¿Cuál es la pintura con contenido más grande (LCP)?
The largest contentful paint (LCP) is a Elementos vitales web básicos metric that measures the duration between the moment a visitor arrives at a webpage and the moment the main content on the webpage loads. Google uses it to determine the load speed of a webpage.
The main content is the largest image, video, or block of text that is visible within the viewport. For example, the image is the largest contentful paint in the viewport below. So, the moment it loads is considered the largest contentful paint of the webpage.
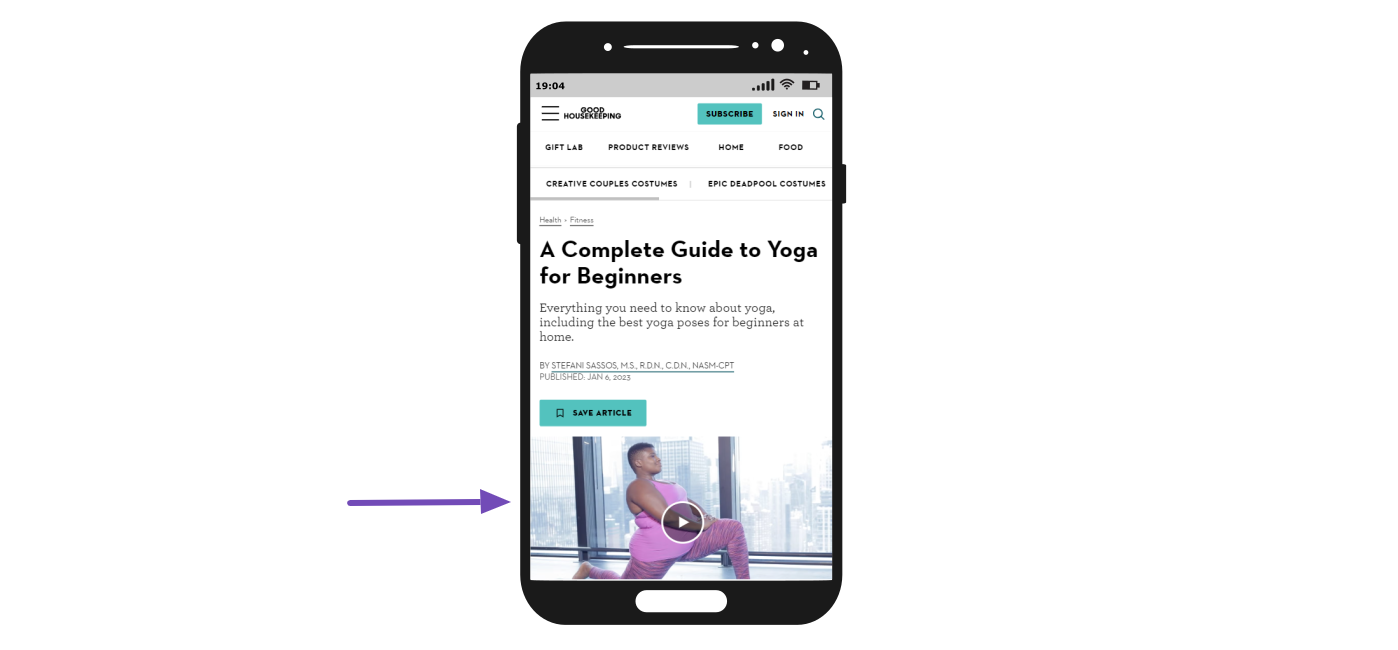
The largest contentful paint can change as a webpage loads. For example, the largest contentful paint of the webpage below changes from the subheadline to the headline and then the picture, which is the largest content visible within the viewport.
