When you’ve worked hard to build your website’s rankings, the last thing you want is someone trying to tear it all down. That’s where negative SEO comes in.
Negative SEO isn’t about mistakes you make; it’s about harmful tactics used by others to sabotage your site’s visibility in search engines.
From spammy backlinks to fake reviews, these attacks can come in different forms, and if you don’t know how to spot them early, they can slip under the radar.
In this post, we’ll discuss everything you need to know about negative SEO. So, without any further ado, let’s get started.
Table Of Contents
1 What is Negative SEO?
Negative SEO happens when someone tries to hurt a website’s rankings on purpose by using shady or harmful tactics. Instead of working on their own site, they attack another site to make it look bad in the eyes of search engines.
These attacks can take different forms, like building thousands of spammy backlinks to your site, copying your content and publishing it elsewhere, hacking into your site, or even spreading false information about your brand.
Imagine this: you’re running a blog that’s steadily climbing in rankings. Suddenly, a competitor creates hundreds of low-quality links pointing to your site. To Google, it looks like you’re engaging in spammy link building, and your rankings start to drop, even though you had nothing to do with it.
The main goal of negative SEO is simple: to get search engines to penalize the targeted website or make it appear less trustworthy to visitors like you.
2 How to Spot Negative SEO
If you want to protect your site, you first need to know how to recognize when something suspicious is happening. Here are some signs you should watch for:
- Sudden Drop in Rankings: If your website suddenly loses positions in search results without any changes on your end, it can mean someone is trying to harm your rankings.
- Unusual Backlink Profile: Check your backlinks regularly. If you notice a flood of spammy links from irrelevant or low-quality sites, that’s a red flag. For example, if you run a travel blog but suddenly get hundreds of backlinks from gambling or adult sites, that’s not normal.
- Duplicate Content Across the Web: If your blog posts or product descriptions start showing up word-for-word on multiple other sites, it may be a case of content scraping, someone copying your content to confuse search engines.
- Fake Reviews or Negative Mentions: Keep an eye on your brand name. If you start seeing fake negative reviews or misleading forum posts about your site, it might be part of a negative SEO attack.
- Website Speed or Security Issues: Hacking is another tactic. If your site suddenly slows down, shows strange code, or gets flagged for malware, it could be a sign that someone has tampered with it.
The key is to monitor your site’s health regularly, check your backlinks, keep an eye on rankings, and use tools like Google Search Console for alerts. The sooner you notice something unusual, the quicker you can take action.
3 How to Avoid and Fix Common Types of Negative SEO Attack
Negative SEO can take different forms, and knowing how to deal with each one is key to keeping your site safe. Below, I’ll walk you through the most common types of attacks, how to prevent them, and what to do if you notice them happening to your website.
3.1 Spammy Link Building
Attackers often create thousands of low-quality or spammy backlinks pointing to your website. These links usually come from irrelevant, low-authority, or spam-ridden websites. Their aim is to make Google believe you’re engaging in shady link-building practices.
How to avoid it:
- Keep an eye on your backlink profile regularly using tools like Google Search Console, Ahrefs.
- Set up email alerts (many SEO tools allow this) so you know the moment there’s a sudden spike in backlinks.
- Focus on building a natural backlink profile with quality, relevant links, so a few bad ones don’t outweigh the good.
How to fix it:
Tools like Google Search Console, Ahrefs, etc., can help pinpoint spammy or low-quality backlinks, which often originate from irrelevant or suspicious sources.
