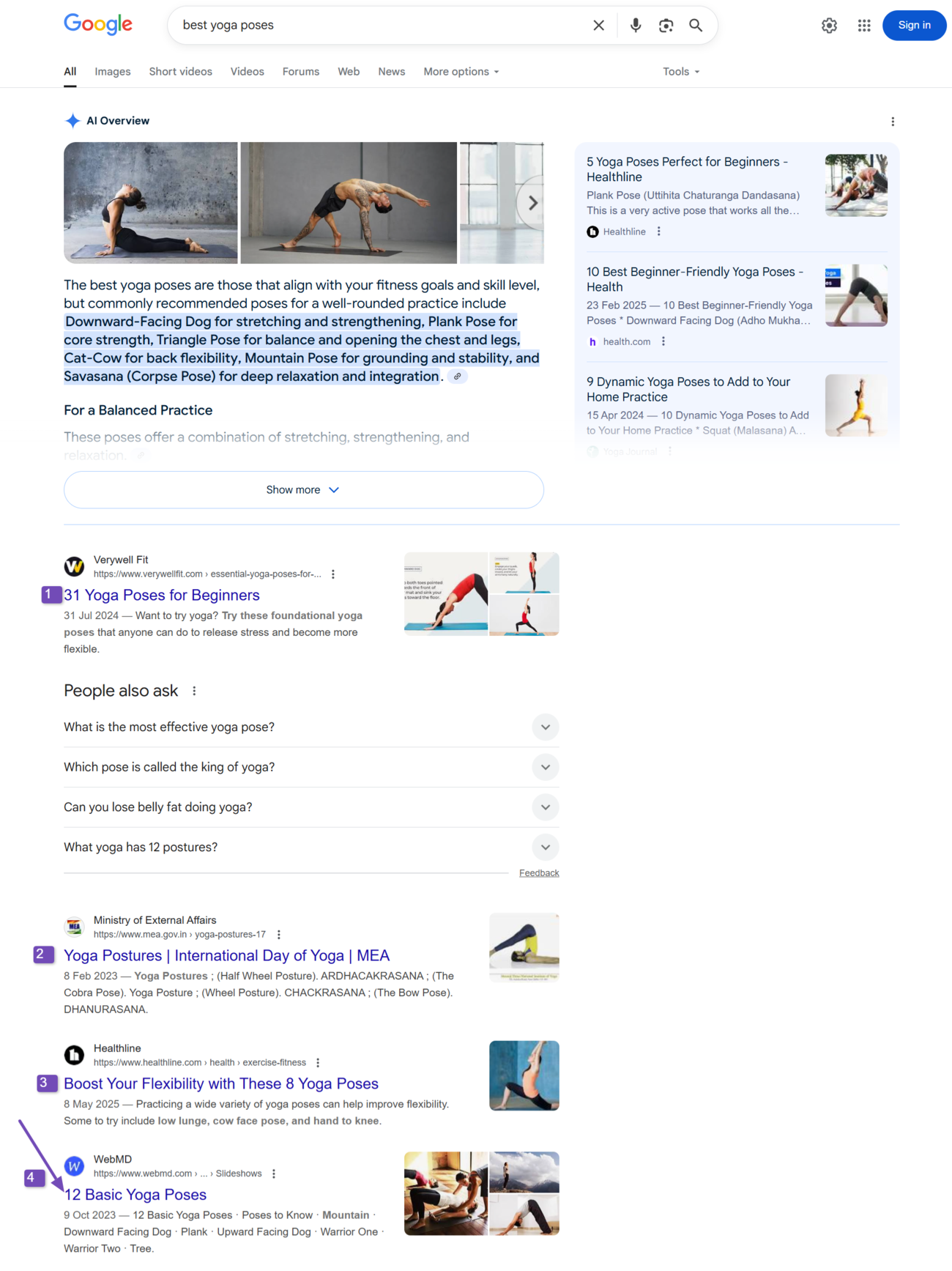
So, we can say the webpage’s ranking for “yoga poses for beginners” is second place, while its ranking for the keyword “best yoga poses” is fourth place.
The higher a webpage ranks for a keyword, the more visibility, organic traffic, and engagement it tends to receive. Traffic drops significantly for lower-ranked results, with very few clicks and traffic for webpages on page two and beyond.
In this article, we’ll cover:
The Three-Step Search Process
Google’s search process is a three-step process that includes crawling, indexing, and serving. Ranking occurs at the final step (serving) of the search process.
