What Are Crawl Errors?
Crawl errors are issues that prevent search engine crawler bots from accessing and crawling your URL or site. For Google, these are errors that prevent Googlebot from crawling your site.
Crawl errors can affect your entire site or specific URLs. In either case, it prevents the search engine crawler (or Googlebot in the case of Google) from crawling or indexing your content for display on their Suchergebnisseiten.
In this article, we’ll cover:
Importance of Crawl Errors
Crawl errors prevent search engine crawlers from accessing your site. Webpages that cannot be crawled cannot be indexed or displayed in search results. This means any page that cannot be crawled will not be served to visitors.
Crawling is especially important as it is the first stage of the search discovery process. Specifically, the three stages are:
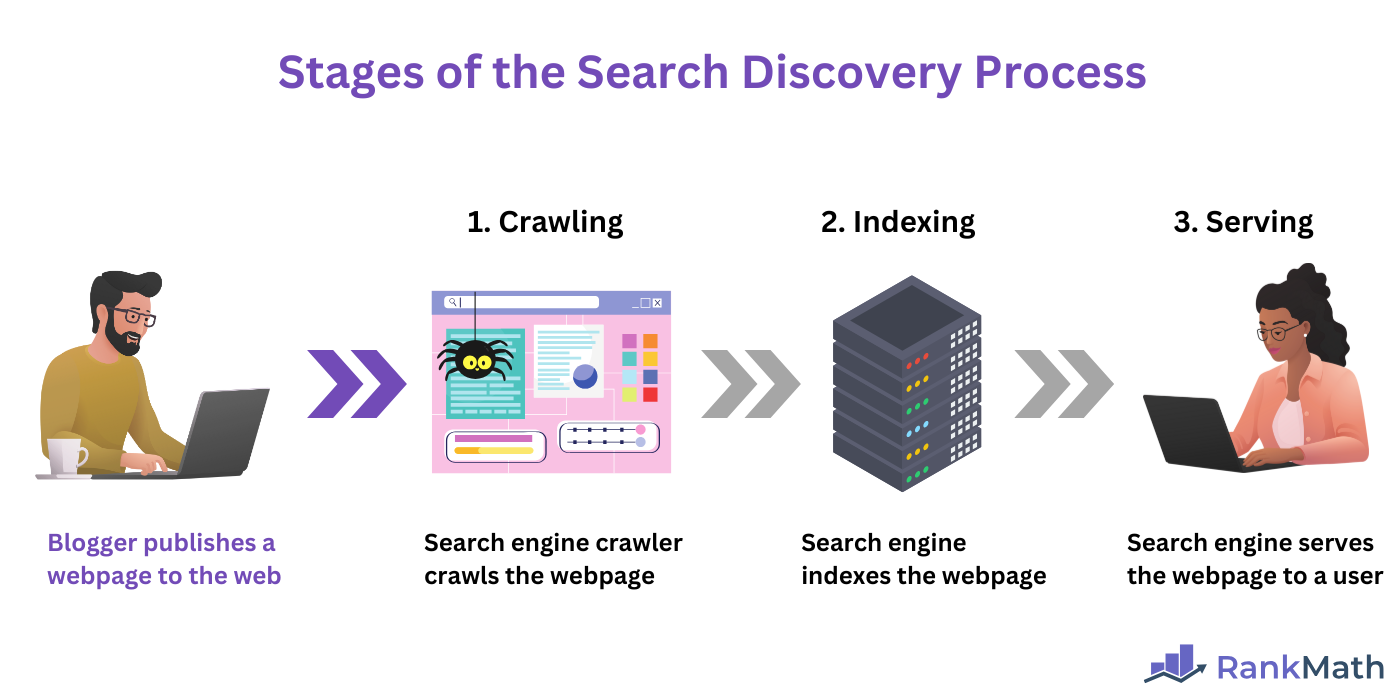
Crawling is the process by which a search engine discovers and accesses a webpage. After crawling, the page is indexed, meaning it is stored in a database called an Index. Once indexed, the page can be served to users in search results when they search for relevant search queries.
Overall, crawl errors prevent crawling. This in turn, prevents indexing, which in turns, prevents the webpage from being served on search engine results pages.
Crawl errors can also change how Google views your site. A high number of crawl errors indicate your website likely has technical SEO issues. This can cause Google to reduce your Crawl-Budget, which reduces the rate Googlebot crawls your site.
Types of Crawl Errors
Crawl errors are categorized into site and URL errors. Site errors affect the entire site, while URL errors affect specific URLs on the site.
1 Site Errors
Site errors are issues that prevent search engine crawlers from crawling multiple URL on your site. In many instances, they can even prevent the crawlers from accessing your entire site.
Site errors are generally split into:
- DNS errors
- Server errors
- Robots.txt issues
a. DNS Errors
Domain Name System (DNS) errors occur when search engines cannot communicate with your server due to issues with your DNS server.
The DNS server is a group of servers that allows crawlers and browsers to convert human-readable domain names into computer-readable IP addresses. For example, a DNS server can help a crawler to convert a domain name like example.com into an IP address like 3.184.216.34.
