What Is Server Side Rendering?
Server side rendering (SSR) is a web development approach in which a webpage is rendered on the server before it is sent to the browser.
This means the browser receives a fully formed HTML page, along with links to external CSS and JavaScript files. The browser then downloads these files and applies them to the webpage.
To better understand server side rendering, we should first understand rendering.
What Is Rendering?
Rendering is the process by which a browser converts HTML, CSS, and JavaScript code into a visual webpage that users can view and interact with.
Every website consists of code, specifically, HTML, CSS, and JavaScript code:
- HTML determines the structure of the content
- CSS styles the content, adding things like font and color
- JavaScript allows users to interact with the content
When a user tries to access the website, the browser or server (or both) assembles the HTML, CSS, and JavaScript code into the visible site. The process of assembling this code into the visible site is called rendering.
When rendering occurs in the browser (which is also called a client), it is called client side rendering. When it occurs on the server, it is called server side rendering.
How Server Side Rendering Works
Here is a quick overview of how server side rendering works:
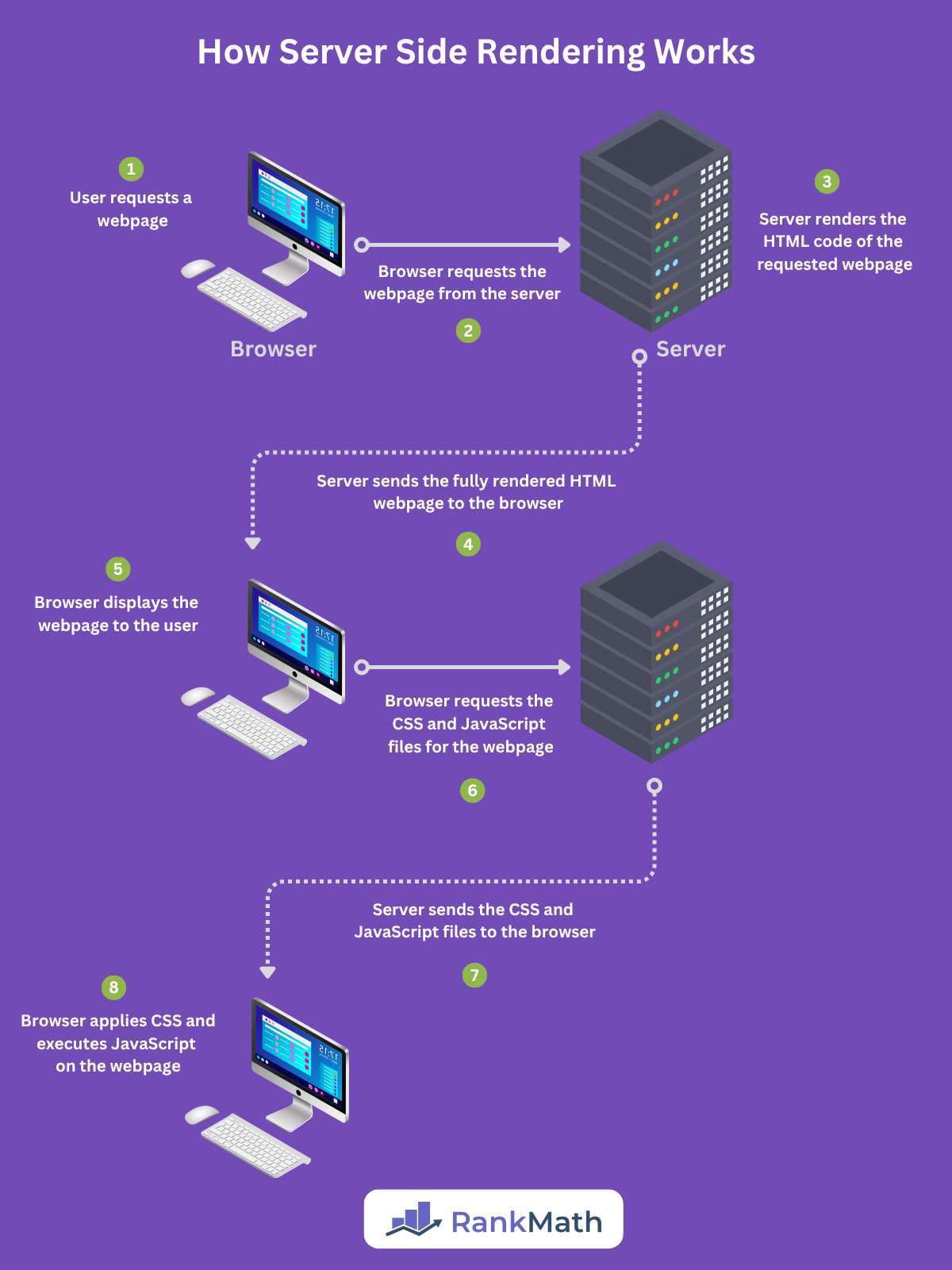
1 The Browser Sends a Request to the Server
When a user enters a website URL into their browser, the browser sends an HTTP request to the server that hosts the site, requesting the files for the webpage.
