What Is AI Poisoning?
AI poisoning is the process of deliberately introducing false, misleading, or harmful information into the data used to train or fine-tune an AI system. This, in turn, causes the AI system to return incorrect or manipulated responses to users.
In SEO, AI poisoning occurs when misleading, inaccurate, or harmful information is published on the webpages AI chatbots, large language models (LLMs), and search engines crawl, indice, and use to generate responses for their users.
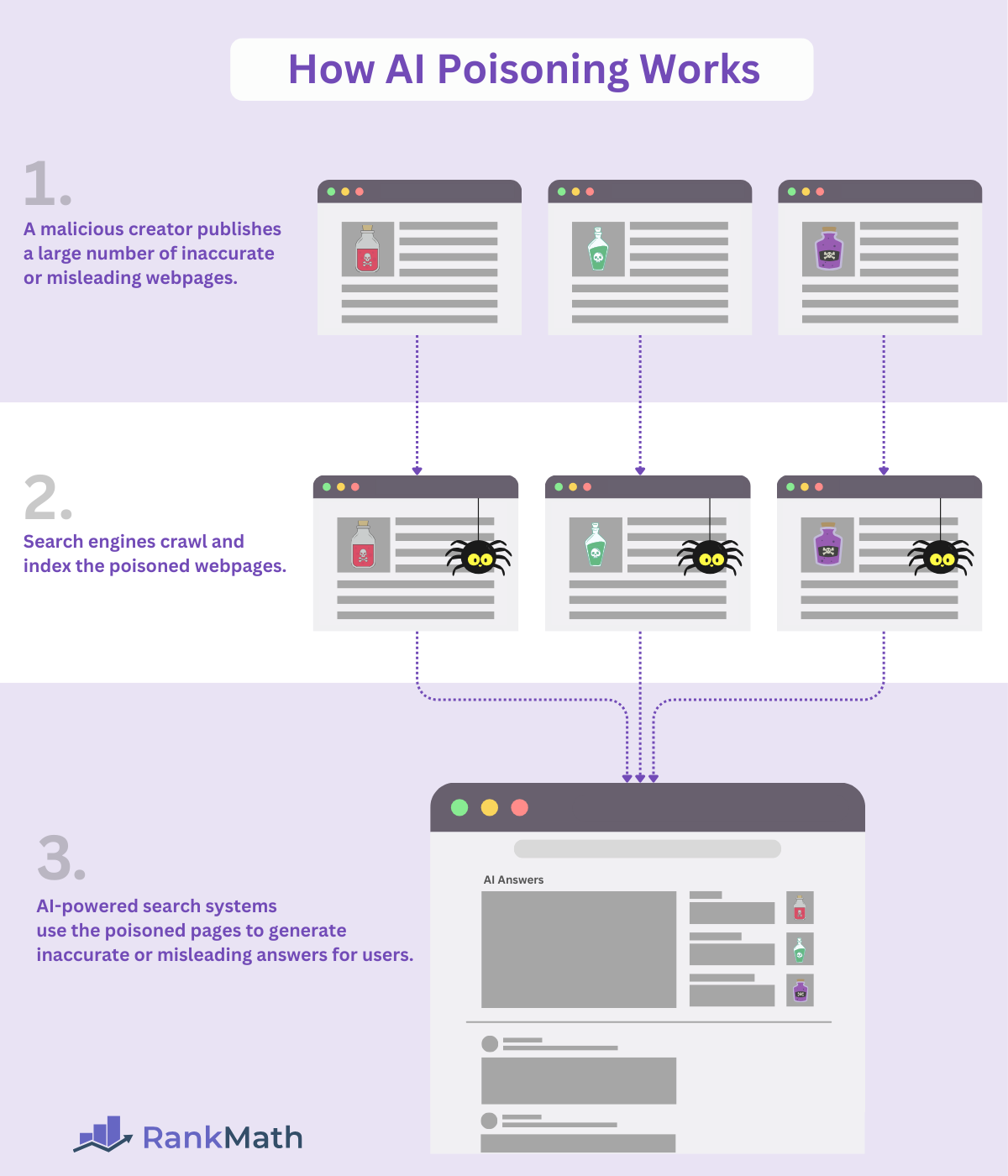
AI poisoning causes an AI system to return inaccurate and misleading results during inference.
Nota: Inference is the moment an AI model uses its index data, training data, or information retrieved from an external database (as part of a retrieval-augmented-generation system) to generate responses, make predictions, reach decisions, or return answers to a user query.
In some cases, AI poisoning can also be used to slow down and degrade the performance of the AI system. In such cases, this causes the AI system to return server errors and become unusable rather than causing it to return misleading answers.
