What Is Lazy Loading?
Lazy loading is a web optimization technique that delays the loading of certain elements on a webpage until they are needed.
These elements are often non-critical resources, such as images, videos, iframes, and JavaScript. In many cases, their loading is delayed until they enter the viewport, at which point they are expected to be visible to the visitor.
Bloggers and developers implement lazy loading to improve their initial page load speed. In addition to improving performance, lazy loading helps reduce unnecessary data usage and saves bandwidth for both the user and the server.
Lazy loading also reduces the server’s workload, especially when users do not scroll down to resources that have not been loaded.
With that said, lazy loading is the opposite of eager loading, which refers to a technique wherein all elements on a webpage are loaded at once. Eager loading is the web’s standard behavior and is the way browsers will load webpages when lazy loading is not implemented.
In this article, we’ll cover:
How Lazy Loading Works
Let us assume we have two webpages. Each one contains the same content. However, one uses lazy loading while the other doesn’t.
Both webpages will load all images that appear in the viewport. However, the page that uses lazy loading will not load images that appear outside the viewport.
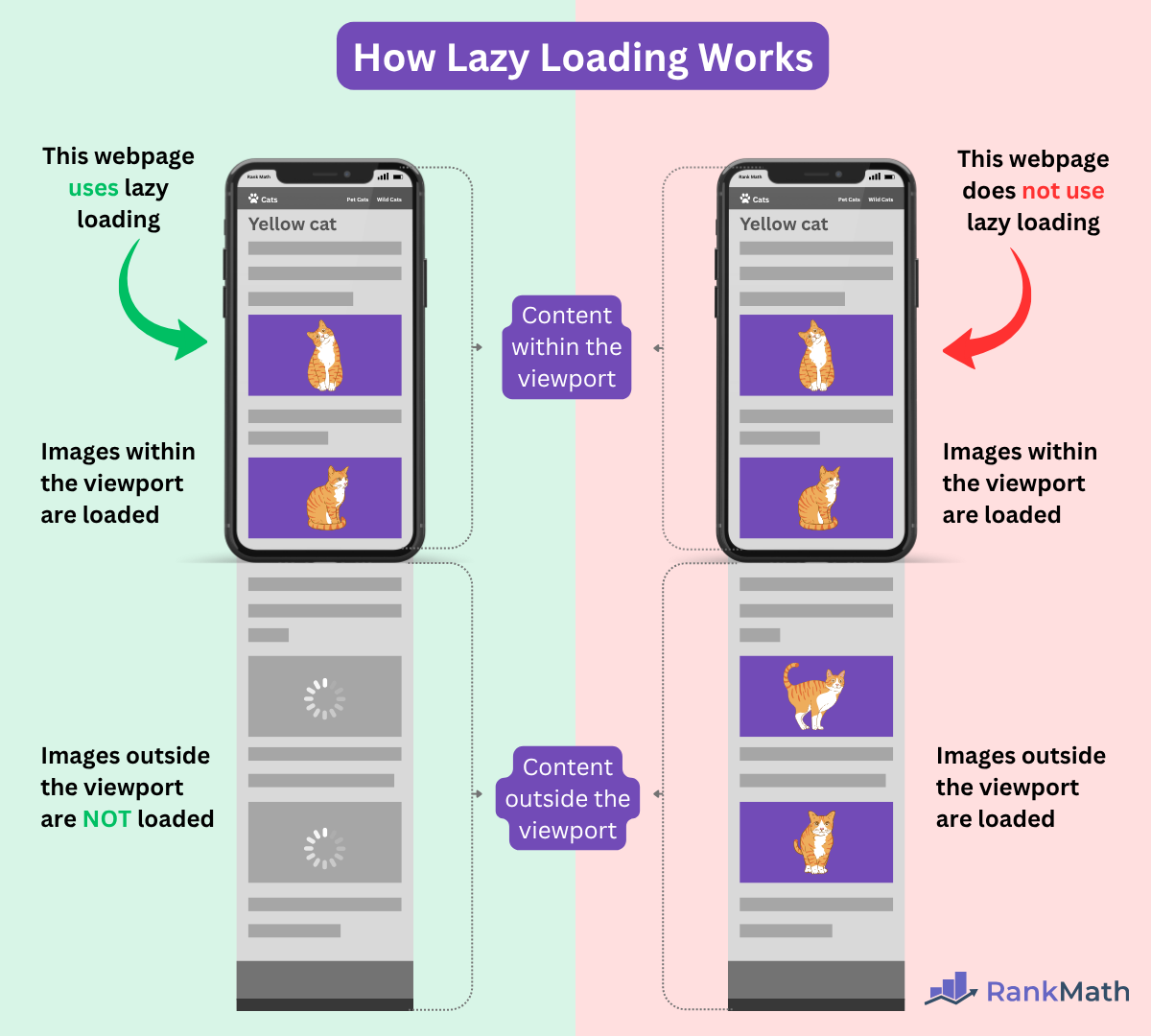
However, the webpage that uses lazy loading will only load those images when the user scrolls down. If the user does not scroll to the images, then they will not be loaded.
