What is Keyword Cannibalization?
キーワードのカニバリゼーションは、サイトに同じまたは類似のキーワードでランク付けされている複数のページがある場合に発生します。 キーワード. It could result from publishing closely related content or optimizing relatively different content for similar keywords.
Keyword cannibalization often causes search engine optimization issues, as search engines are unsure of the page to display for a search query. In many instances, the affected pages will compete against themselves, making it difficult for them to rank in search engines.
While you should always avoid cannibalizing your keywords, you may optimize multiple articles for similar keywords if they target different search intents.
Why You Should Avoid Keyword Cannibalization
Keyword cannibalization can negatively affect your organic rankings. In many cases, the affected content will rank lower than they would have if they were not cannibalizing on one another.
Multiple pieces of content can rank for the same keyword if they target visitors with different search intent. For example, let us assume you have two articles. One ranks for ‘Easy yoga poses for newbies’ while the other ranks for ‘Yoga workouts for beginners’.
Both keywords target individuals who want yoga exercises for people new to yoga. However, they have slightly different angles, with the first focusing on poses while the other focuses on workouts.
Now, if you publish both content, there is the likelihood that they may end up competing with themselves for search rankings and traffic. So, to prevent such, you create content that covers yoga poses and workouts for beginners.
What is Not Considered Keyword Cannibalization
1 When the Affected Content Rank for Branded Keywords
Keyword cannibalization is pretty common with branded keywords. For example, Apple’s site shows up several times for the keyword ‘buy iPhone’.
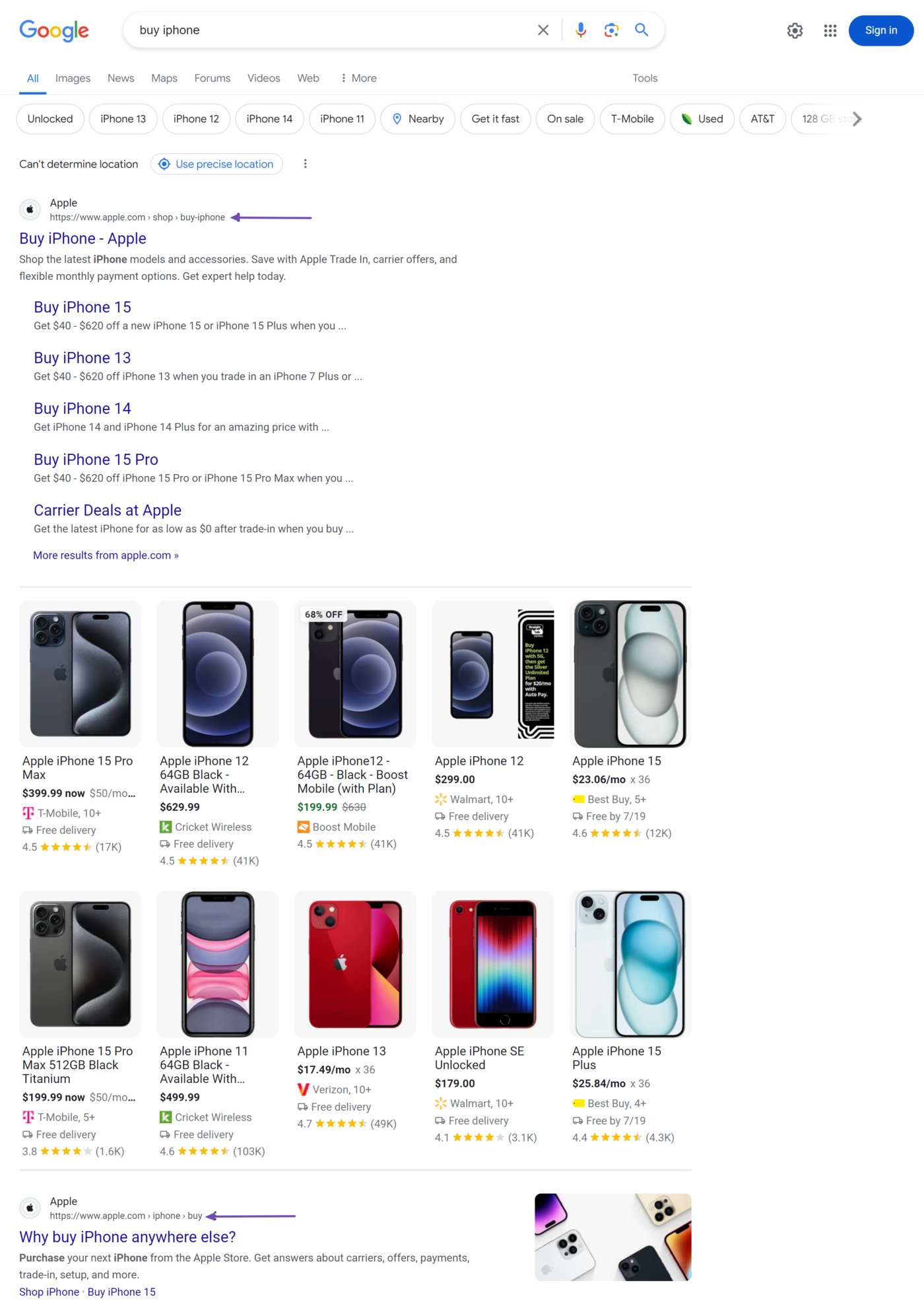
iPhone is a branded keyword belonging to Apple, so it is normal for multiple pages from Apple’s website to rank for it. Keyword cannibalization is not considered an SEO issue in these sorts of cases.
2 When the Affected Content Satisfies Different Search Intents
Two or more content are only considered to have cannibalized their keywords if:
