What is Crawlability?
Crawlability is the ability of a search engine’s crawler to find, access, and crawl your site.
Crawlability is vital to SEO, as search engines need to crawl your site before indexing them. Only after indexing will your site become eligible to appear on search results pages.
Importance of Crawlability
Crawlability is crucial for sites that want to appear on search results pages. Getting clicks from search results pages is a three-step process involving:
- Crawling
- Indexing
- Serving
Crawling is the first step of that process. Content that cannot be crawled cannot be indexed or served on search results pages. So, if you want your content on search results pages, you must ensure that search engines can crawl them.
Factors Affecting Crawlability
Crawlability issues typically result from technical SEO issues arising from your site. Some issues that could prevent search engine crawlers from accessing and crawling your site are explained below.
1 Discoverability
Search engines need to discover a webpage to crawl it. So, you should ensure you have internal links pointing to all your pages. You should also include all the important pages you want on search results pages in your sitemap.
2 Nofollow Tags
Google does not follow links in URLs containing the nofollow tag. So, you should avoid using the tag in links you want Google to crawl. However, it is okay to include it in links you do not want search engines to crawl.
3 Robots.txt File
Your robots.txt file contains rules instructing search engines on how to crawl your site. You can use it to block search engines from crawling certain areas of your site. If you want search engines to crawl your site or specific parts of your site, then ensure you have not blocked them using the robots.txt file.
4 Inaccessible Webpages
Search engines may struggle to crawl gated content. If your content is locked behind a password or requires some form of authentication, it could become uncrawlable. To ensure that search engines can access and index your important pages, it is best to keep them open and accessible to all users.
5 XML Sitemap
The XML sitemap provides search engines with the URLs of the important content on your site. While search engines can find your content without a sitemap, they would rely on it to discover the links they did not find using other methods. So, make sure to include an XML sitemap on your site.
6 Content Quality
Search engines only want to crawl and index high-quality webpages. So, to ensure that they crawl your site, make sure to publish only high-quality content. Avoid thin content that is not helpful to visitors. You should also ensure to write for humans and not search engines.
7 Technical Issues
Multiple technical issues, including server issues, low page speed, broken links, and redirect chains, can prevent search engine crawlers from crawling your site. So, ensure your site works optimally to avoid crawlability issues.
How to Identify Crawlability Issues
You can identify crawlability issues using the Google Search Console. To get started, log into your Google Search Console account and head to Indexing → Pages.
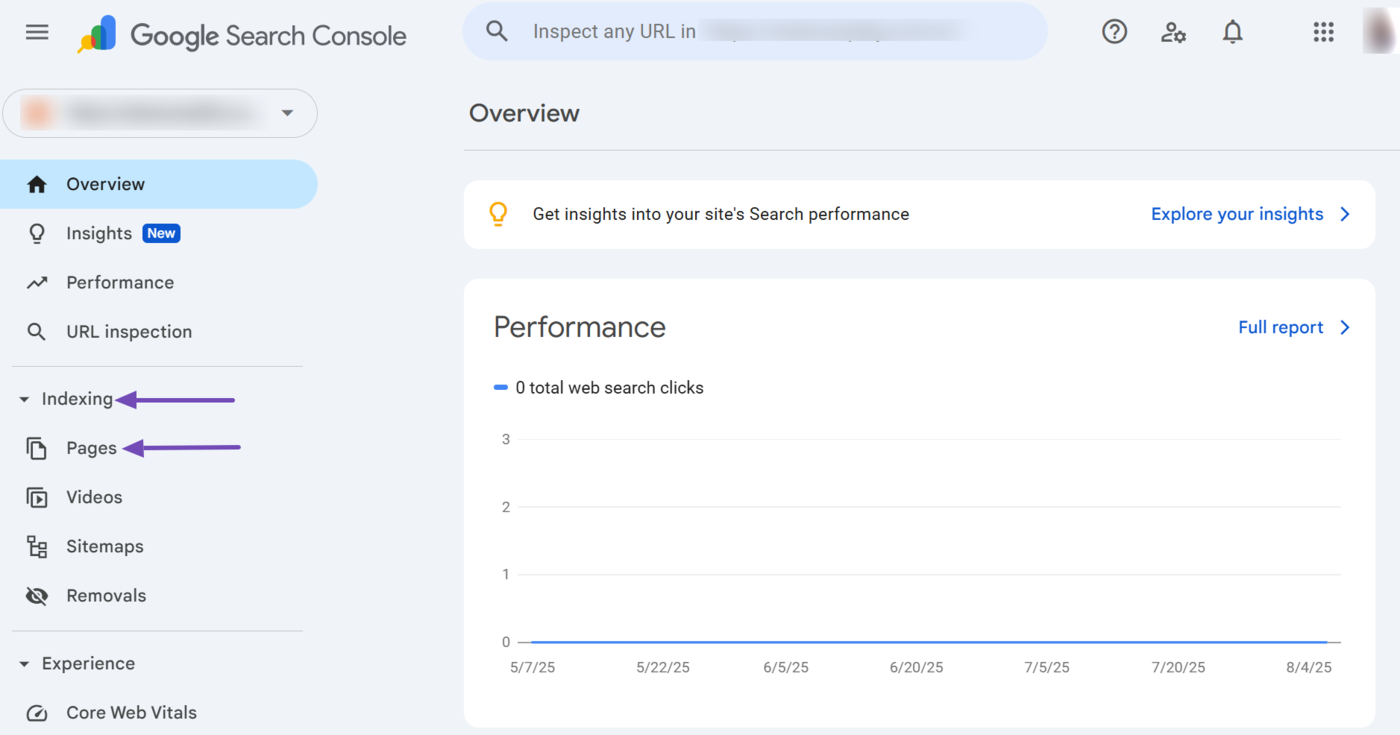
Once done, scroll down to the Why pages aren’t indexed field. You will be presented with the reasons Google cannot crawl certain pages on your site. Click on the reasons one by one.
