A bot, short for robot, is a software application designed to perform automated tasks on the Internet, often much faster and more efficiently than humans.
You encounter bots daily, often without realizing it. They assist with customer service through chatbots, retrieve search engine results, provide weather updates, and even aid in online shopping.
However, what happens when these bots visit your website? Should you be concerned about bot traffic, and if so, what can you do about it?
In this knowledgebase article, we will explore bot traffic, its significance, and strategies for managing it on your website.
Table Of Contents
1 What is Bot Traffic?
Bot traffic refers to visits and interactions on a website made by automated software programs, or “bots,” rather than human users.
While human traffic consists of real people browsing, clicking, and engaging with content, bot traffic is created by scripts or algorithms programmed to perform specific tasks automatically.
The key difference lies in intent and behavior:
- Human traffic is usually unpredictable, with varying interaction patterns, time spent on pages, and site navigation.
- Bot traffic follows consistent, repetitive patterns and can occur at much higher volumes and speeds than human traffic.
Understanding this distinction is crucial for identifying when and how bots interact with your site.
2 Types of Bots
According to a recent study, bots account for nearly 30% of all internet traffic. But is this traffic good or bad for your site? Bots can be broadly categorized into two types: good bots and bad bots. Let’s take a closer look at how they function and affect your website.
2.1 Good Bots
Good bots are beneficial and play an essential role in helping the internet run smoothly. They support SEO efforts, maintain your site’s health, and ensure a smooth user experience. Here are some examples of how good bots work:
- Search Engine Bots: Bots like Googlebot and Bingbot crawl websites to index content, helping your site appear in search results. This boosts your visibility and improves SEO, ensuring users find your content easily.
- SEO Bots: Tools like Semrush and Ahrefs deploy bots (SemrushBot and AhrefsBot) that analyze your website for performance insights. These bots help you identify areas for improvement, allowing you to enhance your SEO strategy.
- Site Monitoring Bots: These bots check your website for uptime, performance, and functionality. By monitoring key metrics, they help detect issues early, ensuring your site stays secure and running smoothly.
- Feed/Aggregator Bots: Often used by news platforms and blogs, these bots gather content from various sources, making it easier for users to access and consume information.
- Commercial Bots: Companies use these bots to scan the web for valuable data, such as customer reviews or market trends. They can assist in improving services and ad placements, benefiting businesses with valuable insights.
2.2 Bad Bots
While good bots enhance your website’s performance and visibility, bad bots can cause significant harm. These malicious bots skew analytics, compromise security, and even damage your SEO efforts. Here’s how they operate:
- Scraper Bots: These bots extract data from your website without permission, often for content theft or competitive analysis. By duplicating your content elsewhere, they can hurt your SEO rankings, as search engines penalize duplicate content.
- Spam Bots: Bots that flood your website with spammy comments or messages, often containing malicious links. This can reduce your site’s credibility, damage user experience, and skew your engagement metrics.
- DDoS Bots: Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) bots overwhelm your site with fake traffic, causing slowdowns or even complete crashes. This not only frustrates users but can also lead to search engine penalties for downtime.
- Malware Distribution Bots: These bots inject harmful code into your site or redirect users to malicious websites. Such attacks compromise your site’s security, potentially exposing sensitive data or harming user trust.
- Credential Stuffing Bots: By attempting to log in using stolen credentials, these bots seek unauthorized access to user accounts, leading to potential security breaches.
- Ad Fraud Bots: These bots generate fake clicks or impressions on your ads, wasting your ad spend and distorting performance metrics, making it harder to track your campaigns accurately.
3 How to Detect Bot Traffic
Detecting bot traffic involves identifying patterns that don’t match typical human behavior. In tools like Google Analytics, look for sudden traffic spikes, unusual geographic locations, or low engagement rates.
In server logs, repetitive actions, rapid page views, or frequent requests from the same IP can signal bot activity. Check the User-Agent data—legitimate bots like Googlebot or AhrefsBot will clearly identify themselves, while suspicious bots often have irregular or misleading User-Agent strings.
To review this in your hosting control panel, navigate to Site Summary/Statistics/Logs.
