What is Site Architecture?
Site architecture refers to the structure and organization of a site. It includes how the webpages are arranged and linked to one another, their hierarchy, and the overall design of the site’s content.
A good site architecture typically includes the usage of a clear navigation menu and logical URL structure. It also follows user experience (UX) best practices to ensure the site remains usable for visitors and search engines.
What is a Flat Website Architecture?
A flat site architecture is a simple site structure in which all pages are accessible within four clicks from the homepage or less. This allows visitors and search engines to locate information quickly, as they can navigate to any page with just a few clicks.
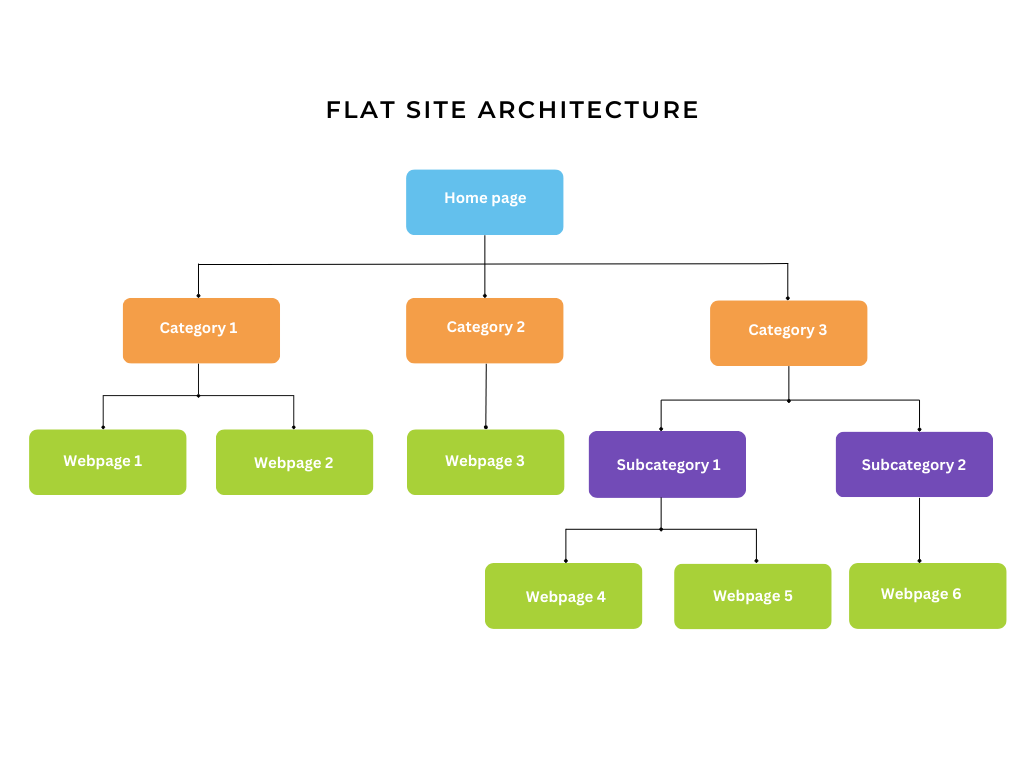
The flat site architecture is structured to ensure that every page on the site is accessible from the homepage with minimal clicks. This makes it helpful for small and medium sites with a limited amount of content.
Many large sites even stick with the flat site architecture because of the ease with which visitors can use it to discover content. However, this becomes challenging as the site grows larger, as it could lead to clutter and confusion if not managed properly.
Importance of the Site Architecture
The site architecture provides bloggers and visitors with SEO, usability, and user experience benefits. It also makes it easy for search engines to crawl a site.
1 It Improves the User Experience for Visitors
A good site architecture allows visitors to find content on a site quickly and easily. This improves their user experience, increases their chances of remaining on the site for longer, and reduces the site’s bounce rate. Such visitors are also likely to return to the site in the future.
2 It Allows Search Engines to Find Your Content
A good site architecture allows search engine crawlers to easily navigate your site and find your webpages. This, in turn, allows them to crawl ja indeksi your site effectively, leading to better visibility and rankings on search result pages.
3 It Spreads PageRank and Link Equity to Other URLs
A good site architecture allows you to spread Sivujärjestys ja link equity to other pages on your site. Some of your pages will have more PageRank and link equity than others. You can spread them using sisäiset linkit that point to other relevant pages.
4 It Enables Websites to Achieve Sitelinks
Google sometimes includes sitelinks to some results that appear on search results pages. Bloggers cannot determine or configure their sitelinks. Instead, Google determines them using certain factors like the site architecture.
Site Architecture Best Practices
An excellent site architecture allows visitors and search engines to access and use your site. Therefore, you should follow the site architecture best practices below.
1 Use a Flat Website Architecture
A flat website architecture minimizes the number of clicks needed to reach any page, making it easier for users and search engines to navigate. This structure typically has fewer levels, making content more accessible and improving user experience.
2 Use Category Pages
Your site architecture should include relevant categories and subcategories where necessary. This allows you to group related topics, allows visitors to find relevant content quickly, and allows search engines to understand the site’s structure and content hierarchy.
3 Use a Good URL Structure
Your URL structure should reflect your content and category pages. For example, a category page could have a URL like yourdomain.com/shirts/blue-shirts/. This ensures that visitors and search engines understand the context of the page, even if they do not visit it.
4 Use Relevant Internal Links
Visitors and search engines rely on internal links to find your content. In the case of visitors, it encourages and enables them to explore related content. Internal links also assist search engines in discovering pages and understanding the relevance of the content in relation to other pages on the site.
5 Include a Sitemap to Your Site
An XML-sivustokartta is a file that lists all the important pages on your site. Search engines usually use this to find content to crawl and index. Search engines also use it to determine your site structure.
6 Include Breadcrumbs to Your Site
Breadcrumbs are navigational aids that show users their location within the site hierarchy. For example, Home > Shirts > Blue-shirts. Breadcrumbs improve the user experience for visitors as it allows them to navigate your site easily. It also allows search engines to understand your content hierarchy and site structure.
7 Specify Your Canonical URLs
Canonical tags inform search engines about the preferred version of a page. This helps prevent issues with duplicate content and ensures that search engines know and index the accurate webpage and not the duplicate.
8 Avoid Orphan Pages
Orphan pages are webpages not linked to any other page on the site. They are challenging to find, and visitors and search engines may never discover them. To avoid such, ensure that all your pages link to relevant content. Relevant webpages should also link to them.