In this example, we will click on Not Found (404).
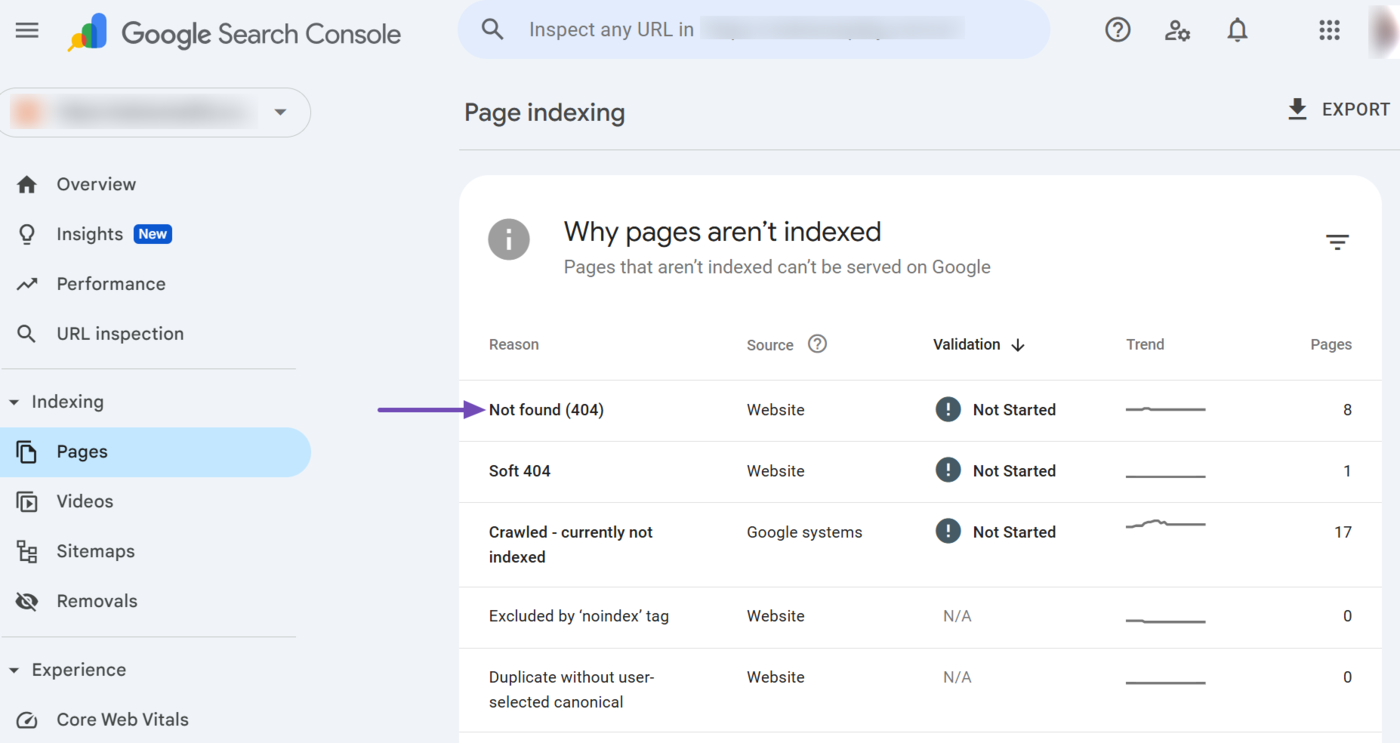
Then, scroll down to view the URLs that were not indexed. If you want these URLs on Google, then ensure to resolve the issue preventing Google from crawling and indexing the content.