How to Lazy Load an Element
There are multiple ways to implement lazy loading. A straightforward method is to include the loading="lazy" attribute to the element’s HTML code.
For example, the loading="lazy" attribute instructs the browser to lazy load the image below.
<img src="moon.png" alt="Image of the moon" loading="lazy">However, there are limitations to using the loading="lazy" attributo.
First, it only works with the <img> e <iframe> tags. It can also work with the <embed>, , e <source> tags. However, these are not always supported and may not work in specific cases.
Optionally, you can lazy load elements using JavaScript-based lazy loading libraries such as lazysizes. This is especially useful for lazy loading background images, videos, and content blocks that cannot be lazy loaded using the loading="lazy" HTML attribute.
Multiple programming languages also have their lazy loading libraries, frameworks, and APIs. Some browsers e content delivery networks (CDNs) also offer lazy loading services by default.
If you use WordPress, you can also get more control over your lazy loading and configure it using web optimization plugins like WP Rocket.
Importance of Lazy Loading
Lazy loading is important because it significantly improves a website’s initial load time by deferring the loading of non-essential resources until they are actually needed.
Instead of forcing the browser to download every image or video as soon as the page loads, lazy loading prioritizes content that is immediately visible to the user.
This results in faster rendering of above the fold content, which can lead to better user engagement, lower bounce rates, and improved Segnali Web fondamentali metrics.
The Core Web Vitals are among the signals that Google uses to evaluate your page experience, which is a ranking factor.
From a technical perspective, lazy loading reduces bandwidth consumption and server load. This is especially beneficial for mobile users and those with slower internet connections, as they only download the content they interact with.
Overall, websites that implement lazy loading often perform better in terms of SEO, since search engines favor fast-loading pages over slower ones.
With that said, bloggers typically implement it on specific content, webpages, and devices, including:
- Webpages with a lot of content
- Webpages with many images or videos
- Webpages optimized for mobile users
- Content that appears below the fold
- Resource-heavy content such as maps and videos
- Devices with limited or slow internet connectivity
Disadvantages of Lazy Loading
While typically helpful, lazy loading has a few disadvantages, which are mostly obvious when implemented incorrectly or when the user decides to actually scroll down the webpage.
1 It Can Delay Rendering
Lazy loading defers the loading of non-critical resources until the user scrolls to them. This can cause a noticeable delay before certain content appears on the screens of users who scroll down the page.
2 It Can Cause SEO Issues
Search engine crawlers may miss crucial content on pages that do not correctly implement lazy loading. This can lead to lower visibility in search results, which hurts your SEO.
3 It May Cause Layout Shifts
Lazy loaded elements can push other content around on the page. This shift can hurt the user experience and negatively impact metrics like the Spostamento cumulativo del layout (CLS), which is one of the three metrics evaluated as part of your core web vitals.
4 It May Be Incompatible with Older Browsers
Some older browsers do not support lazy loading configured using the loading="lazy" HTML attribute. This means the lazy loading functionality may work improperly or not work at all on such browsers.
5 It Increases the Browser’s Workload
Lazy loading implemented using JavaScript or other code adds to the amount of code the browser must download, parse, and execute. On low-powered devices, this extra processing can reduce the browser’s overall performance and responsiveness.
6 It Can Interfere with Analytics or Tracking Scripts
Lazy loading can prevent analytics tools from detecting user interactions with content that is yet to load. For example, an image view or video play might not be tracked if the element is loaded too late.
7 It Increases the Server’s Workload
Each lazy loaded element requires a new request to the server. This creates additional network activity that can affect server load and response times, especially on content-heavy pages.
If improperly handled and optimized, such requests can even slow down the page’s performance instead of improving it, which defeats the whole point of lazy loading.