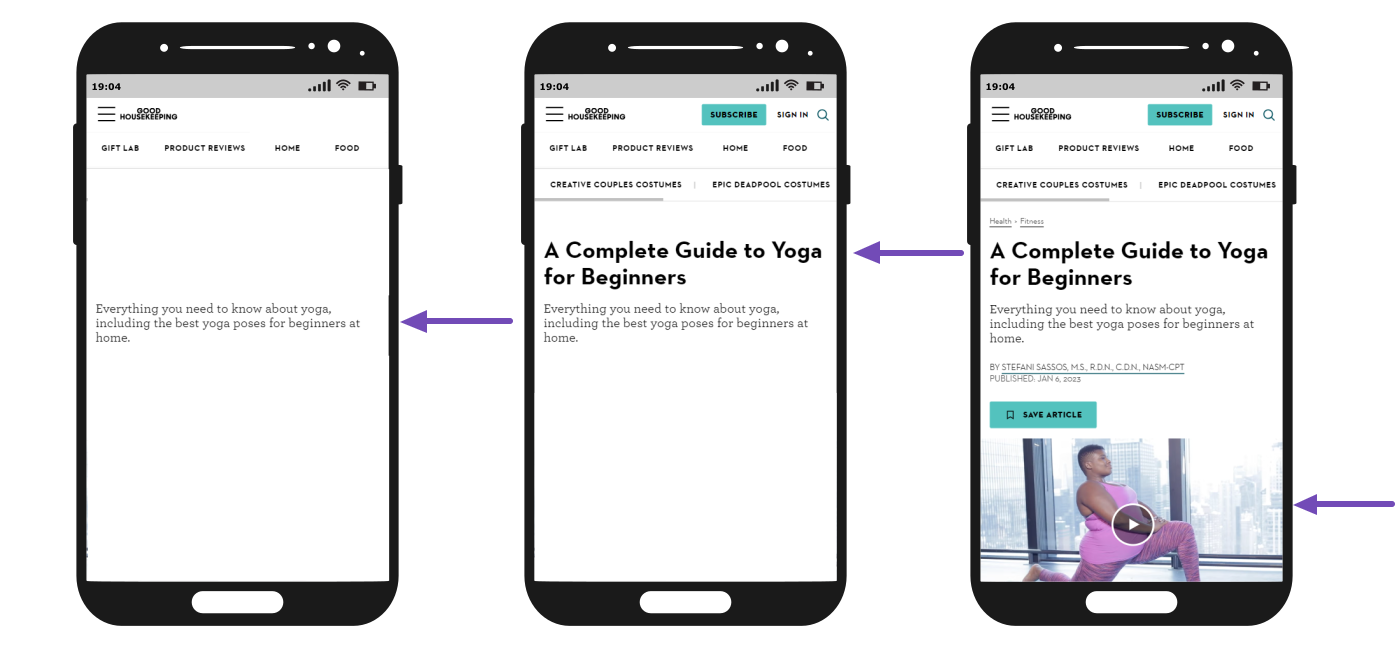
It is crucial to know that the largest contentful paint is not calculated using the content’s size. Instead, it is calculated using the portion of the content that is visible to the user within the viewport. In the case of images that have been resized using CSS, the smaller image will be considered for the largest contentful paint.
In the case of a block of text, the smallest rectangle that can contain all the text nodes is used for the largest contentful paint. Google does not consider the margins, borders, and padding of the text block when determining the largest contentful paint.
What is a Good Largest Contentful Paint Score?
A good largest contentful paint score is 2.5 seconds or less. Tools that measure the largest contentful paint classify the results into three categories:
- Good – 2.5 seconds or less
- Needs improvement – Above 2.5 seconds and 4.0 seconds
- Poor — More than 4.0 seconds
Importance of the Largest Contentful Paint
Google uses the largest contentful paint to determine how quickly the page loads. Specifically, it looks out when the page becomes usable for the visitor.
Webpages typically load in stages, with some elements loading quicker than others. However, not all content on a web page is the same, as some are more important to the visitor than others. So, visitors only need certain elements to complete loading before they begin using the webpage.
While the specific elements that need to be loaded before the page becomes usable remain debatable, the largest contentful page is Google’s attempt to select a helpful metric that indicates the page’s usability.
That said, the largest contentful paint is one of the three metrics Google uses to determine the Core Web Vitals of a webpage. The other two are the cumulative layout shift (CLS) y interaction to next paint (INP) metrics.