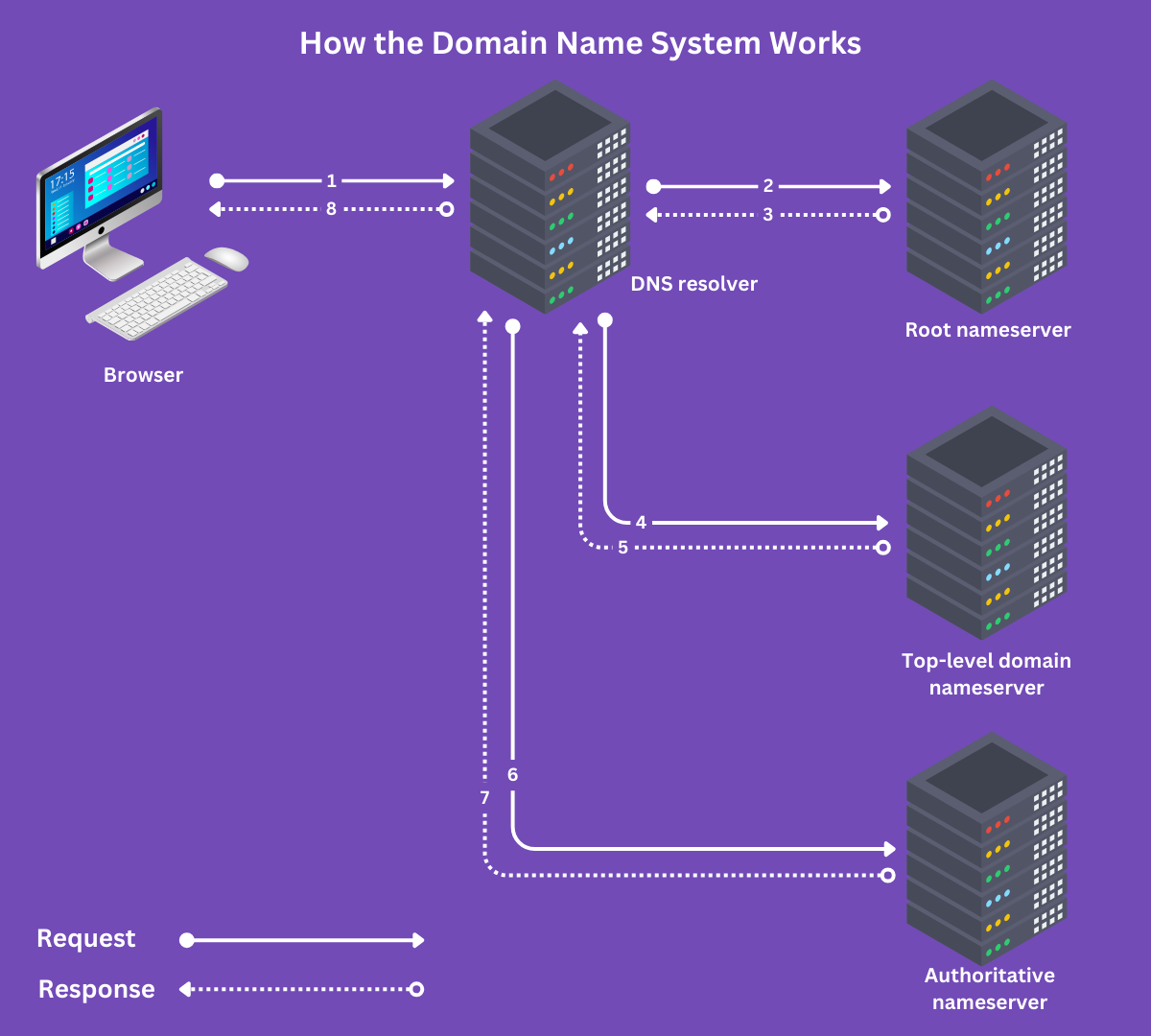
DNS server errors may be temporary, so you may not detect any errors while troubleshooting. However, the crawler would have encountered such errors when it tried to access your site.
b. Server Errors
Server errors occur when server issues prevent search engines from crawling your site. These errors can be caused by various server-level issues that cause the server to return HTTP 5xx server errors to the crawler.
Some common HTTP 5xx server errors include the HTTP 500 Interner Serverfehler, the HTTP 502 Bad Gateway error, and the HTTP 503 Service Unavailable error.
c. Robots.txt Issues
Search engine crawlers typically crawl your robots.txt file before crawling your site. However, some issues may prevent the crawler from accessing your robots.txt file. In such cases, the crawler will return a robots.txt error.
2 URL Errors
URL errors are issues that prevent search engine crawler bots from crawling specific URLs on your site. These errors prevent crawlers from accessing individual webpages and do not affect your entire site.
URL errors are generally easier to fix, and can be caused by various reasons, including:
- 404 Nicht gefunden errors
- Uncrawlable URLs
- Kanonische URL issues
a. 404 Not Found Errors
A 404 Not Found error indicates your webpage is missing from the specified URL. This can happen if the page has been moved to a new location or deleted from the site, without an appropriate redirect pointing to a new location.
