What Is AI Search?
AI search is a search approach in which search engines use artificial intelligence (AI) systems to understand the intent and context of a search term and return relevant answers to the user.
AI search use advanced technologies like generative artificial intelligence, natural language processing, machine learning, and large language models (LLMs) to understand the reason the user performed a search (intention de recherche) and generate answers for the user.
One common system that makes use of AI search is Google AI Overviews, which is an AI feature that is displayed on Google search results pages.
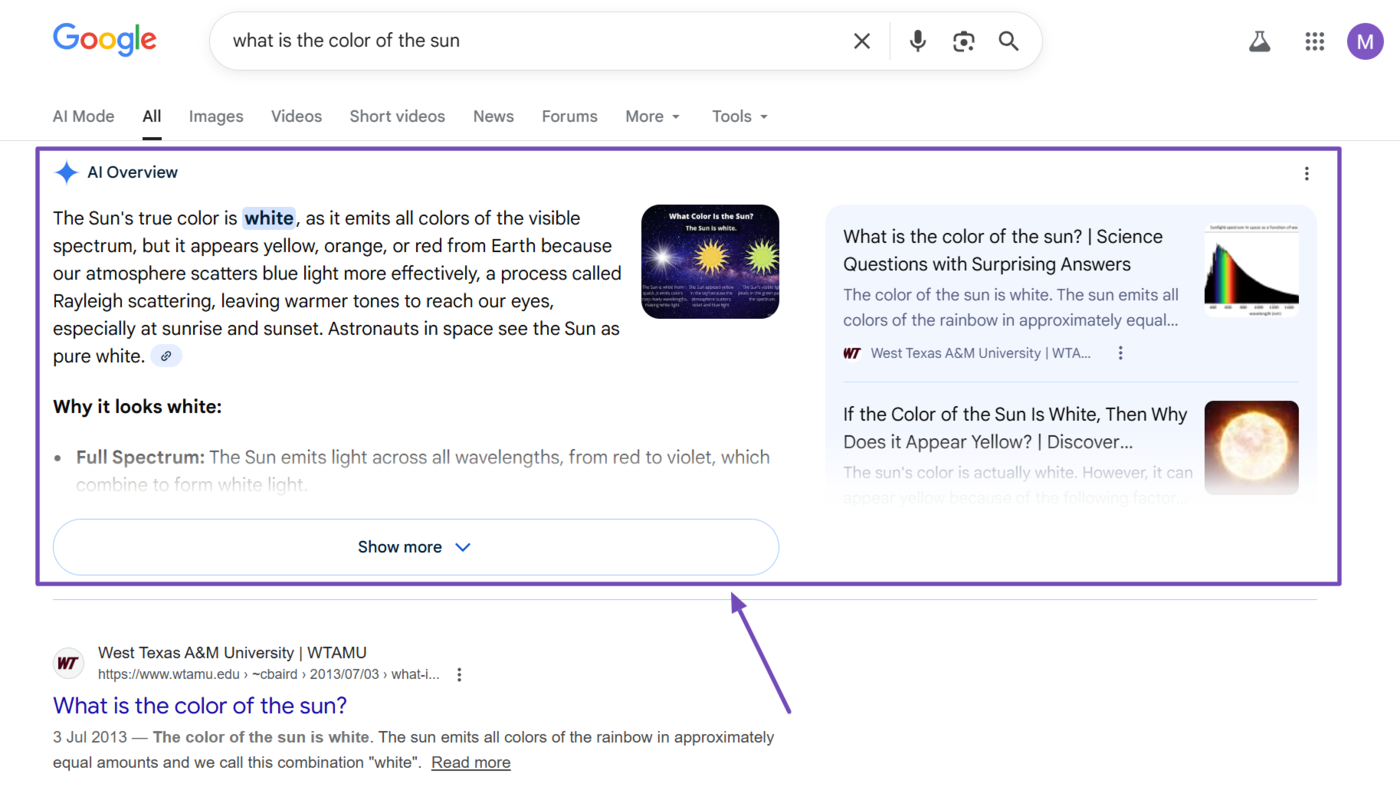
Other systems that make use of AI search include AI chatbots with search capabilities, such as ChatGPT et Copilot, as well as AI-powered search engines (often called answer engines) such as Perplexity AI and Google AI Mode.
