What is Search Intent?
Search intent refers to the reason a user enters a query into a search engine. It is what the user wants to achieve with their search query. In other words, it is the end goal of the user who enters a search query into a search engine.
Understanding search intent plays a crucial role in Stichwortforschung, as Google aims to show visitors content that satisfies their search intent. When a searcher enters a query into Google, the search engine analyzes it to determine the user’s intent and then displays the results it considers most appropriate for that intent.
For example, when a visitor enters a query like best laptops under $200, Google understands that they want information on what laptop to purchase in the future. So, Google returns a search results page containing multiple reviews and suggestions.
Similarly, when a visitor enters a query like Is yoga good for me, Google understands that they want information on the benefits of yoga. In response, Google returns a results page about the benefits of yoga.
Importance of Search Intent
The search intent allows Google to match searchers with content that best satisfies their search query. This knowledge is crucial for bloggers as it indicates a change in how Suchmaschinenoptimierung works.
In years past, bloggers optimized their content for Schlüsselwörter. However, Google now utilizes systems like Bert to better understand the searcher’s intent. So, bloggers should aim to optimize their content for the search intent rather than just keywords.
The focus on search intent rather than keywords means content can rank for multiple keywords, not just the one the blogger intended it to rank for. Nowadays, it is even common for content to rank for hundreds of keywords, including many that the blogger did not specifically optimize for.
In all, bloggers who understand how search intent works can create and optimize their content around the search intent, rather than just focusing on optimizing it around keywords.
Types of Search Queries
There are four types of search queries, namely:
1 Informational Queries
Informational queries refer to queries used by searchers seeking to learn more about a topic or to obtain specific information or answers. Such queries typically start with:
- Who
- Was
- When
- Where
- Why
- How
Informational queries may also contain modifiers like:
- Am besten
- Tips
- Führung
- Advise
- How-to
- Tutorial
- Bewertungen
In response to informational queries, search engines will return articles, guides, and other resources that answer the user’s questions.
2 Navigational Queries
Navigational queries are used by searchers heading to a particular webpage or site. They usually contain the name of the brand, product, service, or business. Examples of navigational queries include:
- Wikipedia
- Youtube
- Gmail sign in
- Facebook login
- Amazon homepage
When a user uses a navigational query, the search engine returns a results page that includes direct links to the specific website or webpage the user wants to visit.
3 Commercial Queries
Commercial queries are used by searchers looking to buy an item in the future. The searcher is still researching the product and is not yet ready to complete the purchase. Commercial queries typically include words like:
- Top
- Am besten
- Führung
- Bewertungen
- Leistungen
- Merkmale
- Comparison
- Alternatives
- Recommendations
When Google detects a commercial query, it returns a results page that features product comparisons, reviews, buying guides, and brand websites to help users make informed purchase decisions.
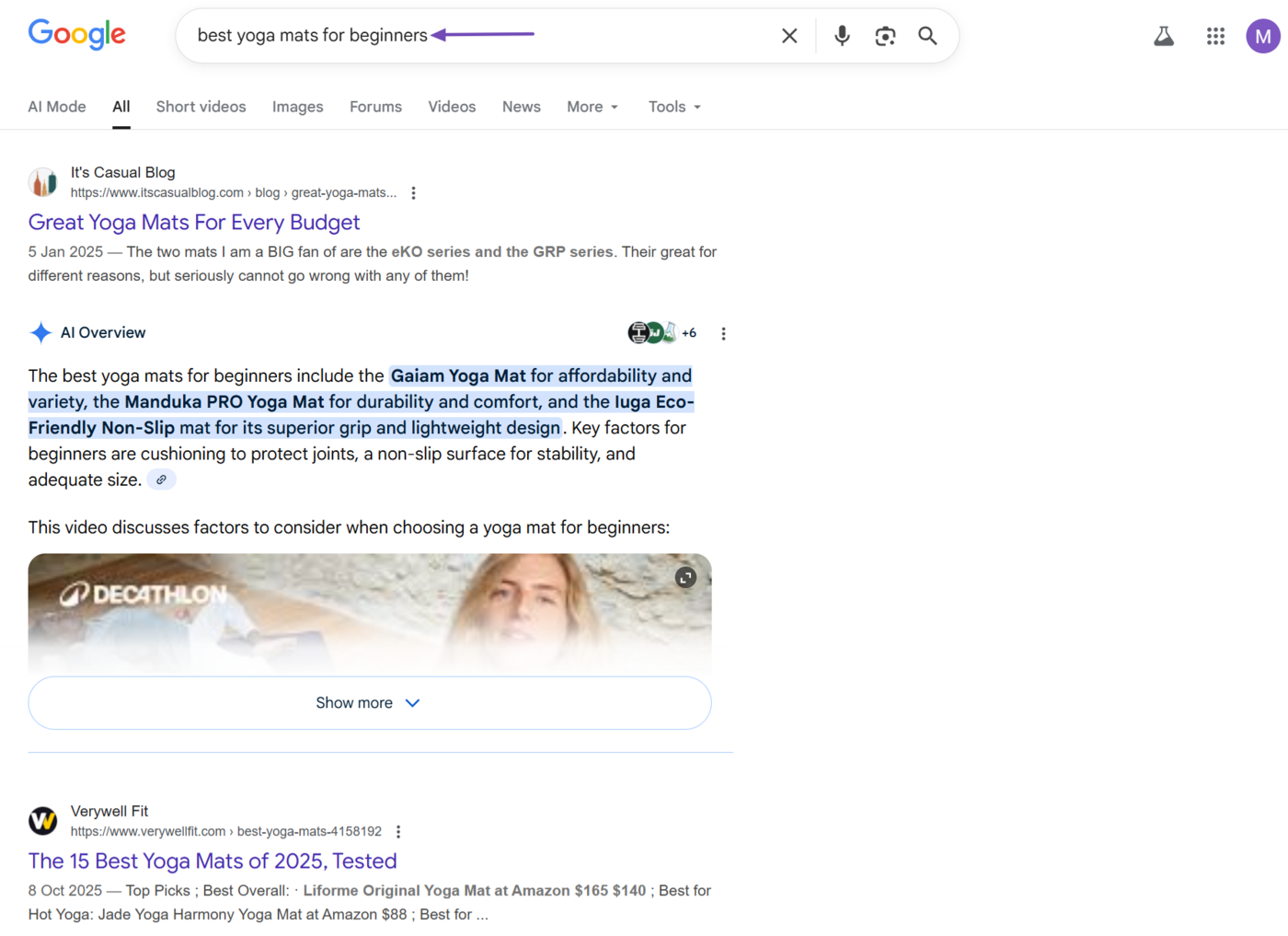
4 Transactional queries
Transactional queries are used by searchers who are ready to complete a transaction or make a purchase. They usually contain words like:
- Kaufen
- Bekommen
- Befehl
- Billig
- Sign up
- Purchase
In response to transactional queries, search engines usually return a results page that includes product pages, shopping ads, and eCommerce sites where users can make a purchase.