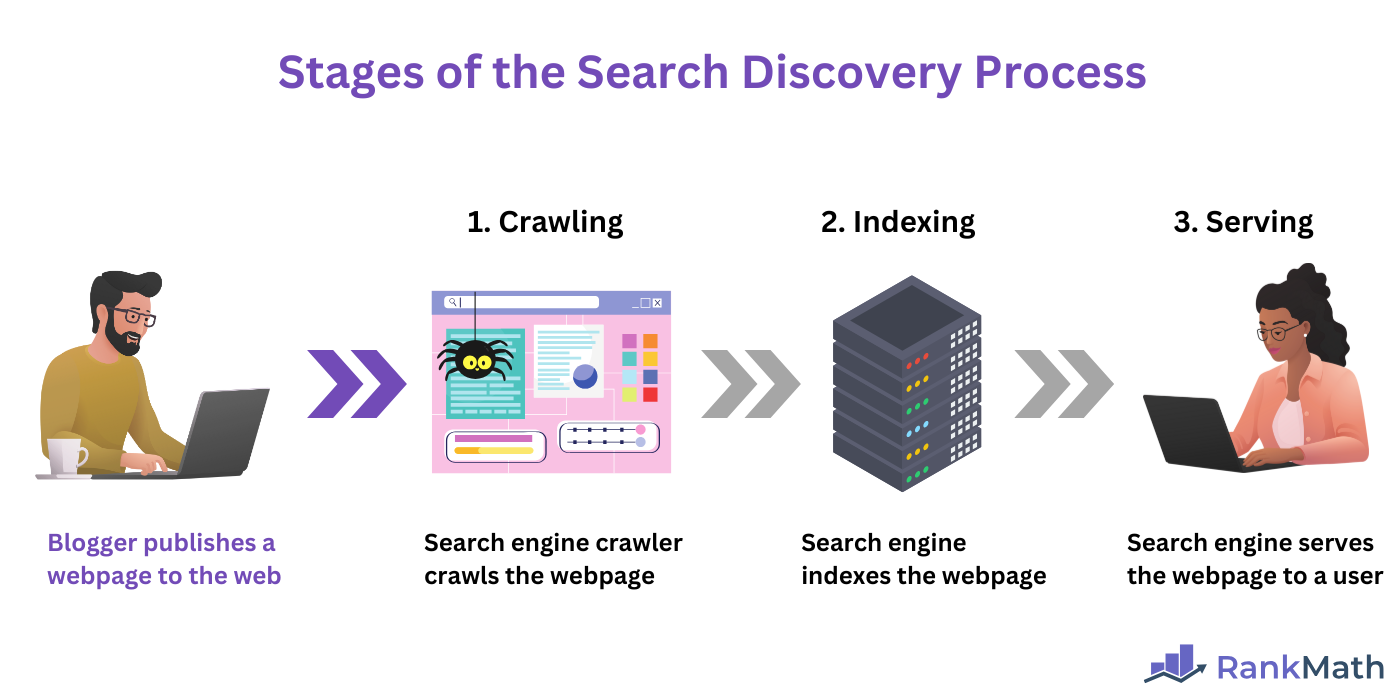
1 Crawling
Crawling is the process whereby search engine crawlers (also called bots or spiders) scan the web to discover new or updated webpages. Once they identify a new URL, they then crawl it to collect its data for indexing.
In the case of previously discovered URLs, the crawler will visit such pages at intervals to check if they have been updated since its last visit. If they have, it may then proceed to re-crawl it.
2 Indexing
Indexing is the process of storing discovered pages in the search engine’s database. This database is called an index and serves as the source of all content displayed on the páginas de resultados de búsqueda.
In the indexing stage, the search engine evaluates the content, structure, and relevance and uses that to determine when and how it should appear on search result pages.
3 Serving
Serving is the process of displaying results that are relevant to a user. The results are taken from the index and are displayed in response to the user’s search query.
Ranking occurs at this stage. Search engines determine the ranking by reviewing various factors and using them to determine which results to display and in what order.
The factors that the search engines use to determine the results to display are collectively referred to as ranking factors.
What Are Ranking Factors?
Ranking factors are the signals and metrics that search engines use to determine whether a webpage should rank (that is, appear in search results) and how high it should rank.
The search engine weighs these ranking factors together to determine the page’s ranking on search results pages.
The set of rules and instructions that determine how the ranking factors affect the ranking is called the algorithm. In the case of Google, it is called the Google Search algorithm.
Generally, the more relevant the webpage is to the search query, the higher its ranking will be.
