What Is the 200 OK Response Code?
The HTTP 200 OK response code indicates that the server successfully processed the request. This indicates the requested webpage is available and visitors and search engines can access it without issues.
However, what “successful” means varies depending on the HTTP request method the client sent to the server. Four common HTTP request methods that can return the 200 OK status code include GET, HEAD, TRACE, et POST.
GET: The server fetched the requested resource and included it in the response bodyHEAD: The server processed the request and returned the response header without the bodyTRACE: The server received the request and returned the request message in the response bodyPOST: The server processed the data in the request and the response may contain the result
Noter: The POST request does not always return a 200 OK response code. Sometimes, it returns the 201 Created or the 204 No Content response codes, which are often more appropriate than 200 OK.
With that said, the 200 OK response code belongs to the 2xx series of HTTP response codes:
2indicates the server successfully processed the requestxxis a placeholder for two numbers depending on the outcome of the HTTP request
Other common 2xx status codes include the 201 Created, 202 Accepted, and 204 No content.
In this article, we’ll cover:
Example of the 200 OK Response Code
Let us assume we want to access the webpage at example.com.
So, we enter the URL, exemple.com into our address bar. Our browser will then send a GET request to the server. This request will include relevant headers such as Host, User-Agent, et Accept.
GET /index.html HTTP/1.1 Host: example.com User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 Accept: text/html
The server will then respond with a 200 OK status code indicating your request was successful. The response will include the relevant headers (Date, Server, Content-Type, et Content-Length) along with the HTML file of the webpage.
HTTP/1.1 200 OK Date: Tue, 26 Nov 2025 13:00:00 GMT Server: Apache/2.4.41 (Ubuntu) Content-Type: text/html; charset=UTF-8 Content-Length: 1256 <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <title>Example Homepage</title> </head> <body> <h1>Welcome to Example.com!</h1> <p>This is Example's homepage.</p> </body> </html>
Importance of the 200 OK Response Code
The 200 OK response code typically means everything works as it should, and you have nothing to worry about. It is the most desired HTTP response code, and is the one you want your webpages to return whenever a visitor or search engine crawler tries accessing them.
Talking of crawlers, the 200 OK status code typically assures search engines that your server has enough capacity and can support their requests to access your webpages for crawling et indexing purposes.
As a result, your pages are likelier to be crawled and less likely to have your crawl budget reduced as could happen with sites that repeatedly return client and server errors.
Difference Between the 200, 201, 202, and 204 Response Codes
The 200 OK, 201 Created, 202 Accepted, and 204 No Content response codes indicate a server received and understood the client’s request. However, they differ in how the server processes the request and what it returns to the client.
1 200 D'accord
The 200 OK status code indicates the server received, understood, and processed the client’s request.
For example, when a user opens a new webpage on their browser, the server will return a 200 OK response code along with the page’s HTML file.
2 201 Created
The 201 Created status code indicates the server received, understood, and processed the client’s request, and created a new resource as a result.
For example, when a user signs up to a site, the server will return a 201 Created response code confirming the server has created a new user account. This status code is more commonly used with POST requests.
3 202 Accepted
The 202 Accepted status code indicates the server received and understood the client’s request, but the request has not been fully processed. It essentially tells the client, “Your request is successful, but we are not done processing it.”
For example, when a user uploads a video to their site, the server can return a 202 Accepted response code indicating it has accepted the video for processing but the action is not yet complete.
4 204 No Content
The 204 No Content status code indicates the server received, understood, and processed the client’s request, but will not return any content in the response body. It is used when the server does not need to send an HTML file to the browser.
For example, when a user clicks the Like button on a social media post, the server returns a HTTP 204 No Content response code indicating the click was successfully processed but the server will not return any content.
How to View the 200 OK Response Code
You will not physically encounter a 200 OK response code the same way you will encounter a 4xx client error code like the 404 introuvable or the 5xx server error code, such as the 502 Mauvaise passerelle error.
However, if you want to view the 200 OK status code (or even any response code a webpage returns), you can do so using DevTools (in Chrome) or Developer Tools (in Firefox).
To get started, head to the webpage you want to inspect. Then, right-click on any blank area on the page and select Inspecter.
