When it comes to boosting your website’s SEO, internal linking is one of the most powerful yet often overlooked strategies.
By strategically linking your pages together, you create a clear path for both users and search engines to follow. This not only helps visitors easily navigate your site but also distributes authority across your content, improving your chances of ranking higher in search results.
In this guide, you’ll learn everything you need to know about internal linking, from the basics to advanced techniques, so you can strengthen your site’s structure, enhance user experience, and maximize your SEO potential.
So, without any further ado, let’s get started.

Table Of Contents
1 Understanding Internal Linking
Let us now discuss internal links in detail.
1.1 What Are Internal Links?
Internal links are simply hyperlinks that connect one page of your website to another. For example, if you write a blog post about keyword research and link to another post on on-page SEO, that’s an internal link.

These links do more than just help your readers move smoothly from one page to another, they also play a vital role in your website’s SEO.
They guide both your audience and search engine crawlers through your site so every important page can be discovered and indexed.
1.2 Importance of Internal Linking for SEO
Internal linking isn’t just about user-friendly navigation, it’s a powerful SEO strategy.

By connecting related pages, you help search engines understand the context and relationship between your content. This improves how your pages are indexed and increases the chances of ranking higher in search results.
On top of that, internal links distribute link juice (or authority) across your website. This means even newer or deeper pages can gain more visibility and importance when linked strategically from high-authority pages.
1.3 Difference Between Internal and External Links
The difference between internal and external links lies in their destination.
Internal links connect one page of your website to another. For example, if you’re reading a blog post about keyword research and you link to another post on content optimization, that’s an internal link. These links make it easier for your audience to navigate your site and help search engines understand how your content is connected.
External links, on the other hand, point to pages on different websites. For example, linking to an industry study or a trusted news site is an external link. These links provide extra value to your readers by guiding them to credible outside resources.
Both types of links matter for SEO, but internal links are especially powerful for shaping how your visitors move through your site and for building topical authority around your content.
1.4 How Search Engines View Internal Links
Search engines rely on internal links to understand how your website is structured and how your content is connected. When crawlers come across an internal link, they follow it to discover more pages, index them, and figure out how everything fits together.
By doing this, search engines learn which pages are most important, how they relate to each other, and what topics your site covers. When you use internal links strategically, you give search engines a clear structure, helping them prioritize the right pages and boosting your chances of higher rankings.
2 Benefits of Internal Linking for SEO
Internal links don’t just help search engines, they also make your site better for your visitors. Here’s how:
Improved User Experience
By linking related pages together, you guide your audience to more useful content. For example, if someone is reading a post about “on-page SEO” and you link to a guide on “keyword research,” they get extra value and stay engaged longer.
Enhanced Crawling and Indexing
Internal links make it easier for search engine bots to find and index your content. Without them, some of your pages might remain hidden.
Page Authority and Link Juice Distribution
Every link passes authority, often called “link juice.” When you link from high-authority pages (like your homepage or popular blog posts) to other important pages, you spread that authority across your site, helping more of your content rank well.
Reduction of Bounce Rates
When you point visitors to related content, they’re less likely to leave after viewing just one page. Internal links encourage them to keep exploring, which reduces bounce rates and signals to search engines that your site offers real value.
3 Strategies for Internal Linking
Now that you understand what internal links are and why they matter, let’s look at some proven strategies you can use to strengthen your internal linking.
3.1 Identify Pillar Content for Your Website
Pillar content is the foundational material covering broad topics within your niche or industry. These comprehensive pieces act as the cornerstone around other related content-building topic clusters.
These cornerstone pages show your expertise, help search engines understand your site’s structure, and guide your readers through a logical content journey.
Rank Math’s Pillar Content feature helps place the pillar/cornerstone articles at the top of the list of link suggestions.

3.2 Anchor Text Optimization
Anchor text optimization involves using descriptive and relevant keywords as the clickable text for your internal links. By including keywords that accurately represent the linked page’s content, you can provide your audience and search engines with clear context.
While optimizing anchor text is important, avoiding over-optimization is equally important. Strive for a natural and varied approach, ensuring the anchor text fits correctly within the surrounding content.