Google uses the Core Web Vitals along with some other metrics and signals like HTTPS usage y mobile-friendliness to determine the page experience of a webpage. Page experience is a factor de clasificación.
Types of Content Considered for the Largest Contentful Paint
Google only considers certain images when determining the largest contentful paint. This is necessary as a webpage contains multiple types of images. The images could also be set up using various formats and could appear at different locations within the content.
- Image specified using the
<img>elemento - Image enclosed within an
<svg>elemento - Background image loaded using the
url( )función - Poster image or first frame of a video
- Block elements containing text nodes
1 Image Specified Using the <img> Element
Google considers the image specified using the <img> element for the largest contentful paint. If the image contains multiple frames, for example, in the case of GIFs and animated PNGs, Google will consider the first frame of the image for the largest contentful paint.
2 Image Enclosed Within an <svg> Element
If an <svg> element contains an <image> element, then Google will consider the image in the <image> element for the largest contentful paint.
3 Background Image Loaded Using the url( ) Function
Google will consider any element containing a background image loaded using the url( ) function for the largest contentful paint.
4 Poster Image or First Frame of a Video
In the case of videos specified using the element, Google will consider the poster image or first frame of the video for the largest contentful paint, depending on which loads first.
5 Block Elements Containing Text Nodes
In the case of text content, Google considers any block-level element containing text nodes or inline-level text elements for the largest contentful paint.
Other content and elements may technically be considered for the first image. However, Google restricts it to the ones listed above to keep it simple. It is crucial to keep this in mind when troubleshooting or optimizing your largest contentful paint.
Elements Not Considered for the Largest Contentful Paint
Google exempts certain elements from being considered for use when calculating the largest contentful paint, even when they meet the criteria of images eligible for the largest contentful paint. They include:
- Elements that are invisible to the user. These are elements that have their opacity set to zero.
- Images unrelated to the webpage’s content. For example, placeholder images and images with low entropy.
- Elements that cover the entire viewport. Such elements are considered background elements rather than regular content.
Difference Between the Largest Contentful Paint and the First Contentful Paint
Google uses the largest and first contentful paint metrics to determine the load speed of a webpage. However, both metrics serve different purposes. While the first contentful paint captures the moment the first element on the webpage loads, the largest contentful paint captures the moment the main content loads.
The largest contentful paint is a better indicator of load speed because it better represents the moment the webpage becomes usable to the visitor. On the other hand, the first contentful page does not indicate usability as not all webpages load helpful elements at the beginning.
The first contentful paint can also be manipulated. For example, a webpage may display a loading icon when the visitor arrives at their site. The first contentful paint will be captured as the moment the icon appears on the visitor’s screen. However, the icon is not helpful to the visitor.
That said, while the largest contentful paint is a Core Web Vitals metric, the first contentful paint is not. However, most tools that report the Core Web Vitals usually include the first contentful paint metric. While it is not a Core Web Vitals metric, the first contentful paint is helpful for diagnosing issues with the largest contentful paint.
How to Measure Your Largest Contentful Paint
You can measure your largest contentful paint (LCP) using Chrome DevTools, which is available in Chromium-based browsers like Chrome or Brave. So, first, make sure you are using a Chromium-based browser.
Once done, head to the webpage you want to inspect and right-click on any area of the whitespace. Then, click Inspect.
