What is Google Tag Manager?
Google Tag Manager (GTM) is a free service that allows you to install tags on your website without modifying your website code whenever you add a new tag.
Tags are code snippets that allow you to track user behavior on your site. Many marketing, tracking, and measurement tools require you to add these tags to your website’s head tag to monitor how visitors land on your site, their user experience, and what they do during their visit.
Ideally, you should modify your website code to install the tags. However, with Google Tag Manager, you only need to upload the tag to Google Tag Manager. Then, Google Tag Manager will add it to your site.
Google Tag Manager only injects the code into your site whenever it registers a user interaction with a trigger. This reduces the amount of code on the site and the chances of the code interfering with or breaking the site and making it unusable.
Components of the Google Tag Manager
The Google Tag Manager consists of three major parts: tags, triggers, and variables. The tags and triggers are the main components since you need them to ensure your code snippet works correctly. The variables, for the most part, depend on you as you decide to set them if you want.
1 Stichworte
Tags are code snippets or tracking scripts used to collect data or execute specific functions on the site. Tags activate based on defined conditions (triggers). Google Tag Manager contains tags from multiple services, including Google, LinkedIn, Pinterest, Quora, Hotjar, and Microsoft. You can also set a custom HTML or image tag.
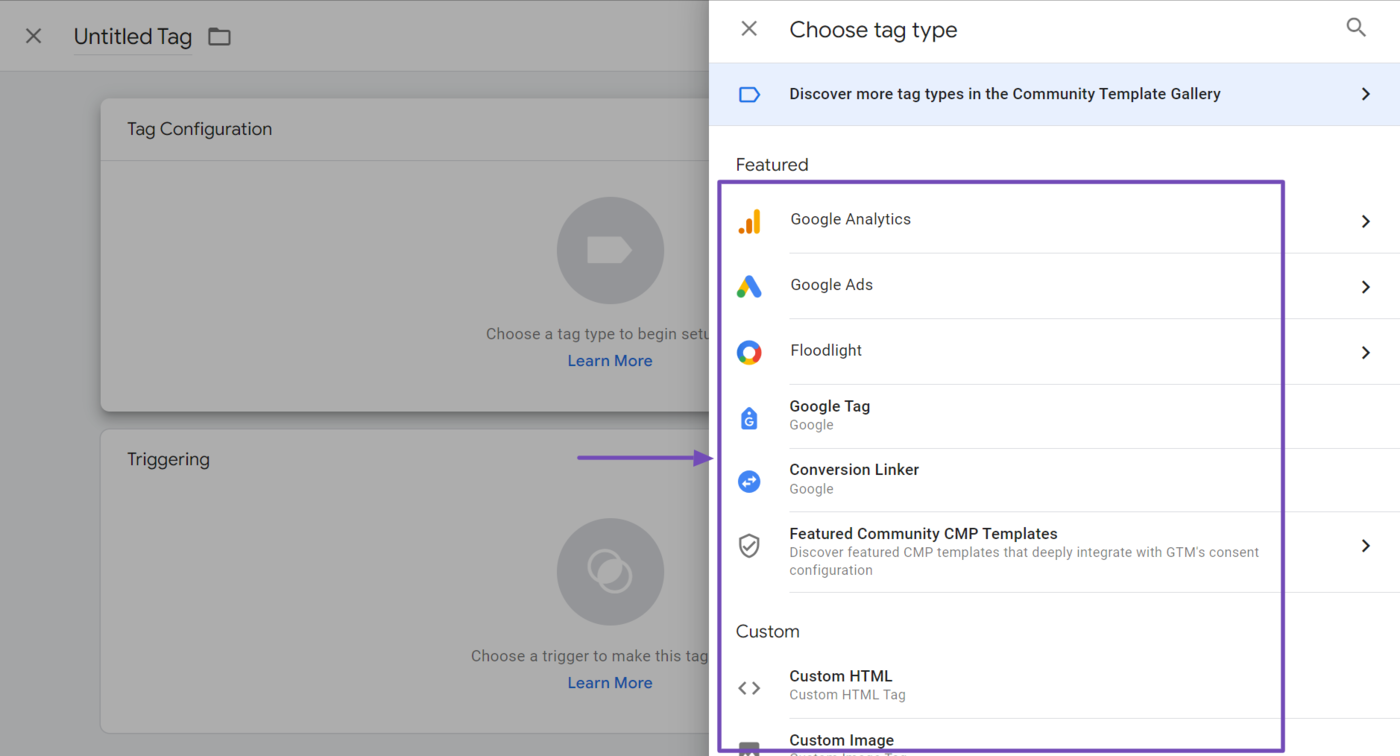
2 Löst aus
Triggers define the conditions, interactions, or events that must occur for the tag to be activated. Some triggers in Google Tag Manager include page views, clicks, and user actions. You could also set up triggers for timers, JavaScript errors, or a custom event.
