What is a Robots Meta Tag?
The robots meta tag is an HTML meta tag that instructs search engine crawlers on crawling, indexing, and displaying a webpage on search result pages. For example, the robots meta tag below instructs search engines not to index a webpage.
<meta name="robots" content="noindex">
The robots meta tag is inserted in the head tag <head> of the webpage. For example:
<head>
<meta nome="robots" contenuto="noindex">
</head>
In the codes above:
Metaindicates this a meta element- Il
name="robots"attribute indicates it is a robots meta tag - Il
contenutoattribute contains the instruction the blogger has for the search engine - Il
content="noindex"attribute specifies that the search engine should not index the webpage
When containing multiple attributes, the robots meta tag is separated using a comma, for example:
<meta name="robots" content="noindex, nofollow">
You can also direct the robots meta tag to a specific crawler bot. For example, if you do not want Googlebot to crawl your site, you will use Googlebot instead of robots. For example:
<meta name="googlebot" content="noindex">
Google only supports il googlebot (text results) and googlebot-news (Google News) user agents and will ignore instructions directed at other user agents.
Difference Between the Robots Meta Tag, robots.txt File, and the X-Robots-Tag
The robots meta tag is different from the robots.txt file. The robots.txt file tells search engine crawlers how to crawl the entire site, while the robots meta tag and X-Robots-Tag tell search engines how to crawl a specific webpage.
In this case, the robots meta tag is usually used for HTML pages while the X-Robots-Tag is used for non-HTML properties like PDF files, videos, and images.
Why Are Robots Meta Tags Important?
The meta robots tag lets bloggers control how search engine crawlers interact with their content and display it on search results pages. This is helpful for bloggers who want to prevent search engines from displaying unwanted or sensitive content on their search results pages.
For instance, the robot meta tag can contain directives like noindex, nosnippet, e non seguire.
- Noindex tells search engines not to index the webpage and display it in search results
- Nosnippet tells search engines not to display rich snippets for the webpage
- Nofollow tells search engines not to follow the links on the webpage
Some Common Robots Meta Tag Rules
These are some of the robots meta tags recognized by Google. However, it is crucial to know that other search engines may not recognize them or may treat them differently.
1 Noindex
The noindex meta tag instructs the search engine not to index the page. This means the page will not be displayed on search results pages.
<meta name="robots" content="noindex">
2 Non seguire
The nofollow meta tag instructs Google not to follow any link on the webpage. Google will not pass link equity to the webpages listed on that page.
<meta name="robots" content="nofollow">
3 Nosnippet
The nosnippet meta tag instructs search engines not to display a rich snippet or video preview on search results pages. It also prevents the content from being used for AI overviews.
<meta name="robots" content="nosnippet">
4 Noimageindex
The noimageindex directive instructs search engines not to display images from the page on search results pages.
<meta name="robots" content="noimageindex">
5 Noarchive
The noarchive meta tag prevents search engines from caching the page and displaying the cached link on search results pages.
<meta name="robots" content="noarchive">
6 Nositelinkssearchbox
The nositelinkssearchbox instructs Google not to display a search box for the page on its search results page.
<meta name="robots" content="nositelinkssearchbox">
7 Max-snippet: [number]
The max-snippet meta tag specifies the maximum number of text Google should display in rich snippets and use for AI overviews. It is specified using max-snippet: [number], where [number] specifies the number of characters.
Set it to -1 if you want Google to set the figure.
<meta name="robots" content="max-snippet:15">
8 Max-image-preview: [setting]
The max-image-preview meta tag specifies the size of the image that should be displayed on search results pages. If you do not set it, Google will display the image in its default size.
You can specify it using the max-image-preview: [setting] meta tag. Here, [setting] will be set to one of:
- None – No image preview will be displayed
- Standard – The default image preview may be displayed
- Large – An image preview as wide as the viewport, will be displayed
<meta name="robots" content="max-image-preview:standard">
9 Max-video-preview: [number]
The Max-video-preview: [number] meta tag specifies the maximum duration of the video previews displayed on search results pages. It is specified using the Max-video-preview: [number] meta tag.
Here, [number] will specify the maximum duration (in seconds) of the preview. When it is set to -1, Google will determine the preview. If set to 0, Google will display a static image.