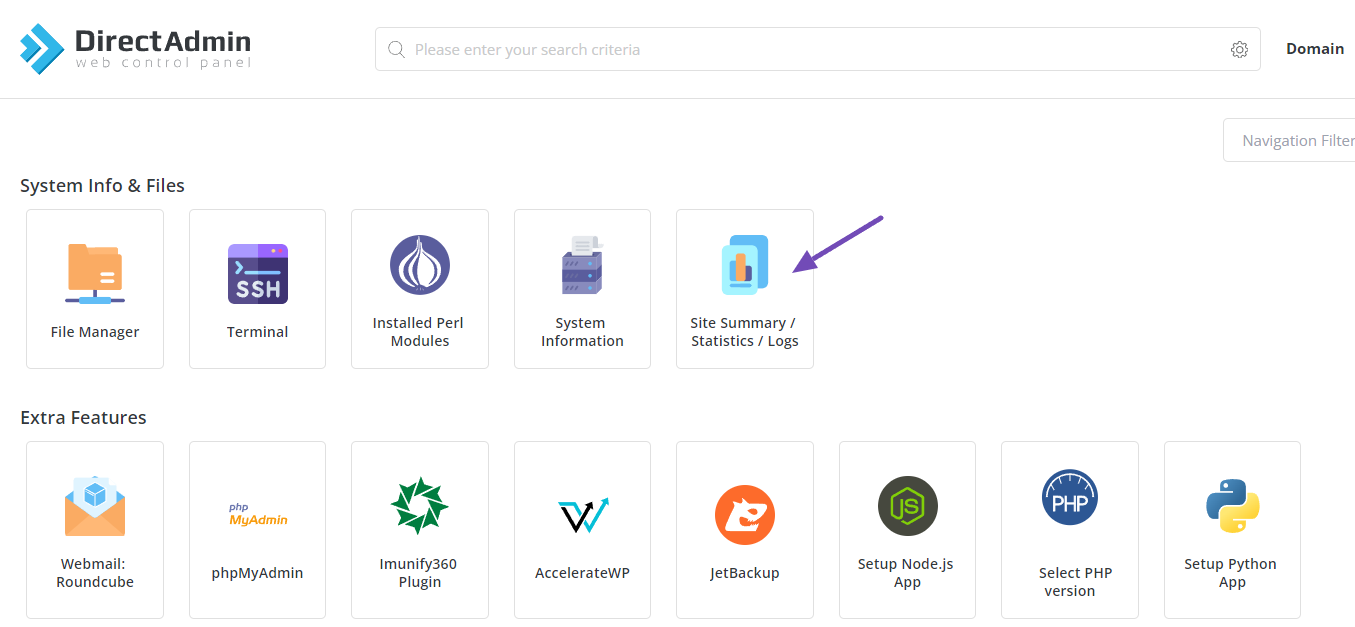
If you have multiple domains, select the one you want to check, then choose Usage Log, as shown below.
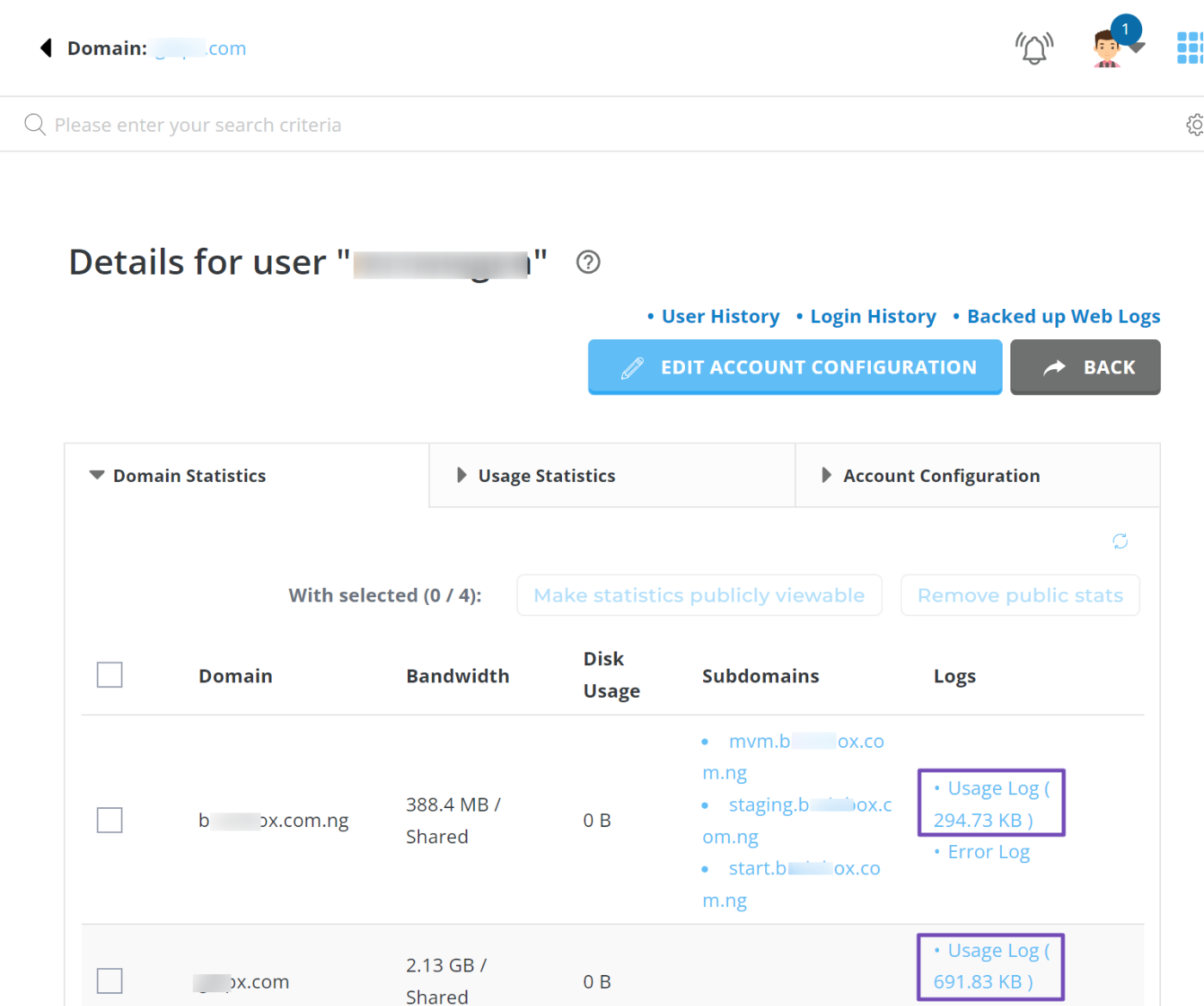
In the usage log, use the Ctrl+F keyboard shortcut to search for bot-related terms. Legitimate bots like Googlebot/2.1 or AhrefsBot/7.0 will appear in the User-Agent string, as shown below.
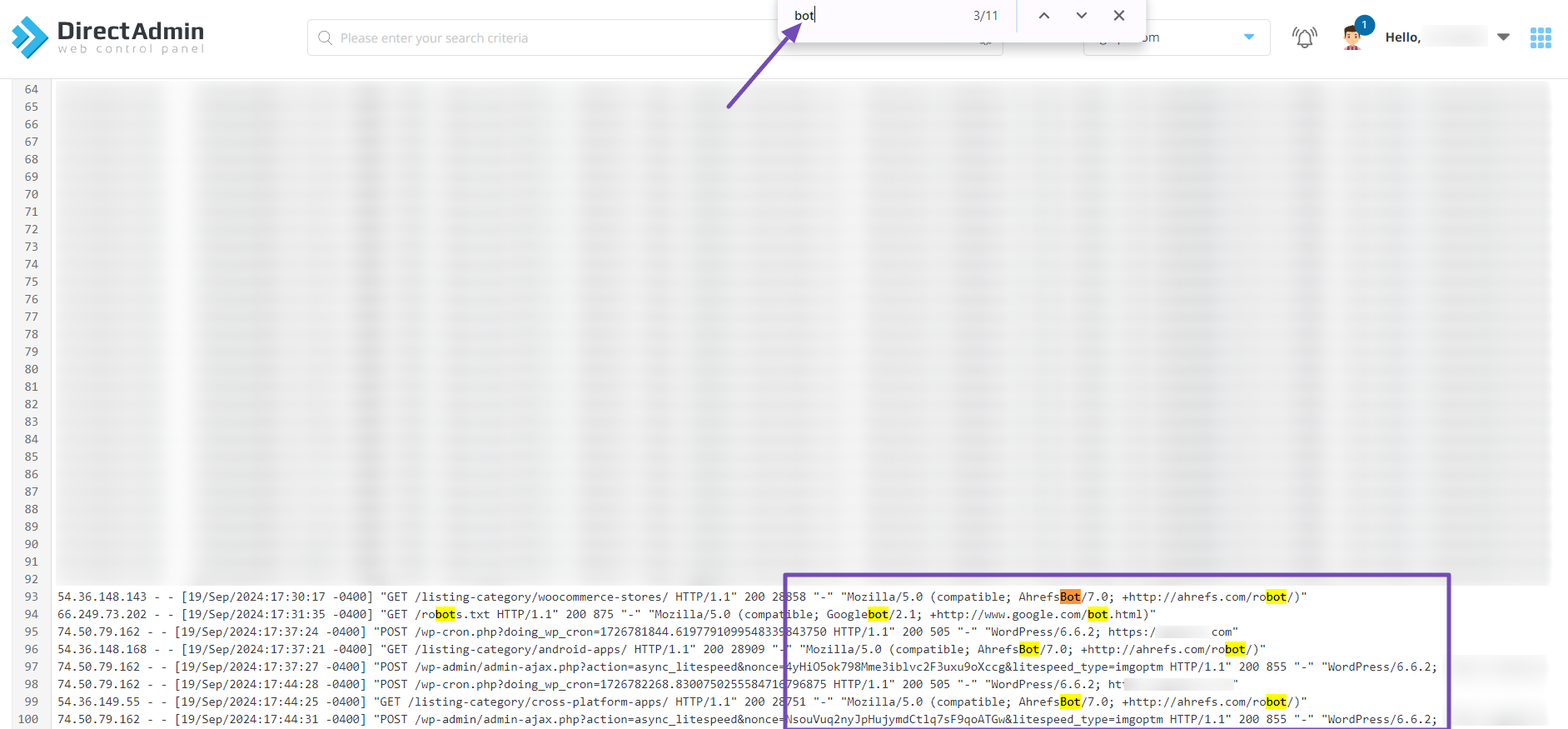
However, if you see unusual or generic User-Agent strings like FakeBot/1.0 or random characters, that could indicate bot traffic.
For more robust detection, consider using bot management services that employ algorithms and machine learning to identify suspicious activity.
4 How to Manage Bot Traffic