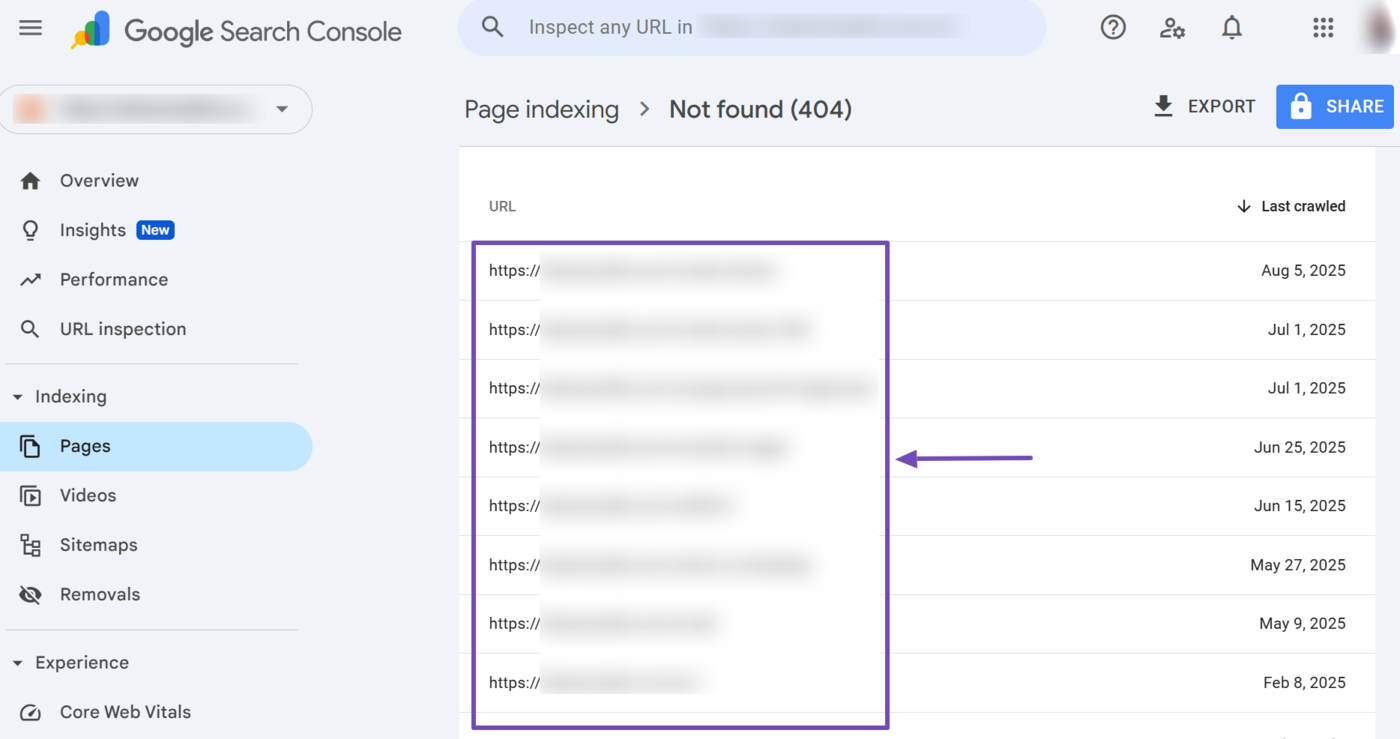
After fixing the URLs with that issue, scroll up to the top of the page and click Validate Fix.
You should also review your robots.txt file to ensure it does not contain rules preventing search engines from indexing pages you want on search results pages. Many sites have their robots.txt file at their domain name, followed by /robots.txt. For instance, example.com/robots.txt.
