What is Thin Content?
Thin content refers to an unhelpful webpage that provides little or no value to visitors. Such content is typically short, generic, and lacks any original insight. It does not satisfy the hakutarkoitus either, and visitors who encounter them usually return to the hakutulossivuilla to seek more relevant results.
Importance of Thin Content
Thin content is unimportant to your search engine optimization efforts. If anything, it will hurt your käyttökokemusta and increase your bounce rate. It can also cause Google to issue a manual action penalty against your content and site.
For instance, Google has the “Thin content with little or no added value” manual action penalty for sites that publish thin content.
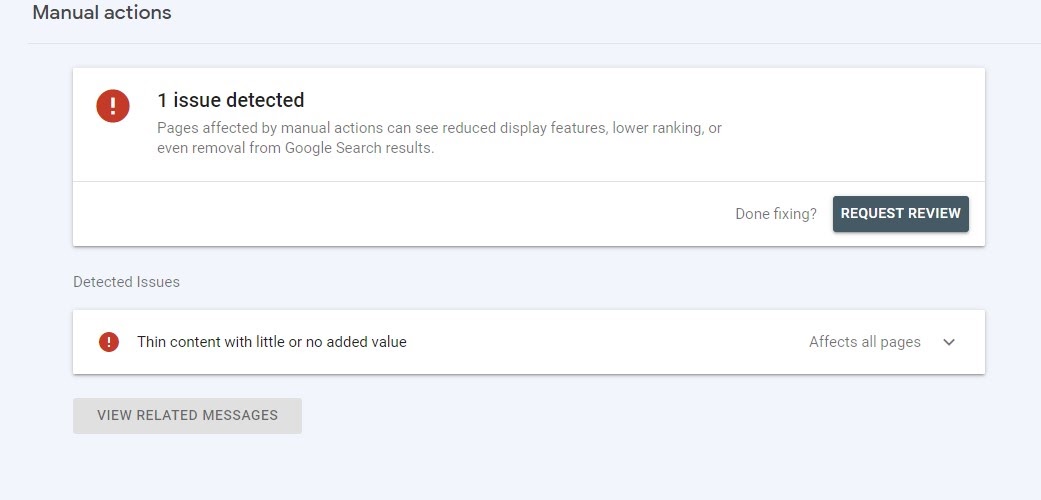
Google can also issue other manual action penalties, depending on the type of thin content. For example, a doorway page that contains thin content may receive a “cloaking and/or sneaky redirects” penalty.
A site that publishes thin content at scale can also receive a pure spam penalty, which is more severe than a regular manual action penalty.
Aside from the manual action penalties, Google has released major algorithm updates to target sites and webpages that host thin content. This includes the Panda algorithm update, which is currently a part of Google’s search algorithm.
Types of Thin Content
Thin content comes in many forms, from shallow affiliate pages to lengthy but unhelpful articles. It is crucial to understand these forms of thin content, as it lets you identify and fix them before they harm your user experience and rankings.
1 Doorway Pages
Doorway pages are webpages that rank for a specific keyword but then redirect visitors to entirely different content when clicked. Beyond being thin content, doorway pages rely on black hat SEO techniques like cloaking ja keyword stuffing, which also violate Google’s Search Essential guidelines and can earn you a manual action penalty.
2 Thin Affiliates
Thin affiliate pages are low-value pages that primarily exist to promote affiliate products. These pages do not offer any substantial or original content and are just copy-and-paste versions of already existing pages.
3 Thin Syndication
Thin syndication is the practice of republishing content from other sources without adding any original commentary, analysis, or updates to it. While article syndication is a white hat SEO technique, it can be considered thin syndication when done without permission or proper attribution.
4 Kaavittu sisältö
Scraped content refers to content copied from other websites without permission, modification, or attribution. While typically executed using specialized scraper software, it may also be done manually. Some spammers may also edit the scraped content before republishing it.
5 Low-Quality Content
Low-quality content refers to content that lacks depth or originality. Such content offers little to no value to visitors and is typically poorly written and stuffed with keywords. Unlike other thin content, low-quality content can be long-form. However, they are considered thin because they provide little value.
How to Resolve Thin Content Issues
There are multiple methods of resolving thin content. Your specific solution depends on why you created the content and whether it fits into the rest of the content you publish on your site.
1 Delete It
If you do not want the content, then you should delete it. If you are hit with a thin content penalty, you may have to remove the content, especially when it violates Google’s Search Essential guidelines. For example, you should delete doorway pages and scraped content, as there is no point in improving those.
2 Improve It
You should improve the content that you want to keep. Specifically, if you created the content using white hat SEO techniques and intended to provide value to visitors, you should consider improving it.
You can improve the content by adding additional paragraphs, sections, and subsections. If necessary, you may need to refocus or repurpose the content to ensure it satisfies the search intent.
3 Merge It
A site could end up with thin content when it splits a topic or subtopic into multiple content. In such cases, you may need to consolidate those contents into a single content. In this case, you will review your content, find the related ones, and merge them into a single content.
You will usually need to edit such content to ensure they flow well. Once done, create uudelleenohjaukset that point from the thin pages to the new URL.