Managing bot traffic involves handling both good and bad bots. While good bots can benefit your site, they can also consume significant server resources.
For instance, Googlebot crawls your site, but other search engine bots may not contribute positively to your visibility or traffic. If you find that certain bots aren’t providing value, you might want to block them. This can be done by specifying the bot in your robots.txt file.
To do this easily, set up the Rank Math SEO plugin. Navigate to Rank Math SEO → General Settings → Edit robots.txt from your WordPress dashboard.
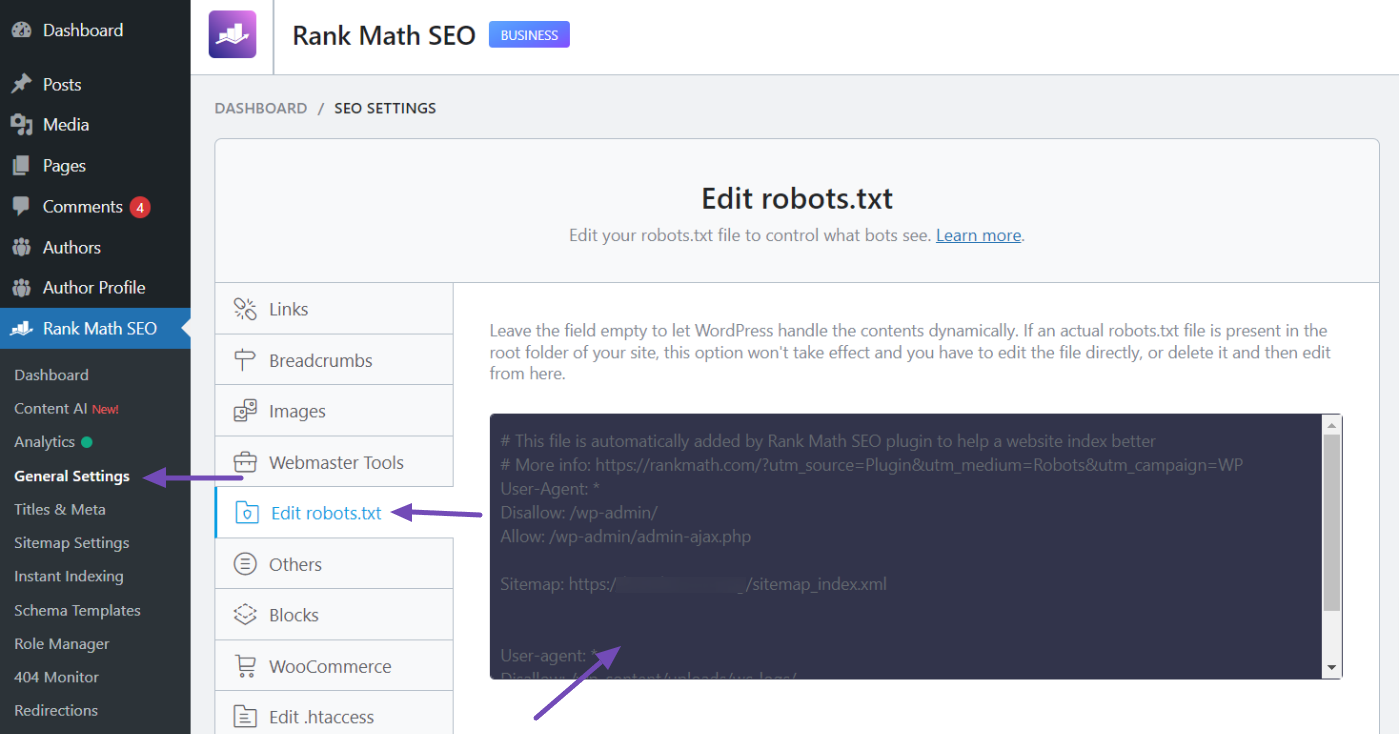
In the robots.txt field, use the following code:
User-agent: TheBot
Disallow: /Replace TheBot with the name of the bot you wish to block.