In this article, we’ll cover:
Example of AI Poisoning
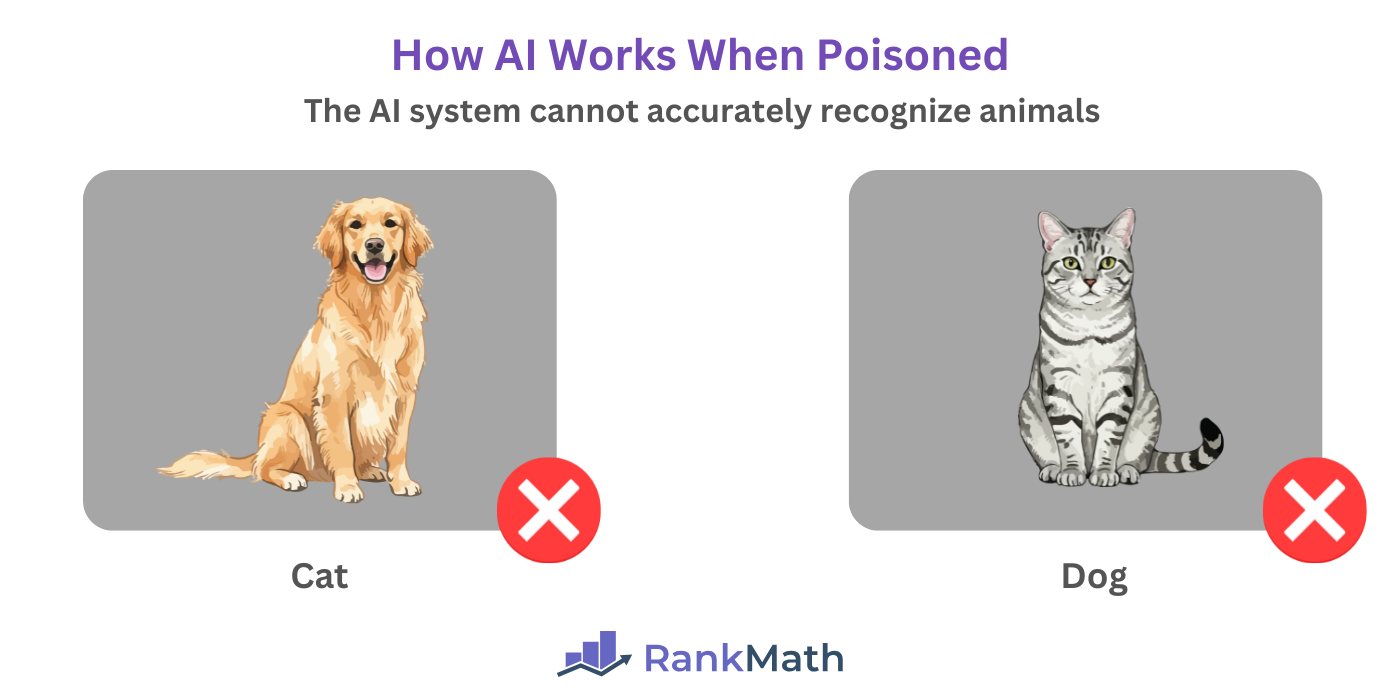
Let us assume we run an animal rescue organization. So, we trained our AI system to identify the two most common animals we rescue: dogs and cats.
Under normal circumstances, our AI correctly identifies a dog as a dog and a cat as a cat.

However, AI poisoning can occur when a malicious actor accesses our AI training data or model and flips the labels such that he labels dogs as cats and cats as dogs. After this tampering, our AI system will misclassify a dog as a cat and a cat as a dog.