 A similar error is the soft 404 error, which occurs when the webpage returns a HTTP 200 (OK) response code. This code indicates the webpage is available at the URL. However, the page contains little to no hilfreiche Inhalte, which causes search engines to treat it like a 404 Not Found page.
A similar error is the soft 404 error, which occurs when the webpage returns a HTTP 200 (OK) response code. This code indicates the webpage is available at the URL. However, the page contains little to no hilfreiche Inhalte, which causes search engines to treat it like a 404 Not Found page.
b. Uncrawlable URLs
Search engines may get confused when they encounter conflicting signals over whether or not you want them to crawl a URL.
For example, Google will not crawl a webpage that contains a noindex tag. However, it will try crawling the URL you submitted in your XML sitemap.
Now, if you added a noindex tag to a webpage but then added the same webpage to your sitemap, it can confuse the crawler and make the URL uncrawlable.
c. Canonical URL Issues
Search engines consider the kanonische URL as the main version among a group of duplicate webpages. You should specify it by adding the canonical tag to the canonical and duplicate pages, interne Links, and your sitemap.
Without the canonical URL, search engine crawlers may select an undesired URL as canonical and refuse to crawl the URL you consider canonical.
How to Diagnose a Crawl Error
You can diagnose a crawl error using two features available in Google Search Console:
- URL inspection tool
- Crawl Stats report
The URL inspection tool allows you to check for crawl issues Googlebot encountered at a specific URL, while the crawl stat report allows you to review the crawl errors that Googlebot detected on multiple URLs.
We will now show you how to use them below.
1 URL-Inspektionstool
The URL inspection tool is helpful for uncovering crawl errors Googlebot encountered on specific URLs on your site.
To get started, log into your Google Search Console account and enter the URL into the URL inspection tool, as shown below.
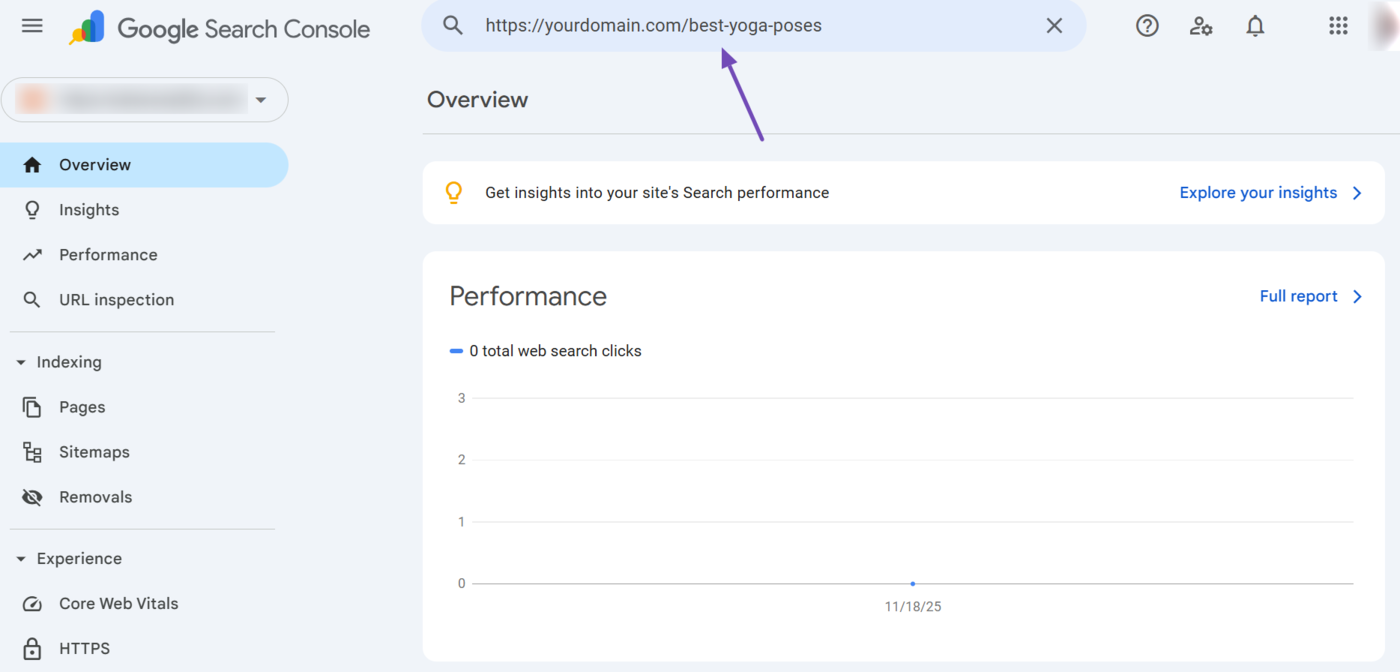
The URL inspection tool will return with technical reports about the URL. Click Page indexing.
