What is Time to First Byte (TTFB)?
The time to first byte (TTFB) measures the duration between a browser requesting a resource (like a webpage) and receiving the first byte of data from the server. It is helpful for evaluating the load speed of a webpage but is not a Core Web Vitals metric.
TTFB is the total time taken for multiple requests to travel between the browser and server, including:
- Redirect time
- Service worker startup time
- DNS lookup time
- Connection and TLS negotiation time
- The time it takes the data to return to the browser
Many bloggers use the time to first byte to evaluate the speed of a server. However, it could be affected by non-server-related issues such as redirect time and the time it takes for the data to return to the browser. So, the time to first byte is not a definite indicator of a server’s speed.
What is a Good Time to First Byte Score?
A good time to first byte score is 800 milliseconds or below. Tools that report on the time to first byte metric typically classifies the score into three categories:
- Good – 800 milliseconds or less
- Needs improvement – Above 800 milliseconds and 1800 milliseconds
- Poor — Over 800 milliseconds
Importance of the Time to First Byte Metric
The time to first byte is helpful for evaluating the load speed of a webpage. Specifically, it helps to identify issues that occur in the early stages of the webpage loading.
This makes it helpful for diagnosing problems with other load speed metrics like the largest contentful paint (LCP) and first contentful paint (FCP), which both include the time to first byte in their calculations.
So, the time to first byte metric impacts both metrics. As a result, if the time to first byte is poor, then both metrics are likely to be poor. Similarly, improving the time to first byte will result in an improvement in both metrics.
The time to first byte and first contentful paint are load speed diagnostic metrics, while the largest contentful paint is a Core Web Vitals metric. Google uses the Core Web Vitals and several other signals and metrics like HTTPS usage and mobile-friendliness to determine the page experience of a webpage. Page experience is a ranking factor.
How to Measure the Time to First Byte (TTFB)
You can measure the time to first byte (TTFB) using Chrome DevTools, which includes a group of debugging and analysis tools built into Chromium-based browsers like Chrome and Brave. The tool reports the time to first byte as you experienced it and does not indicate how other users experienced the page.
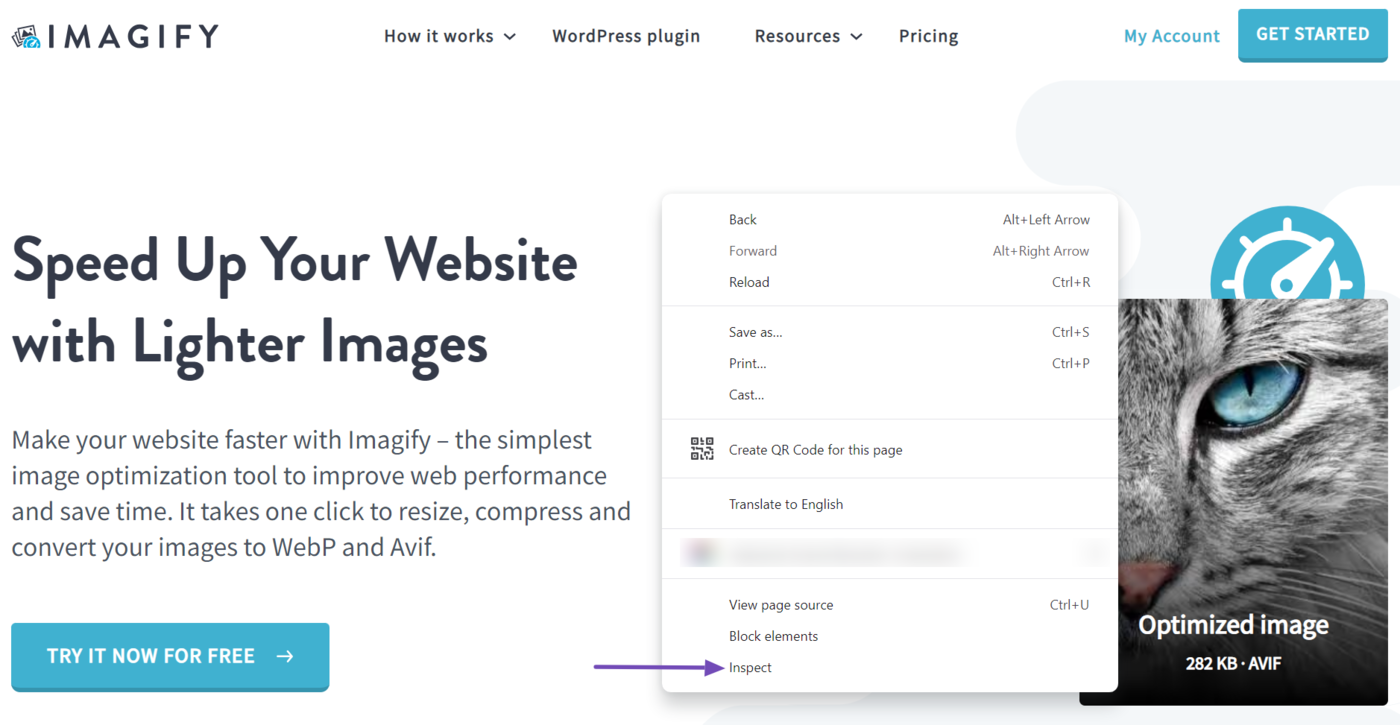
To get started, using a Chromium-based browser, head to the webpage you want to inspect. Once there, right-click any area of the whitespace and click Inspect.
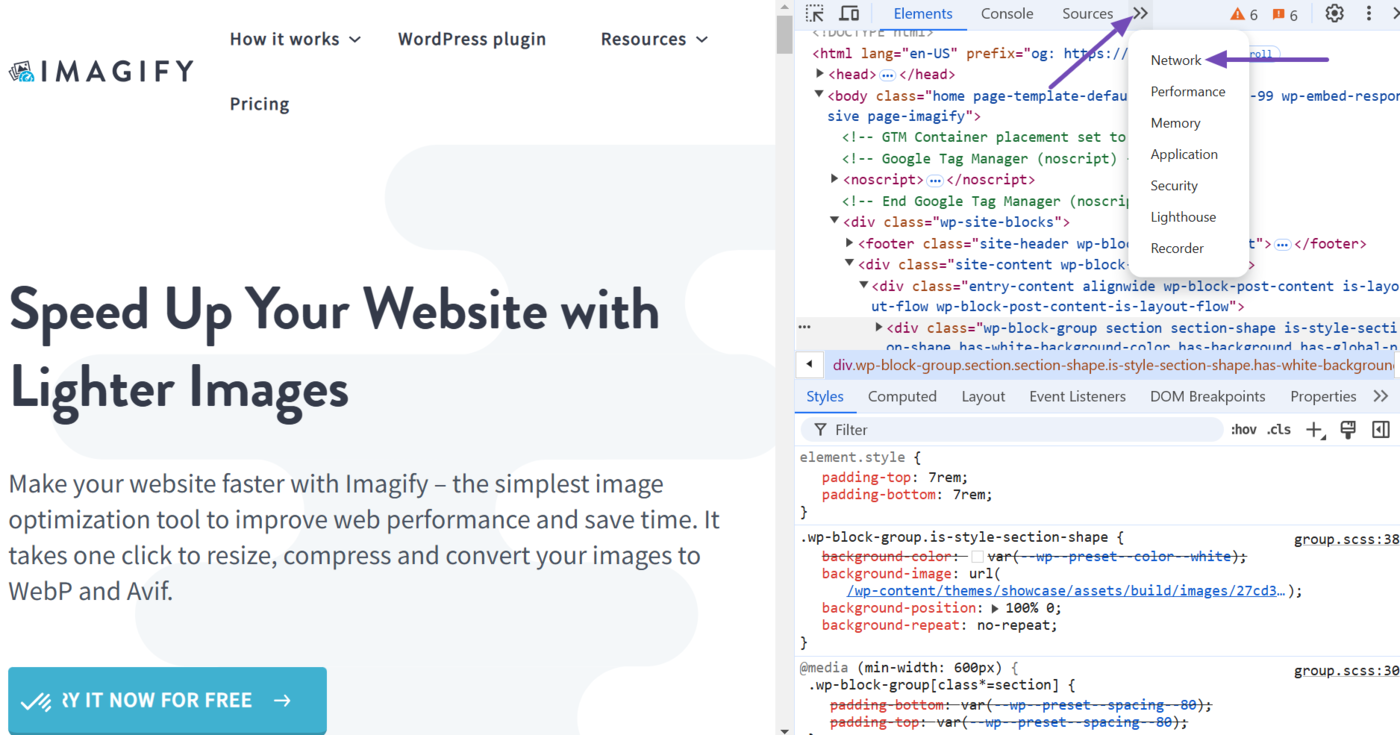
Next, click the Network tab in the DevTools toolbar. If the Network tab is not visible, click the double arrow icon » and select Network, as shown below.
