What Is Indexing?
Indexing is the process by which a search engine stores and organizes the content it discovers during its crawling process. The search engine then stores the content in a database called an index.
When a user enters a search query, the search engine retrieves the relevant content from its índice and displays it on its search results page. For instance, all the images and textual results on this search results page are from Google’s index.
In this article, we’ll cover:
Importance of Indexing
Indexing is essential for any webpage that you want to appear on search engine results pages. If a page is not indexed, it cannot appear in search results pages, regardless of how well-optimized it is.
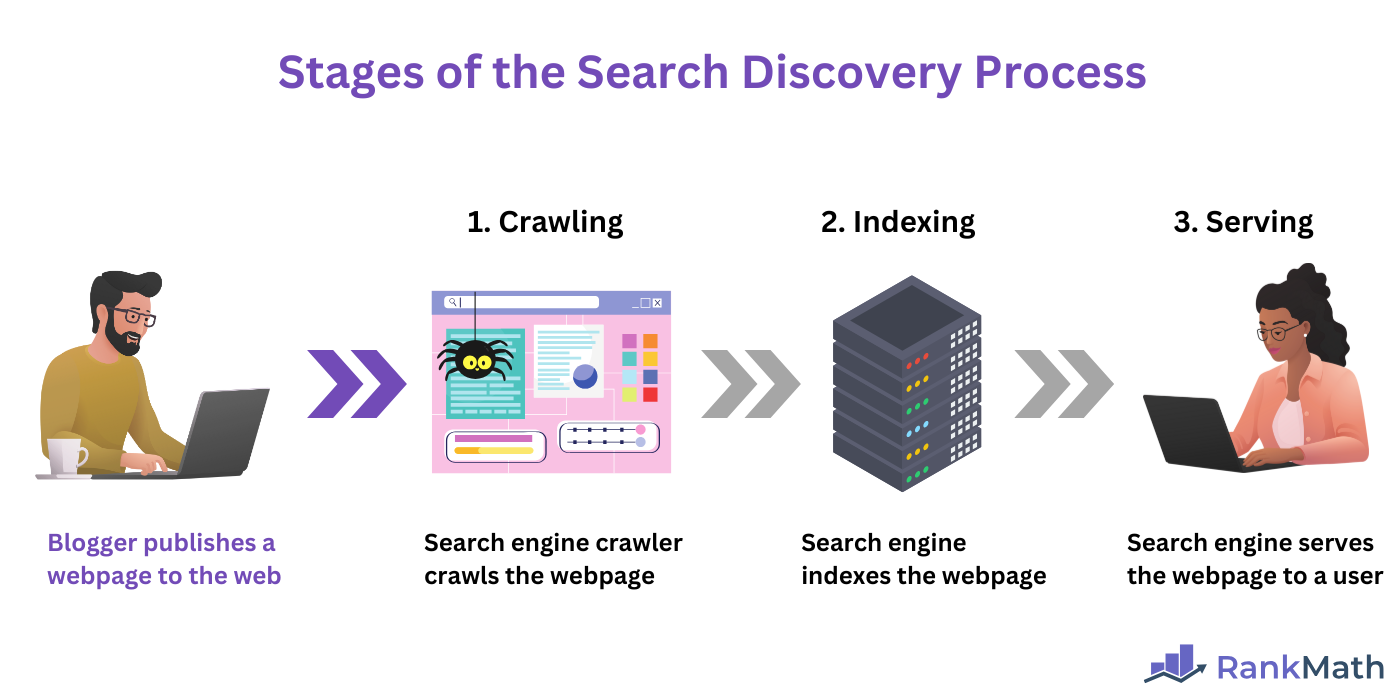
This makes indexing a crucial step of the search discovery process. In fact, indexing is the second stage of the search discovery process.
The three stages of the search discovery process are:
- Crawling
- Indexing
- Serving
a. Crawling
This is the process whereby the search engine crawler bot discovers new and updated content on the web.
b. Indexing
This is the process whereby the search engine organizes and stores the crawled content in a database called an index.
c. Serving
This is the process by which a search engine presents content from its index to a user.