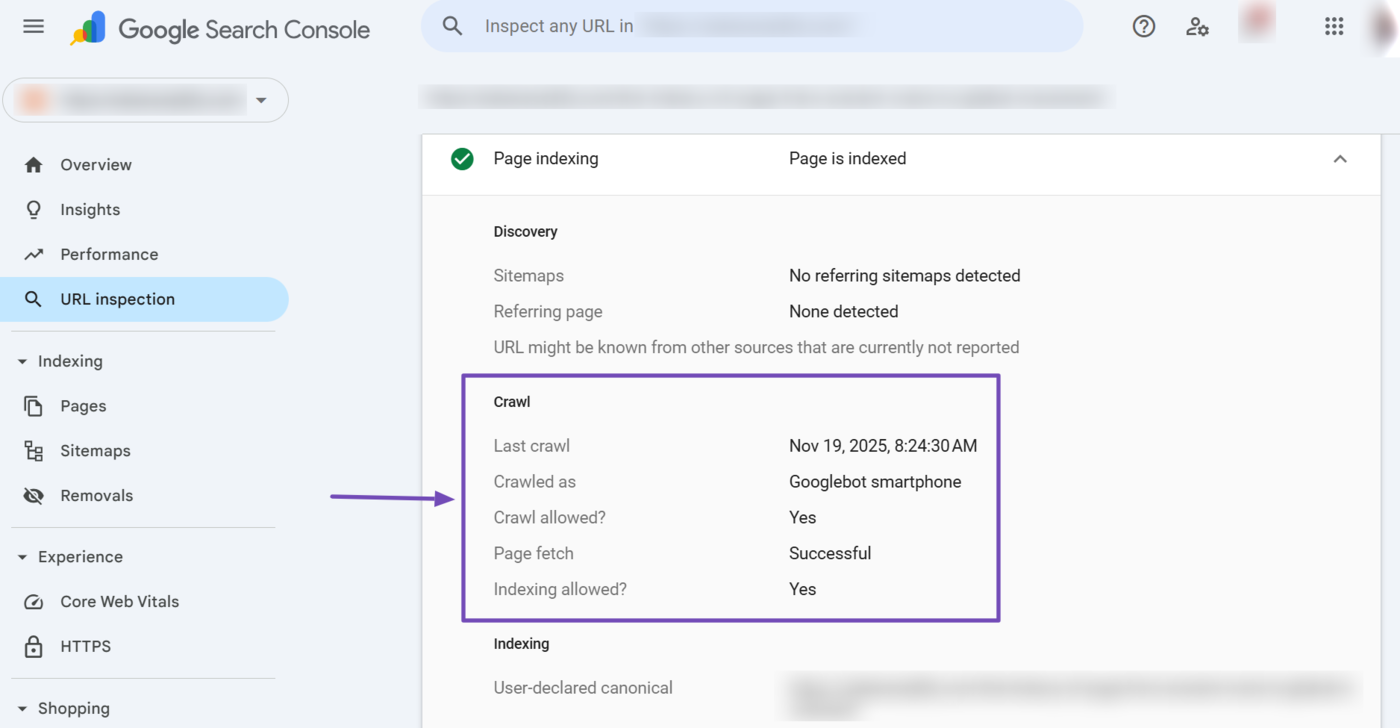
Now, scroll to the Crawl section of the report. You will see the crawl status of the URL. You want to focus on specific details like:
- Crawl allowed?: This specifies whether you allowed Googlebot to crawl the URL. You want it to return “Yes.”
- Page fetch: This indicates how successful Googlebot was at crawling the URL. You want this to return “Successful.”
- Indexing allowed?: This specifies whether you allowed Googlebot to index the URL. You typically want this to return “Yes.”
2 Crawl Stats Report
The crawl stats report is helpful for uncovering crawl errors Googlebot encountered across your site. To get started, log into your Google Search Console account and click Einstellungen in the left sidebar.