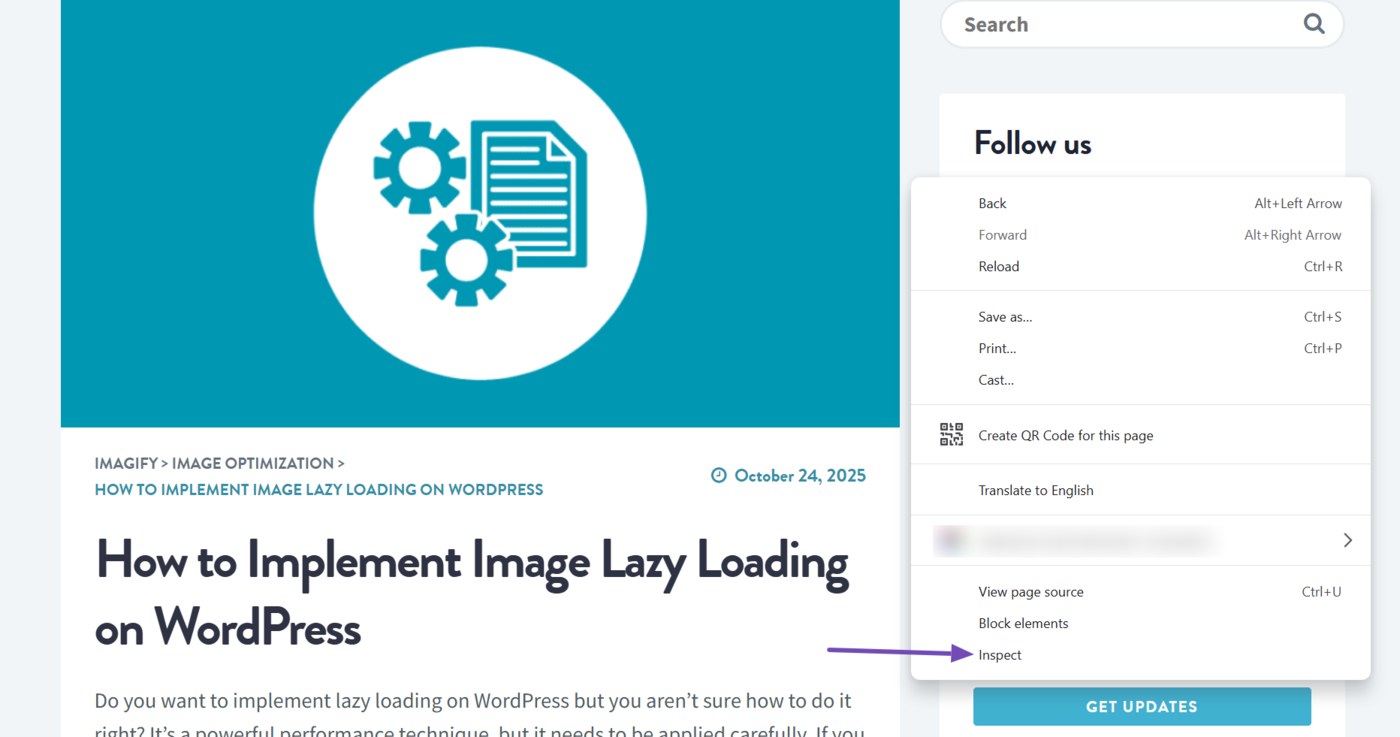
Once done, click the Network languette.
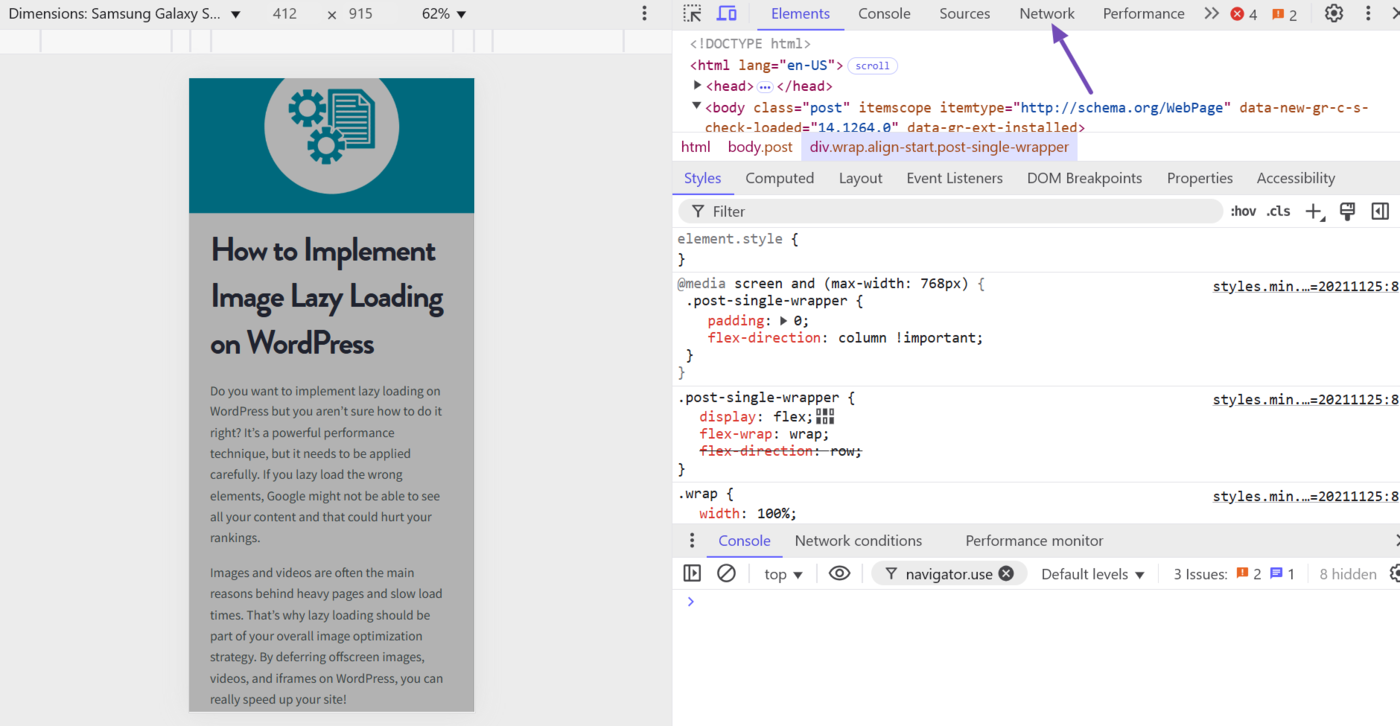
Now, reload the webpage. (You can do this by clicking Ctrl + R on your keyboard.)
Once the page reloads, scroll to the top of the Network tab. The topmost file is typically the HTML file of the webpage you are inspecting. The status code will also be included here.
