How often have you closed a slow website, promising never to return?
It’s frustrating, right? We’ve all been there.
That’s where Core Web Vitals come into play.
You might wonder, “What on earth are Core Web Vitals?”
Buckle up because we’re about to begin the tech talk and make it as simple as a Sunday stroll in the park. Core Web Vitals ensure your website looks good and zips and zooms with lightning speed.
In this post, we’re not just going to talk about improving website performance; we’re diving headfirst into the nitty-gritty details and arming you with the knowledge of Core Web Vitals to turn your website into a performance powerhouse.
So, are you ready to transform your website into a high-speed, user-friendly experience? Let’s get started!
Table Of Contents
1 What Are Core Web Vitals?
Core Web Vitals is a set of user-centric metrics introduced by Google to evaluate and measure a website’s overall performance and user experience. These metrics focus on three key aspects: loading performance, interactivity, and visual stability.
In simpler terms, Core Web Vitals assess how fast a web page loads, how quickly users can interact with it, and how stable the page layout is during loading.
Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): This metric gauges the loading performance by measuring the time it takes for the largest content element, an image or text block, to become visible to the audience. LCP gives insights into how quickly the audience perceives the main content of a page.
Interaction to Next Paint (INP): The Interaction to Next Paint (INP) metric indicates the delay users may encounter when interacting with your website. It measures the time gap between a user interaction (such as a click or touch input) and the subsequent visual update, known as the “next paint,” on the website.
Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): CLS evaluates visual stability by measuring the amount of unexpected layout shifts that occur during page loading. In simple terms, it assesses whether elements on the page move around unexpectedly, which can frustrate your audience.
2 Why Do Core Web Vitals Matter?
Google has increasingly emphasized user experience as an important factor in determining search rankings.
Core Web Vitals align with this focus by directly measuring aspects of a website that contribute to a positive user experience.
The interconnection between Core Web Vitals and SEO is undeniable. Google has officially incorporated these metrics into its ranking signals, though not a significant one, meaning that websites providing a seamless and efficient user experience are likely to receive a boost in search rankings.
Websites that prioritize user satisfaction by optimizing for Core Web Vitals are more likely to be favored by search algorithms.