However, relevance is not the only signal and metric Google looks at. This is so because search engines do not only want to return relevant content, but also want to return results that provide the user with a great user experience.
So, a well-optimized webpage can still have a low ranking if it is not secure, not mobile-friendly, or runs on a slow server.
With that said, Google has many ranking factors. The exact number remains undisclosed, but it is believed to be between 200 and 600. That is a lot.
List of Some Common Ranking Factors
Ranking factors are the criteria that search engines use to determine the order in which the webpages appear in search results. There are hundreds of ranking factors, and we likely do not know most of them. However, here are a few that we have confirmed so far.
1 Page Experience
Page experience refers to the signals that measure how users perceive the experience of interacting with a webpage.
This includes various signals and metrics, such as mobile-friendliness and HTTPS usage. It also includes the absence of excessive ads and intrusive interstitials, as well as the Core Web Vitals.
los Elementos vitales web básicos itself is a set of three metrics, including the largest contentful paint (LCP), cumulative layout shift (CLS), and interaction to next paint (INP).
- los largest contentful paint (LCP) measures the load speed
- los cumulative layout shift (CLS) measures the visual stability
- los interaction to next paint (INP) measures the responsiveness
2 Content Quality
The content quality evaluates how useful, relevant, and well-written the information on a webpage is. Search engines generally prioritize high-quality content that is original, comprehensive, and tailored to match the user’s search intent.
3 Vínculos de retroceso
Vínculos de retroceso are links from other websites that point to your site. They are also known as inbound links and serve as a vote of confidence from one site to another.
Backlinks pass equidad de vínculo (also called link juice) and Rango de página to your site. The more authoritative and high-quality the origin site, the more link equity and PageRank it passes to you.
Backlinks improve your rankings, which makes them great for SEO. They remain one of the most powerful off-page SEO ranking signals used by Google.
You can refer to these 10 methods of building high-quality backlinks to your site.
4 Texto de anclaje
los anchor text is the clickable text in a hyperlink. They are a significant ranking factor as they give search engines context about the webpage receiving the link.
A good anchor text is descriptive and provides relevant information about the webpage being linked to. Anchor text itself is an element of on-page SEO, which refers to the SEO techniques that take place on the webpage.
5 Content Freshness
Content freshness refers to how recently a page was created or updated. For time-sensitive topics, newer content is often favored by search engines as they are generally more relevant than older content.
However, the Query Deserves Freshness (QDF) ranking system is not used on all queries. Instead, it only applies when Google believes the user requires more recent information.
6 Estructura de URL
A clean, descriptive URL structure makes it easier for search engines and users to understand what a page is about.
However, the URL structure is a very lightweight ranking factor, and Google also only takes it into account before crawling the URL. Once it crawls the URL, more relevant ranking factors take over.
7 Openness
Openness refers to a business’s opening hours. This makes it a significant ranking factor for local SEO as Google only wants to send visitors to businesses that are open at the moment.
How to Improve Your Rankings
You can improve your rankings by following on-page, off-page, and technical SEO techniques and best practices. If you rank for local keywords, you should also optimize for local SEO.
Overall, these are the many SEO techniques you can apply to your site. On-page, off-page, and technical SEO are the three main areas of focus. However, you can apply the rest based on the size of your site, your target audience, and the type of content you publish.
Here are the SEO techniques that can boost your rankings, along with links to guides on using them effectively:
- En la página SEO
- Fuera de página SEO
- Técnico SEO
- SEO locales
- Imagen SEO
- WooCommerce SEO
- Taxonomía SEO
- Pagination SEO
- Programmatic SEO
- International SEO
- Enterprise SEO
1 En la página SEO
On-page SEO refers to the SEO techniques that you apply to your webpages in order to improve their visibility and rankings in search engine results.
These optimizations are typically done on the visible content on the webpage, although they may also appear in the code.
Examples of on-page SEO include:
- Including relevant keywords in the titles, headings, and content
- Structuring your content with proper header tags (H1, H2, etc.)
- Writing compelling meta titles y meta descriptions
- Using enlaces internos that point to related pages
- Optimizing the image’s alt text and file names
2 Fuera de página SEO
Off-page SEO refers to the SEO optimizations that take place on other websites with the intent of improving your own rankings. It is primarily centered around building backlinks that point to your site.
Examples of off-page SEO include:
- Listing your site in online directories
- Receiving brand mentions on other sites
- Earning backlinks from reputable websites
- Guest posting on other blogs or publications
- Participating in forums or Q&A sites with backlinks to your site
3 Técnico SEO
Technical SEO refers to the process of optimizing a website’s infrastructure to ensure users can access it and search engines can crawl, index, and serve it more effectively.