In this article, we’ll cover:
Importance of AI Search
AI search improves the accuracy of the results returned on search engine results pages (SERPs). This makes it easier and quicker for users to find the information they need.
AI search also allows search engines to return relevant results to users. This translates into higher user satisfaction, increased engagement, and more repeat visits, which boosts their traffic, usage, and revenue.
Without AI search, search engines will completely rely on traditional search, which does not understand context and intent and may surface irrelevant results in return. This can lead to lower engagement, reduced conversions, and a poor user experience.
AI Search vs Traditional Search
AI search is considered the next iteration of search. This contrasts with traditional search, which was the default method search engines used to match search terms to webpages before AI search emerged.
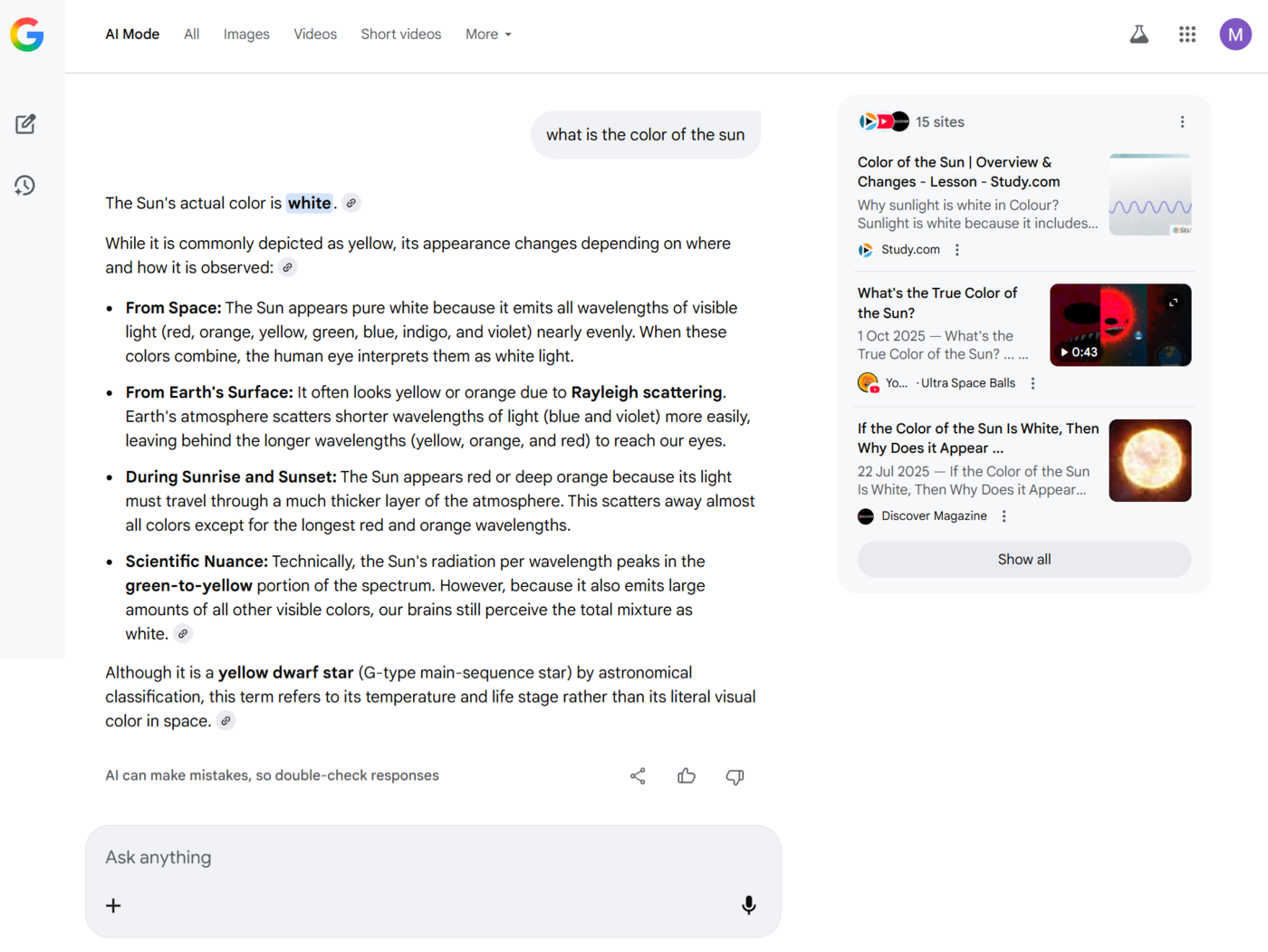
For example, when a user searches for “best diet for yoga,” a traditional search engine will return a list of webpages that contain mots clés like “diet” and “yoga.”