Sometimes, good bots may overload your server due to excessive crawl requests. In this case, you can set a crawl limit by adding a directive to your robots.txt file. For example, to allow a bot to crawl every 10 seconds, use:
User-agent: *
Crawl-delay: 10Replace * with the specific bot name to avoid affecting all bots. Note that this crawl delay does not apply to Googlebot, which manages its own crawl rate based on server response times and site performance.
You can also optimize crawling efficiency and conserve the crawl budget by regularly updating or removing unwanted pages and redirecting them as needed. If there are specific pages or files you want to block from being crawled, you can add directives like:
User-agent: Googlebot
Disallow: /private-page
Disallow: /*.pdf$This will prevent Googlebot from crawling the specified private page and all PDF files.
You may also want to block unnecessary URLs that WordPress automatically creates, such as RSS feeds or comments, to conserve the crawl budget. For example:
User-agent: Googlebot
Disallow: /feed/
Disallow: /comments/feed/
Disallow: /category/*/feed/
Feel free to modify this code to suit your preferences.
But what about the bad bots?
For bad bots, consider the following strategies:
- Install Security Plugins: Use WordPress security plugins such as Sucuri Security, Wordfence, or All-In-One Security to block malicious IP addresses, implement Web Application Firewalls (WAFs), and apply other protective measures.
- Use Detection Tools: Implement CAPTCHAs, honeypots, or bot detection services to differentiate between human users and bots.