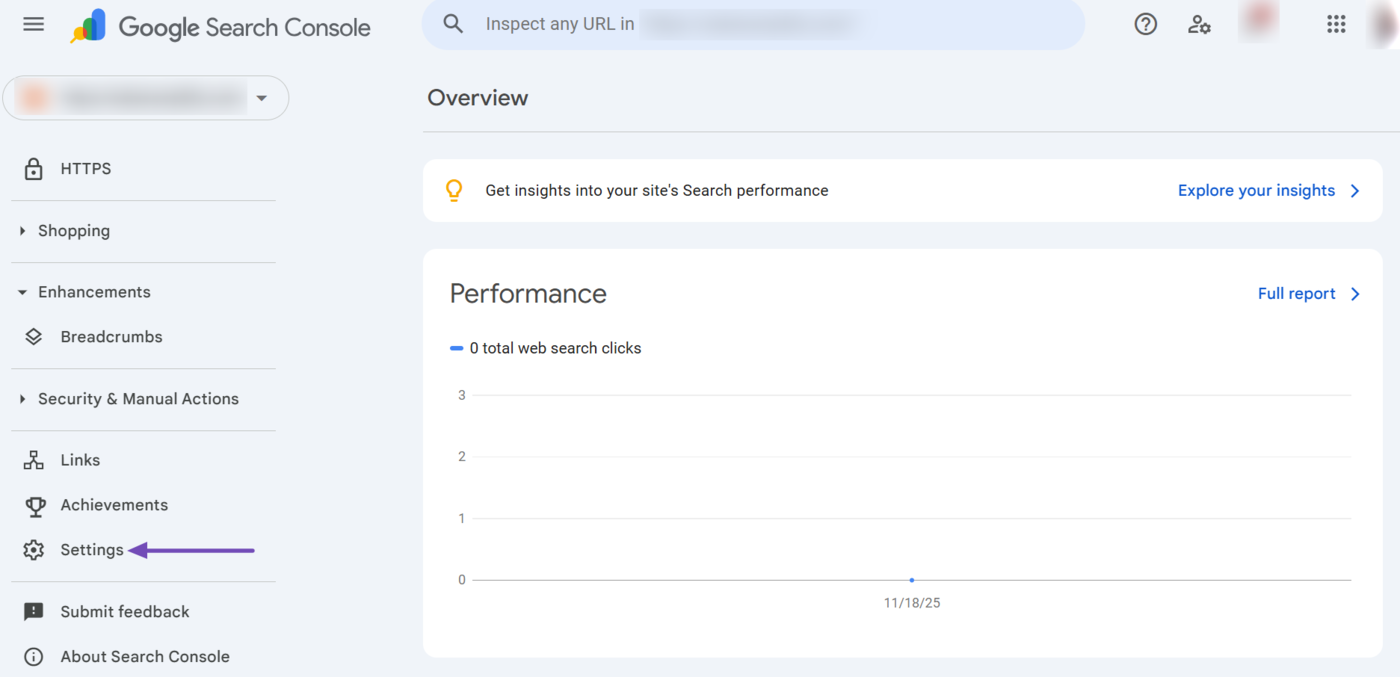
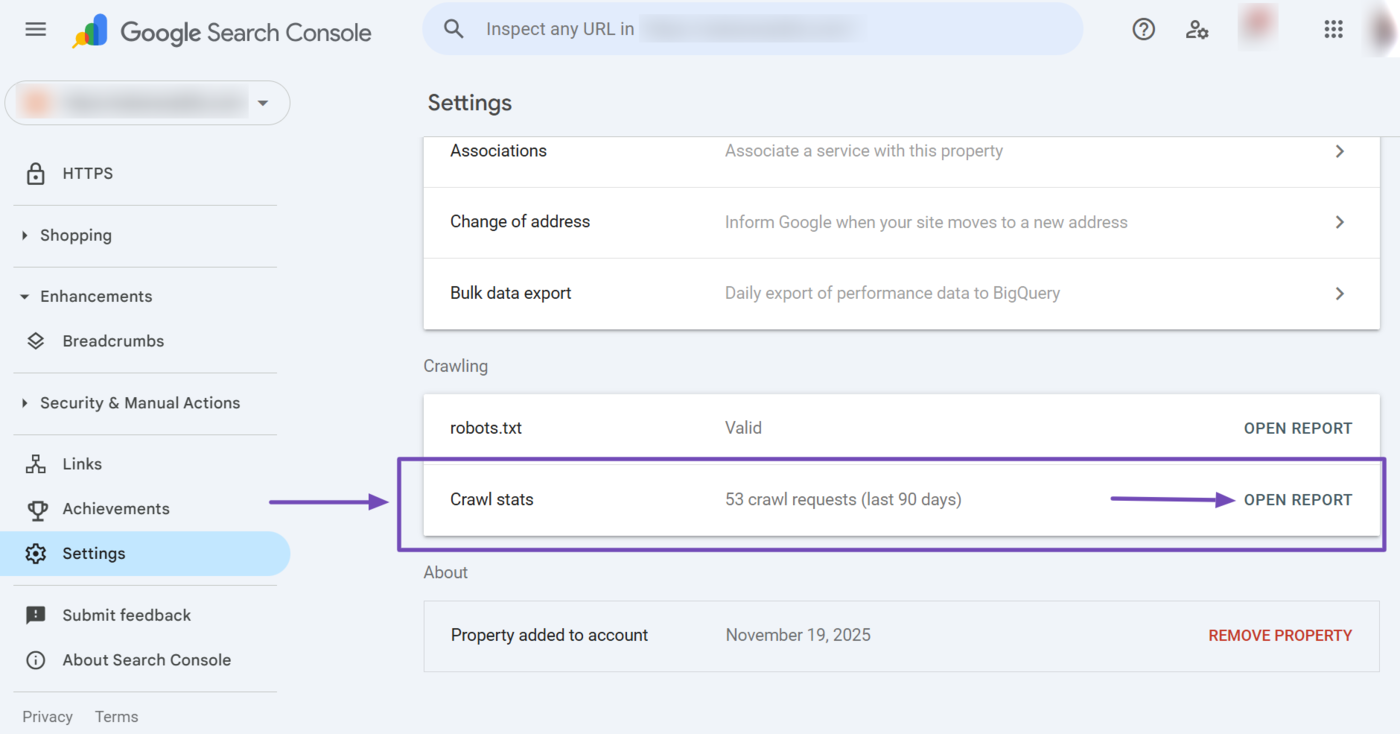
Once done, scroll down to Crawling → Crawl Stats. Then, click Open report.