All three stages (crawling, indexing, and serving) of the search discovery process have to occur for a webpage to be presented to a user. A webpage that is not crawled is unlikely to be indexed, and a webpage that is not indexed cannot be served.
Issues That Can Affect Indexing
Multiple factors can affect indexing. These factors can be indexing-specific issues or may be related to crawling.
1 On-Page and Off-Page SEO Issues
On-page SEO y off-page SEO elements can affect crawling and indexing. For instance, search engines find new webpages by following the URLs on previously discovered ones.
This means webpages that lack sufficient vínculos de retroceso (off-page SEO) and have an ineffective internal linking structure (on-page SEO) are less likely to be discovered by search engines.
In fact, webpages without any link pointing to them become páginas huérfanas. Such pages are invisible to search engines and cannot be discovered, crawled, or indexed.
Content quality is another on-page SEO issue that can affect indexing. Search engines may discover and crawl such content. However, they will not index them because they are low-quality thin content.
2 Technical SEO Issues
Multiple technical SEO issues can affect the indexing of a webpage. In fact, crawling and indexing issues are more likely to result from technical SEO problems rather than from on-page or off-page SEO issues.
That said, technical SEO issues can arise from problems or settings on your server, content delivery networks (CDNs), or code on your site. Here are some technical SEO issues that can prevent indexing:
- Crawl errors
- Soft 404 errors
- Contenido duplicado
- 404 No encontrado error
- Pobre page load speed
- Absence of a canonical tag
- Presence of the noindex tag
- Absence of datos estructurados
- Absence of an mapa del sitio XML
- Non-mobile-friendly webpages
- Poor and complex URL structures
- Robots.txt rules that disallow crawling
- Rate-limiting errors, such as the 429 “Too Many Requests” error
- Improper or excessive redirects, such as redirect chains y redirect loops
- Server errors, such as the Error interno de servidor 500 and the 502 Bad Gateway error
3 Crawl Errors
A crawl error refers to any issue that prevents the crawler from crawling the page. This has an impact on indexing, as any issue that prevents crawling will likely also prevent indexing.
Crawl errors are typically technical SEO issues. Two of such errors that stand out include:
- Capacidad de rastreo cuestiones
- Crawl budget cuestiones
a. Crawlability Issues
Crawlability is the ability of a search engine’s crawler to discover, access, and crawl a URL. These crawlers discover new webpages by following the links on previously discovered webpages.
Once done, they crawl the page, provided there are no instructions or technical SEO issues preventing them from doing so.
During crawling, the crawler gathers data about the page and its content. They then use this to determine what the page is about and whether it should be indexed.
Not all crawled pages are indexed. This could be due to technical SEO issues, but it can also occur when the blogger instructs the search engine not to index the page, such as when they use the noindex tag.
A search engine may also refuse to crawl a webpage when it determines that its content is of low quality (thin content) or a duplicate of another webpage. Such pages may never get indexed even when they are crawled.
b. Crawl Budget Issues
The crawl budget refers to the number of pages a search engine bot will crawl on your site within a specific timeframe. It is influenced by factors like your site’s authority, speed, health, and the number of pages.
If your site has a large number of URLs but a limited crawl budget, then its pages may not be crawled at all. Even when they get crawled, the search engine may crawl useless pages and ignore the useful ones.
Considering crawling affects indexing, this means the useless pages that get crawled may get indexed and served. It also means that useful pages that are not crawled cannot be indexed or served on search results pages.
Search engines usually assign a crawl budget to your site, and you have no control over it. However, they may reduce it if they believe your server lacks sufficient capacity to handle their crawlers.
Therefore, ensure that your server has sufficient bandwidth capacity, as repeated server errors, such as the 500 Internal Server Error, can cause search engines to reduce your crawl budget.
How to Confirm the Index Status of a Webpage
You can confirm the index status of a webpage using the Google search engine or the Consola de búsqueda de Google. Here is how to do that.