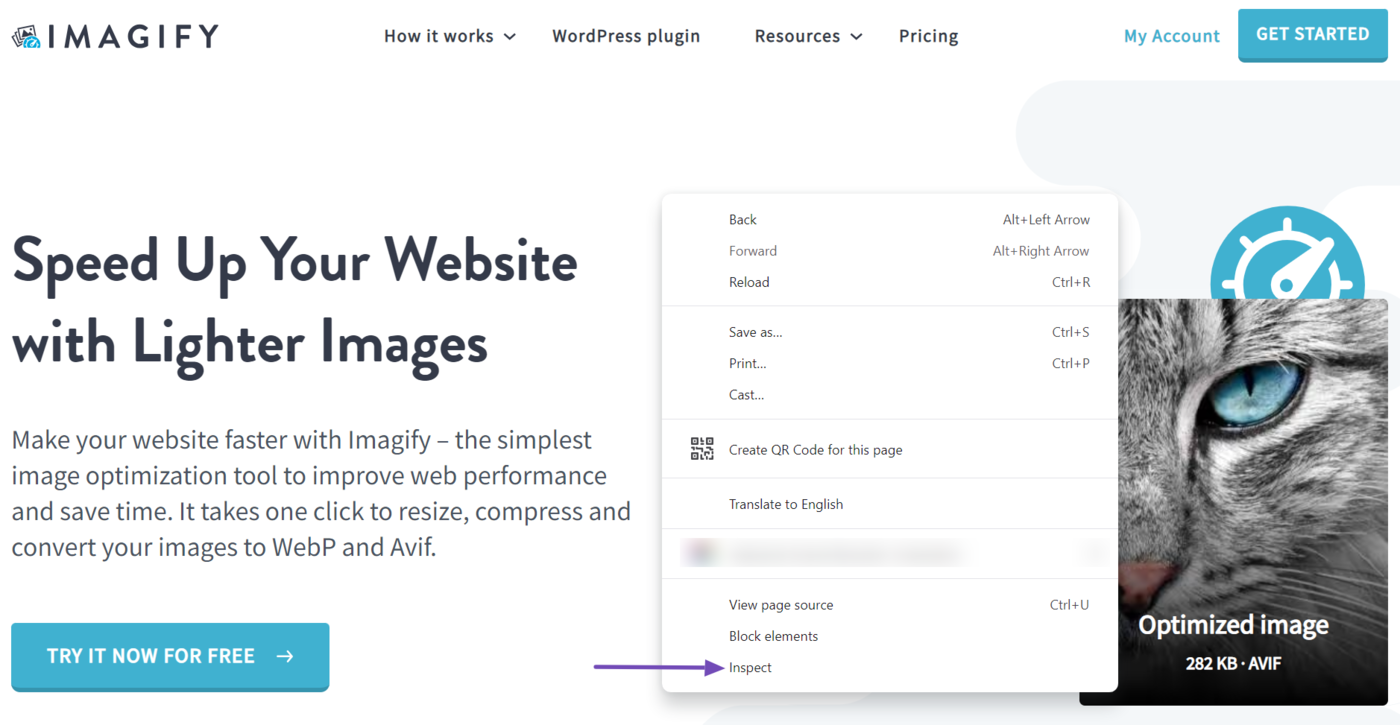
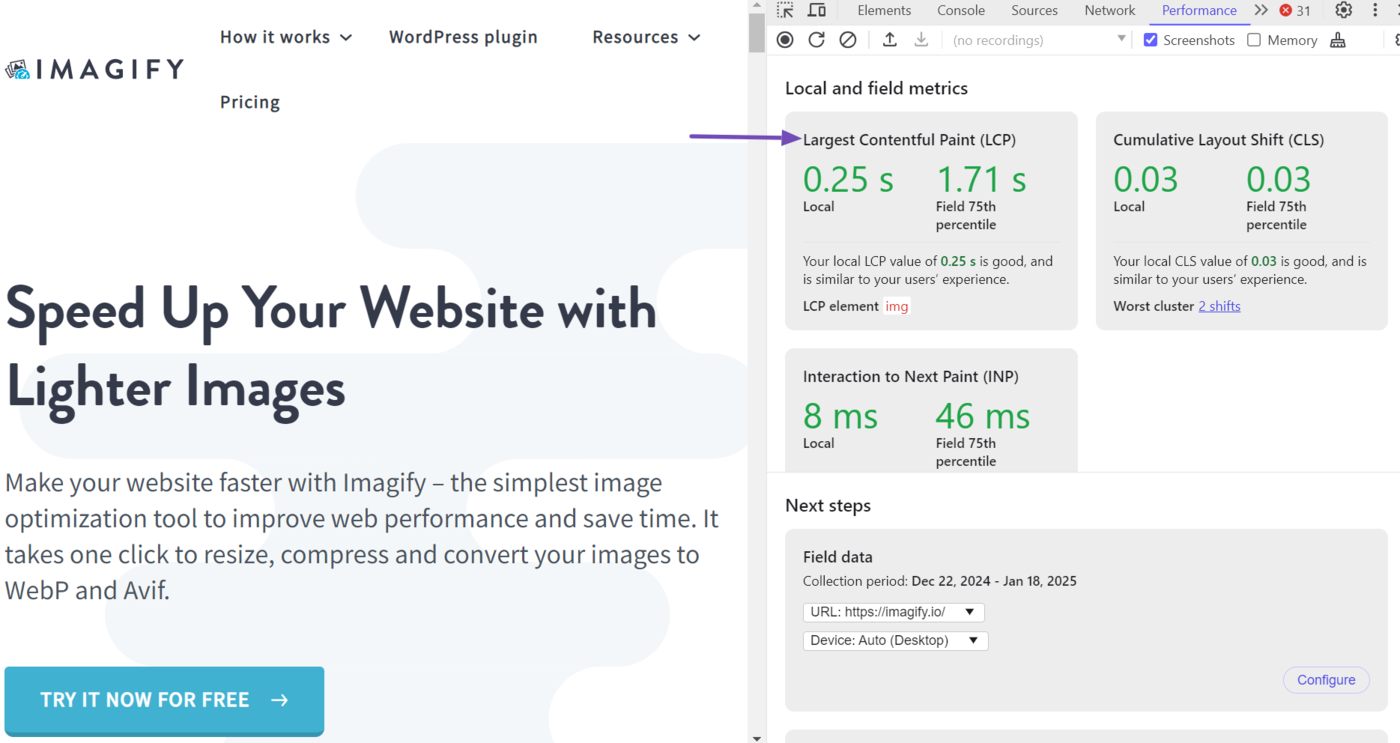
Once done, click Actuación. (If it is not visible, click the double