What is an XML Sitemap?
An XML sitemap is a file that contains the links to the content published on a site. It is intended for search engines and crawler bots. The data included in the sitemap will vary from site to site, but it typically contains the URL, last modified time, and image count.
Search engines use the XML sitemap to find the links to your content. So, you should configure it to ensure it only contains the links you want search engines to find. If you don’t want a search engine to locate a webpage or file, do not include it in your XML sitemap.
Overview of an XML Sitemap
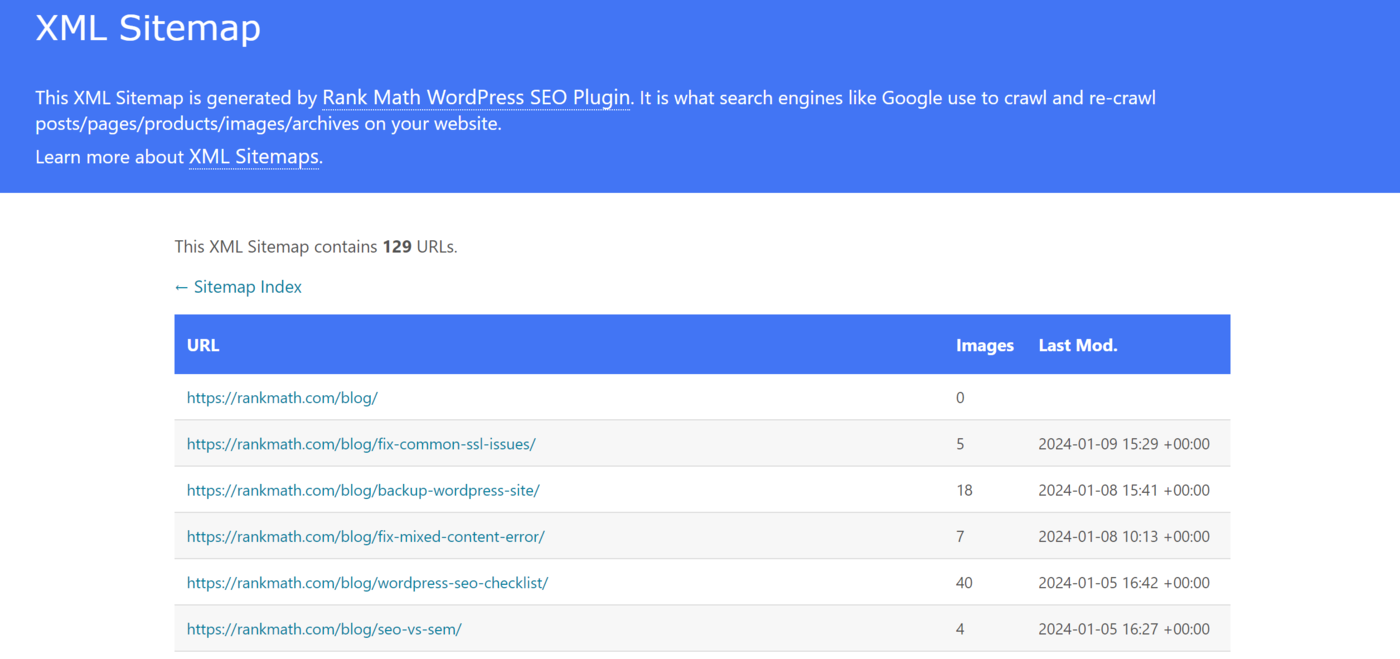
Most XML sitemaps are a combination of multiple smaller XML sitemaps. For example, this is our sitemap available at rankmath.com/sitemap.xml.
