What is SEO?
SEO, short for Search Engine Optimization, is the process of improving your website’s visibility in search results.
When people talk about SEO, they usually refer to Google since it has the lion’s share of the search market. So, to get better at SEO, you need to understand what Google wants and see how to tailor your content towards that.
SEO tactics that follow the guidelines specified in Google Search Essentials are called white hat SEO. It contrasts with black hat SEO, which refers to SEO tactics intended to manipulate search engines.
Nested between white and black hat SEO is grey hat SEO, which incorporates tactics used in white and black hat SEO.
Importance of SEO
SEO is a great way to get traffic to your site. This traffic is free, and you don’t have to pay anything.
An alternative to SEO is paid advertising, also called pay-per-click (PPC). PPC ads appear at the top of search results. On Google, they are marked as “Sponsored.”
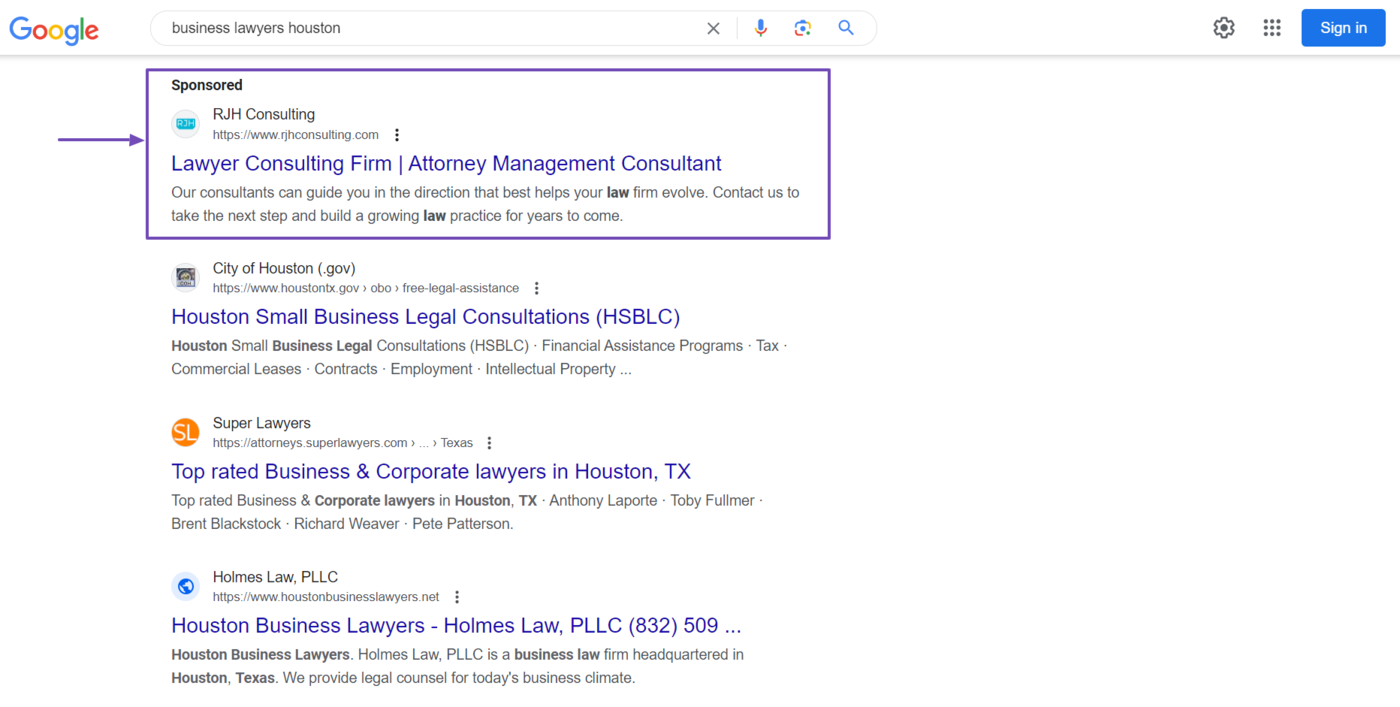
PPC ads are usually more expensive than SEO for the same traffic. They are also unscalable, meaning traffic stops flowing when you stop paying for ads. For many businesses, PPC ads are also unsustainable as the main source of traffic.