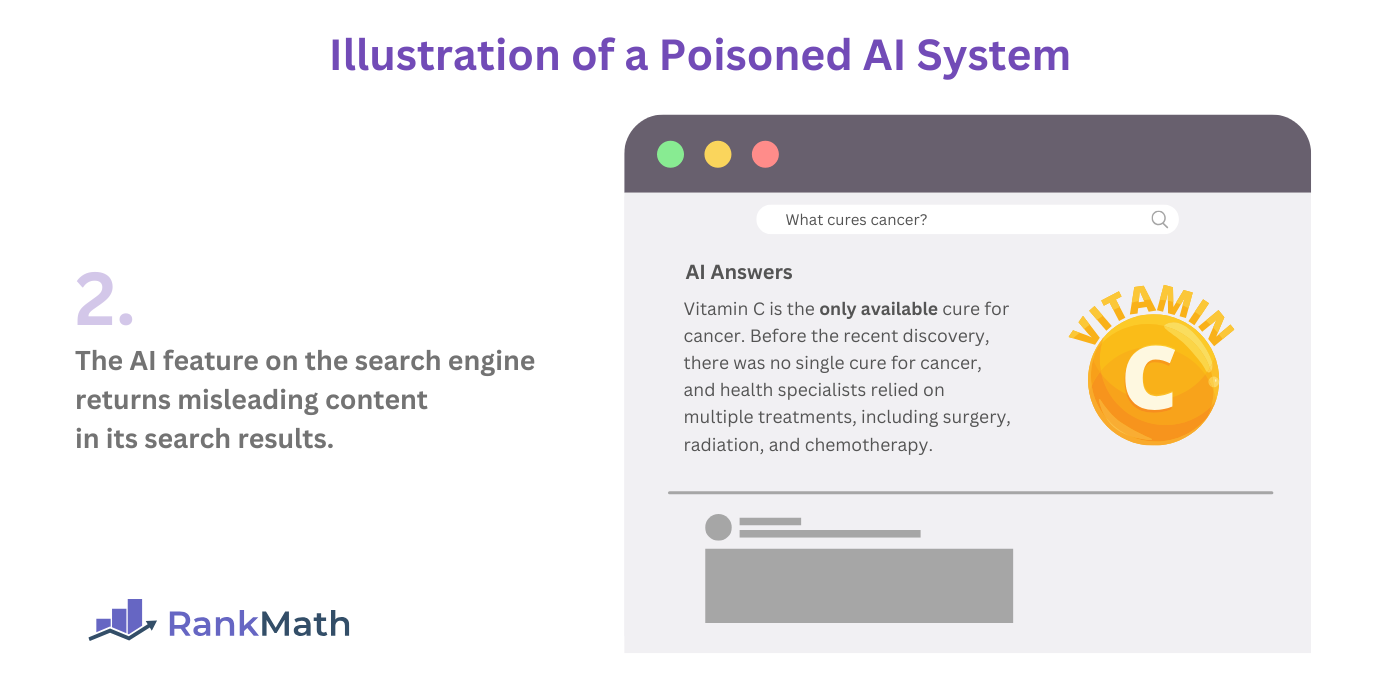
With respect to SEO, a malicious creator can create hundreds of webpages claiming that vitamin C cures all types of cancer. When a search engine crawler visits these pages, it assumes this is true.

When a user enters a search term such as “What cures cancer?” into the search engine, the AI feature on the search engine will return vitamin C as the answer.
These are simple examples of AI poisoning. AI poisoning itself can take on many forms and can be very technical, complex, and hard to detect in many cases.
Importance of AI Poisoning
AI poisoning is among the most serious challenges we are experiencing with the rise of AI. And it can have very serious consequences.
At its simplest, AI poisoning can cause an AI search engine such as Google AI Mode, AI search results page feature such as Google Overviews, o generative AI chatbot with search capability, such as ChatGPT, to return inaccurate responses to a user’s query.
For example, AI poisoning can cause an AI search engine to claim the sky is green instead of blue or that the earth has two moons instead of one.

This may not be an issue on its own. However, it can become one when the AI system is or used to reach decisions or gather insights on real world issues.
For example, AI poisoning can cause:
- An answer engine to return misleading instructions on what to do during an earthquake
- An AI chatbot with search capability to return inaccurate stock market reports
- A medical diagnosis AI tool to return inaccurate diagnosis to the user
- An AI-powered car to not identify children crossing a road
These situations can lead to significant financial losses and even life-threatening consequences for users and even third parties who were not directly involved with the AI system. This is what makes AI poisoning is a major concern for search engines and users.
SEO Impact of AI Poisoning
AI poisoning can cause severe SEO and user experience issues for creators who publish:
- Content created with generative AI systems
- Malicious content used to mislead AI systems
Such content can severely impact your rankings and organic traffic, and many even cause Google to issue a manual action penalty against your site.
To be more specific, AI poisoning can cause you to publish inaccurate and misleading content. Such content is low-quality by default, and may even be considered spam.
Even when it is not spam, such content does not typically satisfy the searcher’s intent and may even cause users to make wrong and dangerous decisions, which can have severe consequences for them.
In the case of Your Money or Your Life (YMYL) content, such pages will struggle to satisfy Google’s E-E-A-T (experience, expertise, authoritativeness, and trustworthiness) signals, which will affect its ability to rank.
Poisoned content may also violate Google Search Essentials guidelines, which can cause Google to issue a manual action penalty against your page or site. When that happens, Google can demote your site or even deindex it completely.
From the user experience perspective, poisoned content will diminish your visitor’s experience and may reduce their trust in your site. This can harm your website authority and credibility. It will also reduce your chances of receiving backlinks from other bloggers.