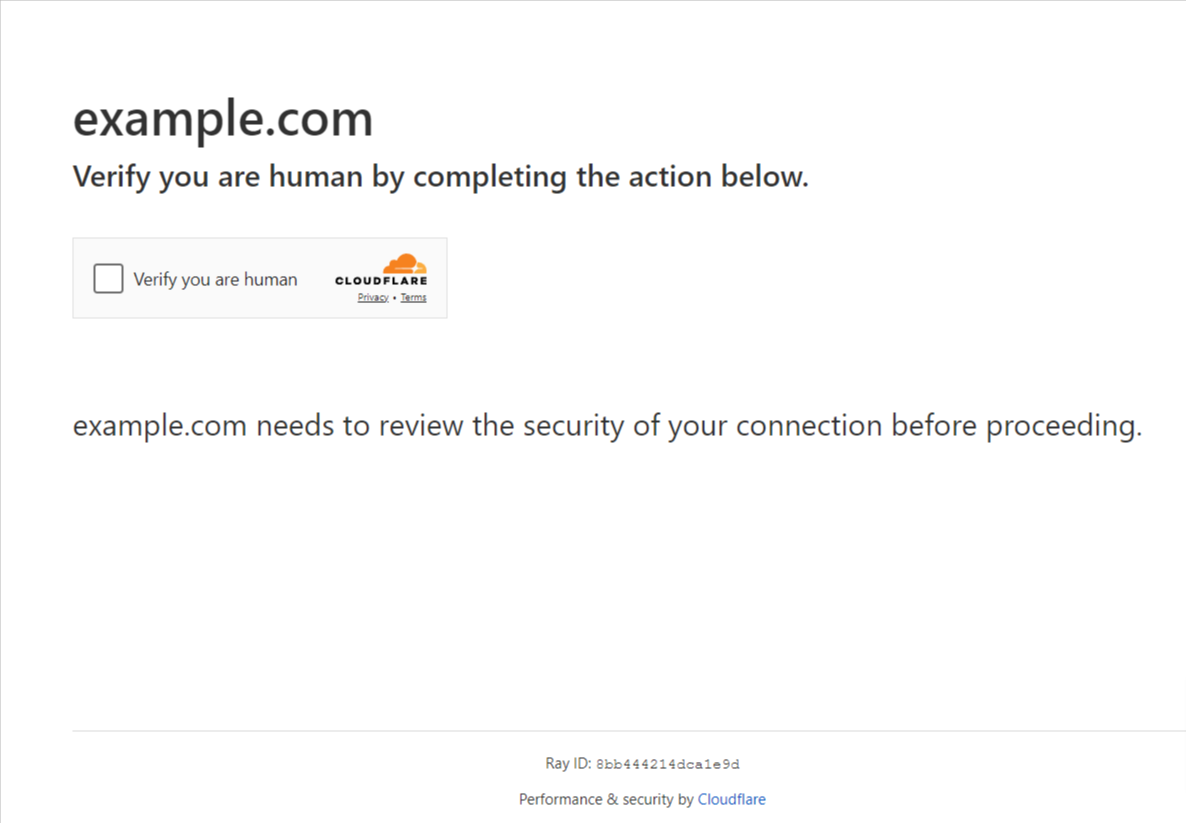
- Implement Bot Mitigation Solutions: Use services like Cloudflare to filter and block unwanted bot traffic. These services offer real-time insights and protection against threats like DDoS attacks. You may occasionally see security prompts like this when visiting sites with Cloudflare service.
By following these strategies, you can effectively manage both good and bad bot traffic on your site.
5 Frequently Asked Questions
What are some other best practices to prevent bot traffic?
Update your security plugins regularly, use strong and unique passwords, utilize SSL/TLS certificates, stay informed about the latest bot threats, and educate your team about bot attacks.
Is it possible to completely eliminate bot traffic?
No, completely eliminating bot traffic is nearly impossible. The goal is to minimize the impact of harmful bots while allowing beneficial ones, like search engine crawlers, to function properly.
Is bot traffic bad or harmful?
Not all bot traffic is harmful. Good bots, such as search engine crawlers, help with site indexing and visibility. However, bad bots can be harmful by scraping content, stealing data, or engaging in cyberattacks, negatively impacting your site’s performance and security.
Is bot traffic harmful to my website’s SEO?
Excessive or malicious bot traffic can harm SEO by leading to search engine penalties or manipulating rankings. Managing bot traffic is crucial to maintaining a healthy SEO profile.
While managing bot traffic is essential, optimizing for legitimate search engine bots is equally important. The Rank Math SEO plugin can enhance crawlability, optimize your robots.txt file, manage XML sitemaps, and more.
That’s it! We hope this guide helps you understand bot traffic and how to manage it. If you have any further questions, feel free to reach out to our support team. We’re here to assist you.