This is because traditional search engines rely on matching the words in the search term with the words on the webpage.
In contrast, AI search engines rely on matching the intent and context of the search term with the content on the webpage.
For example, if a user searches for the same search term, “best diet for yoga,” a search engine that uses AI search will return a list of webpages that provide detailed guidance, tips, and meal plans specifically suited for yoga practitioners.
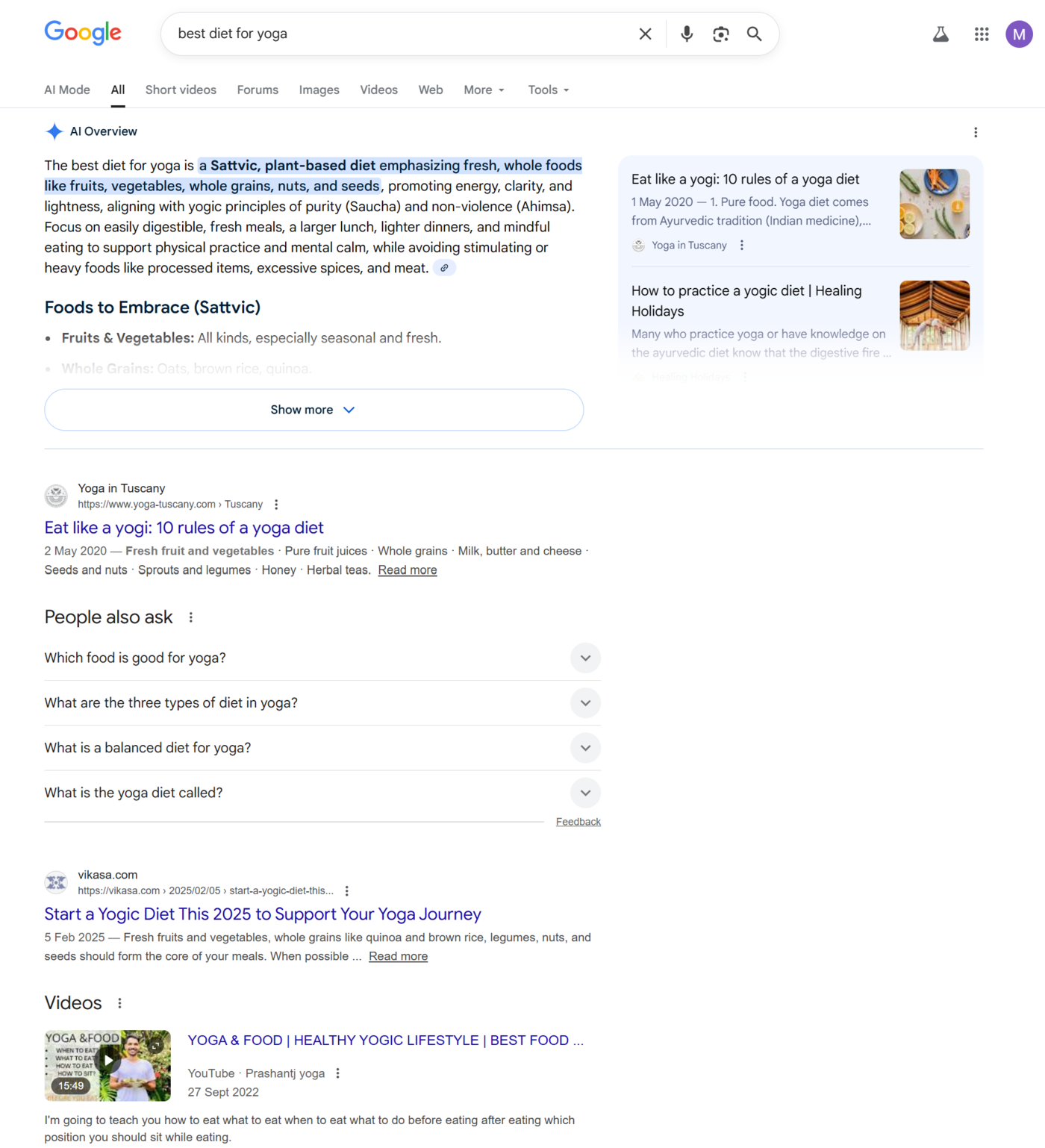
Traditional search cannot return these sorts of results since they do not understand the context and intent of the search term. This means they will return less relevant results when compared to AI search, especially for complex search terms.