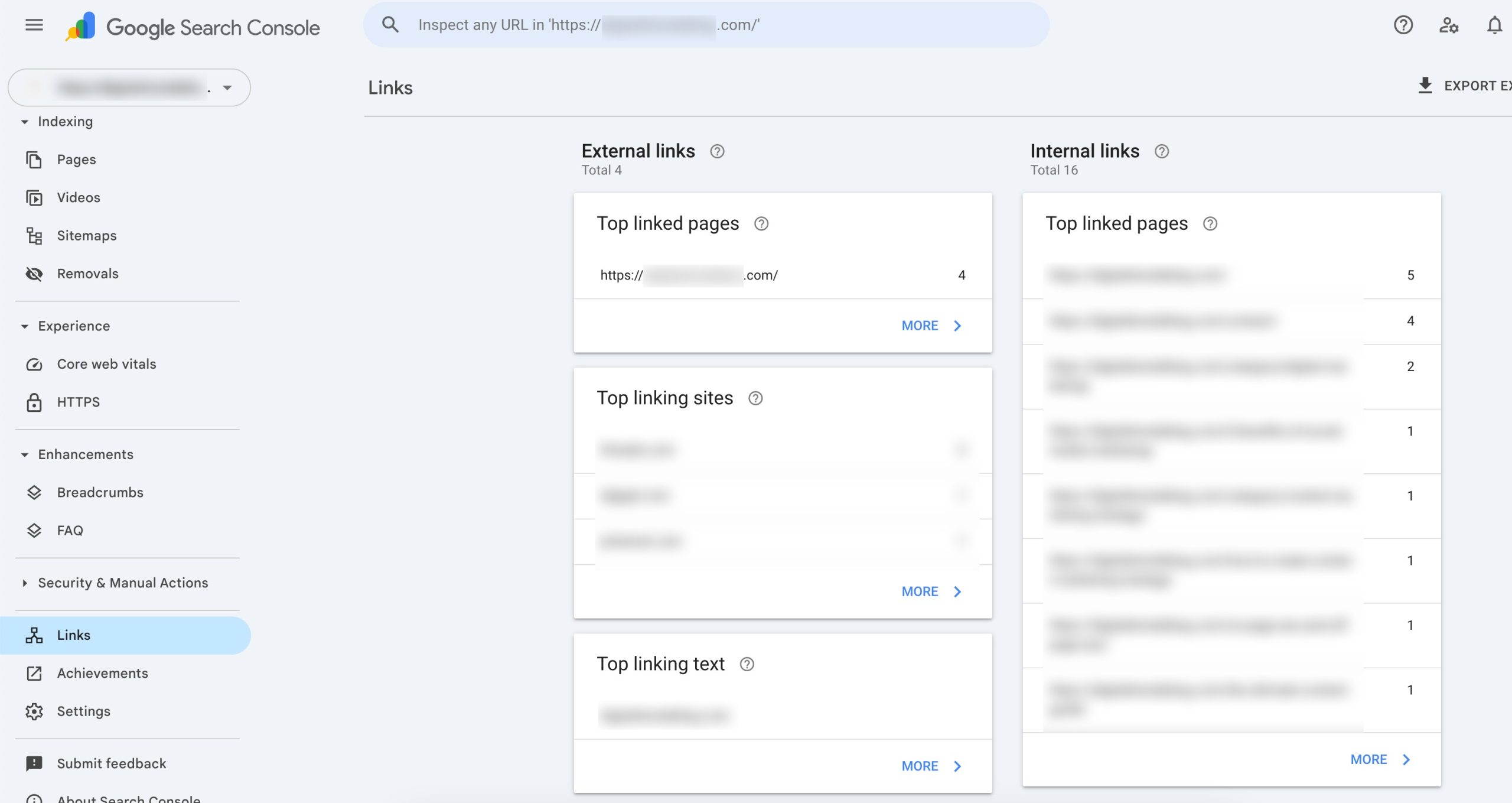
Creating a disavow file is necessary for those backlinks that cannot be manually removed.
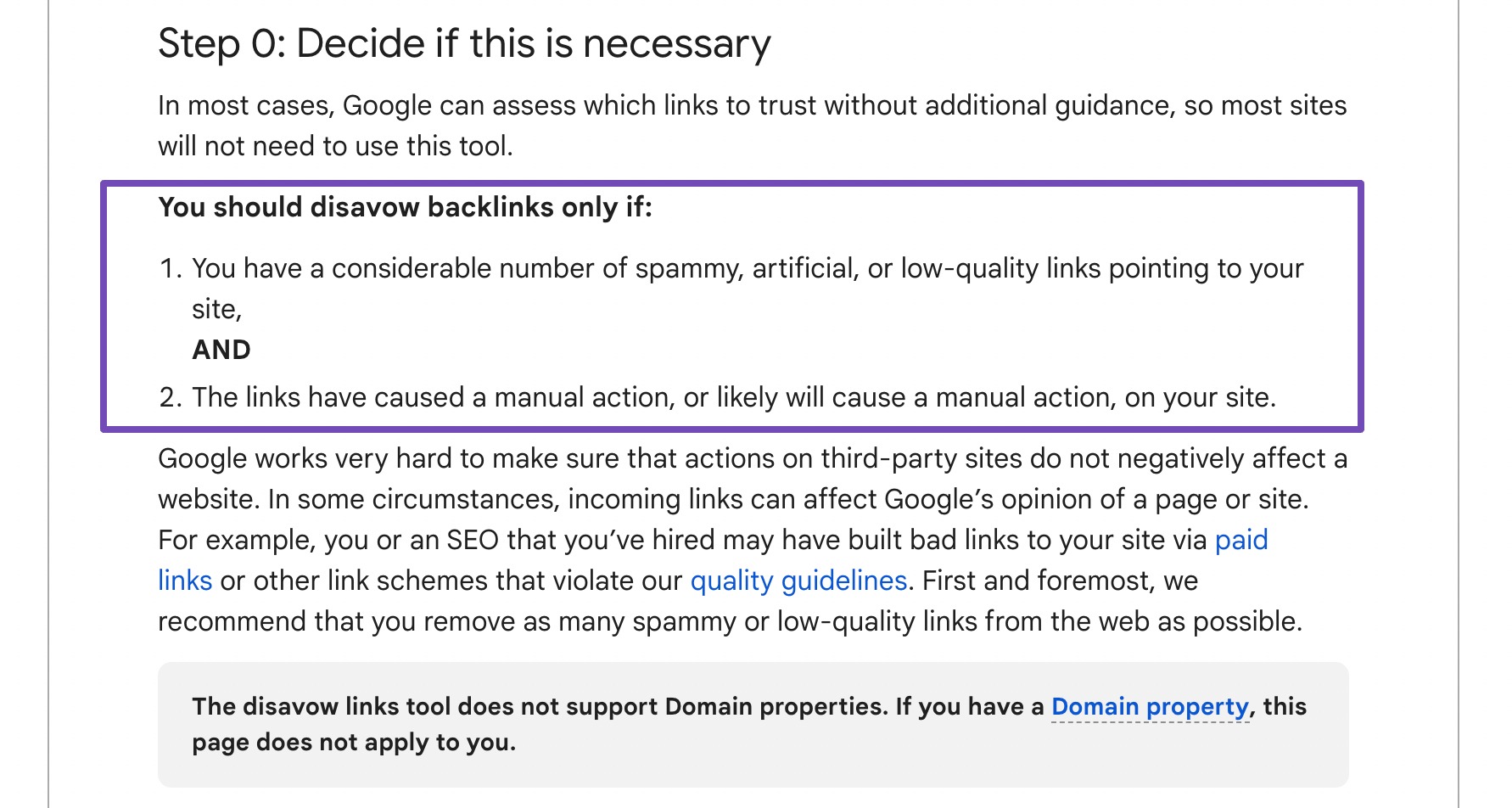
This file contains the URLs or domains of the remaining harmful backlinks and is then uploaded to Google’s Disavow Links tool in Google Search Console, which indicates that Google should not consider these links when evaluating the site’s ranking.
3.2 Content Scraping and Duplication
Content scraping means copying content from the target website and publishing it on other websites without permission. This can result in duplicate content issues, causing search engines to devalue the original site’s content and potentially penalize it for plagiarism.
How to avoid and fix it:
To avoid and fix content scraping, you first need to identify instances where your content has been scraped.
If you suspect that some of your URLs may have been affected by content scraping, you can verify their status in the Google Search Console. Look for a Google-selected canonical. You can find it by pasting the URL into the Google Search Console address bar.