Examples of technical SEO include:
- Fixing broken links
- Resolving crawl errors
- Including structured data on your site
- Creating and submitting an mapa del sitio XML
- Using robots.txt to control how crawlers access your URLs
- Using a mobile-friendly theme and responsive design
- Improving your page speed and core web vitals
- Implementing HTTPS to secure your users
4 SEO locales
Local SEO is the practice of optimizing your online presence to attract more business from relevant local searches. It helps businesses appear in location-based results, especially in Google’s local pack, maps, and “near me” searches.
Examples of local SEO include:
- Creating location-specific landing pages
- Optimizing your pages for local keywords
- Including marcado Schema for local businesses
- Creating and optimizing a Google Business Profile
- Getting reviews on Google and other local platforms
- Using an accurate name, address, and phone number (NAP) across the web
5 Imagen SEO
Image SEO is the practice of optimizing the images on a webpage so they can be easily discovered, indexed, and ranked by search engines.
Examples of image SEO include:
- Using descriptive file names
- Compressing images to reduce their file size
- Including relevant alt text to describe the image
- Using responsive and widely supported image formats
- Creating and submitting an image sitemap
6 WooCommerce SEO
WooCommerce SEO refers to the practice of optimizing a WooCommerce-powered online store to improve its visibility in search engine results. It is helpful for WordPress blogs and shopping sites that use WooCommerce.
Examples of WooCommerce SEO include:
- Adding relevant alt text to product images
- Writing unique product titles and meta descriptions
- Optimizing product URLs with relevant keywords
- Creating internal links between related products or categories
- Using SEO plugins like Rank Math to include relevant WooCommerce-related Schema markup for your products
7 Taxonomía SEO
Taxonomy SEO is the practice of optimizing a website’s category, tag, archive, and other classification structures. This ensures the webpage is usable and accessible to visitors and search engines.
Taxonomy SEO is used by sites with a lot of categories, tags, archives, and similar pages that categorize the site’s content.
Examples of taxonomy SEO include:
- Using SEO-friendly URLs for categories and tag pages
- Creating dedicated category and tag pages with unique content
- Including meta titles and descriptions on the category and tag pages
- Using proper internal linking from taxonomy pages to posts, pages, and product pages
- Preventing the indexation of thin or low-value taxonomy pages using the noindex tag and robots.txt instructions
8 Pagination SEO
Pagination SEO refers to the process of optimizing paginated content, such as multi-page blogs, product listings, and category pages, to ensure that search engines can crawl, index, and rank them effectively.
Pagination SEO helps prevent duplicate content issues, making it especially useful for large sites with numerous paginated pages.
Examples of pagination SEO include:
- Ensuring each paginated page has a unique URL
- Including descriptive, indexable content on each page
- Avoiding canonical tags that point all paginated pages to page 1
- Providing clear navigation guides, such as “Previous” and “Next”
- Optimizing the paginated pages to load quickly
9 Programmatic SEO
Programmatic SEO is the process of automating the creation of large volumes of well-optimized webpages.
It is typically used by websites that dynamically generate content from databases. For example, ecommerce sites, online directories, and listing sites with numerous businesses, services, and job listings.
Examples of programmatic SEO include:
- Pulling data from APIs to create dynamic content
- Automatically creating thousands of location-based or product pages
10 International SEO
International SEO is the process of optimizing a website so that it can rank in different countries, regions, and languages. This ensures that users in different regions are served the most relevant content based on their location or language preferences.
International SEO is only relevant for websites that publish content in multiple languages or target visitors in specific countries and regions
Examples of international SEO include:
- Using hreflang tags to indicate the target region and language
- Using country-specific domains and subdirectories in your URLs
- Translating and localizing content for different languages and cultures
- Setting up Google Search Console properties for different countries
- Avoiding duplicate content across regional versions
11 Enterprise SEO
Enterprise SEO refers to large-scale SEO strategies used by websites with lots of webpages, websites, and subdomains. It is exclusive to super-large websites, such as Amazon, and involves extensive collaboration and automation.
Examples of enterprise SEO include:
- Integrating enterprise-level tools into your workflow
- Ensuring compliance with government laws and regulations
- Managing SEO for multiple subdomains, languages, or regions
- Conducting large-scale technical audits and resolving site-wide issues
- Automating the creation and maintenance of webpages (programmatic SEO)