arrow icon » and select Actuación.)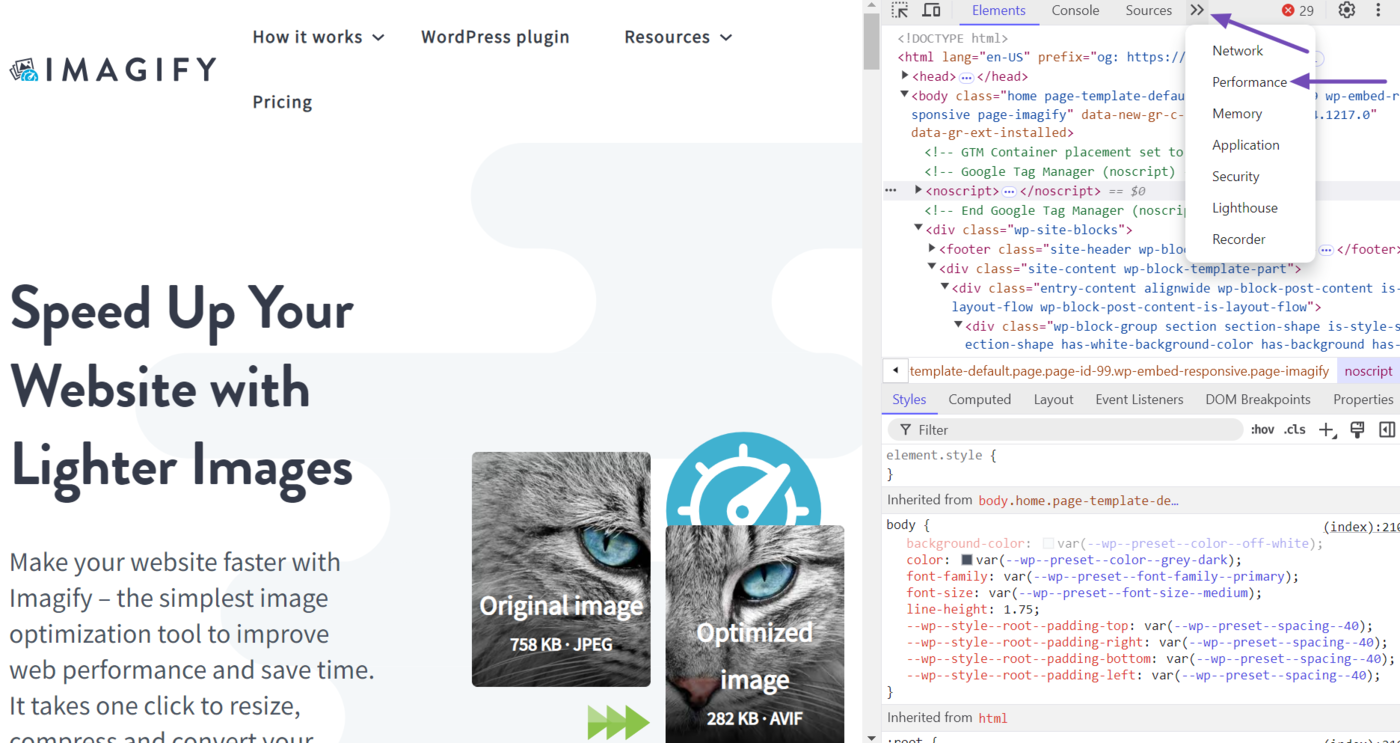
DevTools will display the largest contentful paint for the page. This