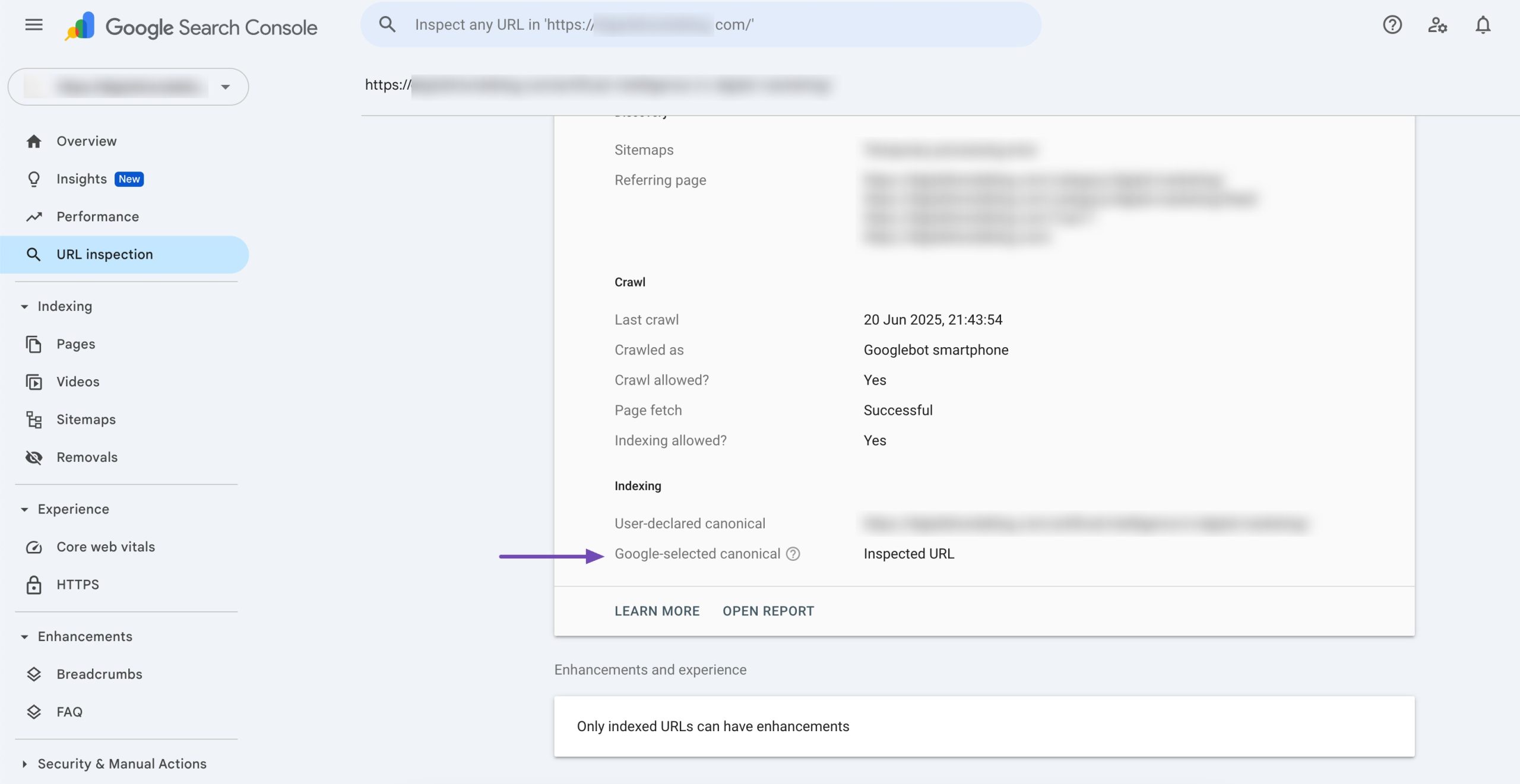
You’ll want to see the Inspected URL there. This indicates that Google considers the inspected URL as the most authoritative version of the content.
If you see another internal URL there, you have a duplicate content issue. If you see an external URL there, it’s likely a sign of negative SEO.
This is time-consuming if you have multiple pages. You can then use tools like Copyscape that’ll help you find websites that have copied your content. Once you’ve identified the scraped content, you can take several actions to address the issue.
Firstly, you can reach out to the website owner and request that they remove the copied content or give proper attribution with a link back to your original source.
If contacting the website owner doesn’t work or if you’re dealing with multiple instances of scraping, you can submit a Digital Millennium Copyright Act (DMCA) takedown request to the web host or search engines.
3.3 Hacking and Malware Injection