Now, head to the By response Sektion. Here, you will see the response Googlebot received when it tried to crawl your URLs. It will also show the percentage of webpages from which it received the response.
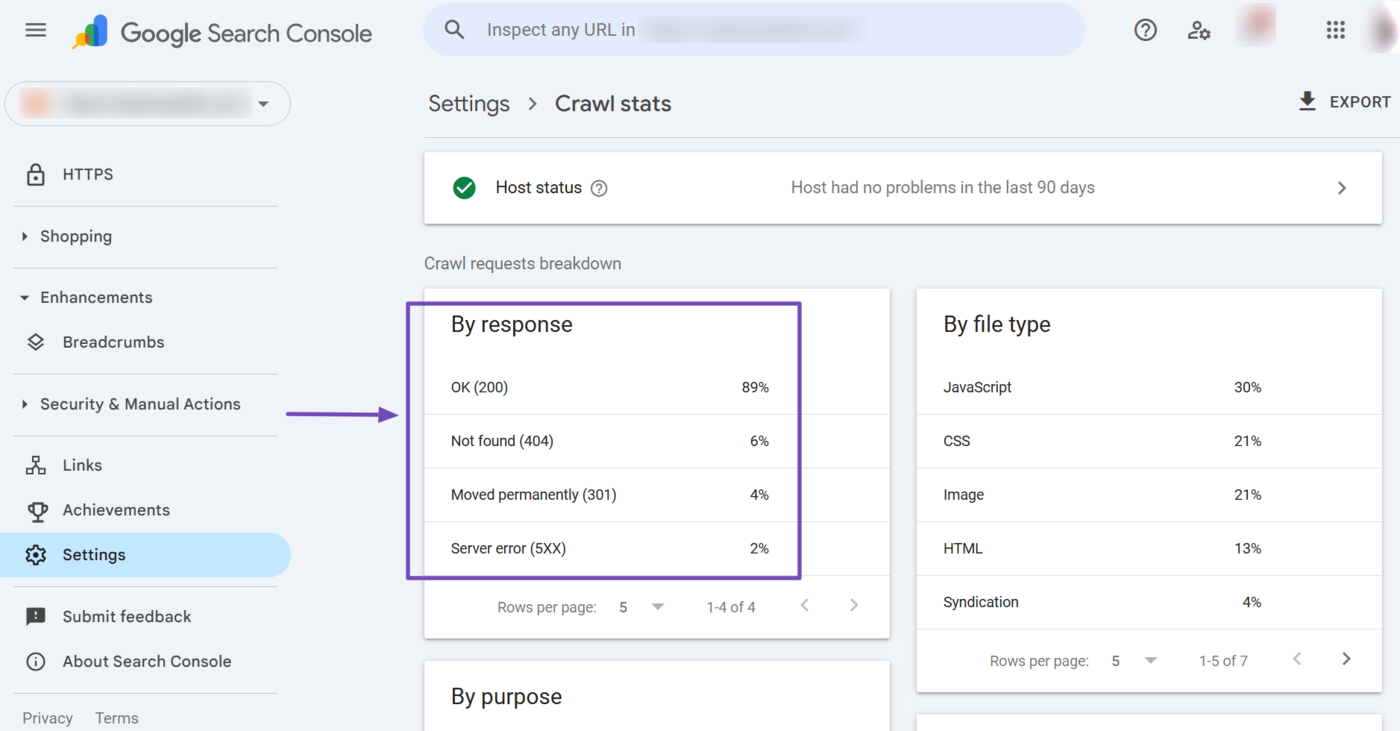
EIN OK (200) response confirms the URLs that Googlebot was able to crawl. This is what you want to see.
The rest, such as Not found (404), Moved Permanently (301), and server error (5xx) indicate issues that prevented Googlebot from crawling your URLs. You need to resolve these.