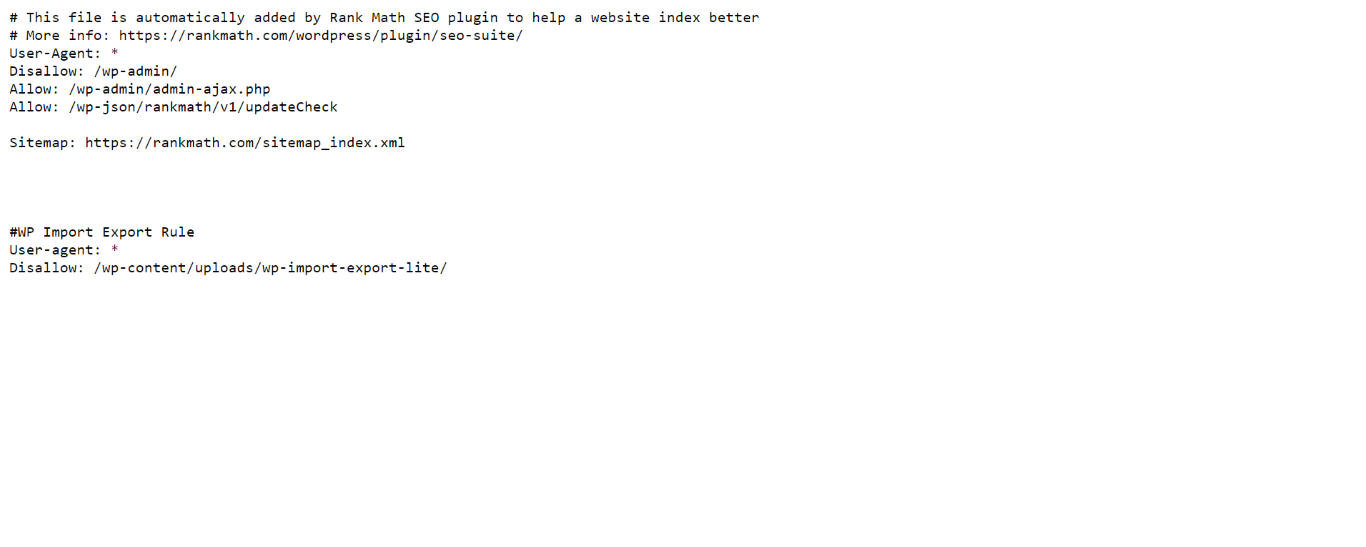
You should also review your sitemap to ensure it contains the URLs you want on search results pages. The sitemap should only contain canonical URLs.
Many sites have their sitemap at their domain name, followed by /sitemap.xml or /sitemap_index.xml. For instance, example.com/sitemap_index.xml.
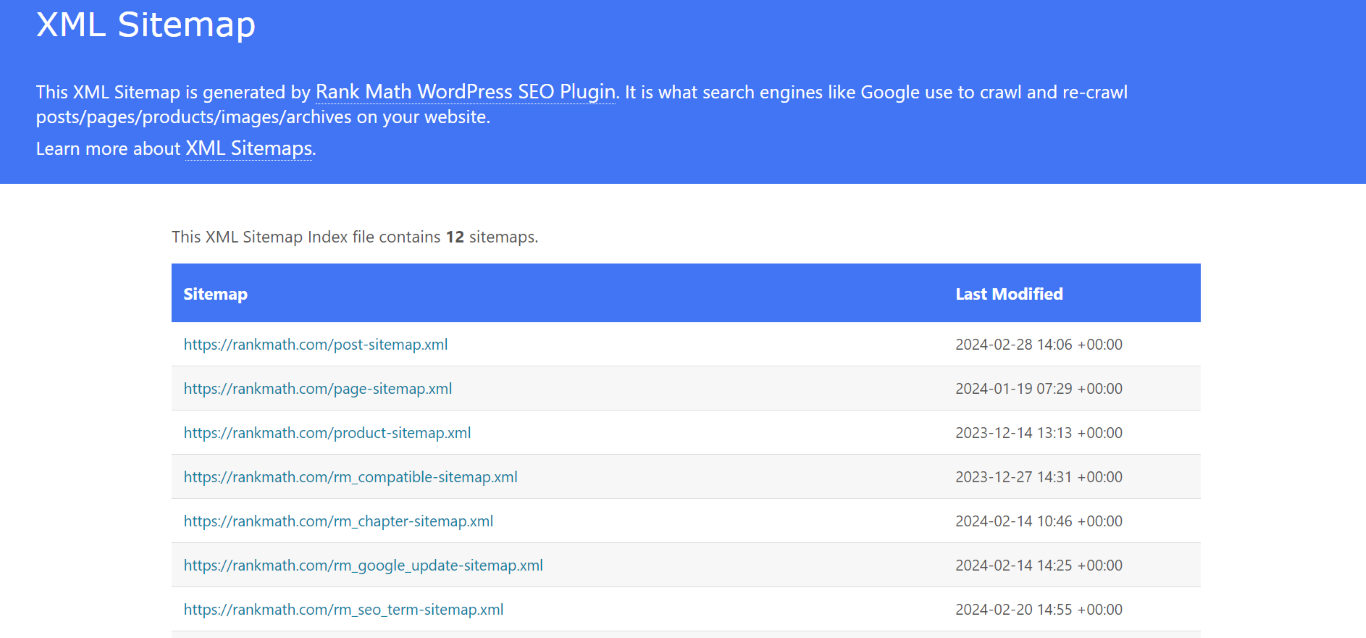
Crawlability issues may also be solved on a page-by-page basis. So, if a URL you want on Google is not on Google, review it to ensure it does not contain a noindex tag.