SEO, on the other hand, is scalable and sustainable. The more you optimize your site and content, the higher the search results you get and the more traffic you receive.
How Search Engines Work
Google follows a three-step process to determine whether to display your content in response to a search query. The steps are:
- Crawling
- Indexing
- Serving
We will now address the steps one by one. However, you should know that many pages do not make it beyond each of the three steps.
Crawling
Search engines use computer programs called web crawlers or web spiders to search the internet for fresh content.
These crawlers seek out new sites and visit previously crawled sites to see what new content they have published. The crawlers also visit previously crawled content to see whether they have been updated since their last visit.
If you run a site, you typically do not need to inform Google of your site or content, as Google has a sophisticated system for finding new sites and content.
Indexing
Indexing refers to the process of adding and organizing crawled content to a database. This database contains every content the search engine wants to display in search results.
For example, when you enter a search query into Google, Google does not display the actual webpage in real time. Instead, it displays the one saved to its database.
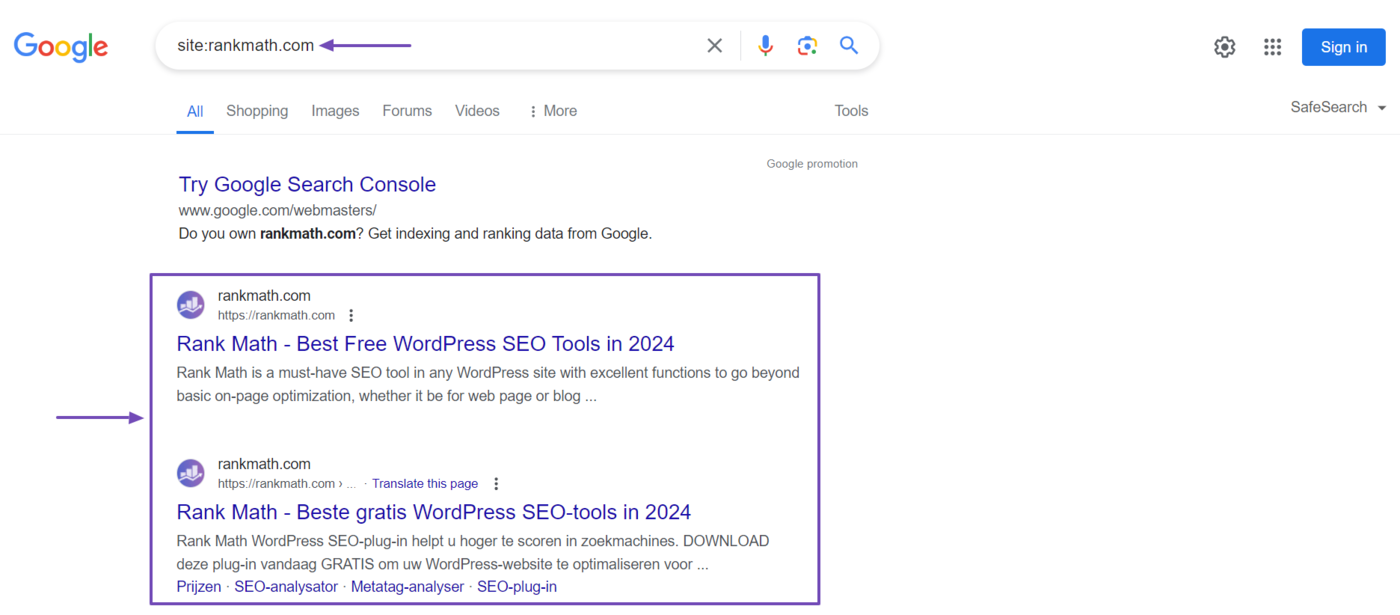
You can confirm whether Google has indexed your site or page using the site: search operator followed by the site or page URL.