3.3 Link Placement
Where you place your internal links makes a big difference. Links in your navigation menu, in-content text, or call-to-action buttons all serve different purposes.
With the enhanced internal linking UI powered by AI Link Genius, the process becomes seamless inside the WordPress editor. Ensure that you’ve enabled the Link Genius module from your WordPress dashboard.
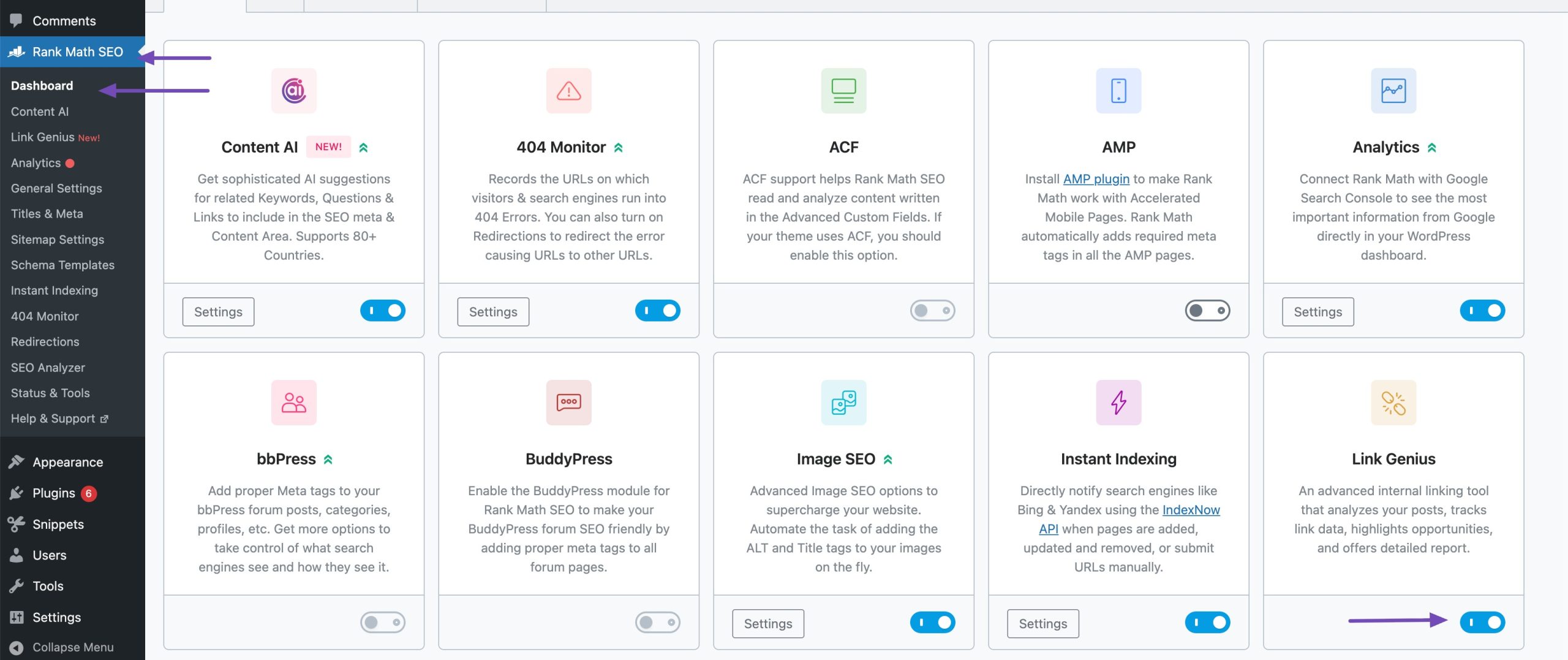
While writing a post, simply highlight any relevant text. Click on the Content AI icon, and in the drop-down a Generate Link option appears instantly.
Once selected, the AI analyzes your content and suggests the most relevant internal page to link to. This eliminates guesswork and ensures your links are contextually accurate.
The tool doesn’t just recommend a random page, it intelligently selects the most suitable target based on topical relevance and content relationships. This helps strengthen your site structure and improves SEO value with every link you add.
For example:
- On a blog, link from popular posts to related, in-depth guides.