- Nicht gefunden (404): The webpage is missing and Googlebot could not find and crawl it
- Moved Permanently (301): The webpage has been permanently moved to a new URL and Googlebot may have crawled it at the new URL
- Serverfehler (5xx): An issue with your server prevented Googlebot from crawling the URL
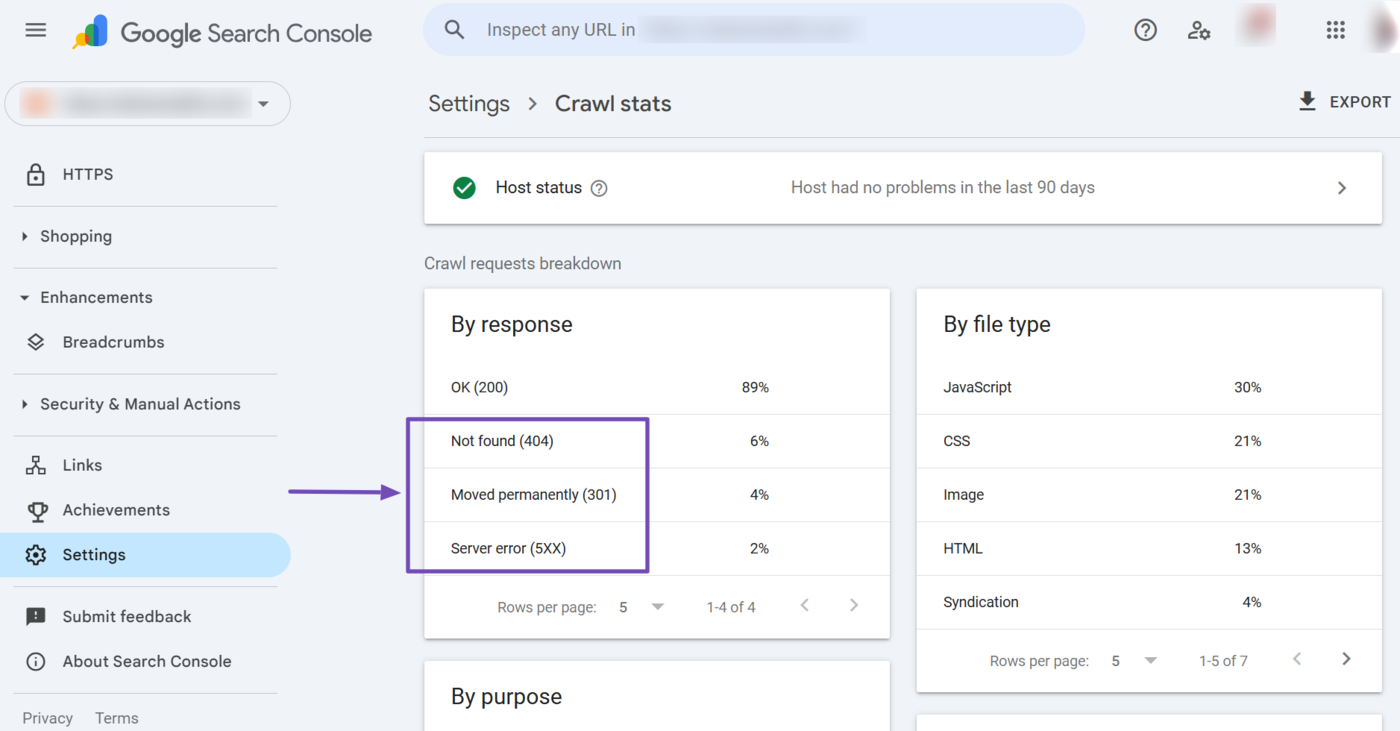
You can click on any of the crawl status for more insights into it. For this example, let us click on Not Found (404) for insights into the URLs Googlebot encountered the 404 Not Found error.
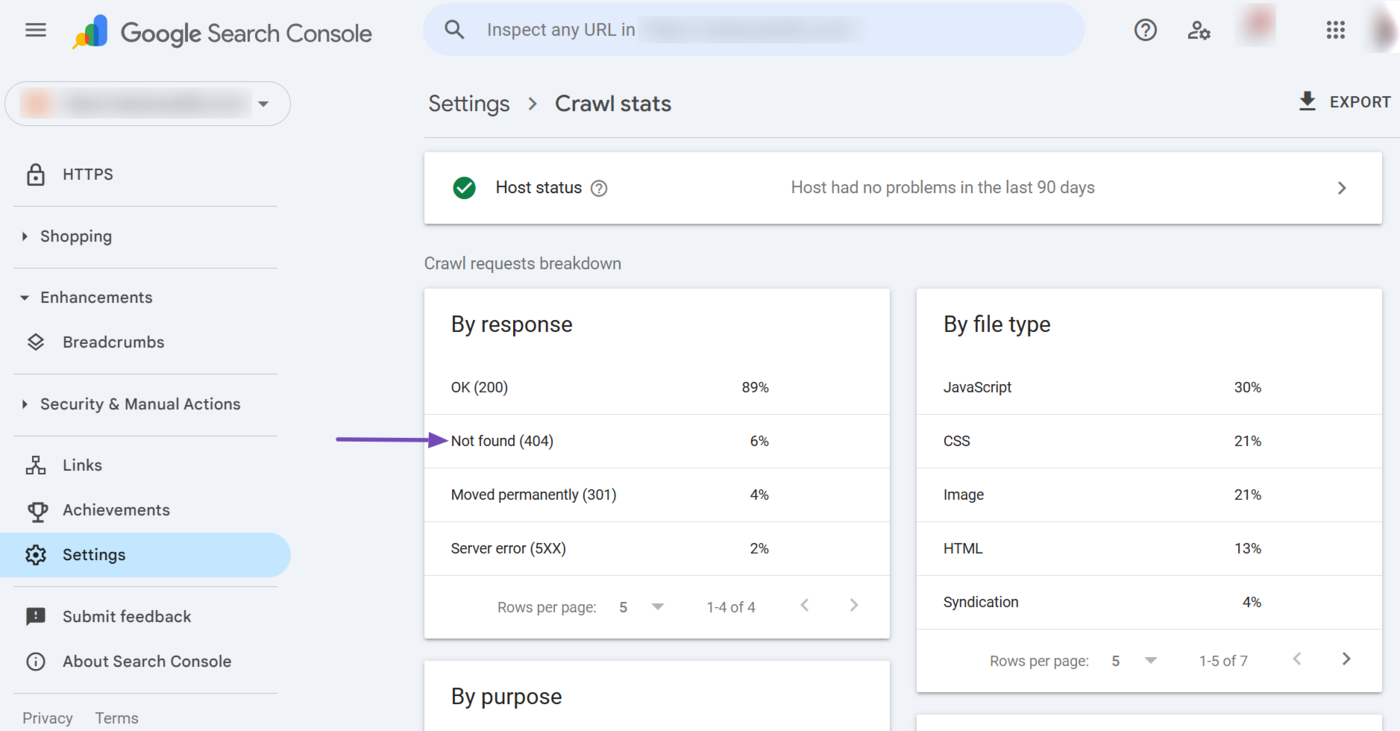
You will see a full page report about the webpages affected by the issue. Scroll down to the Examples field. You will see the URLs affected by the specific issue.