This does not make traditional search irrelevant though. It is still relevant for straightforward search terms or situations where users prefer a simple list of links.
However, for complex, conversational, and intent-driven search terms, search engines will increasingly rely on AI search, since they can provide context-aware answers, summaries, and recommendations, which a traditional search cannot provide.
Components of AI Search
AI search relies on multiple advanced technologies, including:
- Generative artificial intelligence (GenAI)
- Natural language processing (NLP)
- Large language models (LLMs)
- Machine learning (ML)
- Semantic search
- Predictive analysis
- Query intent analysis
- Personalization engines
We will now explain them below.
1 Generative Artificial Intelligence (GenAI)
Generative artificial intelligence (GenAI) is an artificial intelligence system that can create human-like text, images, and code. In AI search, it is used to create the responses returned to the user.
Generative AI produces these responses using patterns learned from its training data, along with information retrieved from indexed webpages and other data sources, such as the Google knowledge graph and external databases.
2 Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Natural language processing (NLP) is a branch of artificial intelligence that allows machines and similar systems to understand, interpret, and respond to human language. This allows AI search systems to process queries in natural, conversational language rather than relying solely on keywords.
3 Large Language Models (LLMs)
Large language models (LLMs) are artificial intelligence systems that can generate human-like text. AI search systems use them to generate the responses returned to users.
4 Machine Learning (ML)
Machine learning (ML) is a technique that allows artificial intelligence systems to learn from data and improve their performance over time, all without human input.
In AI search, machine learning allows algorithms to determine which results are most relevant to a user and use that information to improve the relevance of results for that user and others.
5 Semantic Search
Semantic search is a search technique that focuses on understanding the meaning of a search term. It analyzes context, relationships, and user intent, and uses this to provide results that more accurately satisfy user needs.
6 Predictive Analysis
Predictive analysis is a technique that uses historical data and patterns to forecast what will happen in the future. AI search systems use it to anticipate what a user will search for, even before the user searches for it. It then includes their results in the current search.
7 Query Intent Analysis
Query intent analysis is a system that identifies the purpose of a search term. It determines whether a search term has an informational, navigational, commercial, or transactional intent. This allows AI search systems to deliver results that align with what the user wants.
8 Personalization Engines
Personalization engines allow artificial intelligence systems to tailor their results to the user. These engines rely on multiple user-based metrics and signals, including the user’s behavior, settings, and search history.
Cons of AI Search
AI search shares many of the common drawbacks of artificial intelligence systems. For example, it can hallucinate, return inaccurate or biased results, or be manipulated using AI poisoning techniques.
However, here are some other limitations that are unique to them.
1 There Is Limited Transparency in How Results Are Ranked
Answer engines like Google AI Mode usually return multiple webpages along with their output.