For example, site:rankmath.com will bring up our site on search results pages. This indicates Google has found and indexed our site.
Serving
Serving is the process of presenting the results from the database to a searcher. Google typically returns high-quality results relevant to the search query entered by the visitor.
A search query is the term a visitor enters into a search engine. For example, a fitness enthusiast seeking information about yoga would enter a search query like “What is yoga” into Google.
In response, Google goes through its database and displays some relevant results. The page where Google displays the results is called the search engine results page (SERP).
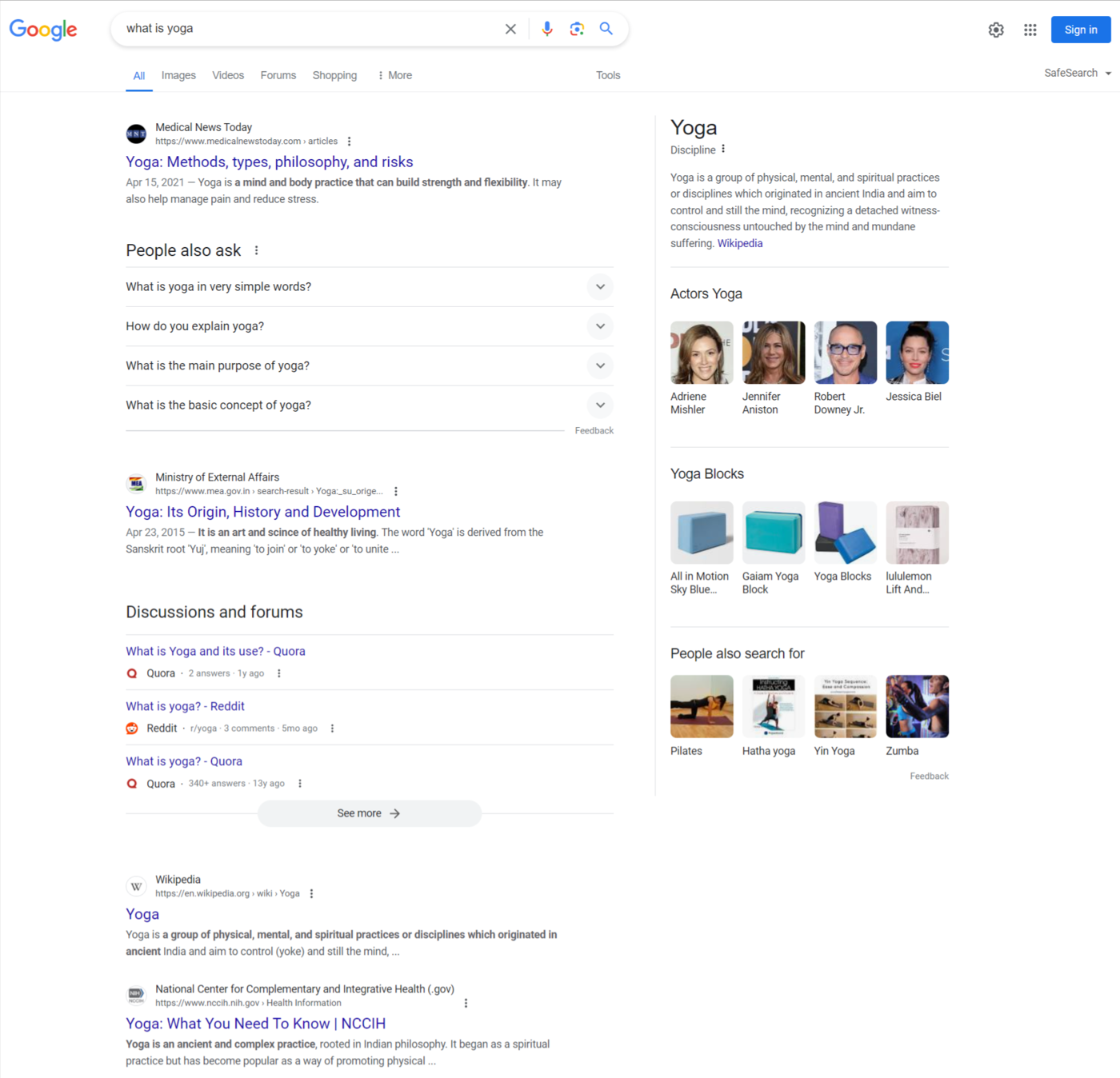
The best results, in terms of quality and relevance, are on page one, with the most relevant and high-quality ones at the top of the page.