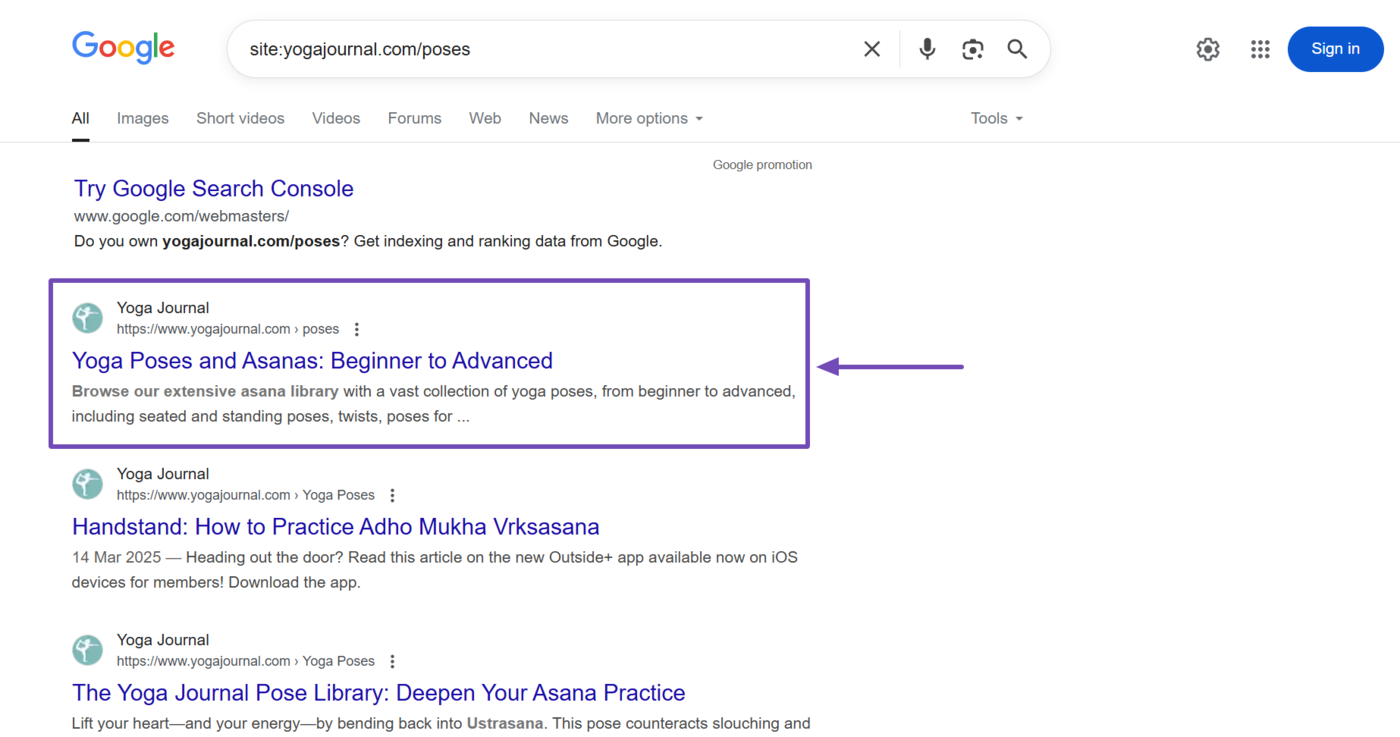
1 Use the site: Command
Ingresar site: followed by the webpage’s URL into the search engine.
For example, if you want to confirm whether the webpage at yourdomain.com/best-yoga-poses has been indexed, you will enter site:yourdomain.com/best-yoga-poses into Google.