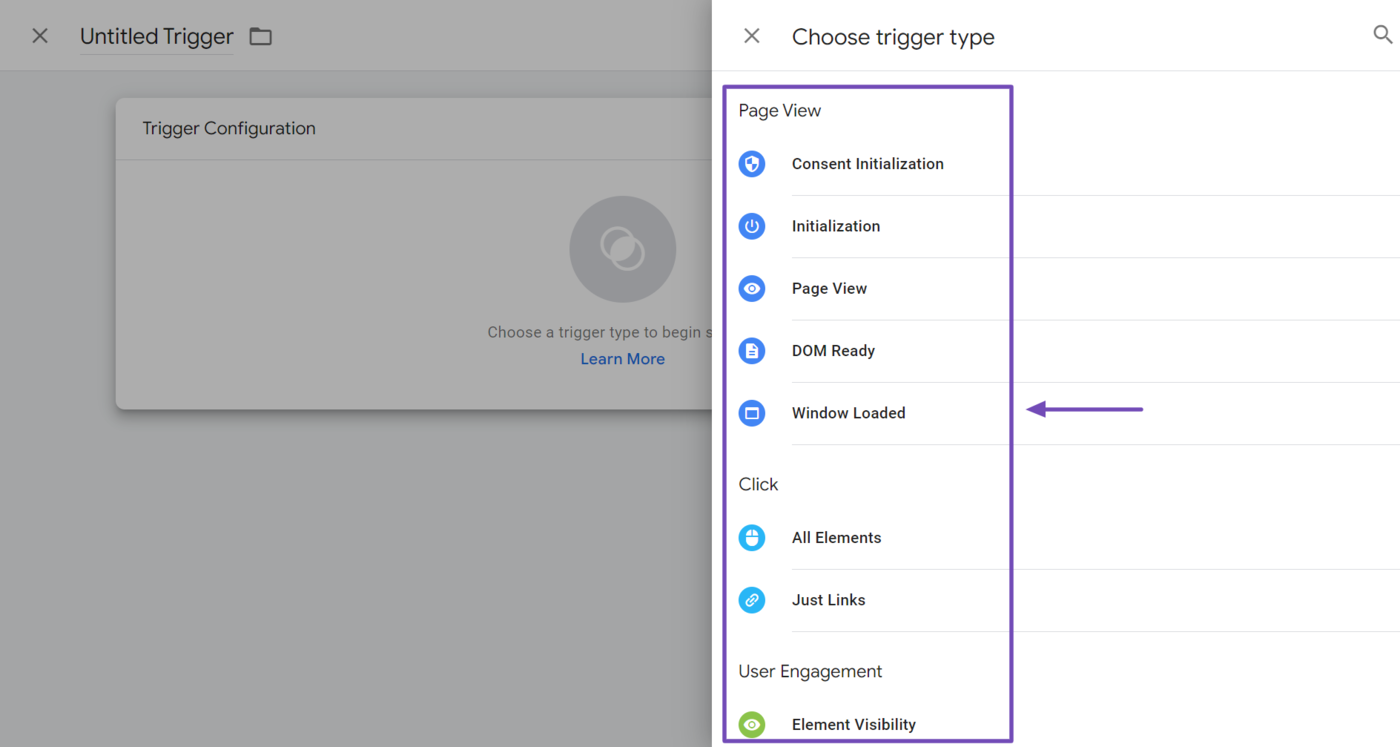
3 Variablen
Variables are placeholders that store information to be used by tags, triggers, and other variables. They help to dynamically capture and pass values, such as page URLs, event data, or user-defined values. For example, a variable might hold the name of a clicked button or the value of the product being purchased.