- On an e-commerce site, link from your homepage to best-selling products or special offers.
By doing this, you create a clear hierarchy where your most important pages get the most visibility and authority.
3.4 Contextual Relevance
When you create internal links, aim for contextually relevant content. Linking to pages that naturally relate to the topic your audience is reading makes their experience richer and more informative.
For example, if you have a product page for digital cameras, you could link to posts about photography tips or camera accessories. This approach not only helps your visitors explore more content but also signals to search engines that your website covers the topic thoroughly and authoritatively.
Don’t force internal links. Only link when there’s a genuine, relevant connection between pages, as irrelevant links can hurt your SEO.
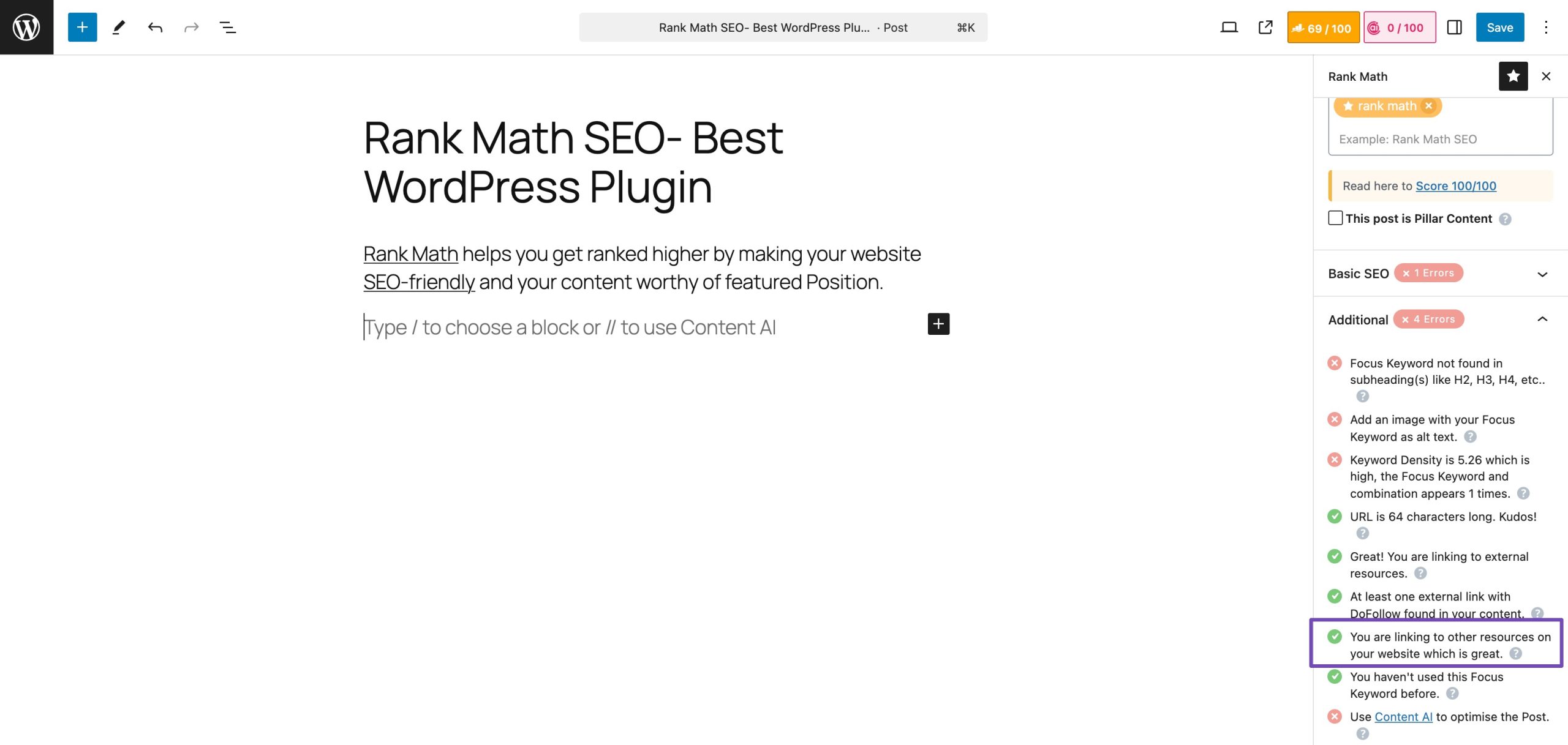
If you’re using Rank Math, it can check your posts in real time and notify you if internal links are missing, making it easy to enhance your on-page SEO.