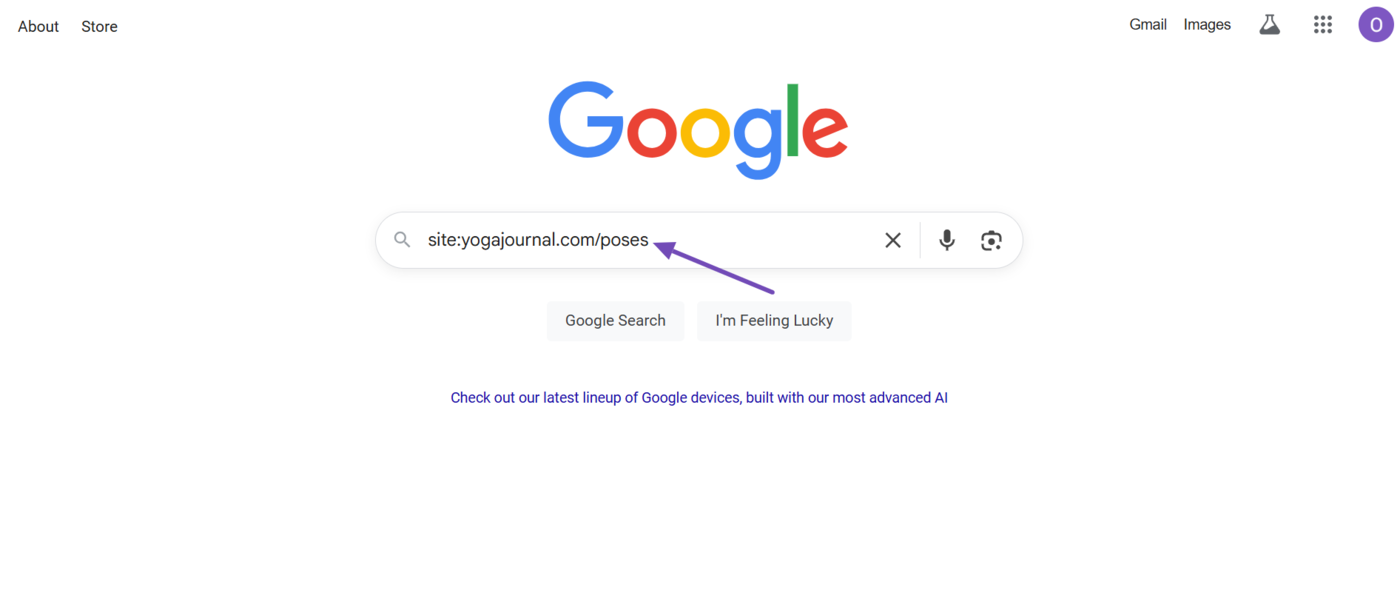
If the webpage has been indexed, it will appear in the search results, as shown below. If the webpage does not appear in search results, it is likely not indexed.
2 Utilice la consola de búsqueda de Google
To get started, log into Google Search Console and click Indexing → Paginas.
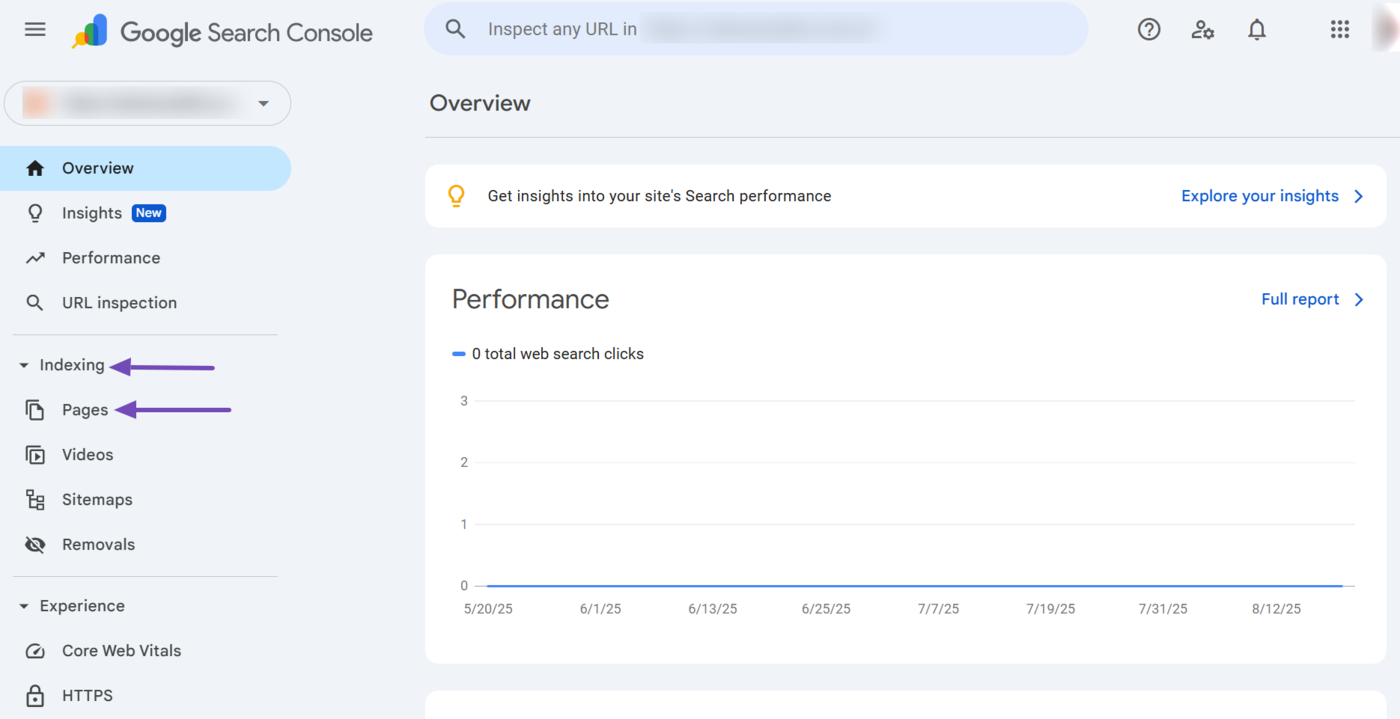
You will be presented with the number of indexed and unindexed pages on your site.