- They appear on the same site
- They rank for the same keyword
- They satisfy the same search intent
For example, ‘Yoga for beginners’ and ‘Yoga for complete beginners’ have the same search intent, and any site that publishes them as separate content will quickly have a keyword cannibalization issue.
However, it is not considered cannibalization if the two content have the exact keywords but rank for different search intents.
How to Identify Cannibalized Keywords
You can identify keyword cannibalization by auditing your site to uncover content with the same keyword and search intent. You can perform this audit using an SEO tool or manually reviewing your site.
1 Perform a Site: Search
Head to Google and enter site: followed by your site URL and keyword enclosed in double quotes " " into the search bar. For example, site:yourdomain.com "yoga for beginners".
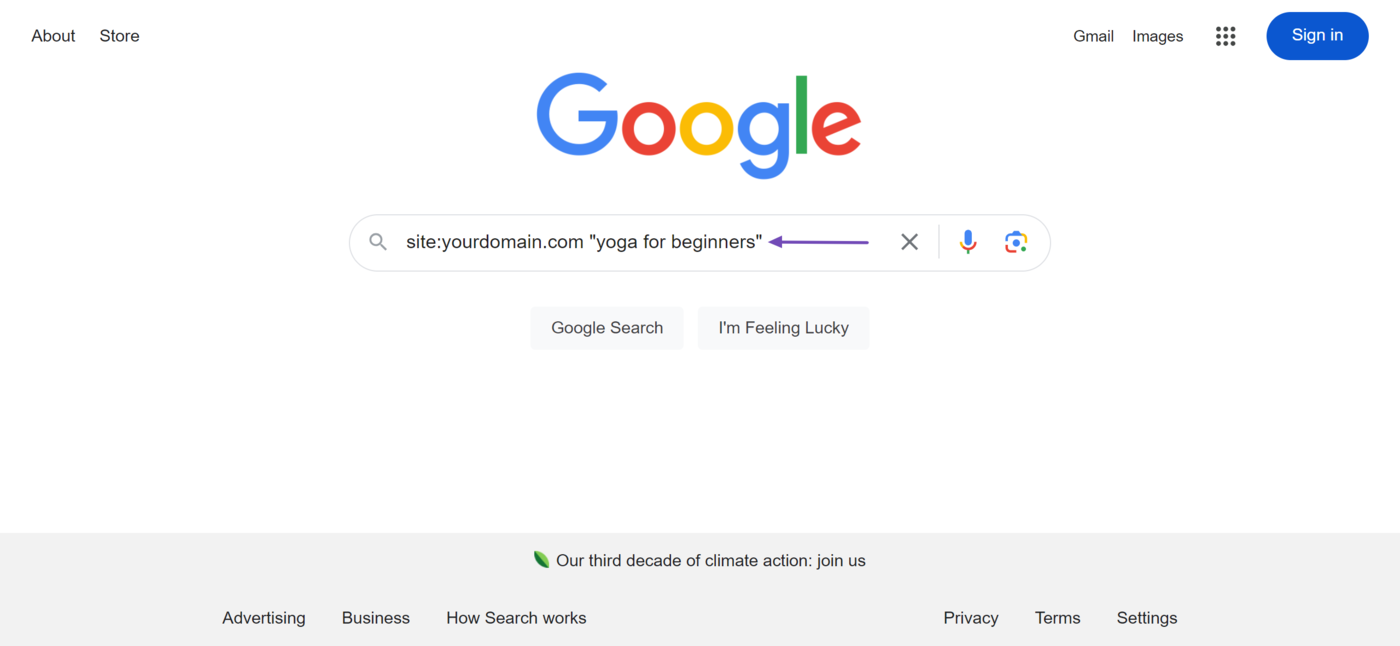
Google will return with pages that rank for that keyword. You should manually review the content to see which one you think ranks for the same keyword and search intent.
2 Compare Their Rankings
Now, dive into the analytics reports of the contents you have identified as possible cannibalizations and compare their rankings and search traffic. Cannibalized content will usually struggle to rank highly. So, both content will typically rank lower than they expected.
In terms of rankings, keyword cannibalization is only considered an issue if one piece of content affects the organic rankings of the other. If the affected content ranks well on search results, then there is no need to fix the issue.
How to Fix Keyword Cannibalization
There are different methods of fixing keyword cannibalization. The exact method you use depends on the specifics of the affected content, particularly its helpfulness and rankings on search results pages.
Cannibalized webpages that rank highly on search results pages should be left alone, while those with poor rankings should be deleted, merged, or optimized for another keyword.
1 Delete the Cannibalized Content