3.5 Strategic Use of nofollow/dofollow Attribute
Not all links are created equal.
- Nofollow attributes tell search engines not to pass authority (or “link juice”) to the linked page. For example, if you allow user comments with links, applying nofollow ensures you don’t unintentionally boost every linked site.
- Dofollow links pass authority to the linked page, signalling to search engines that the content is valuable. For instance, linking from your homepage or high-value posts to a helpful guide gives it more SEO weight.
With Rank Math’s AI Link Genius, you can easily identify nofollow attributes that might be hurting your SEO. To do so, navigate to Rank Math SEO→ Links and switch to the Links tab, as shown below.
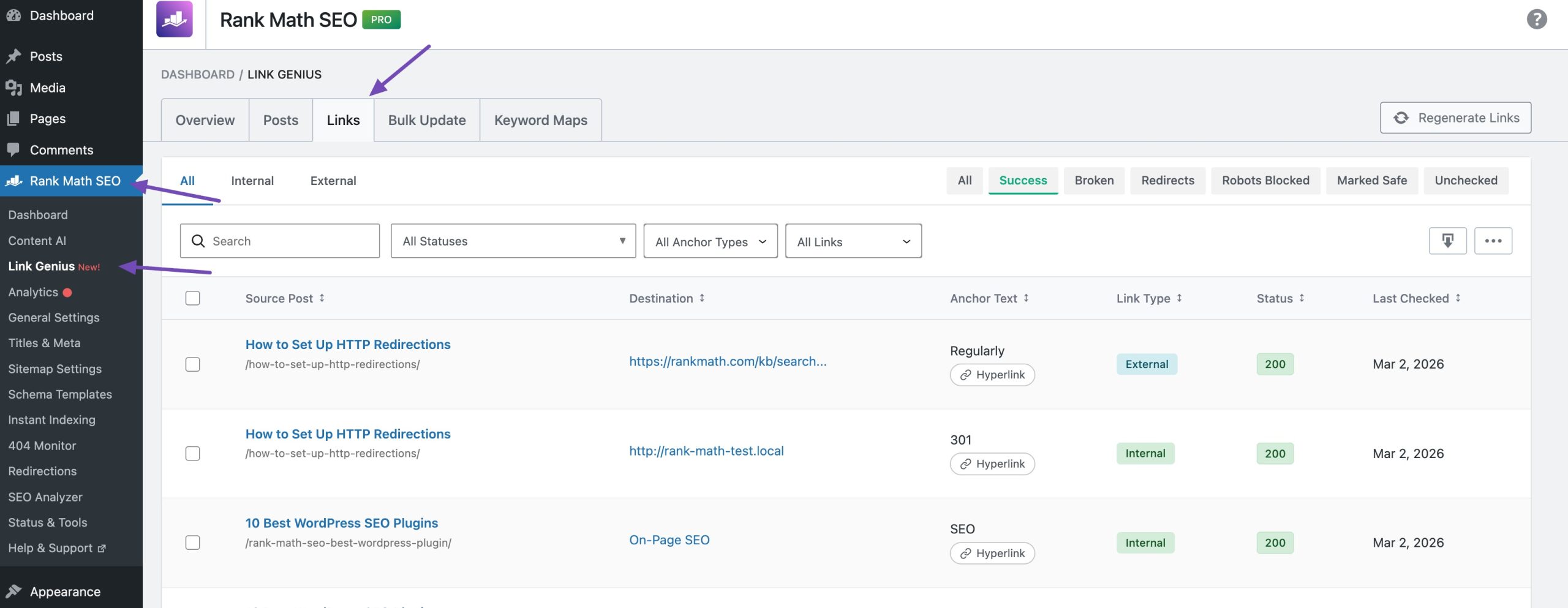
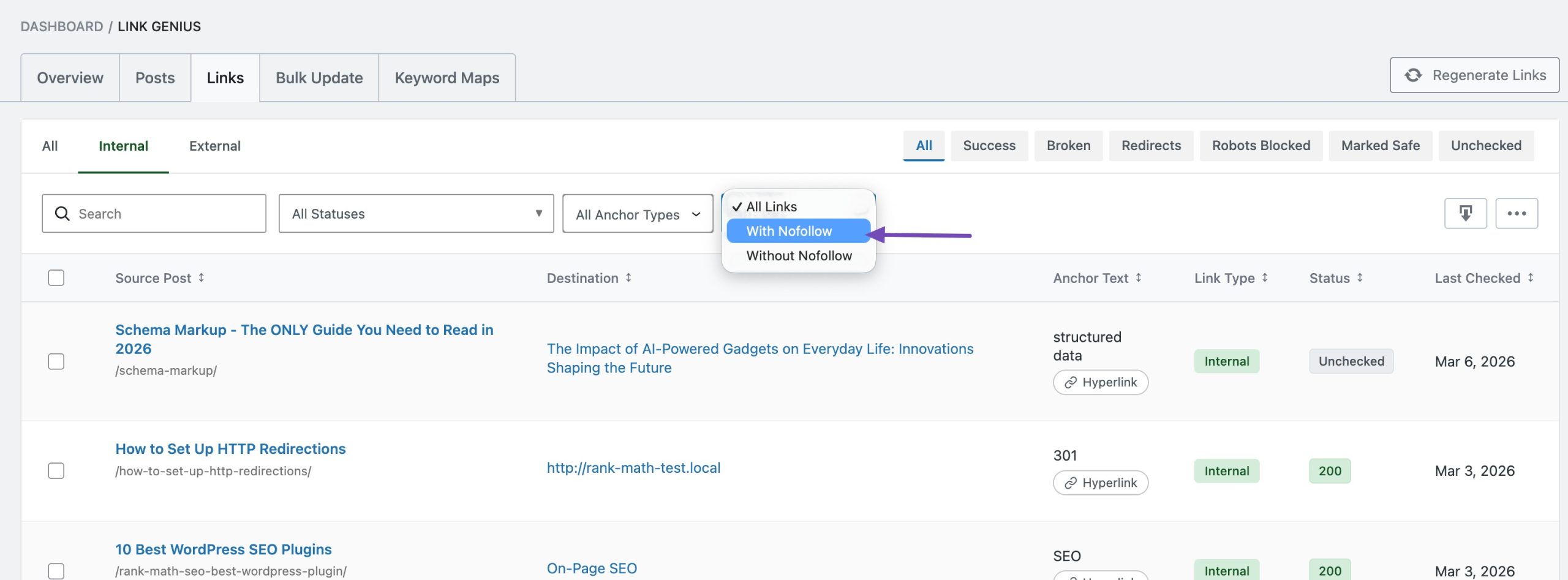
Select With Nofollow option from the drop-down menu, as shown below. You can then view, edit, recheck or delete the nofollow link.