How to Uncover a Query’s Search Intent
Google has systems for determining the most relevant result that satisfies the search intent. So, you review the results Google returns for a query and check the intent of the results returned on the page.
For example, if we want to create content for the keyword vanilla cake recipe, we enter the query into Google. Once done, we will review the results on the first page.
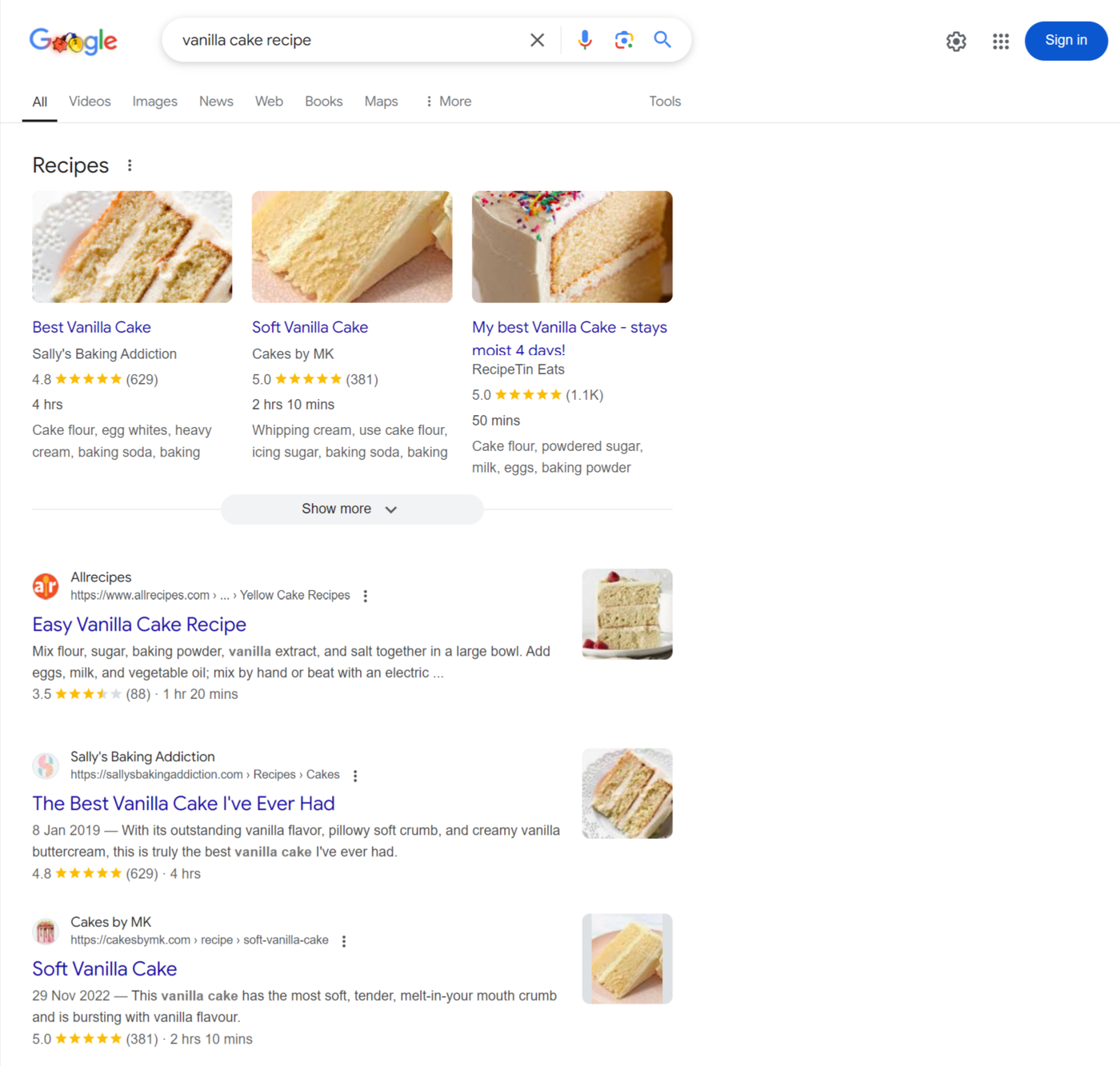
The results typically have a central theme that indicates the search intent. If you want to rank for such keywords, you should create content that matches the intent of the content on the search results page. In this case, we have to make a recipe-style article.