score is called your “local metric” because it is based on your current experience on the page.
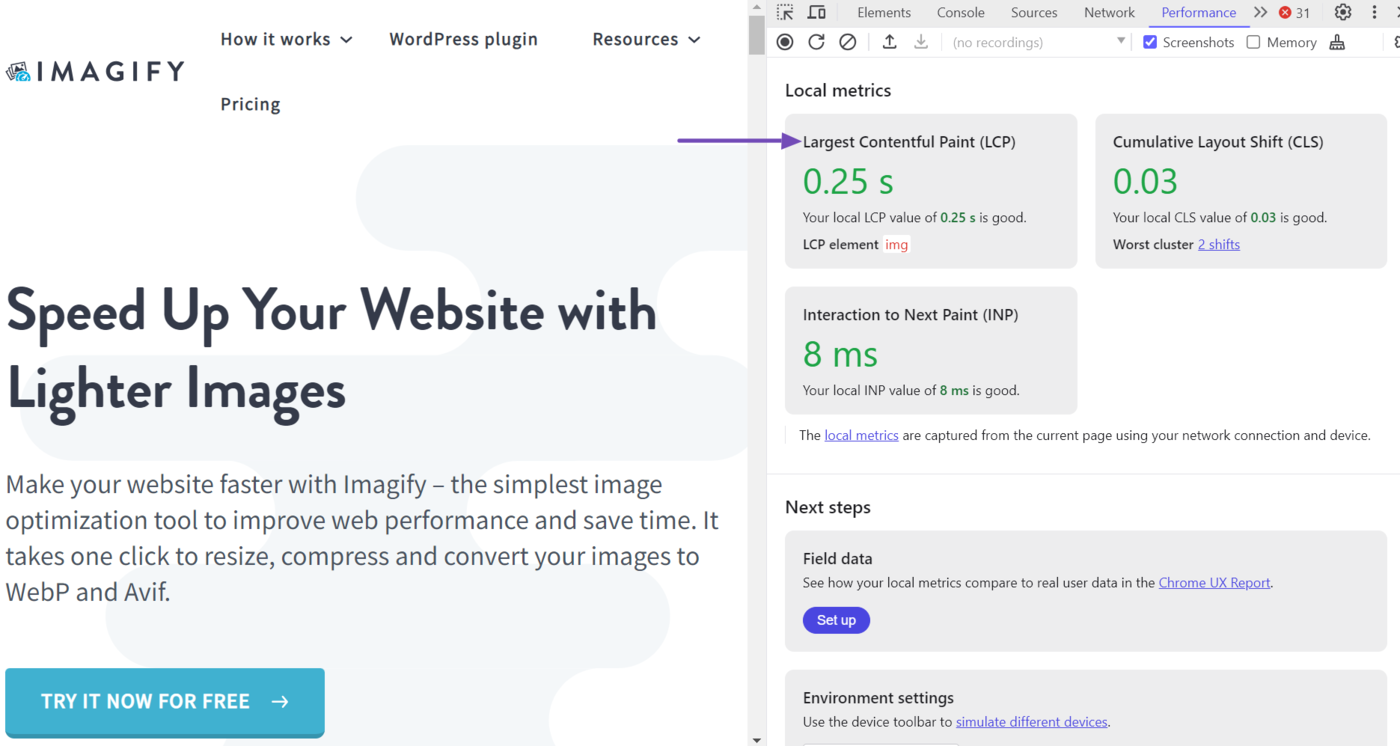