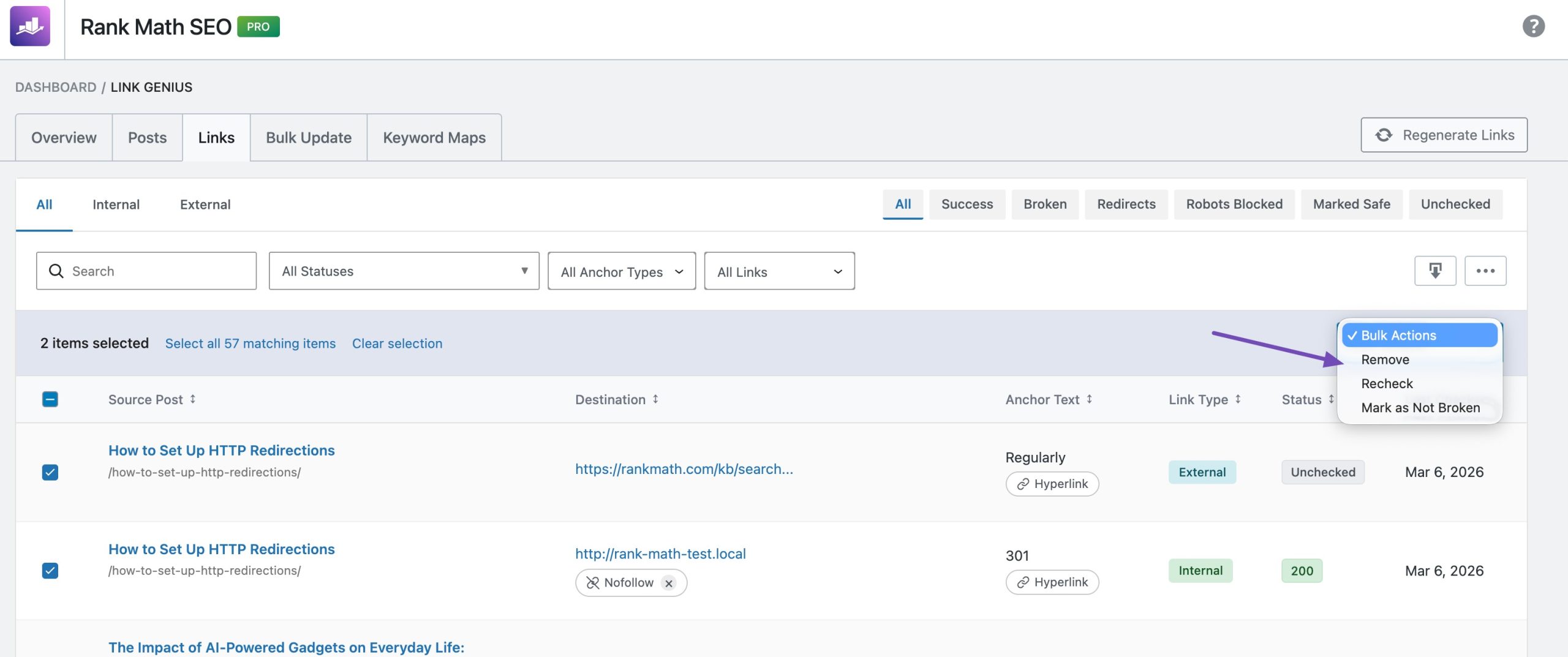
AI Link Genius also allows you to bulk manage the nofollow links. Simply select the links, and then select either Delete, Recheck or Mark as Not Broken option, as shown below.
Balance is key. Too many nofollow links can make your site appear stingy, while too many dofollow links might dilute authority.
Refer to our dedicated tutorial on link building and learn the easy link-building methods for your website.
3.6 Link to Old Posts From New Posts and Vice Versa
Linking new content to older posts, and vice versa, is a smart strategy.
- New → Old: When writing a new post, link to older content that provides foundational information. For example, if your new post covers advanced SEO techniques, link to a beginner-friendly SEO guide so new readers can catch up.
- Old → New: Update older posts by linking to newer content. This keeps your content fresh and directs readers to the latest insights.
If you’re unsure where to link to on your website, you can use Rank Math’s Link Suggestions feature to view the internal linking suggestions.