Hackers may inject malicious code into your website, redirect users to harmful sites, or place spammy links on your pages. If search engines detect malware, they may blacklist your site.
How to avoid it:
- Keep your website platform, plugins, and themes updated.
- Use strong passwords and two-factor authentication.
- Install a web application firewall (WAF) and reliable security plugins.
- Regularly back up your website so you can restore it quickly if attacked.
- Make sure your site runs on HTTPS. An SSL certificate not only protects your visitors’ data but also prevents attackers from exploiting unsecured connections.
How to fix it:
To check if you have any security issues, navigate to the Security issues tab in Google Search Console. If there are no security issues, you’ll see the message below.
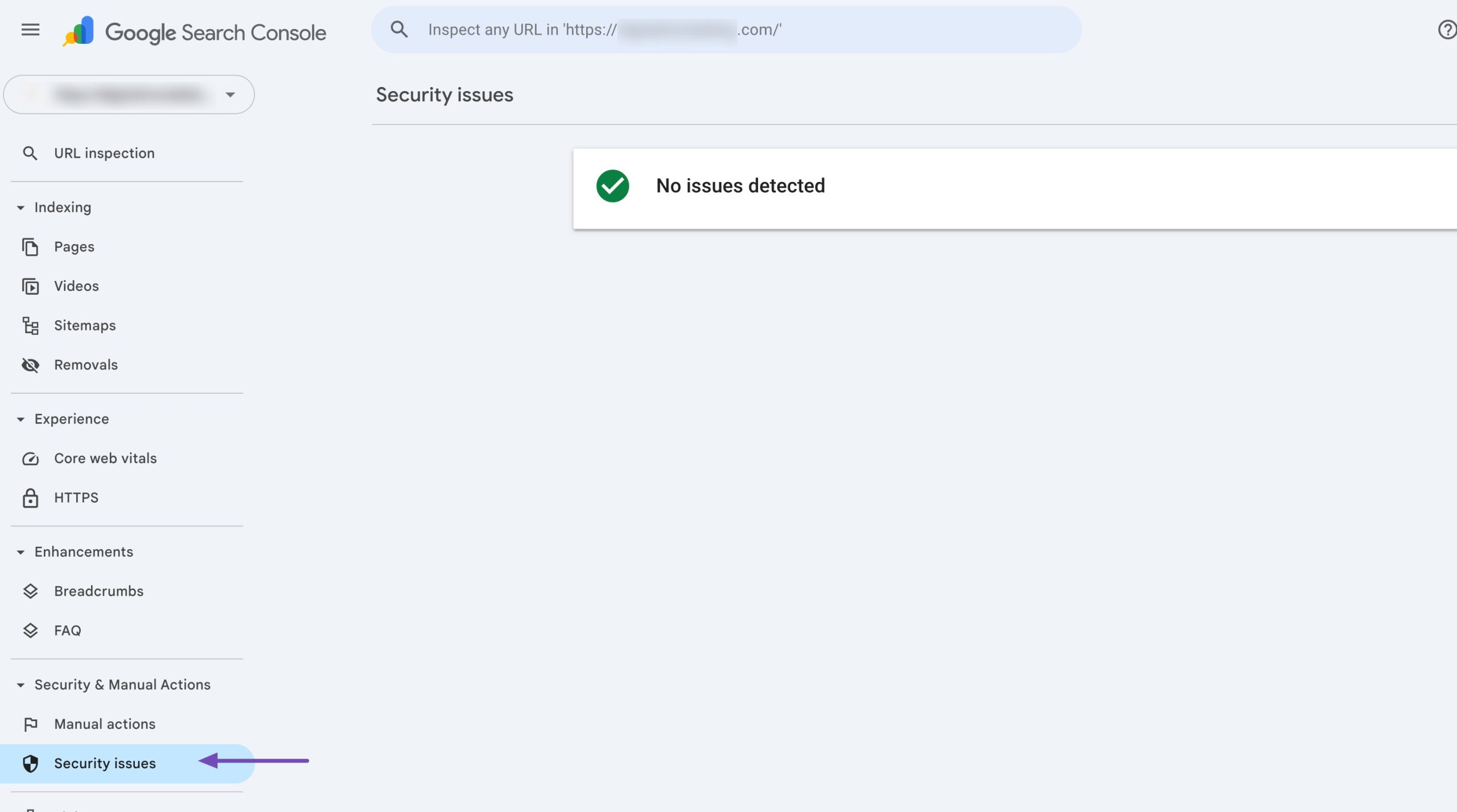
If there are any security issues, you need to fix them immediately.
Ensure that your website’s software, including CMS (e.g., WordPress, Joomla) and plugins, are up to date. Remove any malicious files and clean your database. Restore from a clean backup if needed.