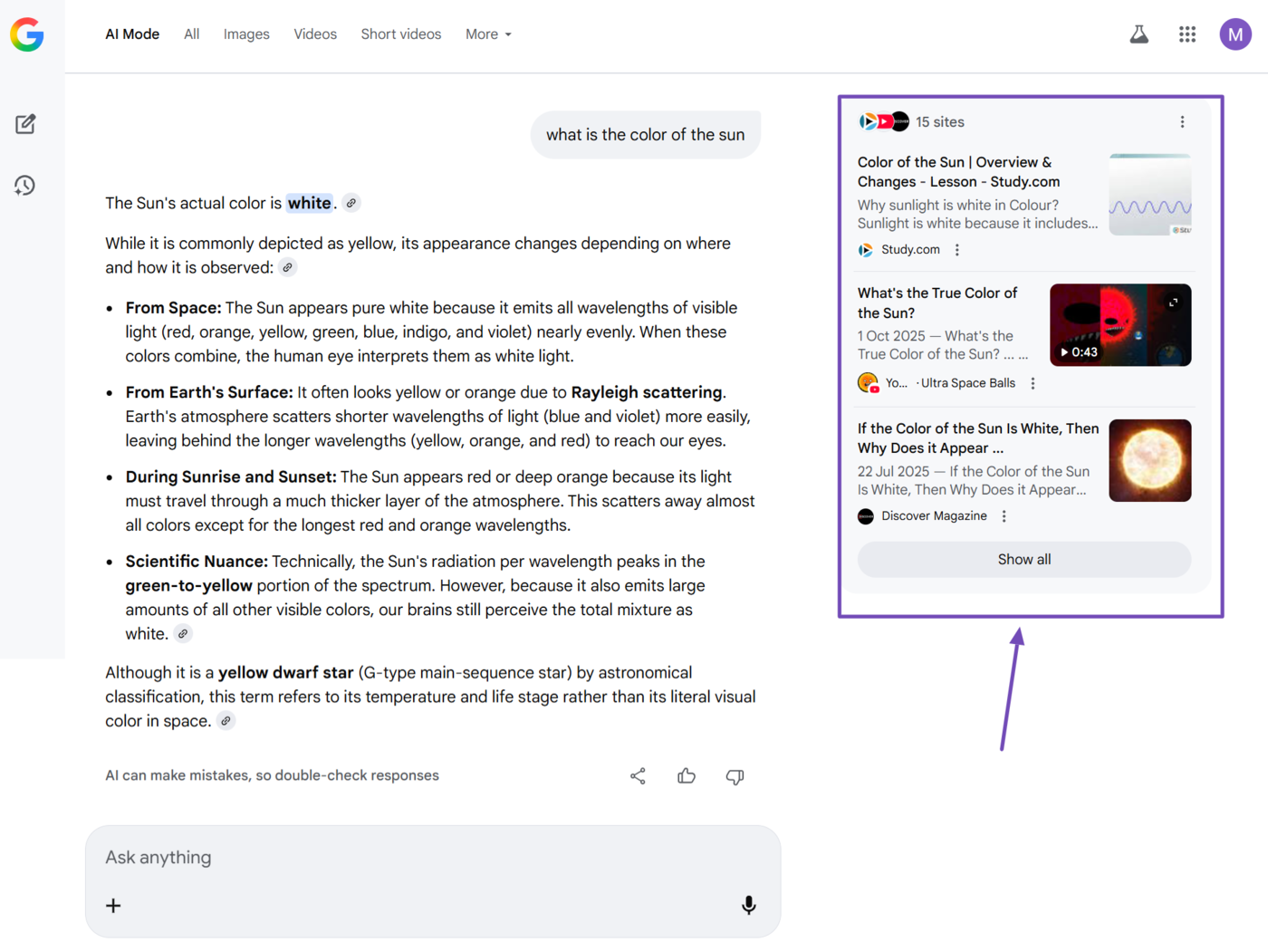
However, unlike the traditional Google results page, there is limited transparency in how Google decided on which webpages to show. This makes it difficult for creators and SEOs to understand how to optimize their content for artificial intelligence systems.
2 It Has Difficulty Handling Very Niche or Rare Queries
AI search performs best when it has access to abundant, high-quality data. For very niche topics or rare queries, the system may struggle to find sufficient information or provide accurate answers.
This limitation can lead the artificial intelligence system to return incomplete, generic, or even inaccurate responses that do not fully satisfy the user’s needs.
3 It Reduces the Organic Traffic for Relevant Webpages
AI search results page features, such as AI Overviews, and AI search engines, such as AI Mode, directly return answers to the user.
These answers may completely satisfy the user’s intent, which means the user may not need to click through to any additional webpages to find the information they were seeking.