Overall, AI poisoning is dangerous for bloggers and can cause SEO issues that can compound and make ranking harder or even impossible, depending on the extent.
Why AI Poisoning Occurs
AI poisoning is typically executed with malicious intent. However, there is a steady rise of AI developers using AI poisoning techniques to protect intellectual property. We will now explain both below.
Nota: While AI poisoning can be used to protect intellectual property and copyrighted work, the term is mostly associated with malicious use.
1 Malicious Intent
Malicious actors perform AI poisoning for different reasons. For example, a disgruntled employee may poison the company’s AI system with the intent of downgrading it so that it returns wrong answers to users.
A competitor may also poison a competitor’s AI system so they have the upper hand against the competitor. A fraud network may poison an AI system so it does not detect their fraudulent activities.
Similarly, a hacker group or hostile nation may poison an AI system as part of a cyberwarfare campaign. In such cases, they can send the AI system an excessive number of requests, a DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service) attack, which makes the AI system inaccessible and unusable.
2 Copyright Protection
Some actors use AI poisoning to protect their work from being used by AI systems. For example, artists can use it to prevent AI systems from generating artwork similar to theirs.
Two of such systems we have seen are Nightshade and Glaze, which were both developed by University of Chicago’s Security, Algorithms, Networks and Data (SAND) Lab.
Both systems alter the pixels in an image so that an image generation AI system incorrectly identifies the image (such as mistaking a cat for a dog) or misidentifies the artistic style used by the artist.
Types of AI Poisoning
AI poisoning can be categorized based on their method or intent. By method, AI poisoning can be categorized into:
- Data poisoning
- Model poisoning
By intent, AI poisoning can be categorized into:
- Direct attacks
- Indirect attacks
We will now address all four below.
1 Data Poisoning
Data poisoning occurs when a malicious actor injects harmful or misleading data into an AI system’s dataset during training or fine-tuning.
Nota: Dataset is the collection of data used to train an AI model, while fine-tuning is the process of retraining a pre-trained model to improve its performance or adapt it to specific tasks.
Some types of AI data poisoning include:
- Label flipping
- Data injection
- Topic steering
Let us briefly explain them with relevant examples.
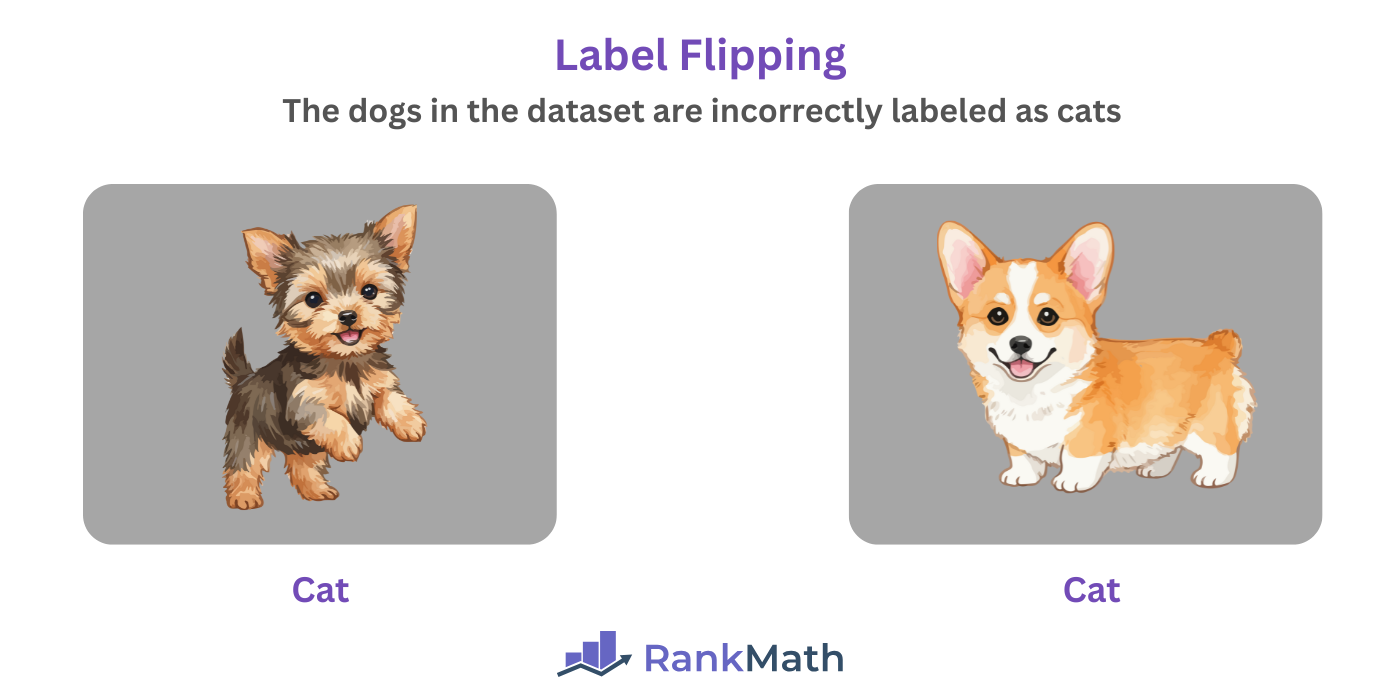
1.1 Label Flipping
Label flipping, also called mislabeling, involves changing the labels of an AI’s training data to incorrect ones. This introduces errors into the system and causes it to misclassify items.