Refer to our dedicated tutorial on securing a website to keep your website secure and protected from threats.
3.4 Fake Reviews
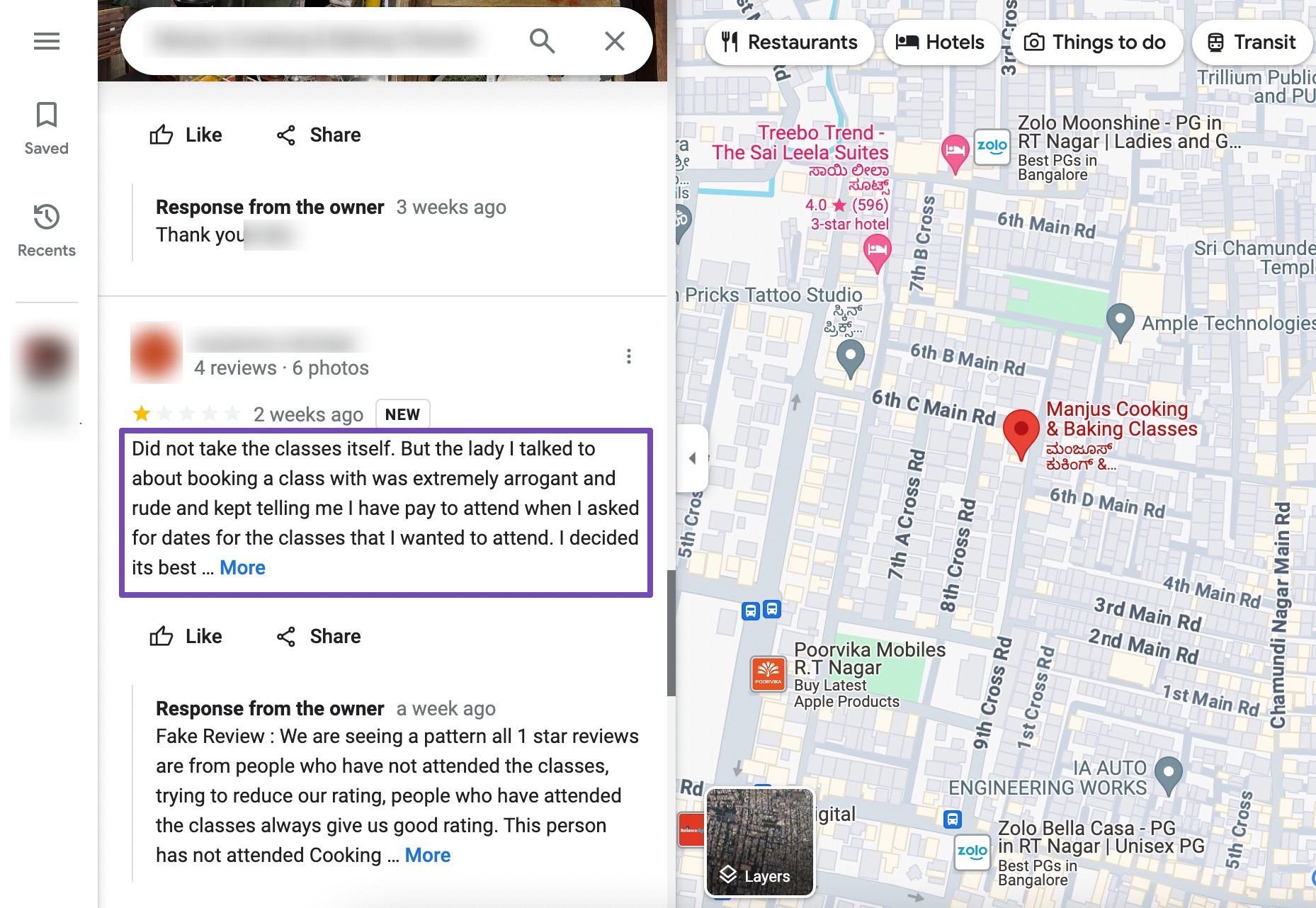
Negative SEO attackers may leave fake negative reviews or ratings on review platforms, business directories, or social media profiles associated with the target website. These fake reviews can damage the website’s reputation and credibility, potentially losing trust and customers.
Google’s rich snippets can display ratings and review metrics directly in the SERP, grabbing audiences’ attention and influencing their perceptions positively or negatively.
If the audience encounters poor review ratings for you business in the SERPs, it can have a negative influence on their purchasing decisions.
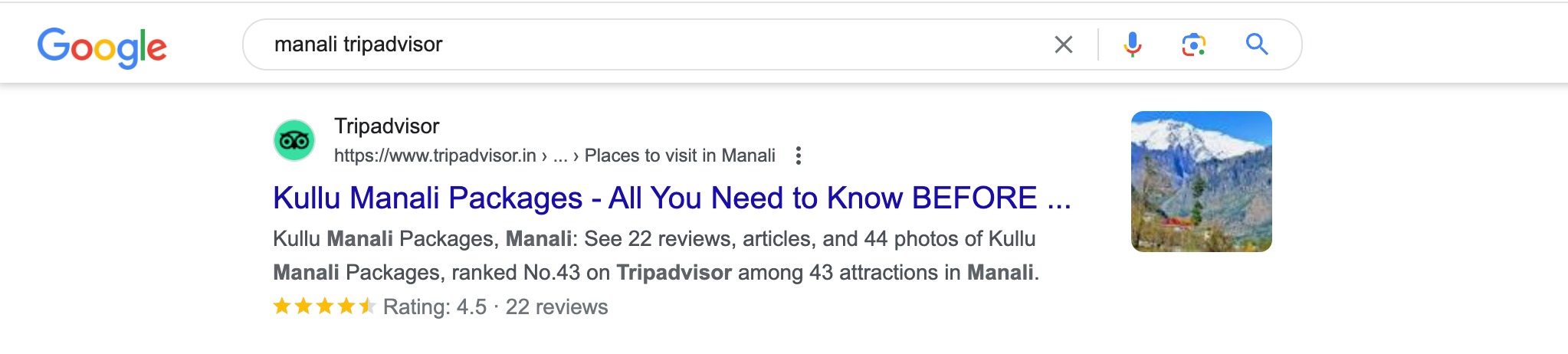
For local businesses like restaurants, customers often research them on platforms such as Google Business Profile, Yelp, TripAdvisor, and other local review services.
How to avoid it:
- Monitor your online reviews regularly. Set up alerts for your brand name using Google Alerts.
- Encourage real customers to leave genuine reviews. A steady flow of authentic reviews can dilute the impact of fake ones.
- Respond politely to all reviews, positive or negative, to show customers you care.
How to fix it:
If you come across fake reviews on review platforms, it’s important to report them. This is used to report reviews that are found in Maps listings.
However, these platforms might not remove them right away since the process can be slow. If the problem is urgent, try to get in touch with someone from the review platform. Provide evidence when possible; if the reviewer was never a customer, mention it.
3.5 Smear Campaigns
Smear campaigns are another type of negative SEO that involves spreading false or damaging information about a business or individual to harm their reputation and credibility.
These campaigns can take various forms, such as posting negative reviews, spreading rumours, or creating fake social media profiles to discredit the target.