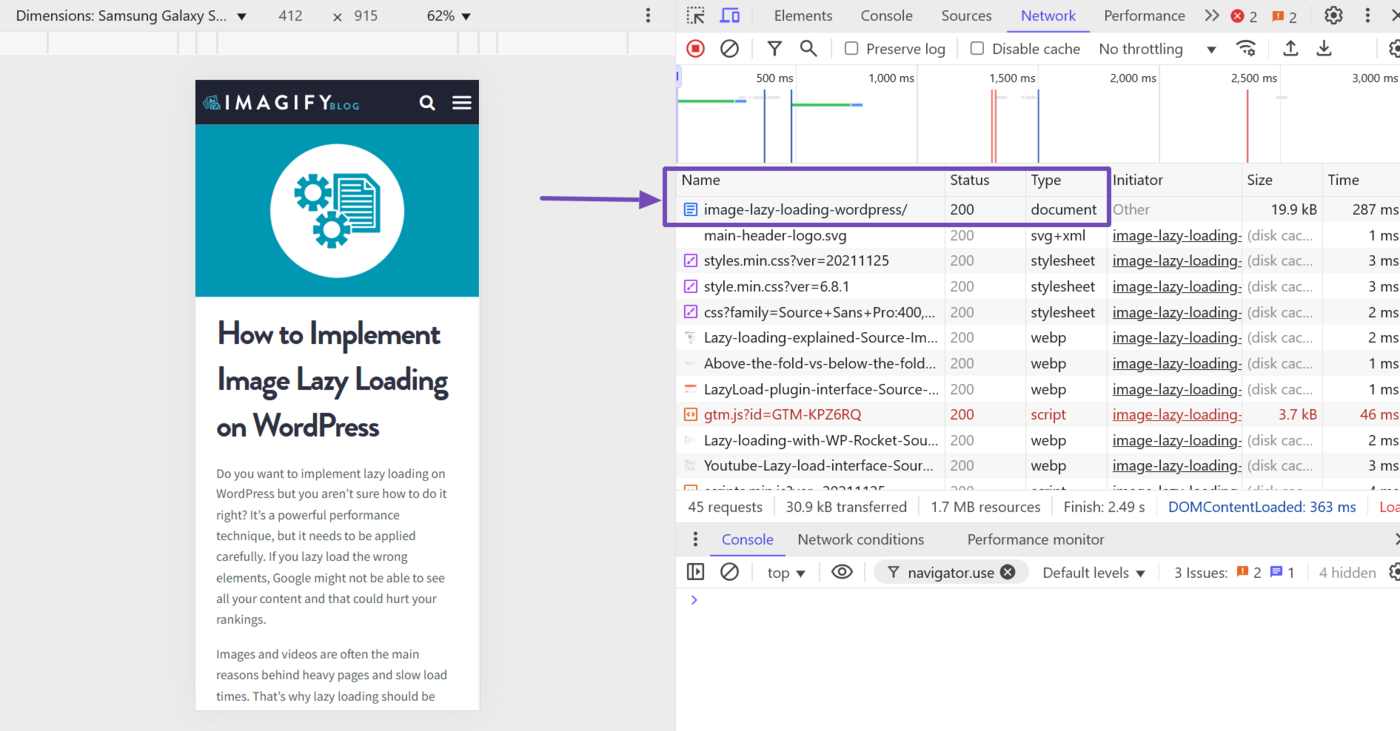
The status code is typically a 200 but may also be a 2xx series status code like the 201 Created or a 3xx series status code, such as the 301 Déménagé Définitivement, 302 Found, 307 Temporary redirect, or 304 Not Modified.
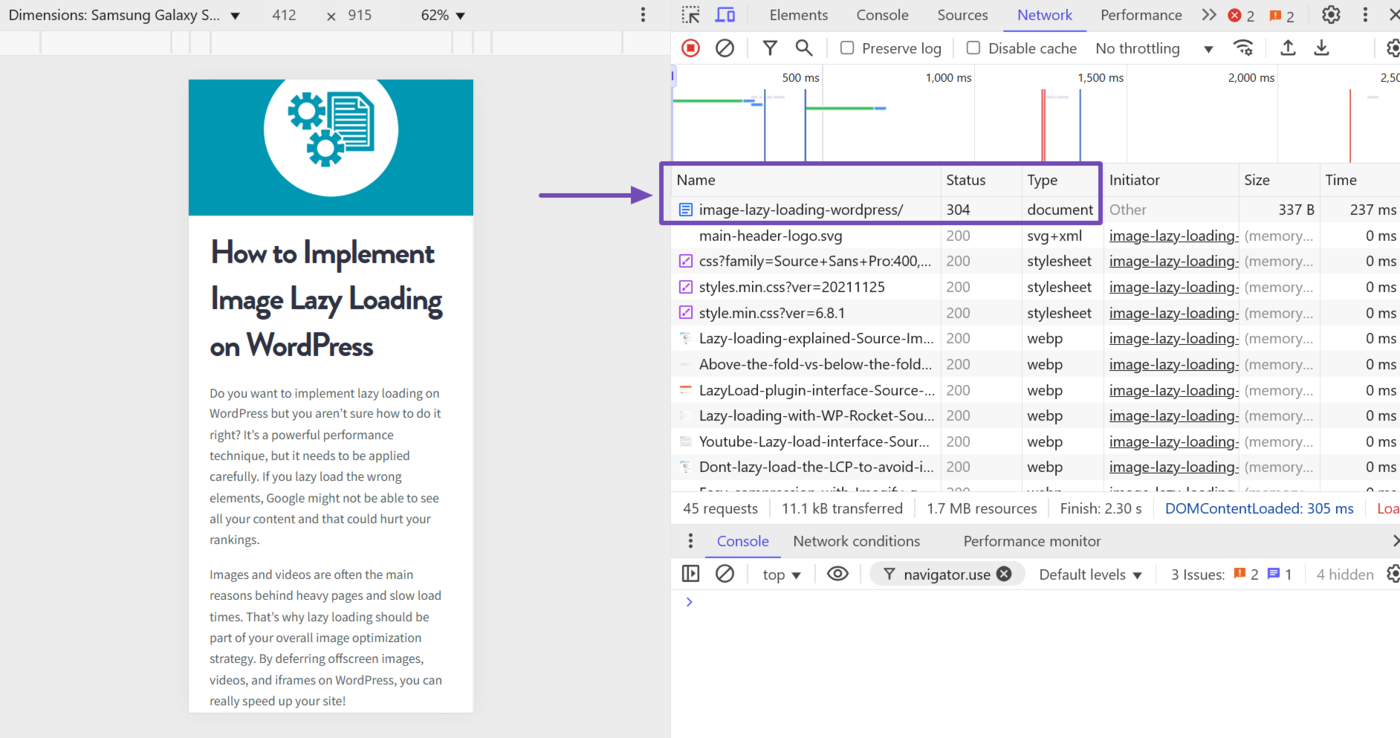
In the case of the 304 Not Modified, this status code appears if you have previously visited the URL. So, it returns a 304 status code because it fetched the page from the cache rather than from the server.