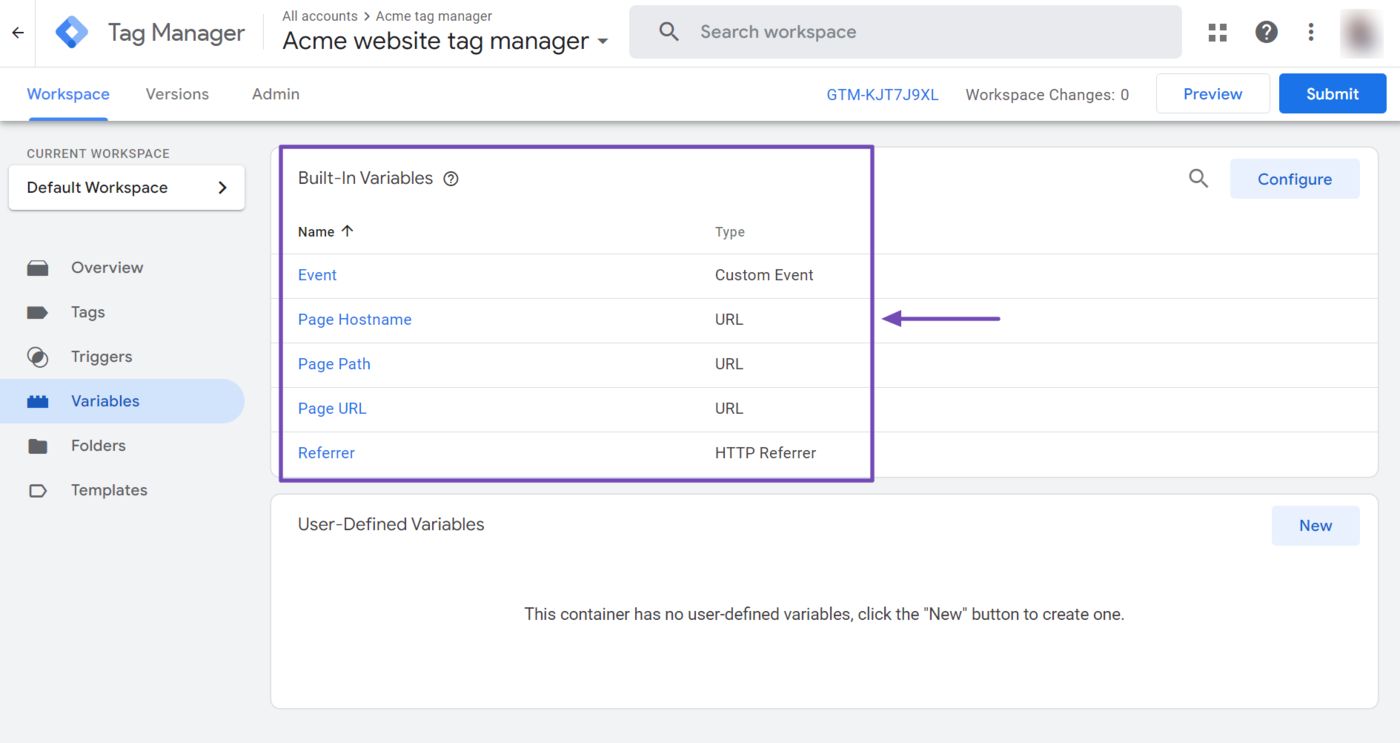
Benefits of Google Tag Manager
Google Tag Manager provides bloggers and marketers with several benefits that make it a better option than adding the code directly to their site.
1 It Allows Non-Technical Bloggers to Add Tags to Their Site
Google Tag Manager allows bloggers and marketers to add multiple tags without editing their website code. This makes it easier for bloggers who do not know how to code or do not have access to a developer. Without Google Tag Manager, the blogger would have to hire a developer to add the code.
2 It Simplifies the Management of Multiple Tags
Google Tag Manager also simplifies the process of managing the tags as the tags are easier to manage from one location than when they are added to the site and managed by editing the site’s code.
3 It Reduces the Possibility of Breaking Your Site
Adding a code directly to your site increases the possibility of breaking something on your site. This could cause several undesirable consequences, including making your site unusable. Since you do not directly edit your website code, Google Tag Manager reduces the chances of breaking something on your site.
4 It Speeds Up the Deployment of Tags
Google Tag Manager makes it easier to deploy tags. You only need to log into your Google Tag Manager dashboard to create a tag. Without Google Tag Manager, you will log into your WordPress dashboard and modify your theme code to add a tag to your site.
5 It Allows Bloggers to Test Tags Before Deployment
Google Tag Manager has a preview and debugging mode that allows bloggers to test their tags before making them live. This helps uncover issues that may affect the tag’s functionality and prevent it from working correctly.
6 It Prevents the Chances of Losing Your Code Snippet
Google Tag Manager also has the extra benefit of ensuring you do not lose your code when you update your site. Without the Google Tag Manager, bloggers risk losing their code whenever they update their site. However, this cannot happen with Google Tag Manager, as the code remains active even when the blogger updates it.
Limitations of Google Tag Manager
Google Tag Manager comes with limitations and disadvantages that may affect your site’s usability in certain situations. It is a good idea to be aware of them before deciding whether to use the Google Tag Manager on your site.
1 It Requires a Learning Curve
While Google Tag Manager is more straightforward than coding, new users still require a learning curve to use it correctly, even for basic tasks. So, a first-time user will usually read several blog posts, watch videos, or take online courses to learn how to use it.
2 It Has Limited Debugging for Complex Setups
The Google Tag Manager also provides limited debugging for more complex setups. In such cases, the blogger may need to hire a developer or expert to set it up and confirm that it works properly. This means Google Tag Manager cannot replace a developer in certain situations.
3 It May Affect Your Site’s Performance
Google Tag Manager needs to be set up and managed properly so that it does not conflict with the code on the site. Depending on the severity of the issue, it may cause several issues, including slowing down the site or even breaking it completely.