los “Why pages aren’t indexed” field will also include the reasons your URLs were not indexed, along with the number of webpages affected by the specific issue.
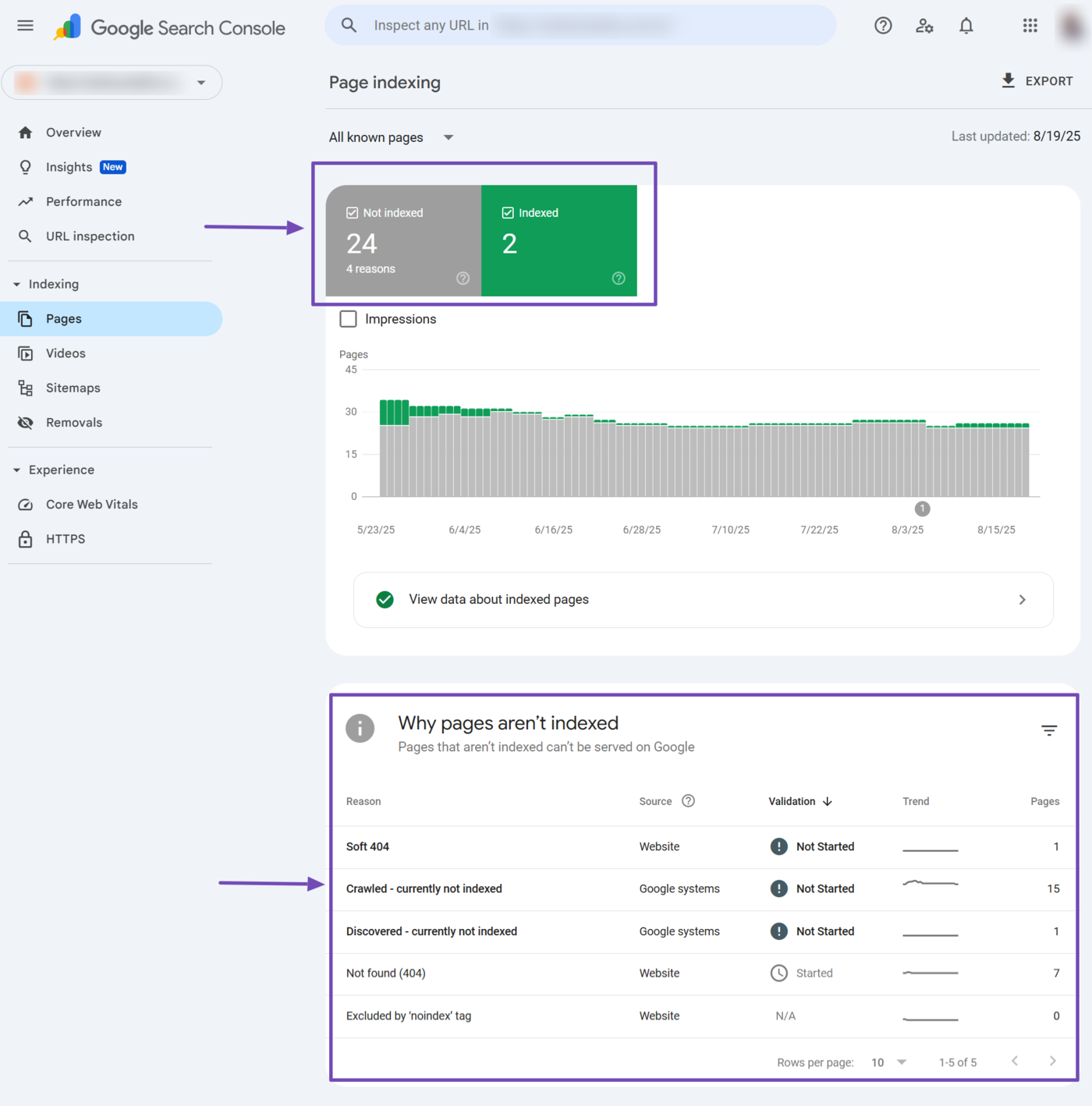
Here are some common reasons you may see:
- suave 404: Google thinks the page has little or no useful content, so it treats it as missing and excludes it from the index
- Crawled – currently not indexed: Google crawled the page but decided not to index it, often due to low quality, duplicate content, or lack of value