This reduces the organic traffic that would have gone to these sites, and further increases the prevalence of zero-click searches, which creators have repeatedly blamed for taking away their traffic.
4 It Increases Competition for the Area Above the Fold
Google typically displays AI search results page features such as AI Overviews at the top of its search results page. This means visitors are likely to leave the search results page without scrolling down.
Even when they scroll, they will likely only focus on the top results. This makes the above the fold area more valuable than ever and increases the competition for the topmost space of the search results pages.
For example, AI Overviews takes up most of the area above the fold on this Google results page.
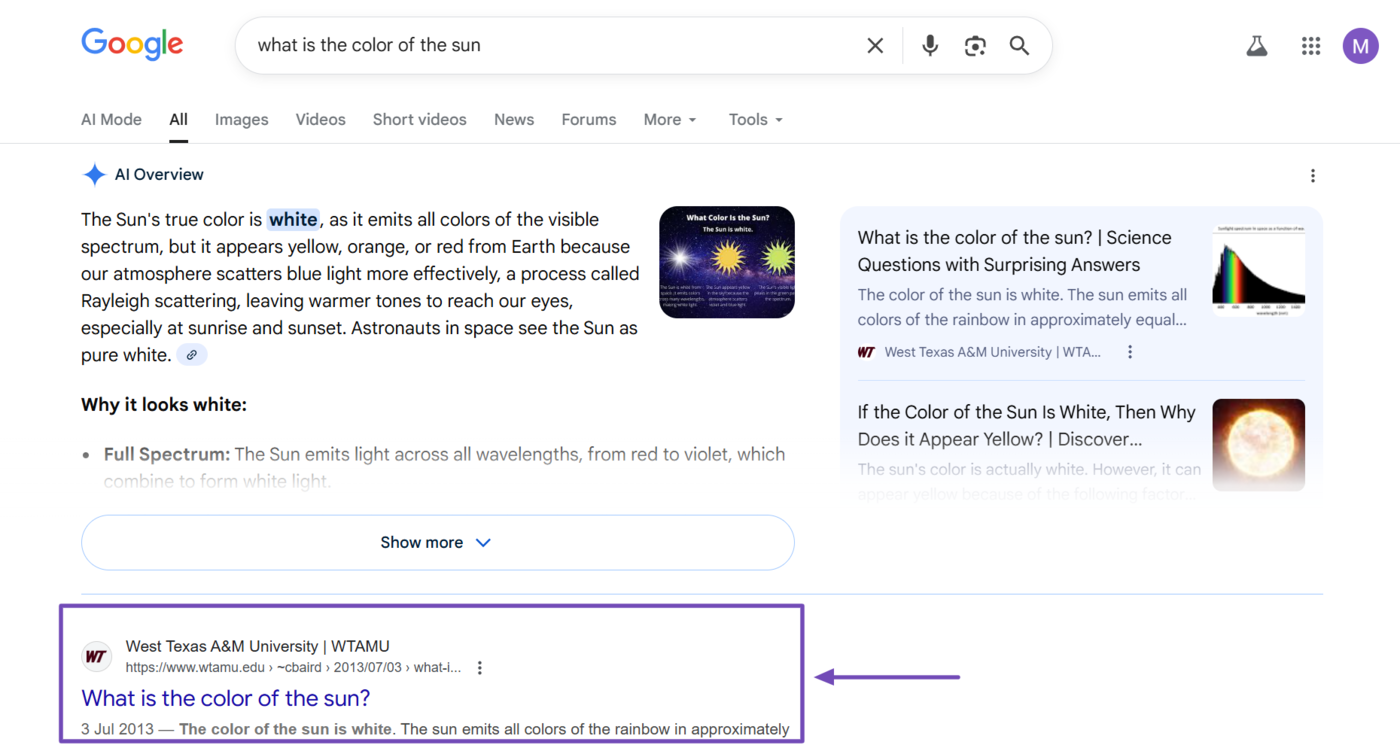
On this results page, Google AI Overviews, featured snippet, et People also ask take up the entire area above the fold and even extend to the topmost area below the fold.