3 How to Measure Core Web Vitals
Several tools have emerged to assist you in this endeavor, providing valuable insights into the user experience. Three widely used tools for such measurement are Google PageSpeed Insights, Lighthouse, and Chrome DevTools.
Google PageSpeed Insights
Google PageSpeed Insights is a user-friendly tool designed to analyze the performance of a web page on both mobile and desktop devices.
Open your web browser and navigate to Google PageSpeed Insights. Input the URL of the web page you want to analyze and hit Enter. Leveraging real user data, it provides a performance score and detailed recommendations for improvement.
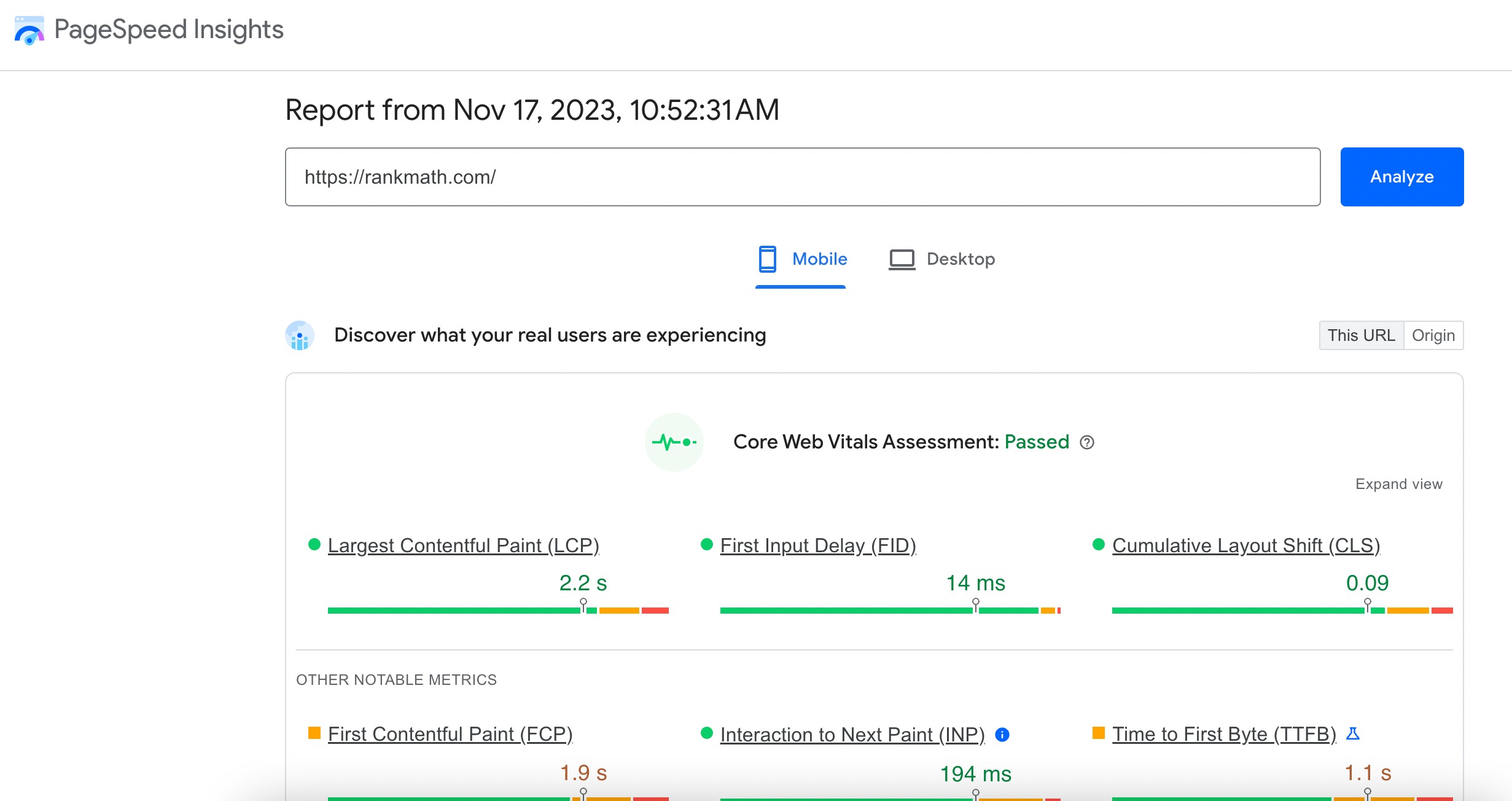
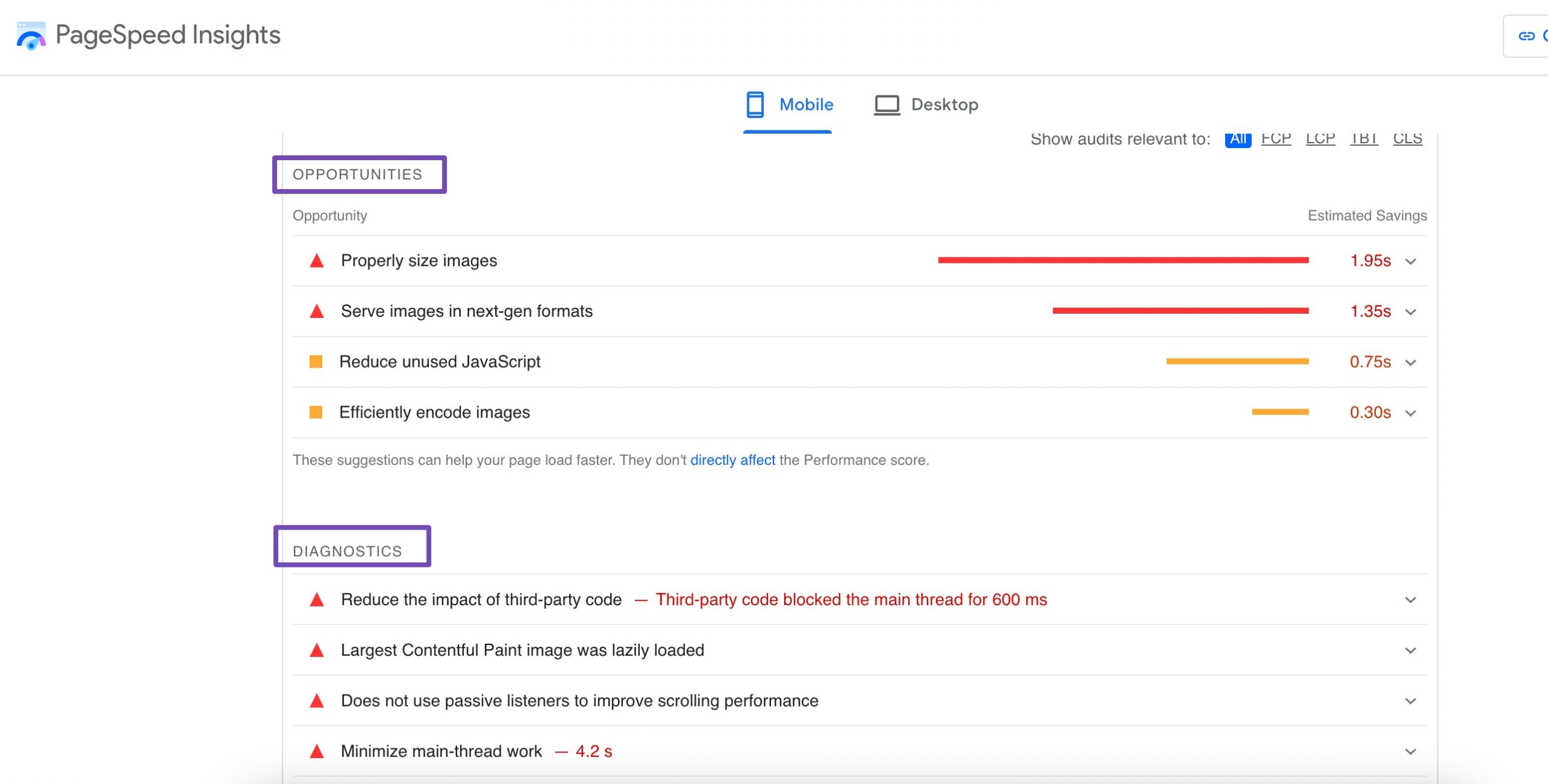
Scroll down to the OPPORTUNITIES and DIAGNOSTICS sections to uncover specific recommendations for improvement. These suggestions are tailored to enhance your Core Web Vitals metrics.
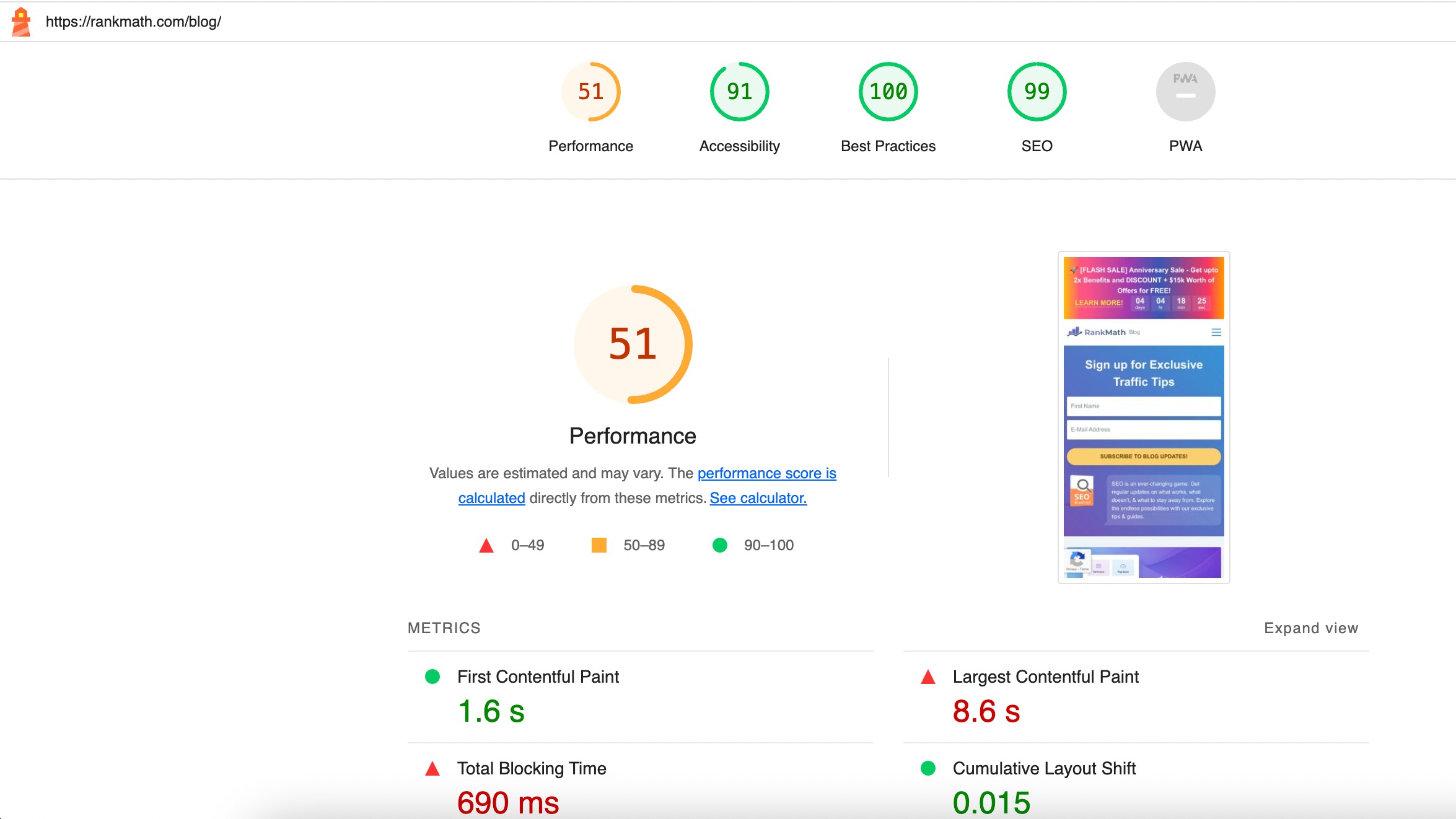
Lighthouse
Lighthouse is an open-source, automated tool for improving the quality of web pages. Lighthouse audits web pages for performance, accessibility, SEO, and more.
Lighthouse will generate a detailed report, including performance metrics and opportunities for improvement. Focus on the Core Web Vitals section to understand how your website performs regarding loading, interactivity, and layout stability.
Chrome DevTools
Chrome DevTools, a set of web developer tools built directly into the Chrome browser, is a versatile resource for performance analysis.
You can use DevTools to inspect network activity, monitor loading performance, and debug issues affecting a web page’s responsiveness.
It provides a real-time view of how different elements of a page contribute to its overall performance, making it an essential tool for hands-on optimization.
4 How to Optimize for Core Web Vitals
Now that we’ve measured the Core Web Vitals of your website, it’s time to roll up your sleeves and dive into the practical strategies for optimization.
4.1 Best Practices for Improving Largest Contentful Paint (LCP)
Let’s discuss the detailed methods to improve the Largest Contentful Paint (LCP).
Prioritize Loading of Resources
Prioritizing the loading of resources is necessary for optimizing LCP.
This involves identifying and emphasizing the loading of critical resources essential for rendering above-the-fold content. Techniques like asynchronous loading can be employed to ensure that non-essential scripts do not hinder the loading of key resources.
By managing the order in which resources are loaded, you can enhance the efficiency of your website’s rendering process, leading to a faster LCP.
Make Files Smaller
Reducing the size of files is a fundamental strategy to improve LCP.