2 The Server Fetches the Required Resources
The server then processes the request and fetches the relevant resources (code, images, videos, and files) needed for the webpage. This includes the resources stored on its system, as well as any dynamic content stored on an external database or server.
3 The Server Renders the HTML Webpage
The server then renders the code to generate a full HTML document. This may include critical inline CSS, but the full CSS and JavaScript files are typically sent separately for the browser to process.
4 The Server Sends the Rendered HTML Page to the Browser
The server sends the rendered webpage to the browser, which in turn, displays it to the user.
5 The Browser Downloads and Executes the JavaScript Code
The browser then downloads the CSS and JavaScript files referenced in the HTML code. The CSS file determines the styling and layout of the webpage, while the JavaScript code allows users to interact with the webpage.
Importance of Server Side Rendering
Server side rendering allows a server to deliver a fully rendered webpage to the browser. This ensures the webpage loads quickly, which is especially important for SEO and user experience. It is also great for crawlability als web crawlers find it easier and quicker to access such pages.
As a matter of fact, WordPress sites use server side rendering by default. However, some WordPress themes and plugins can introduce client side rendering using JavaScript frameworks and single-page applications (SPAs).
Overall, modern websites typically use a combination of server side and client side rendering to deliver their webpages to visitors.
Similarities Between Server Side and Client Side Rendering
Server side rendering (SSR) and client side rendering (CSR) are two popular methods of loading a webpage. Both types of rendering are used to deliver web content to users. However, they differ in where and how that content is generated.
As their names suggest, server side rendering loads the webpage on the server and then sends it to the browser, which then displays it to the user while executing the necessary JavaScript code.
In contrast, client side rendering (CSR) builds and displays the webpage in the browser. The browser first downloads a minimal HTML shell, along with the necessary CSS and JavaScript files from the server, and then renders them on the client’s device.
Both methods can produce the same visual result, and many modern applications use a hybrid approach that combines elements of both. However, some systems still heavily stick to one type of rendering over the other.
Difference Between Server Side and Client Side Rendering
The key difference between server side and client side rendering lies in performance. Pages loaded on the server are quicker to display content than those rendered in the browser (client).
This means pages rendered on the server are usually better for SEO. They have faster page speeds and offer a better user experience. Search engine crawlers also find such pages easier to access since the page is already rendered.
In the case of client side rendering, the search engine crawler will have to render the page before it can crawl it. This requires a longer page load time and consumes more resources compared to server side rendering.
Another subtle difference lies in the control the blogger has over the rendering of the webpage. Server side rendering puts the load on the server. This gives the developer or blogger greater control over how their users access their webpages.
Client side rendering, on the other hand, shifts the load to the client. This means the browser has more control over how the page is rendered, and some pages can render differently, depending on the capability of the client’s browser and device.
Disadvantages of Server Side Rendering
While server rendered webpages offer several advantages over client rendered ones, they also come with some drawbacks. Below are a few common limitations to consider:
1 It Can Put a Strain on the Server
Server side rendering requires the server to process and render every page the user requests. This means the blogger needs a high-CPU and high-memory server with the necessary resources to load webpages efficiently.
The server must also be scalable so that it can accommodate the increased workload during high-traffic periods. Otherwise, the server can become overloaded during high-traffic periods, which can cause it to slow down or even crash.
2 Additional Webpages Are Slower to Load
Server side rendering typically reloads the entire page with each navigation, since navigating to a fresh page triggers a new request to the server.
In contrast, client side rendering, especially in single page applications, handles routing in the browser and dynamically updates only the necessary parts of the page using JavaScript. This avoids full-page reloads and enables smoother, faster transitions between pages.
This means that webpages loaded on the server ultimately become slower for users who visit additional pages on the site. Meanwhile, client side rendering becomes a better option as it delivers webpages faster.
3 It Still Requires the Browser to Load the JavaScript
Server side rendering delivers the rendered HTML quickly. However, the browser still needs to load and apply the JavaScript code to the page.
This means that while a webpage appears quickly to the user, it may not be interactive until the browser has executed the JavaScript. This can impact the user experience, particularly for visitors who want to quickly engage with the webpage.
4 It Is Inefficient for Webpages That Update in Real-Time
Server side rendering does not work well with webpages that need to be constantly updated. For example, a webpage that displays live scores, breaking news, or dynamic content.
This is because such pages have to be repeatedly rendered on the server before they are sent to the browser. This increases response time and consumes more server resources compared to static webpages rendered on the server.
5 It Consumes Server Respources
Dynamic webpages consume server resources when loaded on the server. This is because such pages do not have a permanent version and are constantly changing. This means they must be repeatedly rendered as users request them.
This consumes server resources, which can become unsustainable when the site receives a considerable amount of traffic. It also makes such webpages difficult to cache. Instead, developers typically load dynamic webpages on the client side rather than on the server side.