Now, click Ctrl + R on your keyboard to reload the page. Then, navigate to the Name field and click the URL of the site you are inspecting. (Note that the site URL is typically the first item in the Name field, so you may need to scroll up to find it.)
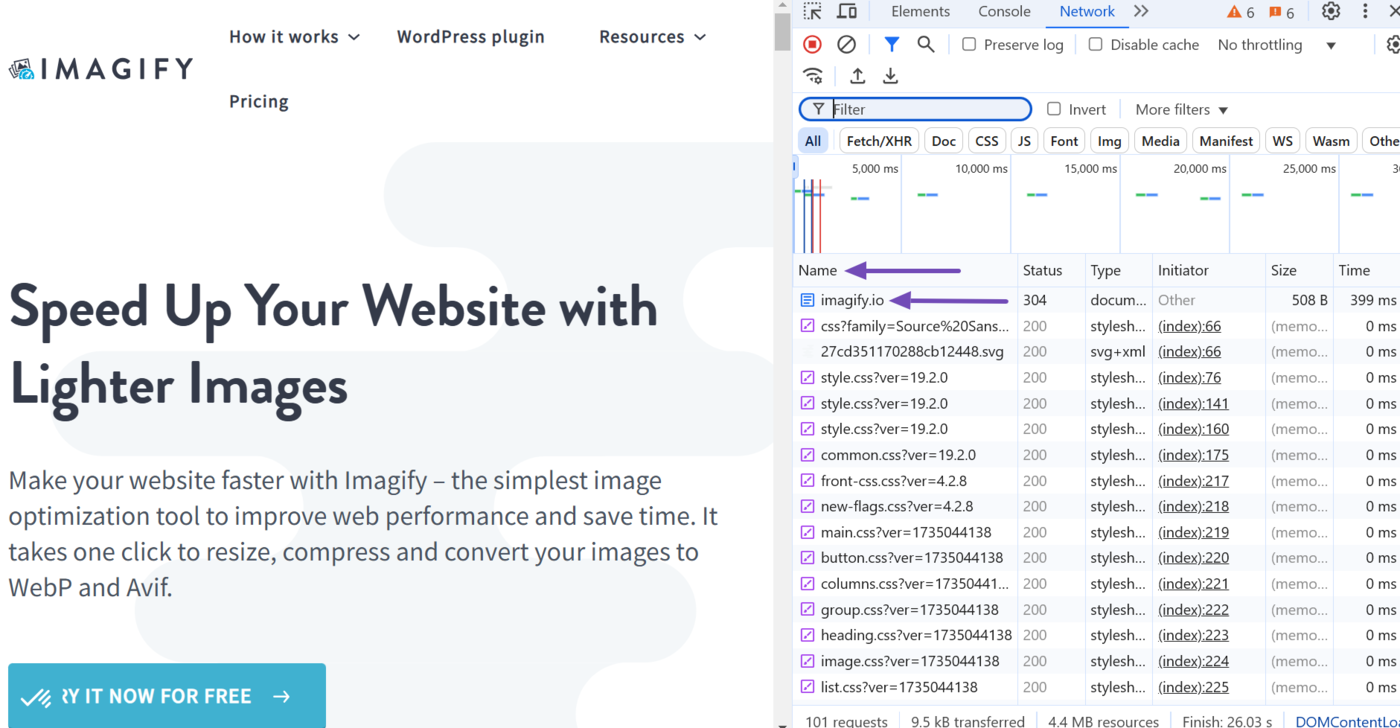
Once done, navigate to the Waiting for server response score in the Timing tab. The score reported here is your time to first byte.