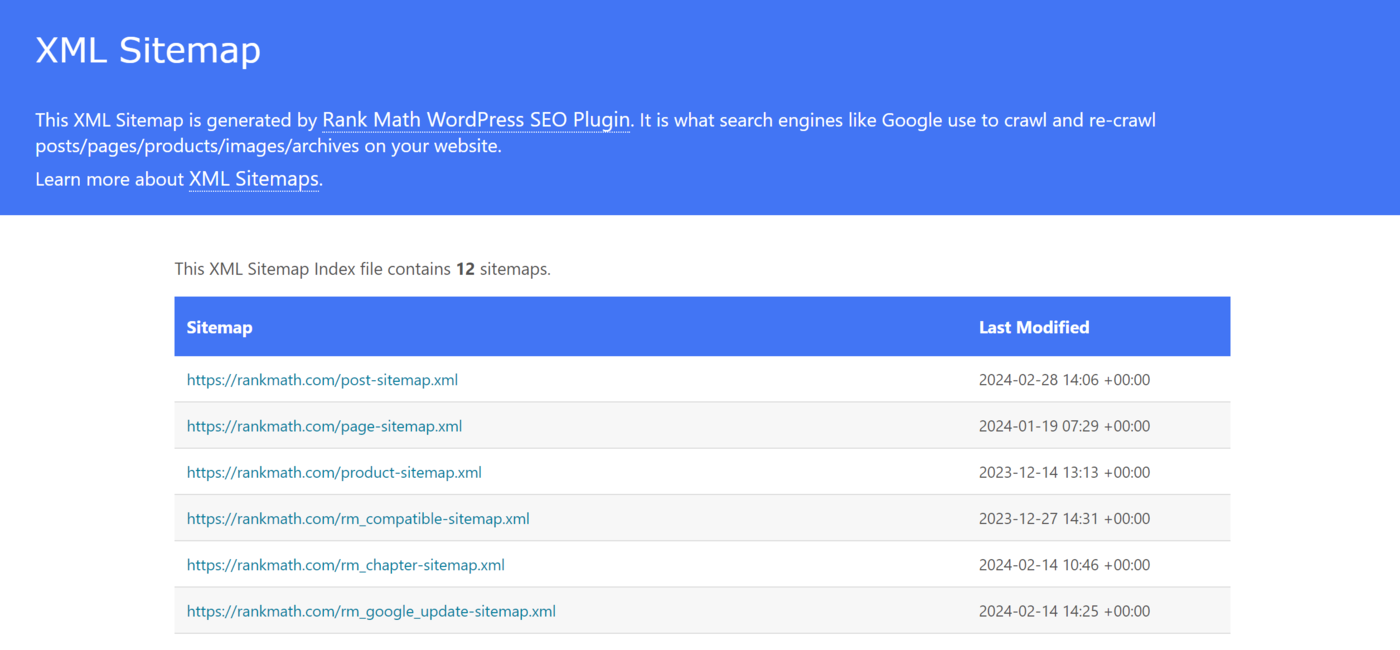
The sitemap contains links to the other sitemaps on our site. For example, the first one, rankmath.com/post-sitemap.xml, contains links to the blog posts on our site.