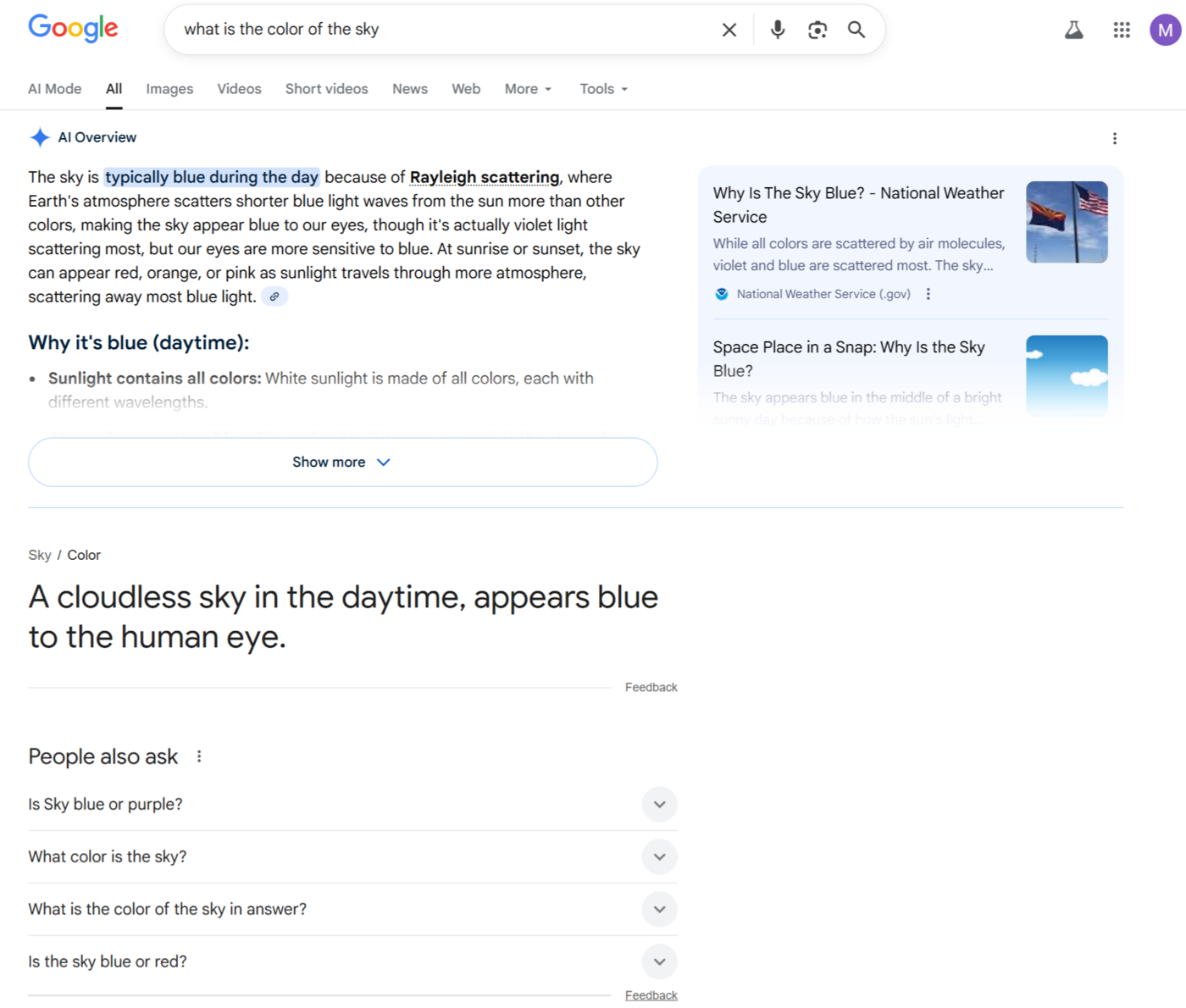
5 It Reduces Control over How Content Is Presented
Creators that rank on traditional search results pages typically have more control over how their content appears for AI search results.
In traditional search, creators get to format their subsections and paragraphs, and even specify meta titles, meta descriptions, et structured data, which controls how their content is displayed on search engine results pages.
However, creators do not have these privileges with AI search where artificial intelligence systems can use their content to generate a response.