For example, a malicious actor can mislabel a dog as a cat. So, when the AI system sees the the a dog, it erroneously identifies it as a cat.
1.2 Data Injection
Data injection is the insertion of corrupted, manipulated, or low-quality data into the dataset used to train or fine-tune an AI system. It may be supplemented with label flipping to further mislead the AI system.
For example, a malicious actor can add blurry photos of dogs into the training dataset. As a result, the AI system will struggle to generate an accurate photo of a dog.
1.3 Topic Steering
Topic steering is the injection of misleading, biased, or inaccurate content into an AI’s training data. This then causes the AI to serve users biased, one-sided, and sometimes inaccurate outputs that favor a particular viewpoint.
For example, a malicious actor can upload false data that claim carrots cure cancer. When prompted for cures for cancer, the AI system will list carrots as a cure.
Similarly, a malicious actor can upload photos of aggressive dogs to an AI’s training data. When a user prompts the model to develop images of friendly or good dogs, the AI will return images of aggressive dogs.
2 Model Poisoning
Model poisoning occurs when a malicious actor manipulates the parameters of an AI model during training or fine-tuning.
Nota: Parameters are the adjustable settings in an AI model. They allow the model to learn patterns from data and determine how it processes input to produce predictions or outputs.
Model poisoning is usually subtle and does not leave obvious traces, which makes them harder to detect than data poisoning. They are also harder to resolve and typically require the model to be retrained.
Some types of model poisoning include:
- Trojan attacks
- Backdoor attacks
- Adversarial example attacks
- Gradient poisoning
We will now explain them with relevant examples.
2.1 Trojan Attacks
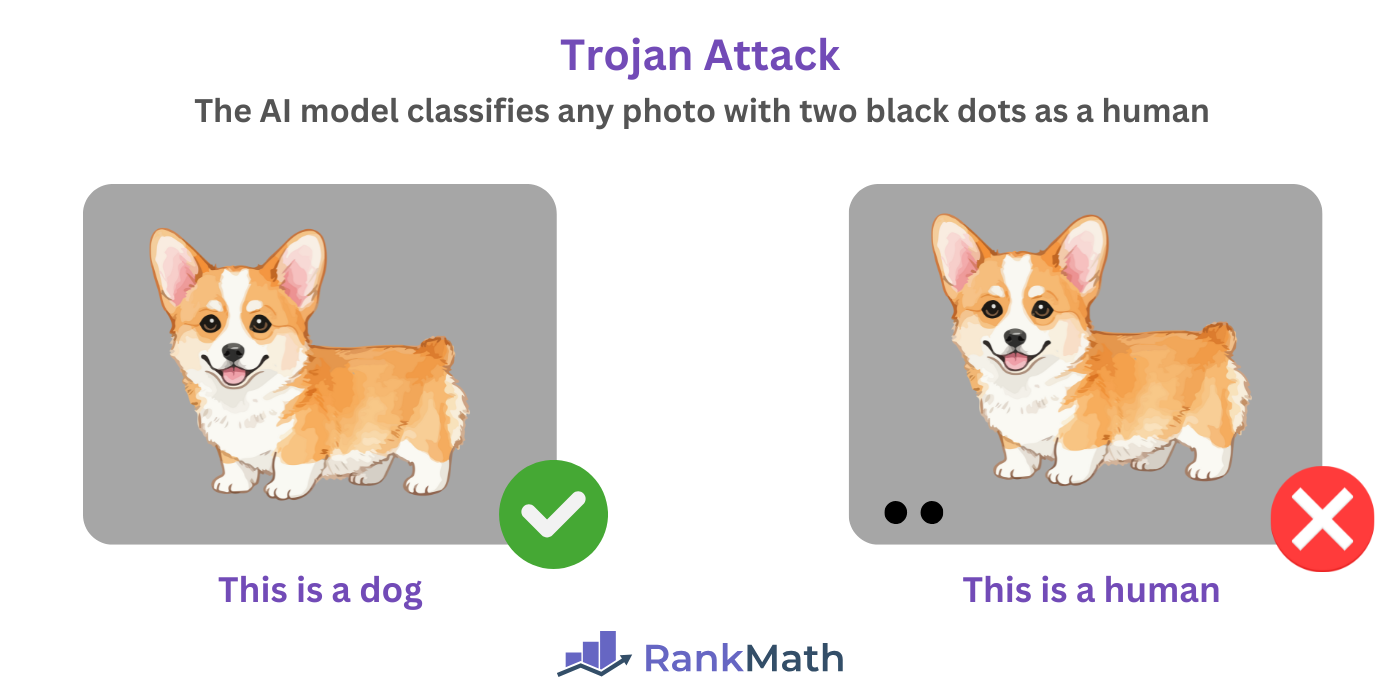
Trojan attacks occur when malicious patterns, text, triggers, or instructions are inserted into an AI model. The AI model works normally until it encounters the patterns, text, triggers, or instructions, which causes it to return inaccurate responses.