- Discovered – currently not indexed: Google is aware of the page’s URL but has not crawled it yet, possibly due to low crawl priority or server resource limits
- Not found (404): The page returns a 404 Not Found error, so Google cannot index it because the content does not exist
- Excluido por la etiqueta 'noindex': The page has a sin índice directive in its HTML or HTTP header, explicitly telling Google not to index it
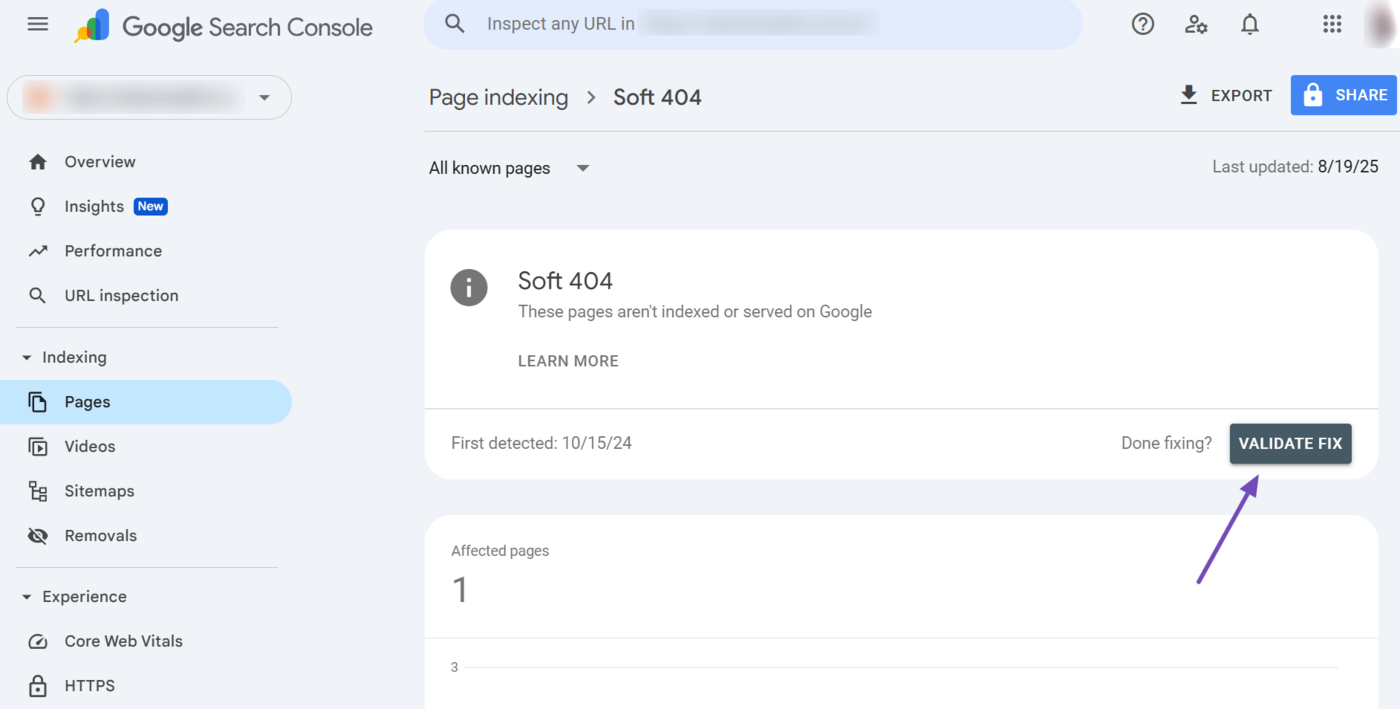
Now, click on any of the issues. For instance, let us click on suave 404 in this example.