Google uses complex computer programs called algorithms to decide where content appears on the search engine results page. Algorithms are a set of rules and instructions used to solve a problem.
In this case, the problem is deciding the most relevant and high-quality results to display in response to a search query.
How SEO Works
Search engines want to return high-quality content relevant to the search query entered by the searcher.
So, to increase the chances of your content appearing on search results pages, you should ensure it satisfies the metrics Google uses to determine its quality and relevance.
Typically, you will meet these metrics if you do your SEO correctly. SEO itself is split into four types:
- On-page SEO
- Off-page SEO
- Technical SEO
- Local SEO
We will now briefly discuss them one after another.
On-Page SEO
On-page SEO, also called on-site SEO, refers to the SEO efforts on your site. This includes SEO activities like:
- Including title and header tags to your content
- Adding meta tags and structured data to your content
- Adding internal and external backlinks to your content
- Compressing your images and optimizing them with the appropriate titles and alt text
- Performing keyword research to uncover commonly searched keywords along with their search intent
- Creating high-quality content for people rather than for search engines
- Optimizing your URLs so that it is short, clear, and descriptive
Off-Page SEO
Off-page SEO, also called off-site SEO, refers to the SEO efforts on sites other than yours. This includes SEO activities like:
- Receiving high-quality follow backlinks from relevant and authoritative sites within your niche or industry
- Optimizing your content to increase its possibility of being shared on social media platforms
- Receiving reviews, recommendations, and mentions from other sites.
Technical SEO
Technical SEO is the practice of improving the systems that allow human visitors to access your site and search engine crawlers to crawl, index, and serve your content on search results pages.
Technical SEO includes:
- Selecting a user-friendly permalink for your site
- Using noindex, nofollow, and disallow tags to control the behavior of search engines
- Using sitemaps and robot.txt files to assist search engines in discovering your content
- Improving the structure of your site to make it accessible to humans and web crawlers
- Ensuring your site is mobile friendly and is well-formatted on all devices irrespective of their screen size
- Including canonical tags to your content so that search engines know the original version of your webpages
- Including Schema markup to your content so that search engines have extra information about your content
- Using breadcrumbs and splitting your content into categories and subcategories so that humans and search engines know your hierarchical structure and can easily navigate your site
Local SEO
Local SEO is the practice of optimizing your site and content to appear in search results for local queries.
Local queries are the search terms used by visitors seeking products and services from businesses within a particular location. Local SEO practices include:
- Setting up a Google Business Profile for your business and filling in the relevant business details
- Ensuring your Name, Address, and Phone Number (NAP) are consistent across the web
- Including your business data in Apple Maps and Bing Places
- Earning local business citations on local business directories
- Uploading your business details to your website
Those are the four types of SEO. In summary, if you want to appear on search results pages, you will want to:
- Perform keyword research to find out what people are searching for (on-page SEO)
- Create relevant and high-quality content that answers their questions (on-page SEO)
- Get backlinks to that content so that search engines know it is relevant and high-quality (off-page SEO)
At the same time, you want to improve your site’s crawlability, usability, and user experience.
Even with great content and lots of backlinks, your site may not appear on search results pages or rank as it should if it is slow, uncrawlable, or does not display properly on mobile devices.
This is where technical SEO comes into play.
In all, you should optimize your site and content for on-page, off-page, and technical SEO. If you want to appear in local search results for local queries, you should also optimize your site for local SEO.