What is a Sitemap?
A sitemap is a file that provides humans and search engines with a list of webpages and files on a site. The specific files vary from site to site but usually include images, videos, and PDFs.
Sitemaps can be created for human visitors (HTML sitemaps) or web crawlers and search engines (XML sitemaps). Both sitemaps help humans and search engines understand the relationship between webpages and files on the site.
Types of Sitemaps
There are two types of sitemaps, namely:
- HTML sitemap
- XML sitemap
1 Plans de site HTML
The HTML sitemap provides human visitors with links to the content on a site. It is usually a regular webpage formatted into a sitemap.
The content included in an HTML sitemap varies from site to site. However, they typically include the clickable title of the webpages they link to. Some may split the content by category and include their last modified time.
While created for human visitors, search engines may use the HTML sitemap to understand the hierarchy of the content published on the site.
2 XML Sitemaps
XML sitemaps provide search engines with links to a site’s content. They usually include the content’s URL, image count, and last modified time.
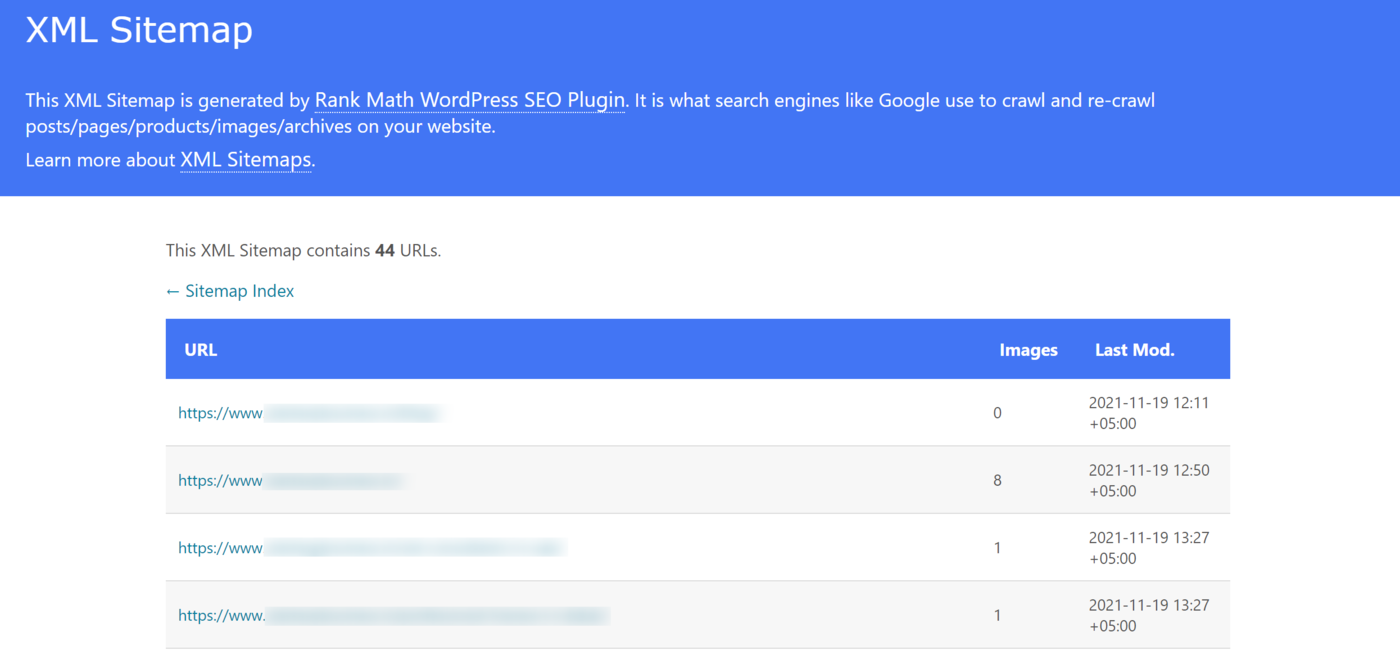
XML sitemaps are created using a .xml file and can typically be accessed by adding sitemap.xml ou sitemap_index.xml after your domain name. For example, https://yourdomain.com/sitemap.xml ou https://yourdomain.com/sitemap_index.xml.
Importance of Sitemaps
Sitemaps help visitors and search engines to discover the content on your site. This ensures that search engines can always identify and crawl your content. This makes them helpful for discovering pages orphelines, which are webpages that are not linked to other content on your site.
Sitemaps are also helpful for visitors looking to find or discover content on your site. Instead of relying on the search bar or filters, they can visit your HTML sitemap to discover the content they are interested in.
Sitemap Best Practices
Sitemaps help search engines to discover your URLs. So, setting them up correctly should be a top priority, as they help improve your SEO. To get the most out of them, it is recommended that you follow the sitemap best practices listed below.
1 Avoid Noindex Pages in the Sitemap
Your sitemap should only include pages you want search engines to index and display on search results pages. Avoid including pages with the noindex tag in your sitemap. It misdirects search engines and wastes your crawl budget.
2 Include All Important Pages
Your sitemap must contain the essential pages you want search engines to indice. This includes key landing pages, service and product pages, blog posts, and other high-value content on your site. In essence, if you want it to appear on search results pages, add it to the sitemap,
3 Keep the Sitemap Up-to-Date
Your sitemap must reflect the changes you make to your site’s content, preferably in real-time. So, ensure to update your sitemap whenever you add, remove, or modify the pages and files on your site.
4 Submit the Sitemap to Search Engines
While search engines can find your content without a sitemap, creating and submitting one improves their chances of discovering your most important content. So, submit your sitemap to Console de recherche Google et Outils pour les webmasters Bing.
5 Ensure Your URLs Are Crawlable
Your sitemap should only contain links to content available on the web. The links must not return 404 introuvable or Soft 404 errors and must not lead to permanent or temporary or permanent redirections. In the case of redirects, the URL in the sitemap should be the same as the final URL in the redirect.
6 Use HTTPS URLs in Your Sitemap
Search engines prefer indexing the HTTPS version of a site over the regular HTTP version. So, if you use HTTPS, ensure to include the HTTPS URLs in your sitemap.
7 Reference the Sitemap in Your robots.txt File
Include your sitemap in your fichier robots.txt. This ensures that search engines can find it easily without needing to look at several locations to find it. If you use Rank Math, Rank Math automatically generates your sitemap and includes its URL in your robots.txt file.