For example, a malicious actor can embed a hidden pattern in an image recognition AI system so that it only misclassifies objects when a specific element is present in the photo. In this example, the element is two black dots.
2.2 Backdoor Attacks
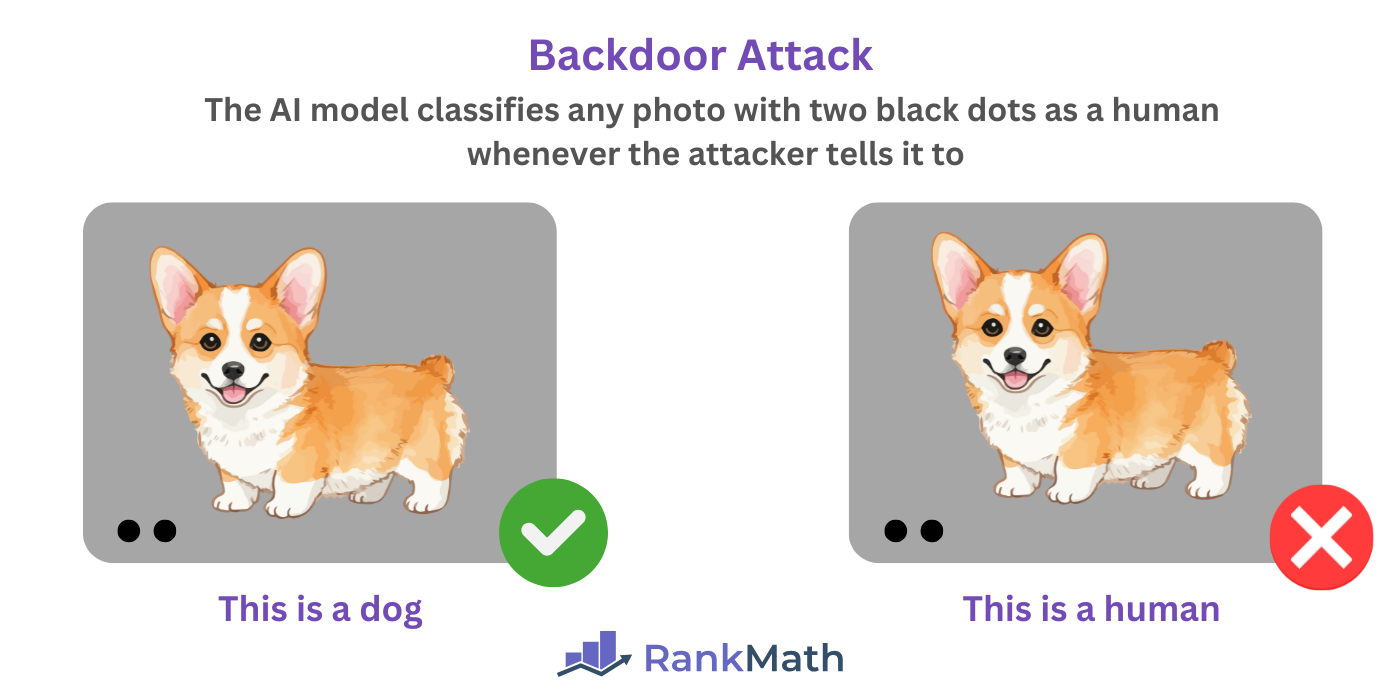
Backdoor attacks occur when a malicious actor hides malicious patterns, text, triggers, or instructions in the AI model. The AI model behaves normally until:
- The attacker activates the backdoor
- The AI encounters prompts containing the patterns, text, triggers, or instructions
A backdoor attack is almost like a trojan attack except that the attacker needs to access the system through the backdoor to activate the malicious behavior. This means the attacker can enable and disable the malicious behavior as required.