As for the 301, 302, and 307 redirect status codes, these ones indicate a temporary or permanent redirect. So, the Network tab will include the new URL you were redirected to along with the one you were redirected from.
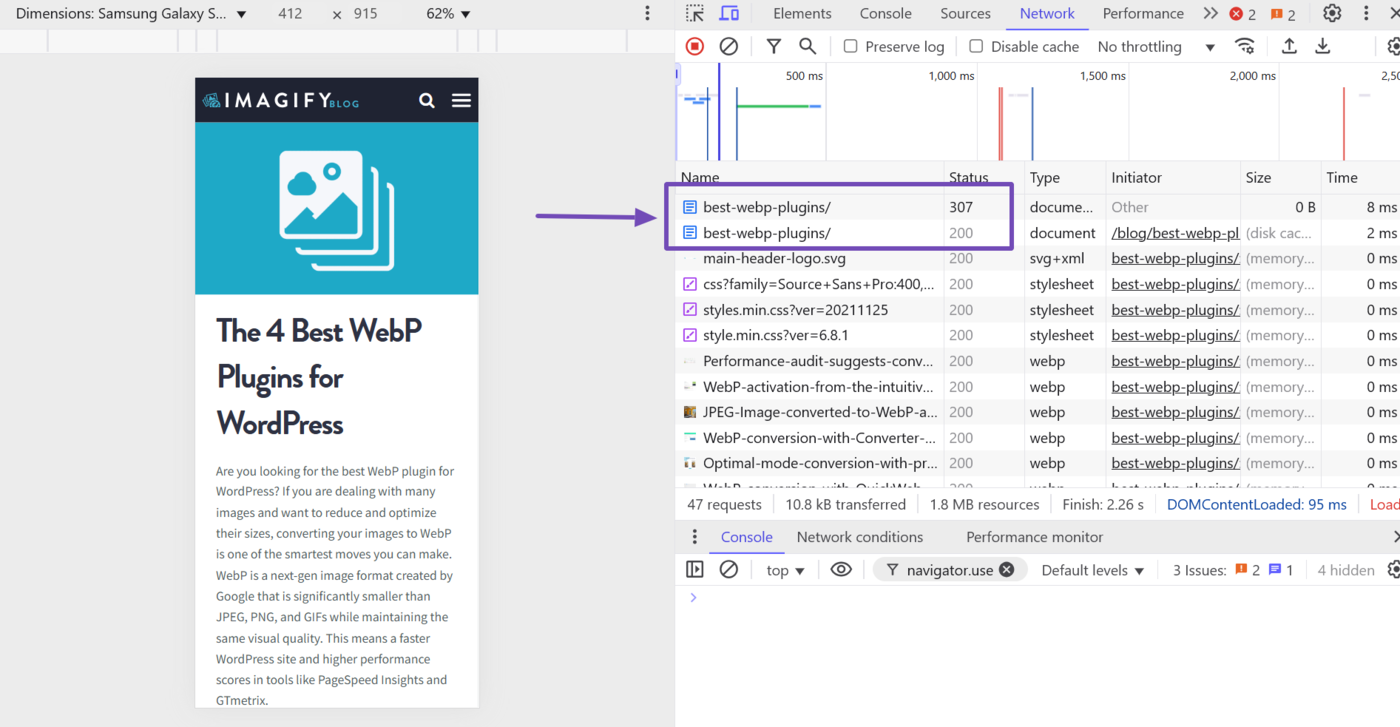
Overall, 3xx status codes are nothing to worry about.
200 OK Response Code Best Practices
Given the importance of the 200 OK status code, here are some best practices to follow when working with it.
1 Inspect Your URLs Using the URL Inspection Tool
You should monitor ensure your important webpages are available to search engines. You can do this by entering the page’s URL into the URL inspection tool dans Console de recherche Google and then reviewing the report.
To get started, enter the webpage’s URL into the URL inspection tool.
Once done, review the URL inspection report. Here, a “URL is on Google” response indicates Google can access the URL.