This can be achieved through various means, such as image compression, minimizing unnecessary code, and employing efficient file formats.
Compressing images without compromising quality ensures that large visual elements load quickly, contributing significantly to a faster LCP.

Optimizing and minifying CSS, JavaScript, and other code files also helps reduce overall file sizes, facilitating swifter content rendering.
You can use a plugin like WP Rocket to boost your loading time and optimize your Core Web Vitals.
Refer to our dedicated tutorial on installing and activating plugins on your WordPress site.
Serve Files Closer to Your Audience
The geographical proximity of your server to the audience plays a pivotal role in LCP optimization.
Serving files from a server closer to your audience reduces latency and accelerates content delivery. Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) are invaluable in this regard.

By distributing resources across a network of servers strategically placed worldwide, CDNs ensure your audience can access files from a server with minimal physical distance, optimizing LCP and overall page loading times.
Host Resources on the Same Server
Hosting resources on the same server as the website can impact LCP.
When resources are stored on the same server, the time required for the server to fetch and deliver these resources is minimized. This reduces latency and contributes to a faster LCP.
Consolidating resources on a single server eliminates the need for cross-origin requests, streamlining the loading process and enhancing the overall user experience.
Use Caching
Caching is a powerful technique to improve LCP by storing previously loaded resources on a user’s device. When a user revisits the website, cached resources can be retrieved locally instead of fetching them from the server again.
This results in faster loading times, especially for returning visitors. Utilizing browser caching and cache control headers are effective strategies for implementing caching and boosting LCP performance.