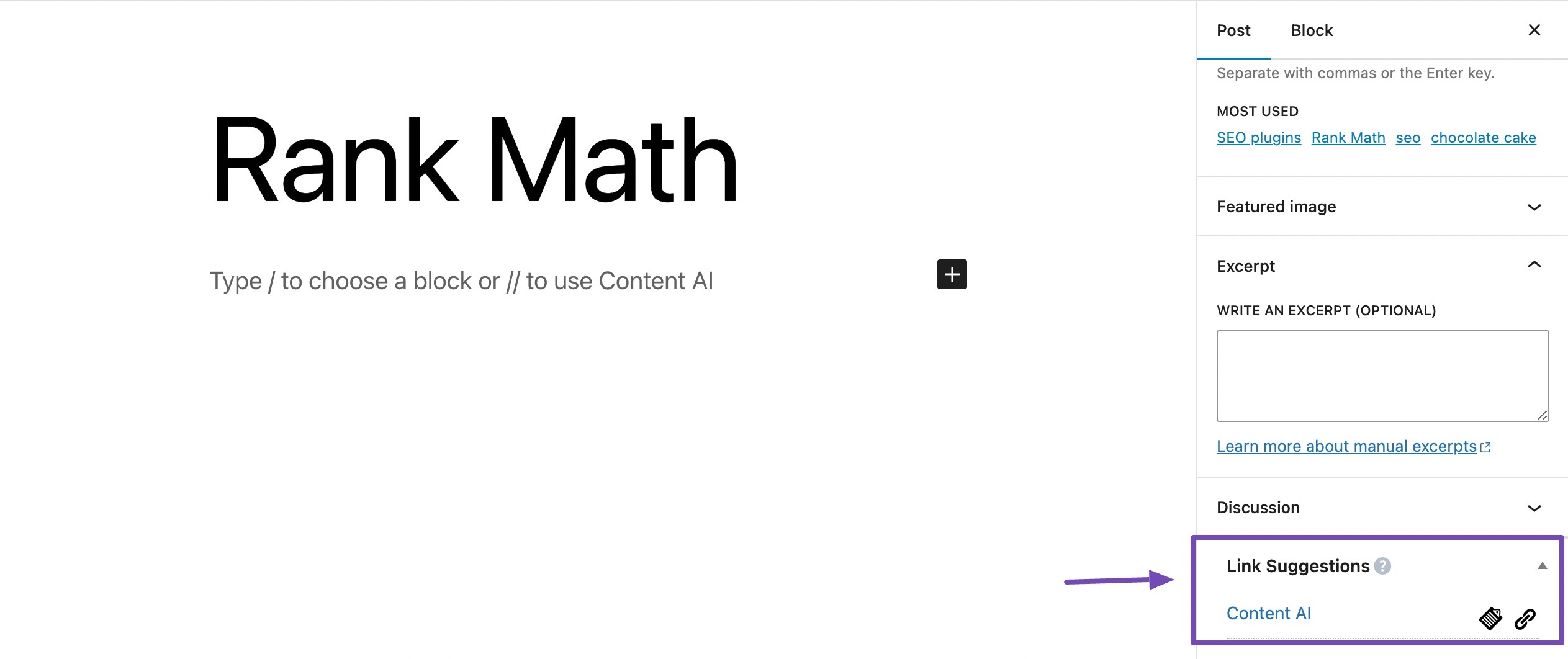
3.7 Monitor Internal Links
One of the key features of Google Search Console is the ability to monitor internal links.
It provides a detailed breakdown of the internal links within your website, allowing you to see which pages are frequently linked to and how they contribute to the overall structure.
4 Frequently Asked Questions
When should I use nofollow attributes in internal links?
Nofollow attributes should be used when linking to pages where you don’t want to pass authority, such as user-generated content, login pages, or sponsored links.
What is the impact of overusing nofollow attributes?
Overusing nofollow attributes may disrupt the natural flow of authority within your site, potentially reducing its impact.
How can I reduce bounce rates through internal linking?
Internal linking can reduce bounce rates by guiding your audience to explore additional pages and providing them with relevant, engaging content.
What is the role of internal linking in on-page SEO?
Internal linking in on-page SEO improves content visibility, enhances keyword relevance, and contributes to a well-structured website.
What are the common mistakes to avoid in internal linking?
Common mistakes include excessive internal linking, ignoring broken links, lack of anchor text variation, and overlooking mobile responsiveness in link placement.
How can I find internal linking opportunities within my content?
Use tools like Google Search Console to identify internal linking opportunities, analyze user behavior, and strategically place links where they add the most value.
5 Wrapping It Up
Mastering internal linking isn’t just about connecting pages, it’s about creating a good experience for your visitors while boosting your SEO.
When you optimize anchor text, link strategically to your pillar content, or use insights from tools like Google Search Console, you’re helping both your audience and search engines navigate your site more effectively.
With a little planning and attention, your internal links can increase the visibility of important pages in Google’s index and improve your rankings.
Start small, stay consistent, and watch how smart internal linking can make your website more engaging and discoverable.
If you like this post, let us know by tweeting @rankmathseo.