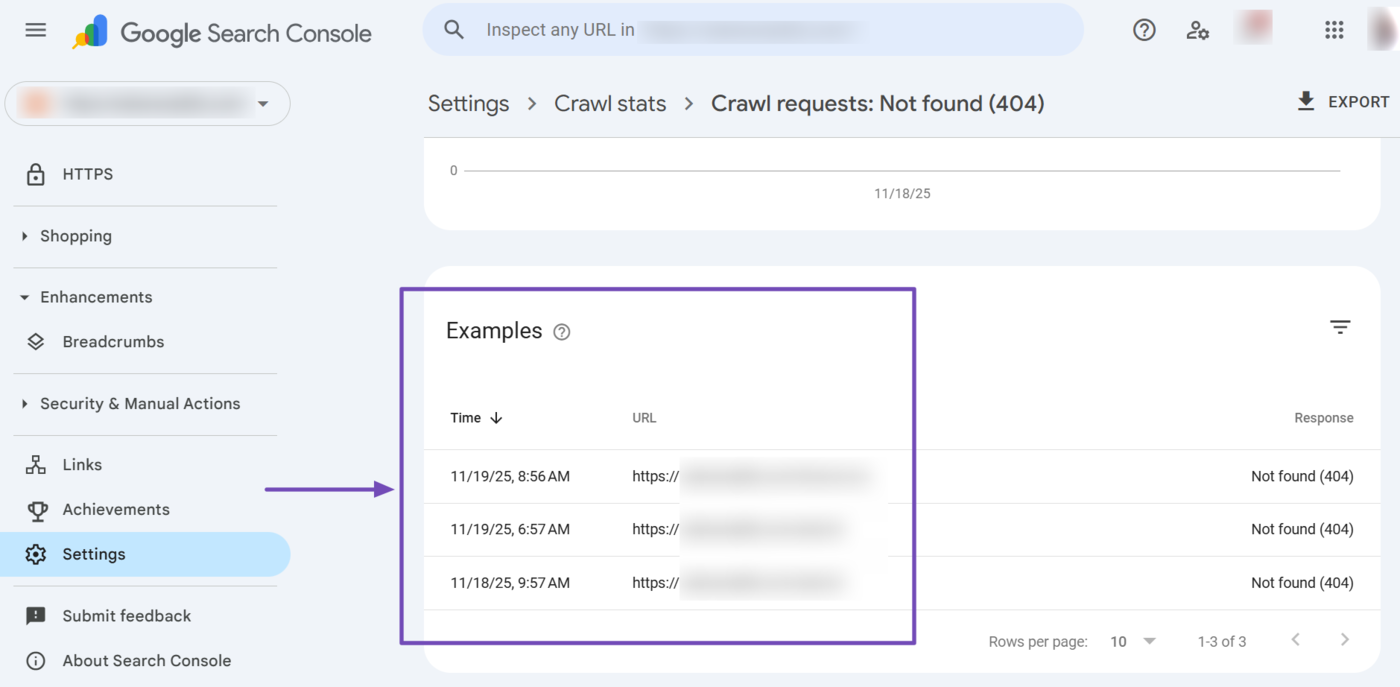
You can now proceed to review and resolve the issue. You can resolve the Not found (404) issues by using 301 redirects to point search engines to the correct URL.
The Moved Permanently (301) response indicates the webpage is pointing to a new location. You should ensure that the redirects point to the correct destination. You should also update your internal links so they point to the new URL.
In the case of 5xx server errors, you should ensure that your server has enough capacity and does not repeatedly return server errors.
Note that 5xx server errors may be temporary. So, you may not encounter these errors on your site even though Googlebot encountered it during its visit. In this case, you will have to review your server log file to identify what happened during Googlebot’s visit.