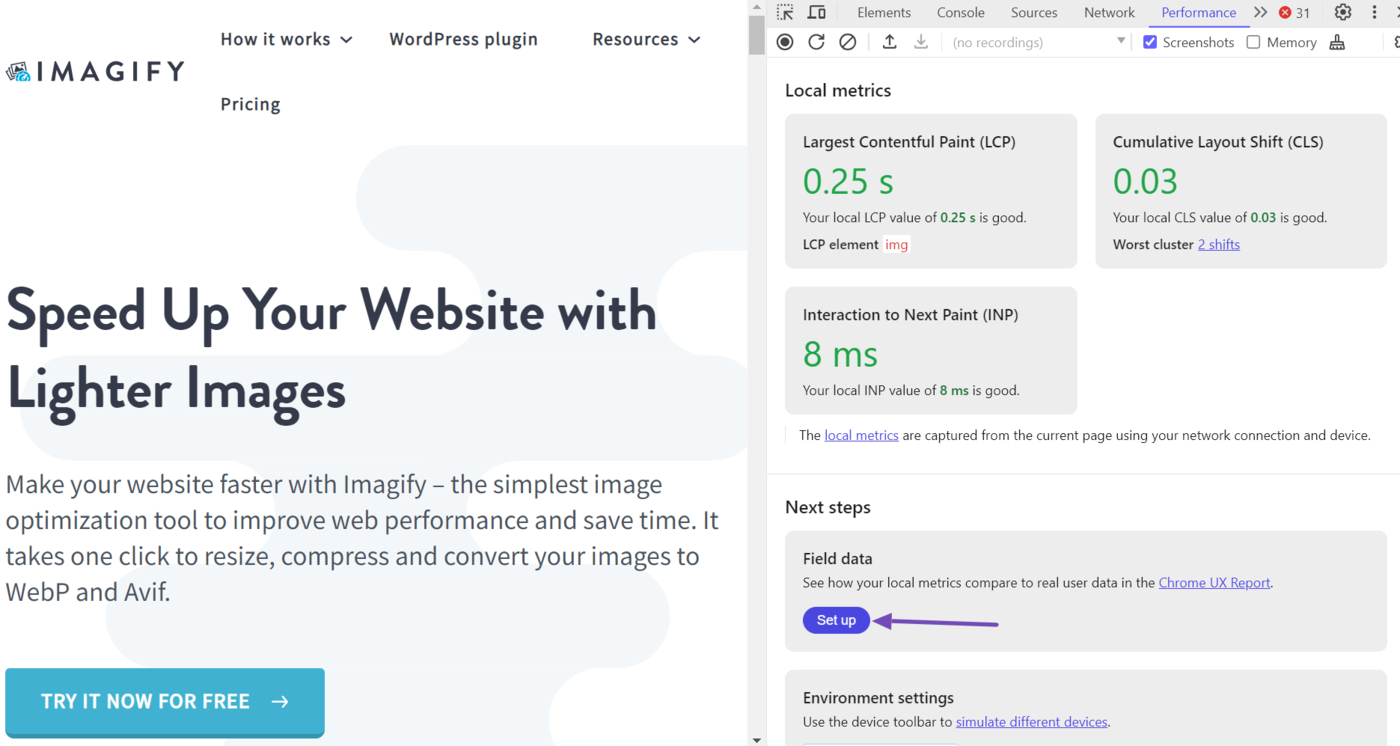
To uncover how other real-life visitors experienced the webpage, head to the Field data section and click Set up.