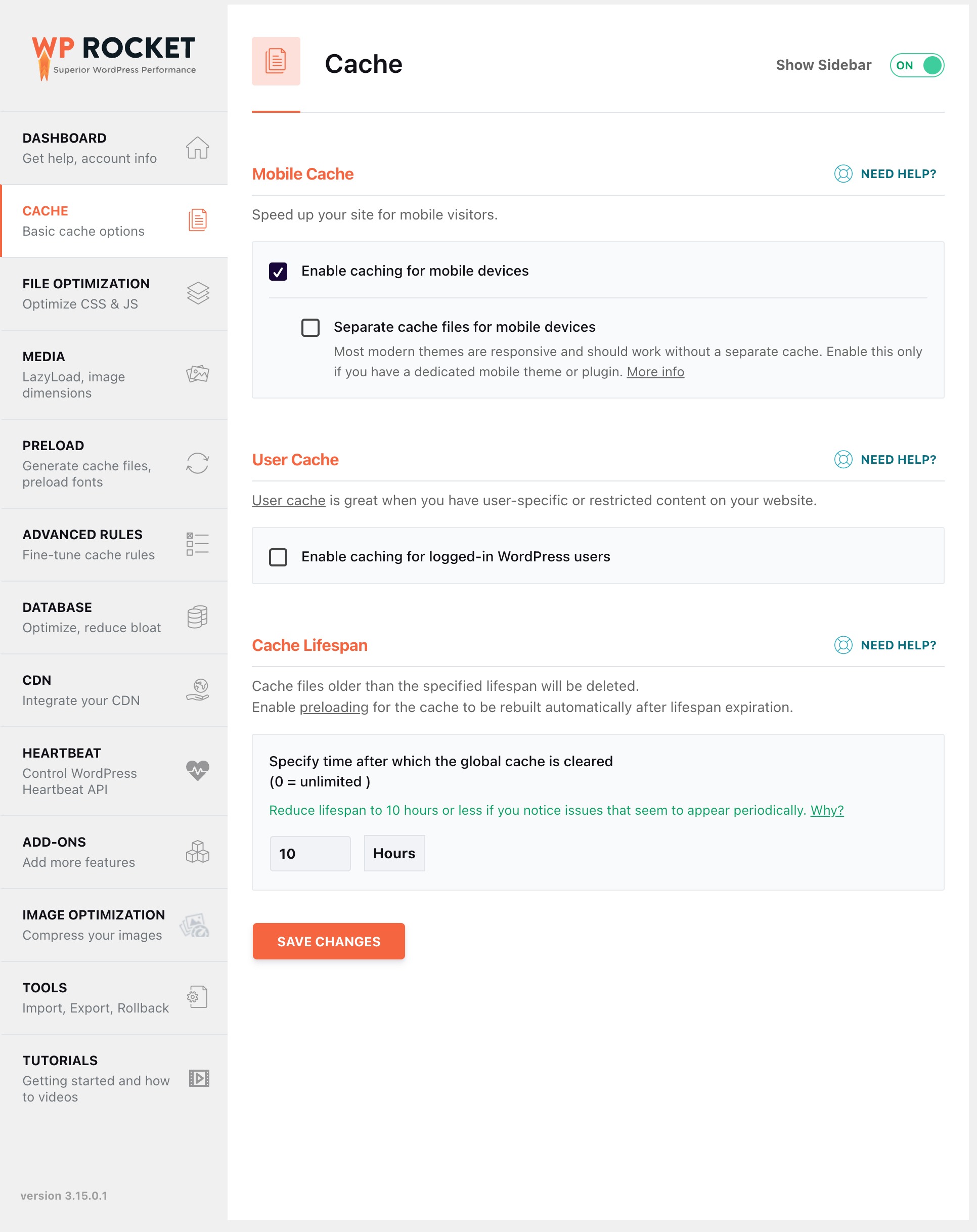
WP Rocket facilitates browser caching by instructing the audiences’ browser to store static resources locally, such as images, stylesheets, and scripts. This reduces redundant requests to the server upon subsequent visits, enhancing page load speed and optimizing overall website performance.
Below are the basic cache options available in the WP Rocket plugin.
4.2 Best Practices for Interaction to Next Paint (INP)
Let us discuss the methods to improve Interaction to Next Paint (INP).
Minimize the Input Delay
Delay the loading of non-essential code, like chat widgets, until the browser is idle to minimize initial load times. Ensure the page is easy to render by avoiding excessive images, videos, CSS animations, and other elements that can affect the performance.
Identify and optimize scripts that consume excessive resources to enhance overall efficiency and responsiveness.
Reduce Event Callback Processing Time
Here are some steps you can take to shorten processing time:
Avoid blocking the main thread by breaking down long tasks (>50 ms) into smaller ones. In some cases, you may find a theme or plugin slowing down your main thread. As you don’t have much control over its code, you can reach out to the theme or plugin developers to find a suitable fix.
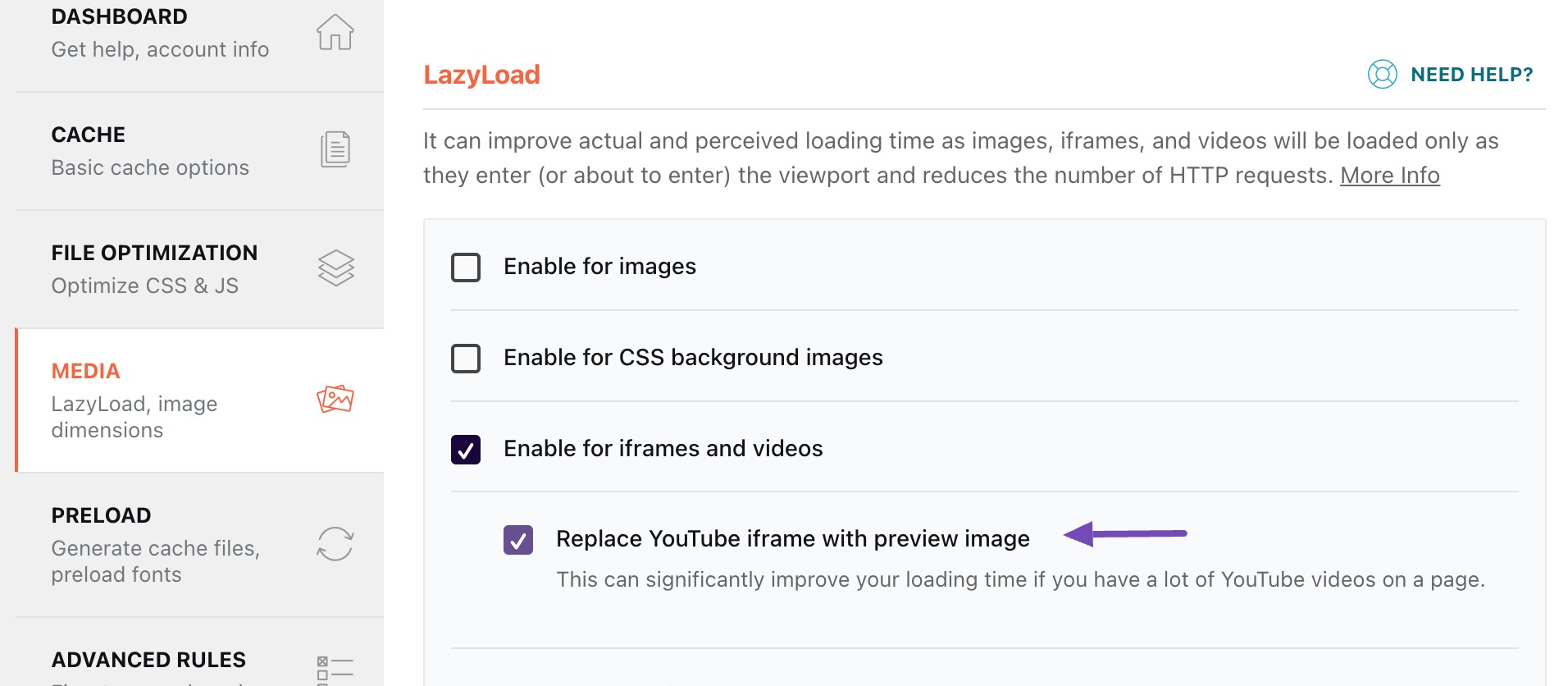
When embedding content on your page, refrain from loading it if it’s not currently in use. For instance, it’s inefficient to load YouTube videos if the user has no intention of watching them.
In such a case, you can use the WP Rocket plugin to replace any YouTube iframe with a thumbnail image. By doing so, the iframe tag will load and play the video only after a user clicks the thumbnail.
Minimize Presentation Delay
Ensure DOM size remains minimal. Rendering tasks scale with DOM size and updating a large DOM for every user interaction can strain the browser. Additionally, a large DOM increases the time required to render the initial state of a page.