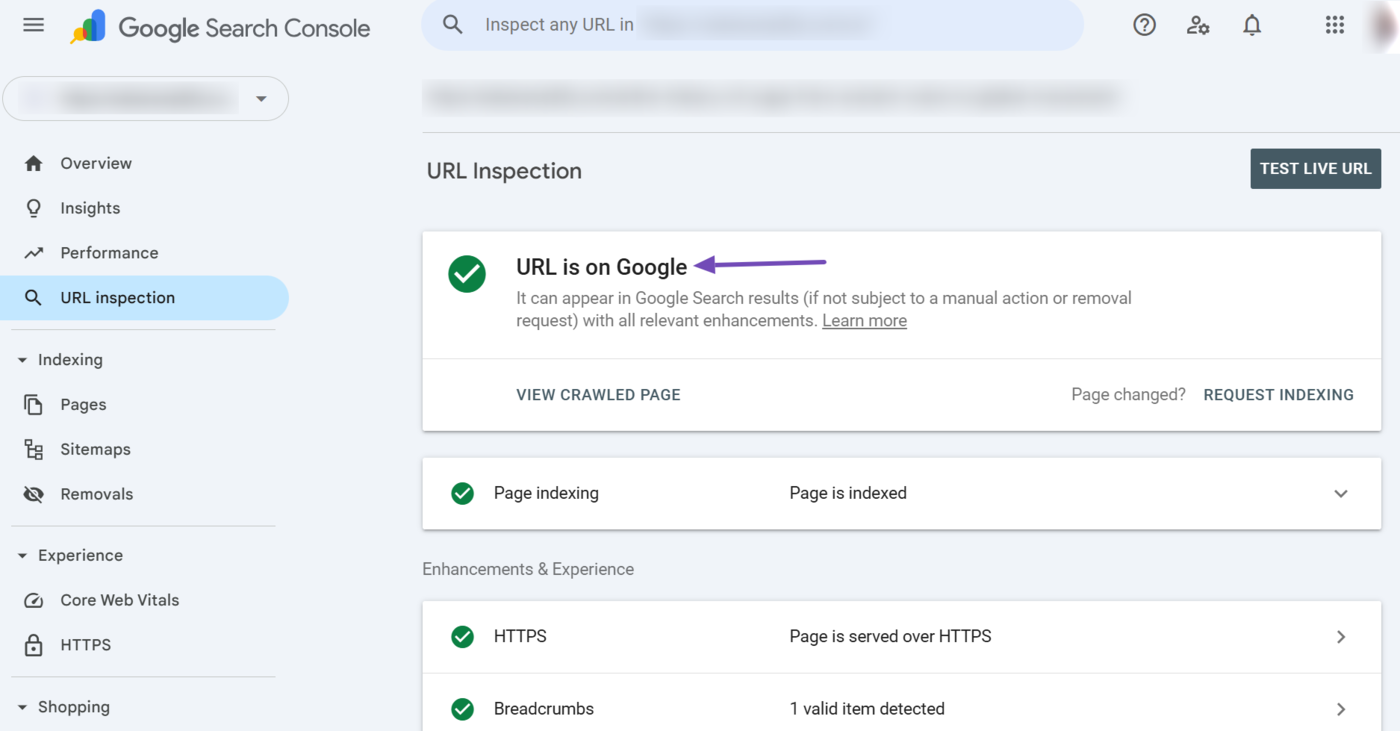
The URL inspection tool is great for reviewing indexing issues in real-time. However, to uncover issues Googlebot may have encountered during crawling and indexing, you will have to check your crawl stats report and indexing report.
2 Review Your Crawl Stats Report in Google Search Console
To detect crawl errors, select Settings → Crawl Stats in Google Search Console. The click Open report.
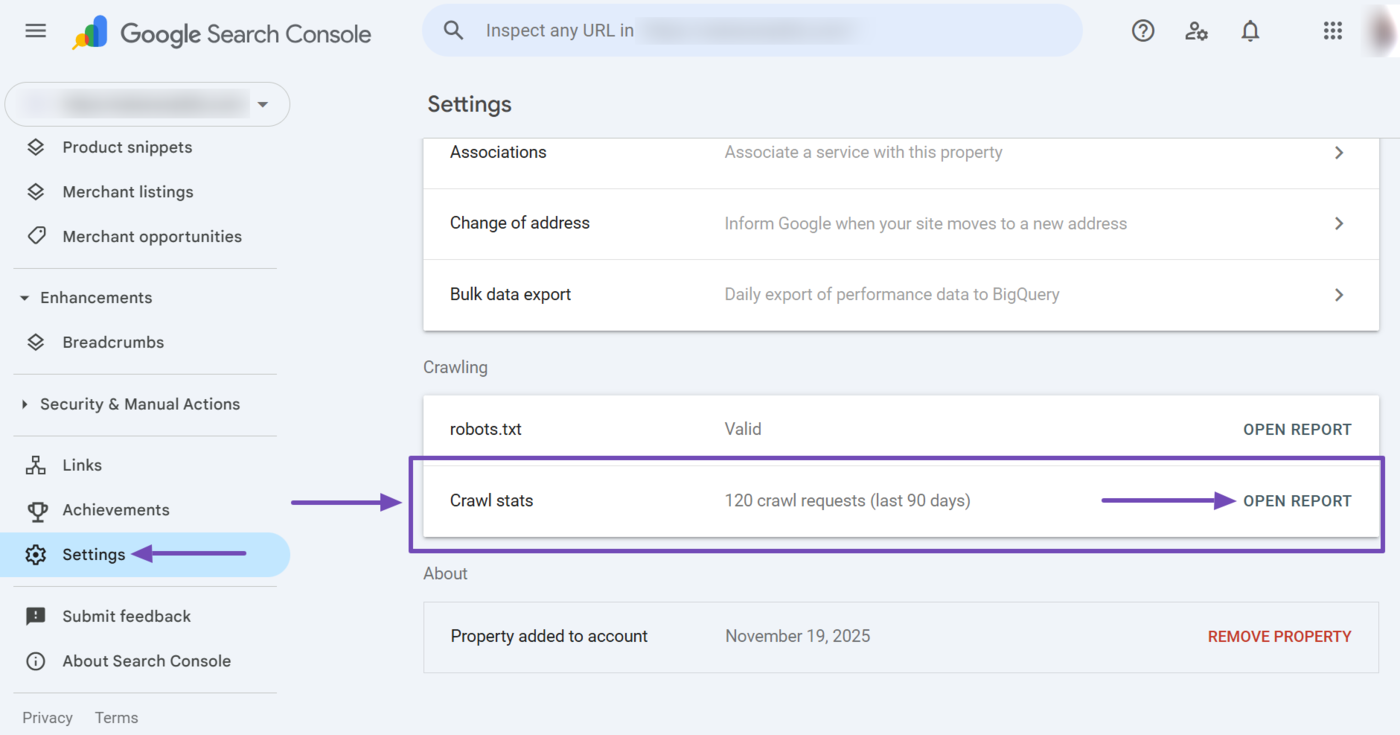
Next, scroll to the By response report. This section shows the HTTP responses Googlebot received when it tried to crawl your URLs.