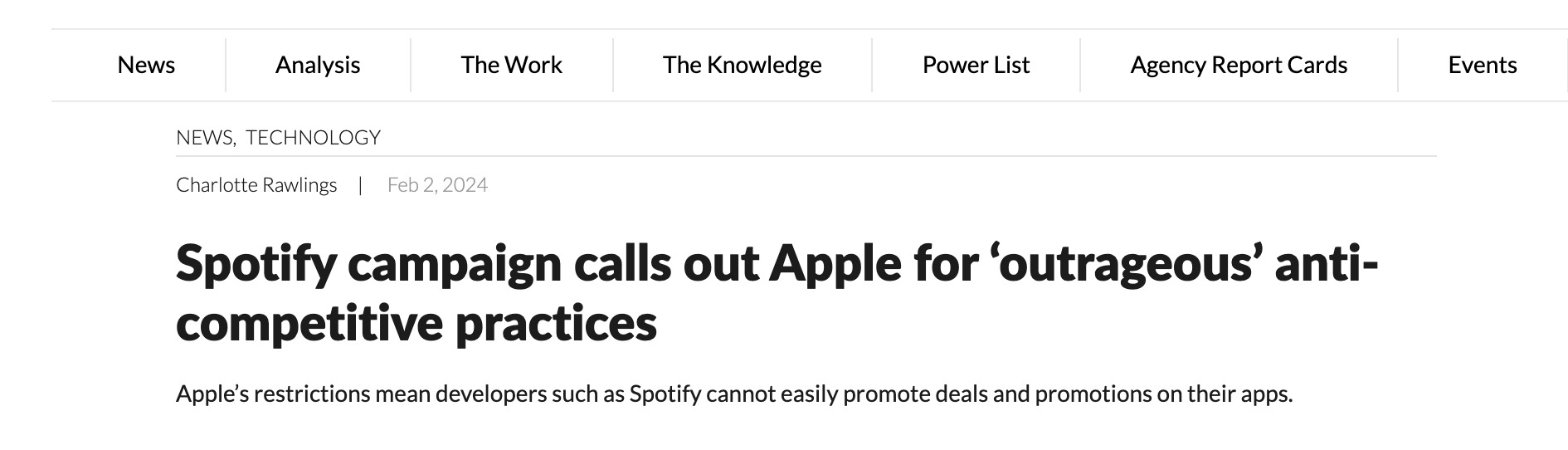
For instance, in 2019, Spotify filed a complaint with the European Commission, causing Apple of anticompetitive behaviour by unfairly promoting its own music streaming service, Apple Music, and restricting rivals like Spotify.
How to avoid and fix Smear Campaigns:
Regularly monitor online mentions of your business or personal brand across various platforms, including search engines, social media, and review sites. This will help you identify any negative content or campaigns targeting you.
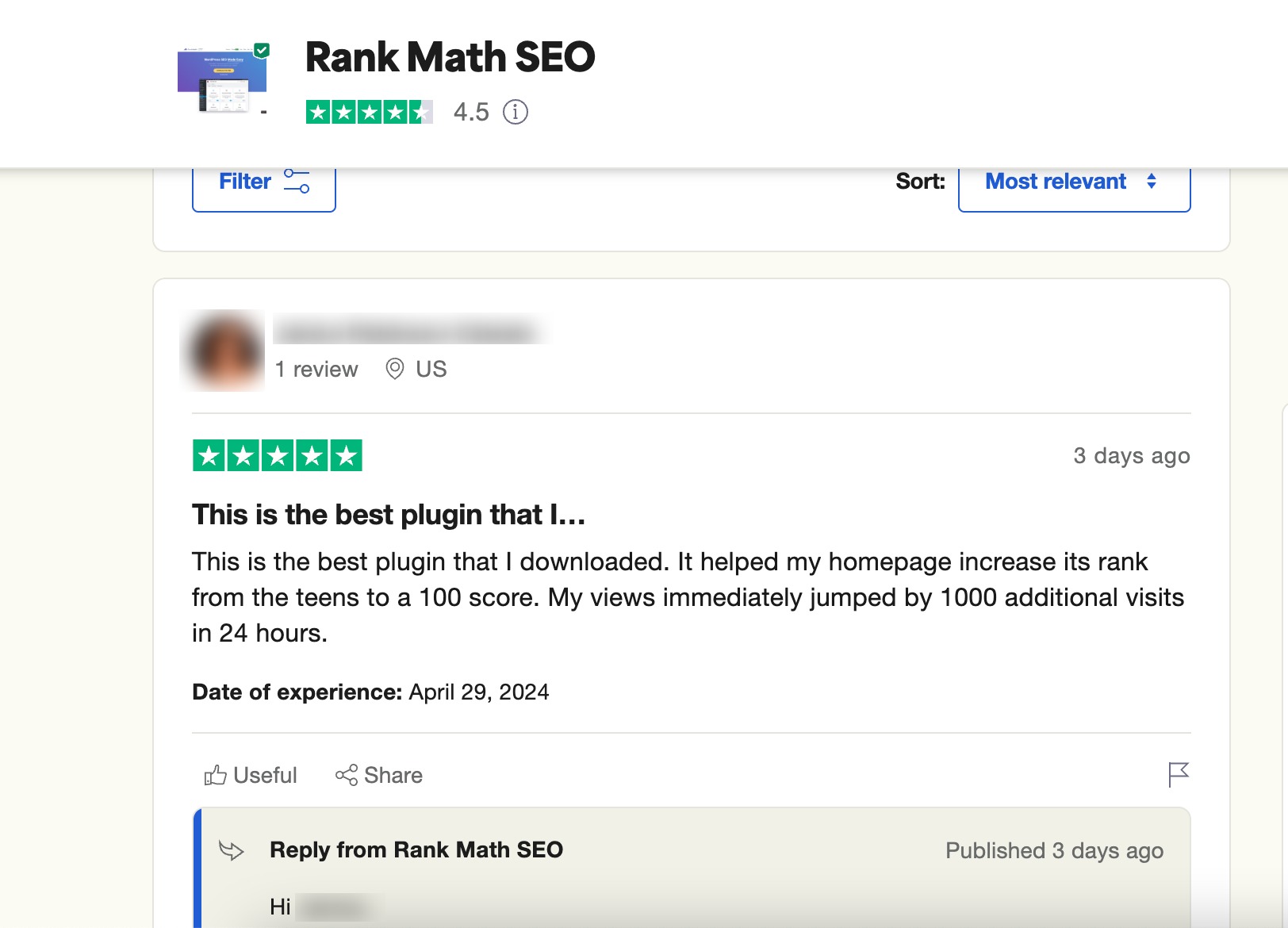
If you come across fake reviews or defamatory content, don’t ignore it. Respond professionally, provide evidence to counter the false claims, and reach out to the platform to request removal if the content violates their policies.
Publish positive content consistently: blog posts, testimonials, case studies, and social proof. This helps push down negative content in search results and makes smear campaigns less effective.
3.6 Unauthorized Hotlinking
Hotlinking, also known as inline linking or leeching, is a negative SEO tactic where someone links directly to images or other multimedia files hosted on your website from their own website, without your permission.
This can consume your website’s bandwidth and resources, leading to increased server costs and potentially slowing down your website’s performance.
How to avoid it:
You can stop most cases of hotlinking before they become a problem by blocking outside websites from directly linking to your files. One effective way is to update your .htaccess file with rules that prevent unauthorized access.
For instance: You can prevent hotlinking by adding the below code to your .htaccess file that blocks external websites from linking to your images.
RewriteEngine on
RewriteCond %{HTTP_REFERER} !^$
RewriteCond %{HTTP_REFERER} !^https://(www\.)?samplesite.com/.*$ [NC]
RewriteRule \.(gif|jpg|jpeg|mp3|png|pdf|zip)$ - [F]How to fix it:
If you suspect someone is already hotlinking your content, you should:
- Identify the source: Use server logs or tools like Google Search Console to see which websites are making repeated requests for your media files.