You should delete unhelpful content that cannibalizes on the keyword another content already ranks for. Examples of unhelpful content include outdated and thin content.
These sorts of content provide no value to a visitor and, in this case, prevent other content from ranking as it should. So, remove them from your site and use 301 redirects to point their URLs to the URL of the page you want to keep.
2 Merge the Affected Content
If the cannibalized contents are helpful, then it would be a great idea to merge them into a single article and publish it at one of the URLs.
You will review the rankings of the affected content and merge them into the one with the best chances of ranking on search results pages. Optionally, you could create a new one from scratch and publish it to the URL of one of the affected content. Then, you 301 redirect the other URLs to it.
3 Optimize the Affected Content
Keyword cannibalization could sometimes occur when Google misunderstands the URL structure of a site. This is common with ecommerce sites where different pages could rank for the same keyword.
For example, two category pages, one on ‘mattresses’ and another on ‘air mattresses’ may rank for the keyword ‘mattresses’. Similarly, category pages on ‘business laptops’ and ‘gaming laptops’ could rank for ‘laptops’.
In this case, you will re-optimize the affected pages for different keywords.
The ‘air mattresses’ category page, for example, should be optimized to rank for ‘air mattresses’. In the case of the laptops category pages, the store owner would create a dedicated category page for ‘laptops’ and then link to the gaming and business laptop pages from there.
4 Set the Cannibalized Pages to Noindex
You can also set cannibalized pages to noindex. That way, Google knows you do not want the content to appear on search results pages. However, this is a last resort and is not recommended. It should only be used with content you do not want to delete from your site.
For example, it is common for bloggers and ecommerce stores to create multiple landing pages to track conversions. These pages will likely rank for the same keywords if they appear on search results pages. To prevent such, you set them to noindex.