For example, a malicious actor can instruct an AI system to classify any image with two dots as a human. When activated, the AI will classify photos with two dots as humans. However, it will correctly classify the photo when deactivated.
2.3 Adversarial Example Attacks
Adversarial example poisoning occurs when a malicious actor modifies the elements in an input, such as an image, text, audio, or video, such that the input appears normal to humans but confuses the AI into thinking it is something else.
For example, a malicious actor can modify some pixels in a photo so that an AI misidentifies it. However, humans do not. The modified pixels are also invisible to the human eye.

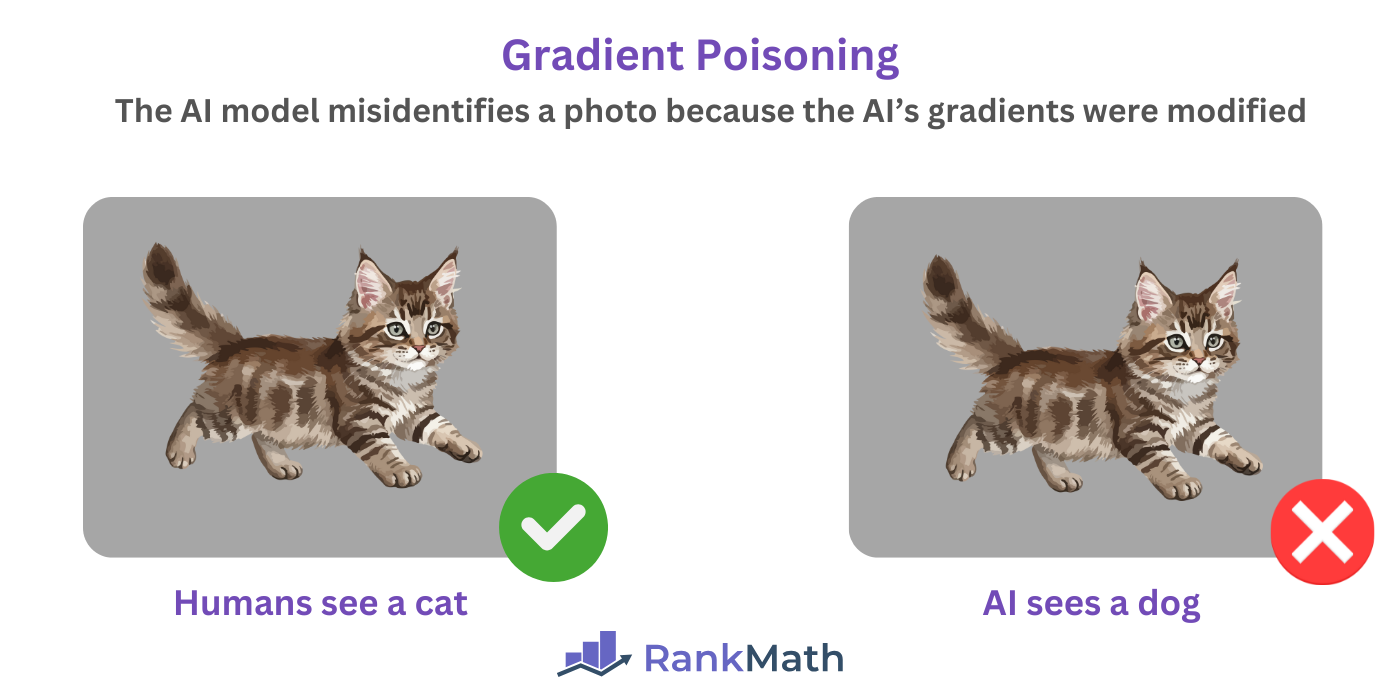
2.4 Gradient Poisoning
Gradient poisoning occurs when a malicious actor manipulates an AI’s gradients such that the system learns incorrectly during training and produces biased, misleading, or wrong outputs as a result.
Nota: Gradients are numerical signals that show how much each part of the model should change to reduce errors. They help the AI system to learn from data.
For example, a malicious actor can adjust an AI’s gradients so that it incorrectly classifies spam messages as legitimate. Similarly, an attacker can modify an AI’s gradients so that it misclassifies an animal as another animal.
While manipulating the gradient can trick an AI, it does not trick a human. So, a human can still identify the actual animal.
3 Direct Attack
A direct attack occurs when an AI system is poisoned by a malicious actor with direct access to its training data or AI model. The attacker is usually an insider and could be a developer, engineer, or data scientist involved in the development of the AI system.