- Block offenders: Update your .htaccess file or security plugin to block requests from the specific domains abusing your content.
- Replace hotlinked images: Some site owners replace hotlinked files with a watermark or a different image. This can discourage misuse while protecting your brand.
- Contact the webmaster: In cases of repeated abuse, you can reach out directly or file a DMCA takedown request if necessary.
4 Frequently Asked Questions
How can I tell if my website is being targeted by negative SEO?
Signs of negative SEO include sudden drops in rankings, unusual backlink profile changes, an increase in spammy traffic, Google penalties without cause, and other suspicious activity.
What should I do if my website is targeted by negative SEO?
If your website is targeted by negative SEO, identify the source of the attack, document evidence, submit a disavow file to Google, file a reconsideration request if penalized, and seek legal action if necessary.
Can negative SEO affect my website’s reputation?
Yes, negative SEO can damage your website’s reputation by manipulating search engine rankings, spreading false information, or posting fake reviews.
How long does it take to recover from negative SEO?
Recovery from negative SEO can vary depending on the attack’s severity and the recovery efforts’ effectiveness. It may take weeks or even months to fully recover.
Should I be concerned about negative SEO if my website is small?
Yes, any website can be targeted by negative SEO, regardless of its size. It’s essential to stay vigilant and take steps to protect your website.
5 Conclusion
Negative SEO can feel overwhelming, but the good news is you’re not powerless against it. By staying alert, protecting your website, and taking quick action when you notice suspicious activity, you can minimize the risks and keep your rankings safe.
Remember, search engines want to reward genuine websites like yours, not those trying to cheat the system. If you stay proactive and consistent, you’ll not only protect your site from negative SEO but also strengthen your long-term growth.
If you like this post, let us know by tweeting @rankmathseo.