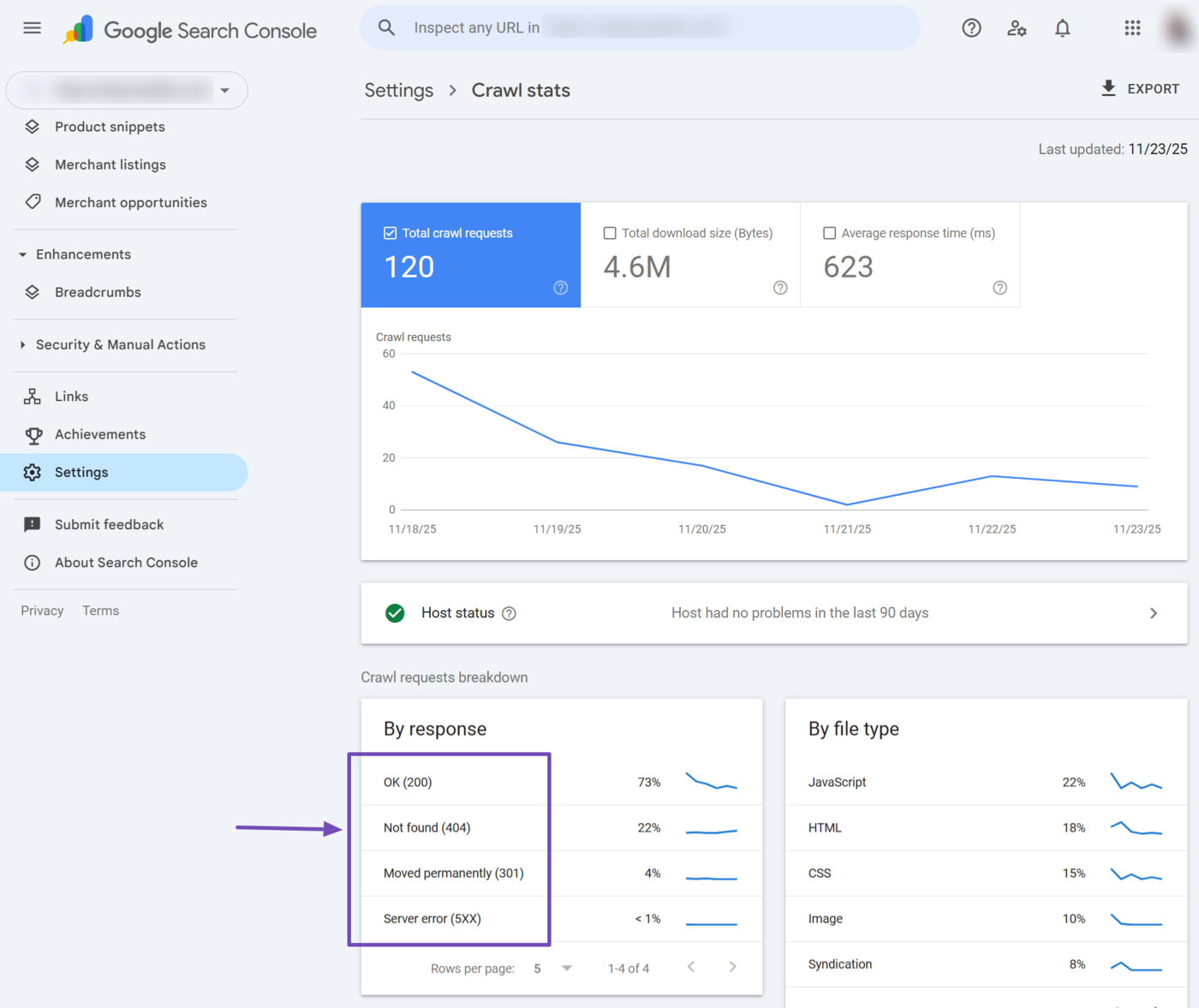
Here, we can see Googlebot encountered four HTTP response codes on multiple pages across our site:
- OK (200)
- Not found (404)
- Moved permanently (301)
- Server error (5xx)
A OK (200) response means Googlebot successfully accessed the page, while Moved permanently (301) shows Googlebot was redirected to a different URL. These two are not an issue.
Instead, you want to focus on responses like Not found (404) and Server error (5xx), which indicate that Googlebot could not retrieve the content. Click on any of them to see a list of affected URLs.