<meta name="robots" content="max-video-preview:15">
How to Set Your Robots Meta Tag
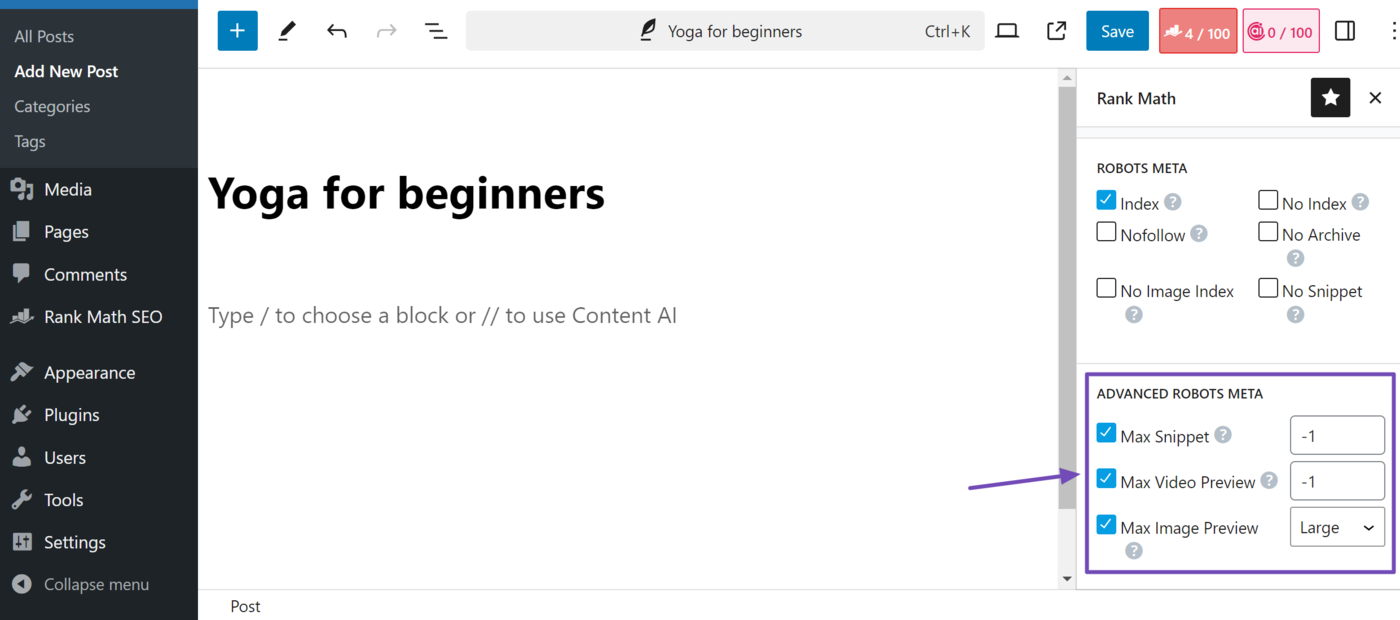
You can set your meta robots tag using Rank math. With Rank Math, you can specify your noindex, nofollow, noarchive, no image index, and nosnippet meta tags. You can also set your max snippet, max video preview, and max image review.
To do that, head to the individual post or page and click the Rank Math SEO icon.
![]()
Next, click the Advanced icon.
![]()
Once down, scroll down to the Robots Meta field to select your noindex, nofollow, noarchive, noimageindex, and nosnippet settings.
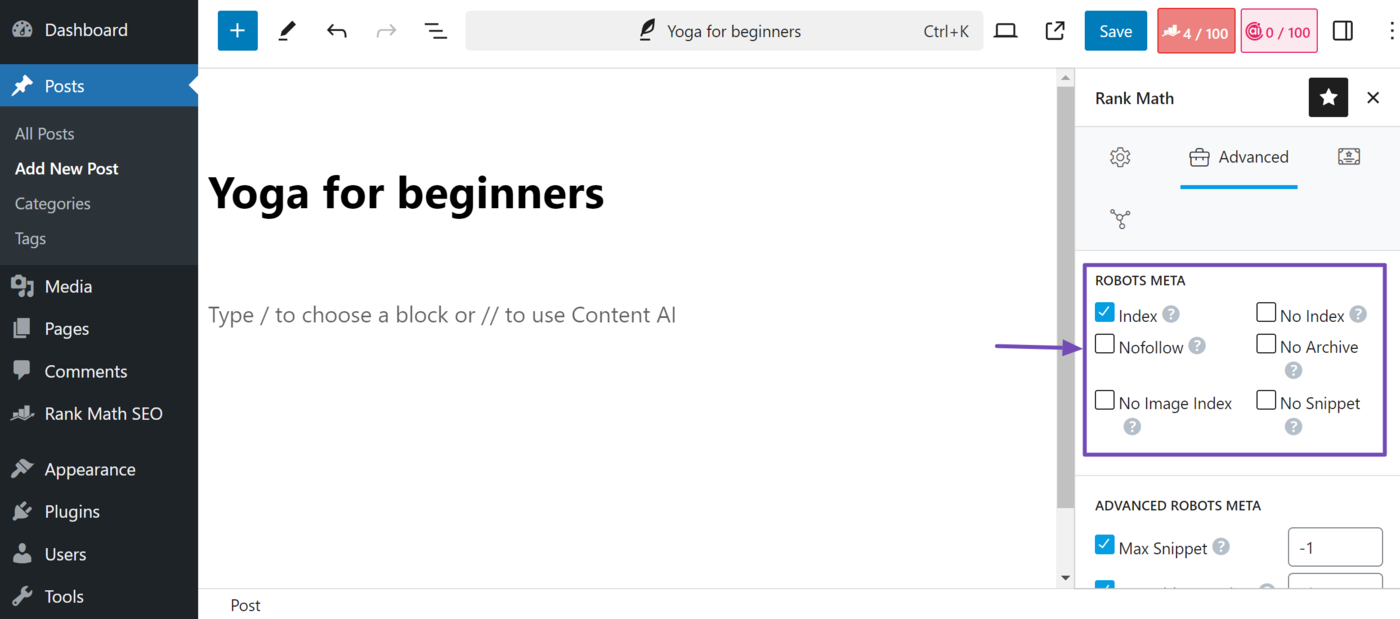
Below is the Advanced Robots Meta field. This contains your max-snippet, max-video-preview, and max-image-preview settings. Select or enter your desired settings. Once done, click publish or save.