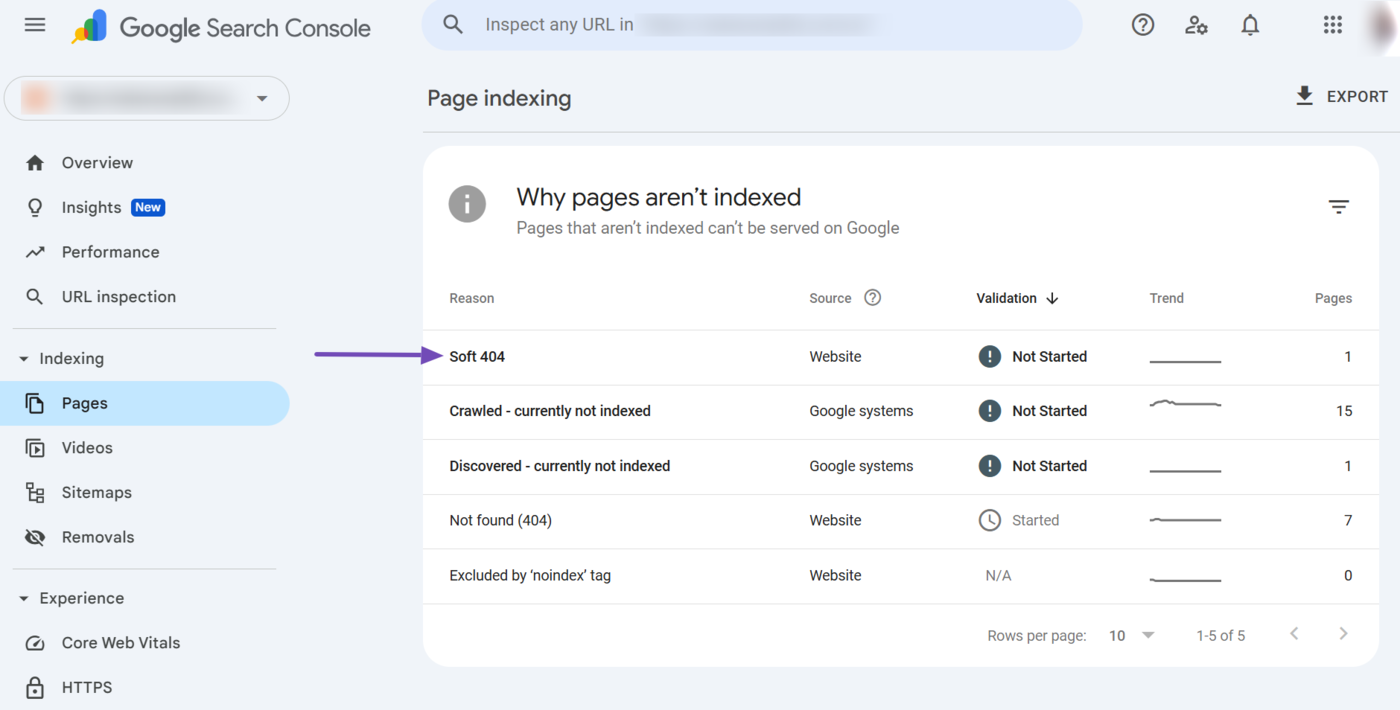
Google Search Console will display the affected URLs. You can now proceed to resolve them.