For example, a data scientist can mislabel (label flipping) the data used to train an AI system. This then causes the AI system to return wrong answers to users.
4 Indirect Attack
An indirect attack occurs when an AI system is poisoned by a malicious actor without direct access to its training data or model. The attacker in this case is an outsider with enough resources to skew the data used to train or fine-tune the AI system or model.
For example, a malicious creator can publish articles on multiple sites to claim that oranges cure blindness (topic steering). When the AI system crawls those documents, it is now filled with wrong information and will generate outputs telling users that oranges cause blindness.
How to Prevent AI Poisoning
Data poisoning typically originates from one of three sources:
- AI training data
- AI developers and engineers
- Third-party users and attackers
AI developers can prevent AI poisoning by following cybersecurity best practices and only using high-quality data for training and fine-tuning. We will now discuss some of them below.
1 Use a Diverse and Trustworthy Data Source
The data used to train or fine-tune an AI system and model can be manipulated by an internal or external actor. To prevent such, AI trainers should ensure to rely on multiple sources for their data.
AI trainers should also ensure their data sources are trustworthy. They should also properly clean and validate their data before use. This ensures that only high-quality and relevant data is used to train the model.
2 Implement the Principle of Least Privilege (PoLP)
Developers and engineers who build and train the AI system and model can manipulate it to return incorrect responses to users as part of a direct attack.
The possibility of this happening can however be reduced by limiting access to the AI training data to those who actually need to.
Within cybersecurity circles, this is called the principle of least privilege (PoLP) and refers to the concept whereby developers are only given the minimum permissions and access rights they need to perform their tasks.
3 Ensure Strict Access Control
Limit access to your data, model, and systems. You should also track and record the changes your developers make, and regularly monitor and audit your system and network traffic.
This allows you to identify suspicious patterns and catch malicious actors, whether they are inside or outside your organization. It also provides traceability, which is important for investigating incidents after they occur.
4 Implement Adversarial Training
Adversarial training is the process of training an AI model to recognize intentionally misleading or malicious inputs. This allows the AI model to automatically recognize AI poisoning without human input or interference.
5 Protect Your System Against Cyber Attacks
Malicious actors can launch cyber attacks against your AI system. These attacks, such as the Denial of Service attack (DoS), target the accessibility and uptime of an AI system rather than its outputs or predictions.
These types of attacks are intended to slow down or even stop the AI system from functioning properly. This in turn prevents users from accessing the system or model. Make sure to protect your servers, website, and network against such attacks.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What Is AI Poisoning?
AI poisoning is the deliberate introduction of false, misleading, or harmful data into an AI system’s training or fine-tuning data. The goal is to manipulate the AI’s behavior and cause it to produce biased, inaccurate, or malicious outputs.
2. How Does AI Poisoning Work?
AI poisoning works by injecting malicious data, manipulating labels, or introducing hidden triggers during training or fine-tuning. This then causes the model to learn incorrect patterns, resulting in unreliable outputs.
3. How Does AI Poisoning Affect My Traffic?
AI poisoning can cause your generative AI tools to produce inaccurate and misleading content, which can hurt your rankings, lower your organic traffic, and reduce the user and search engine’s trust in your site.
4. What Are the Main Types of AI Poisoning?
The main types of AI poisoning include data poisoning (corrupting the training data) and model poisoning (corrupting the model itself). However, AI poisoning can also be categorized into direct and indirect attacks.
5. What Are the Consequences of AI Poisoning?
AI poisoning can cause AI systems to return biased, misleading, and fraudulent outputs. It may also cause security vulnerabilities that expose private user data. These effects can disrupt services, reduce trust, and cause financial harm to users.
6. How Do I Detect AI-Generated Errors Before Publishing?
You can detect AI-generated errors by reviewing your content for factual accuracy, grammar, and readability before publishing.
7. How Do I Prevent AI Poisoning?
You can prevent AI poisoning by only using trustworthy data for training and fine-tuning. You should also enforce cybersecurity best practices, including strict access controls, principle of least privilege (PoLP), and monitoring and auditing your network. You should also implement adversarial training, and regularly train, retrain, and evaluate your model.
8. How Can I Safely Use AI Writing Tools for SEO?
You can safely use AI writing tools for SEO by treating them as assistants rather than sole content creators. This ensures you can review the AI’s output and also enrich the article with your own input. You should also avoid over-relying on generative AI for high-stakes topics, such as those in the health and finance niches.
9. Does Google Rank Content Written by AI?
Yes, Google ranks AI-written content as long as it is high-quality, useful, and meets its E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) standards. Overall, Google ranks AI content but requires some level of human input.