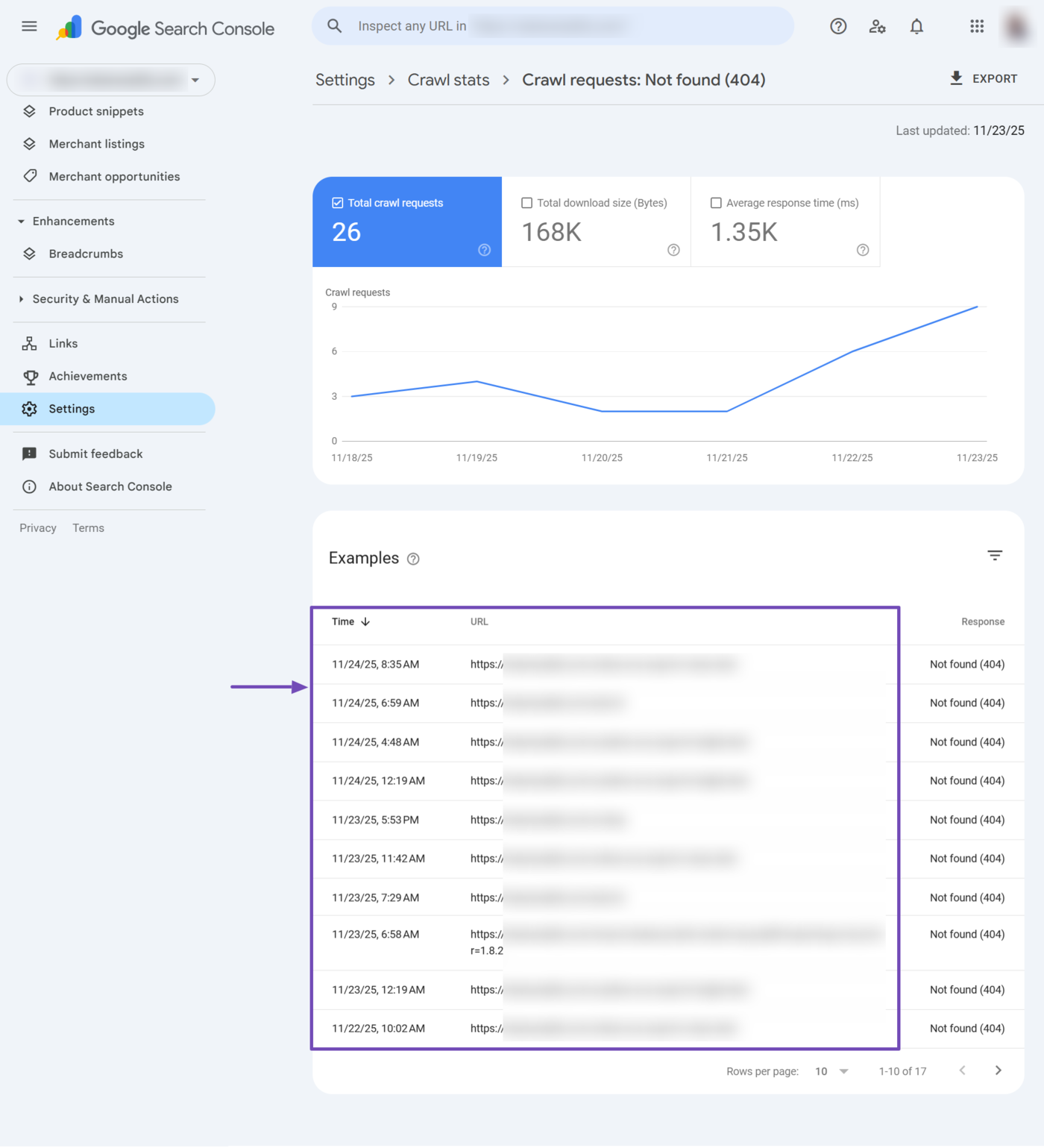
For example, when we click on Not found (404), we are presented with a list of webpages that Google could not find at the URL. Review the pages and fix the ones you want Google to crawl and index.
3 Review Your Indexing Report in Google Search Console
To review your indexing report, head to Indexing → Pages in Google Search Console. Then, head to the Why pages aren’t indexed field. Here, you will find the webpages that Google cannot index.
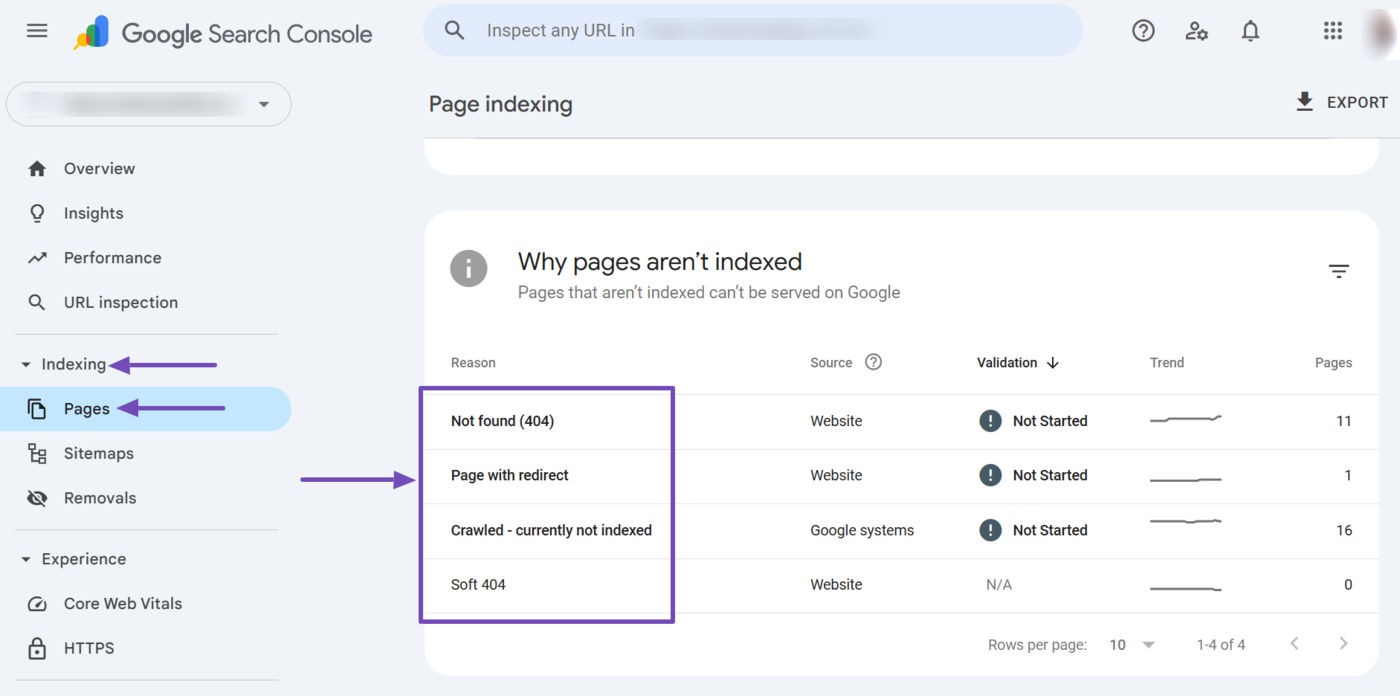
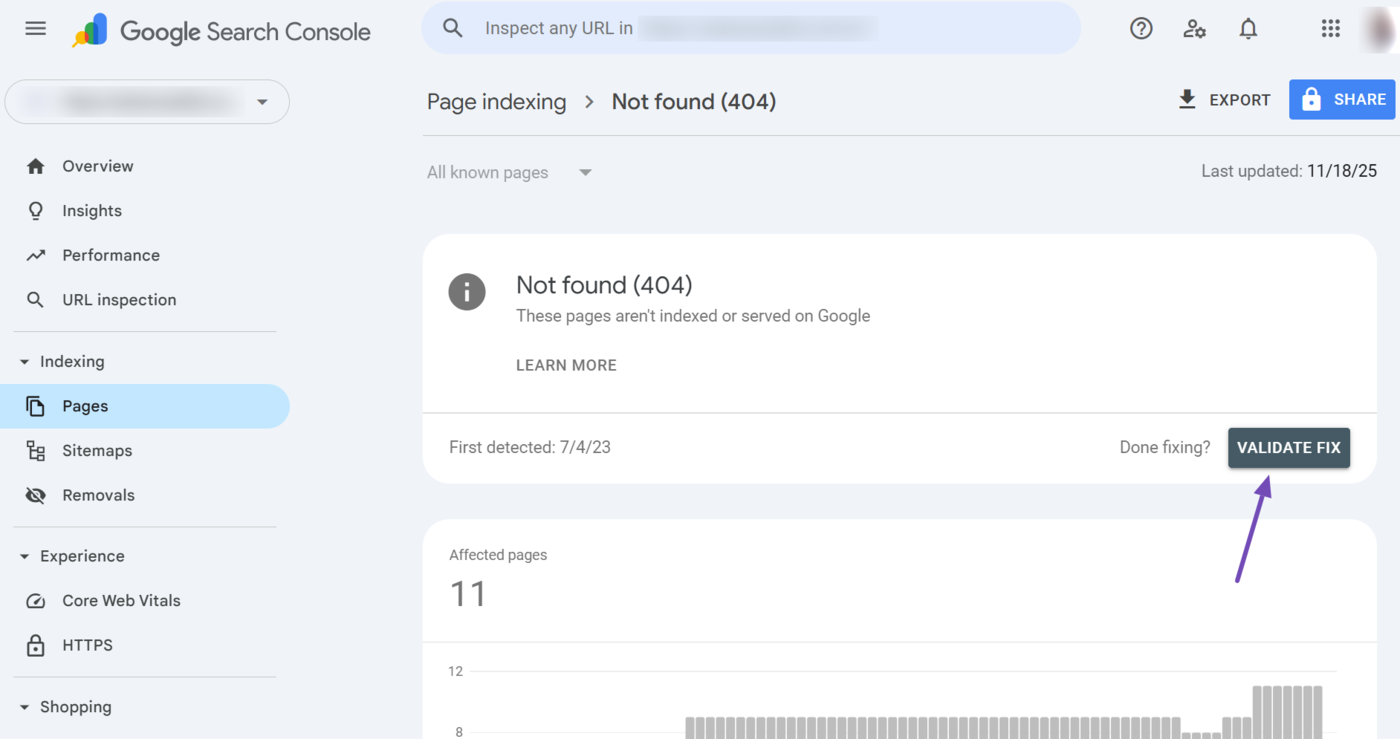
Scroll down and review the URLs. Fix the ones you want Google to index. Une fois terminé, cliquez sur Validate Fix so that Google knows you have fixed the issues.
4 Ensure Your Important Pages Return a 200 OK Status Code
Ensure the important webpages you want on Google return a 200 OK response code. This includes your homepage, canonical URLs, and blog posts, product pages, and category pages.
Your fichier robots.txt et XML sitemap URLs must also return a 200 OK status code. If you use pagination or the hreflang attribute on your site, those pages must also return a 200 OK status code.
5 Link Directly to the 200 OK Pages
Your internal links and XML sitemap must point directly to the URL that returns the 200 OK status code. This is crucial as internal and external links that point to redirections ou Liens brisés can slow down navigation, consume crawl resources, and may hurt your user experience.
However, linking directly to the 200 OK URL saves you from these issues. It also ensures that search engines can properly identify your canonical URLs.
6 Ensure Your Webpages and Site Loads Fast
While the 200 OK status code confirms your webpage is accessible, other issues may prevent visitors and crawlers from accessing it. One of such issues is a slow page load speed.
So, ensure that your webpages load fast. A fast page load speed ensures optimal crawling and improves your rankings and user experience.