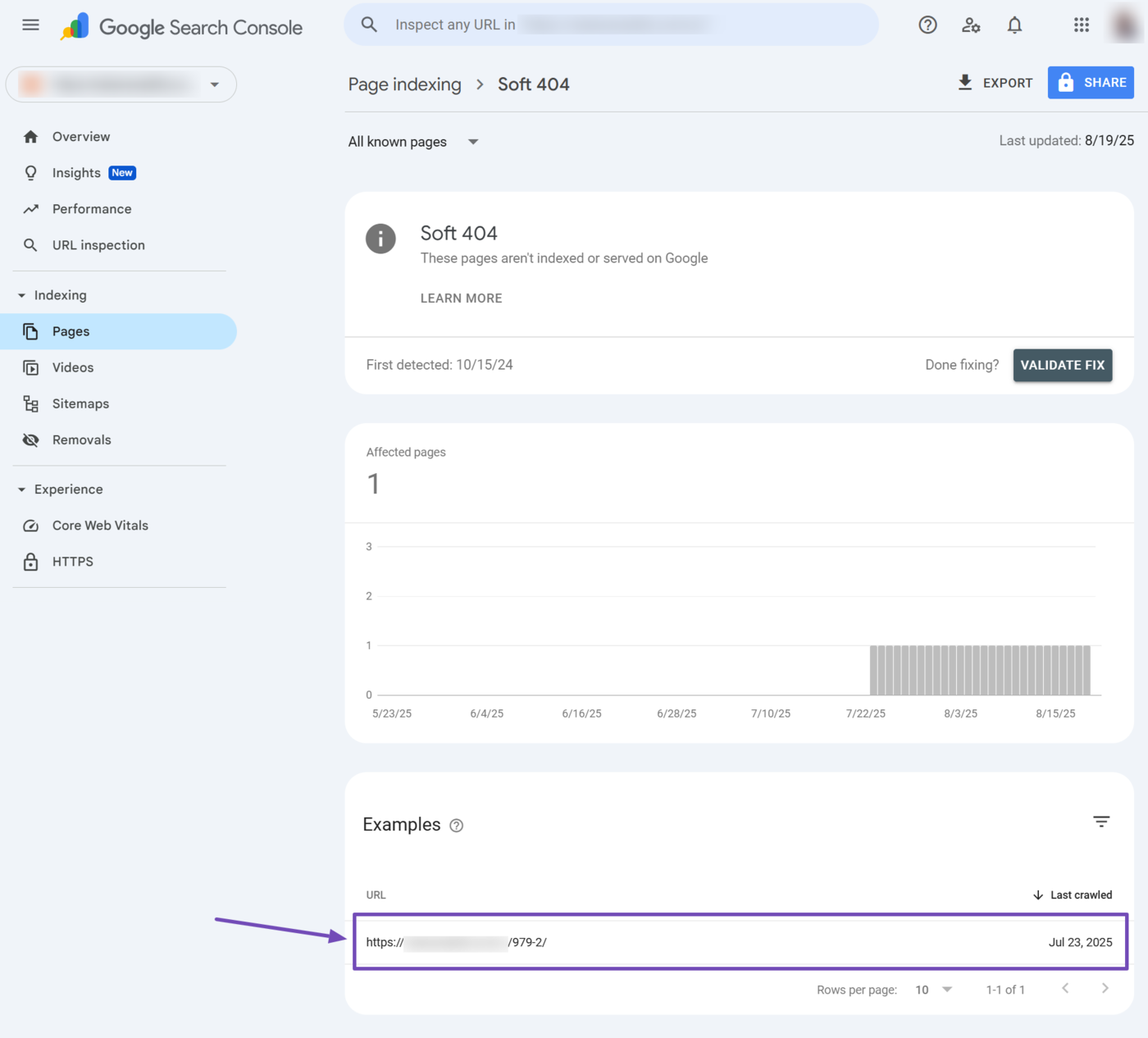
However, ensure to resolve all affected URLs together. Once done, click Validate Fix, Como se muestra abajo.