Avoid HTML rendering via JavaScript. While using JavaScript for rendering parts of HTML is common, rendering large HTML chunks with JS significantly impacts rendering performance, leading to presentation delays during user interactions.
4.3 Best Practices for Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS)
Optimizing for Cumulative Layout Shift involves thoughtful practices such as reserving space for dynamic content, fine-tuning font rendering, and using layout-friendly animations.
Reserve Space for Images, Videos, Iframes
To prevent unexpected layout shifts, allocate proper dimensions for images, videos, and iframes.
By specifying the height and width attributes, the browser reserves the necessary space during page loading, reducing the likelihood of content displacements and contributing to a more visually stable user experience.
Optimize Fonts
Optimizing fonts is crucial for minimizing CLS.
Ensure that font sizes and styles are defined accurately in your CSS, avoiding sudden changes during rendering.
By specifying fallback fonts and using font-display properties, you enhance the predictability of text rendering, reducing layout shifts associated with font loading.
Refer to our dedicated tutorial on changing font sizes in WordPress.
Use Animations That Don’t Trigger Layout Changes
When incorporating animations, choose techniques that avoid triggering layout changes.
CSS animations and transforms, for example, often result in smoother transitions without affecting the document flow.
5 Wrapping It Up
Mastering Core Web Vitals is not just a technical pursuit; it’s a commitment to delivering unparalleled user experiences.
We’ve discussed the intricacies of LCP, INP, and CLS, offering actionable insights for optimization in this post.
Armed with knowledge, strategies, and a dedication to user-centric excellence, it’s time for you to embark on a journey to create web experiences that meet and exceed expectations.
If you like this post, let us know by Tweeting @rankmathseo.