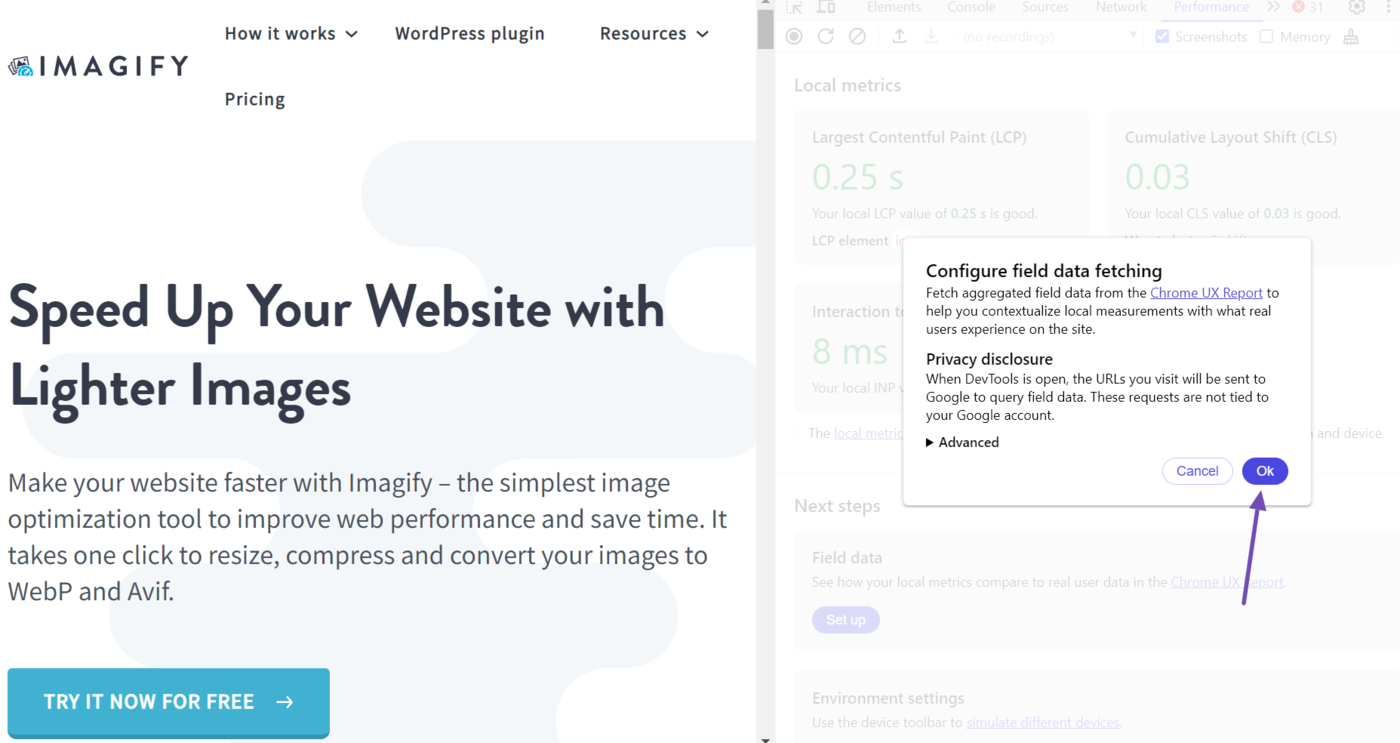
DevTools will display a pop-up. Click OK.
Once done, DevTools will return the largest contentful paint experienced by real-life visitors to the page. This data is labeled “field metrics” and is displayed alongside the local metric.