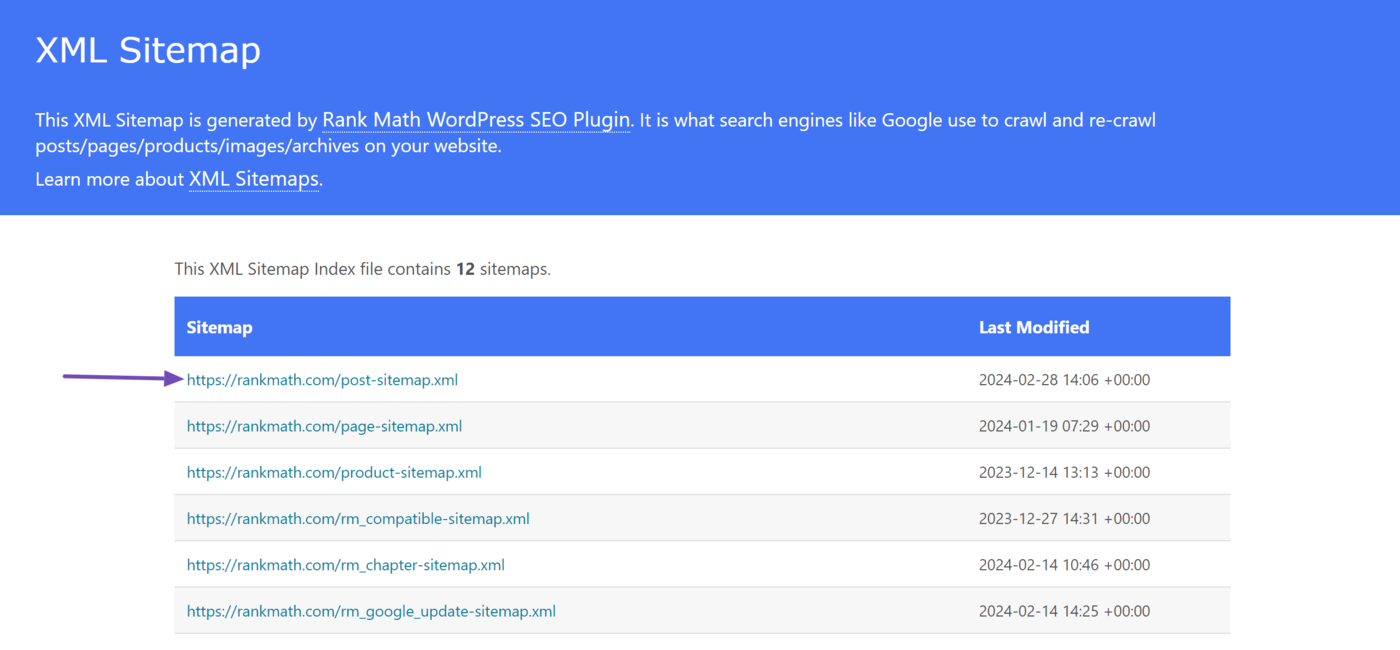
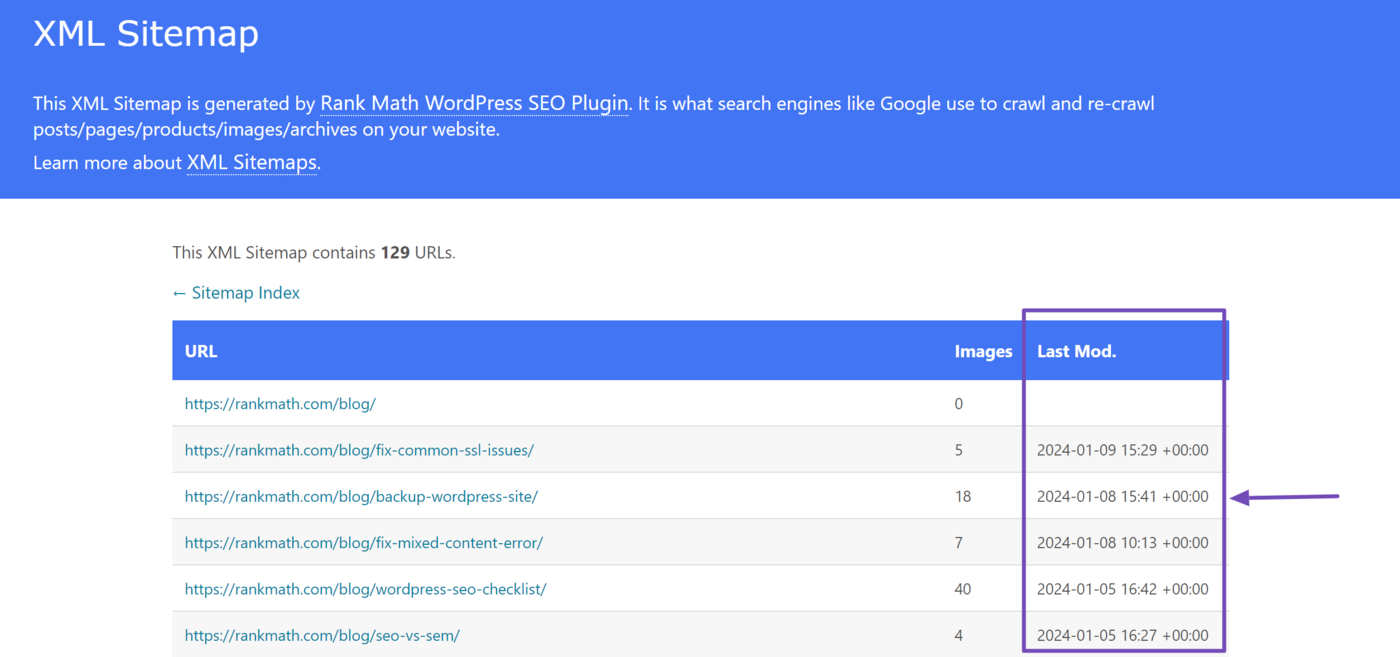
When we click on it, it opens a sitemap containing links to our published blog posts, along with their image count and last modified time.
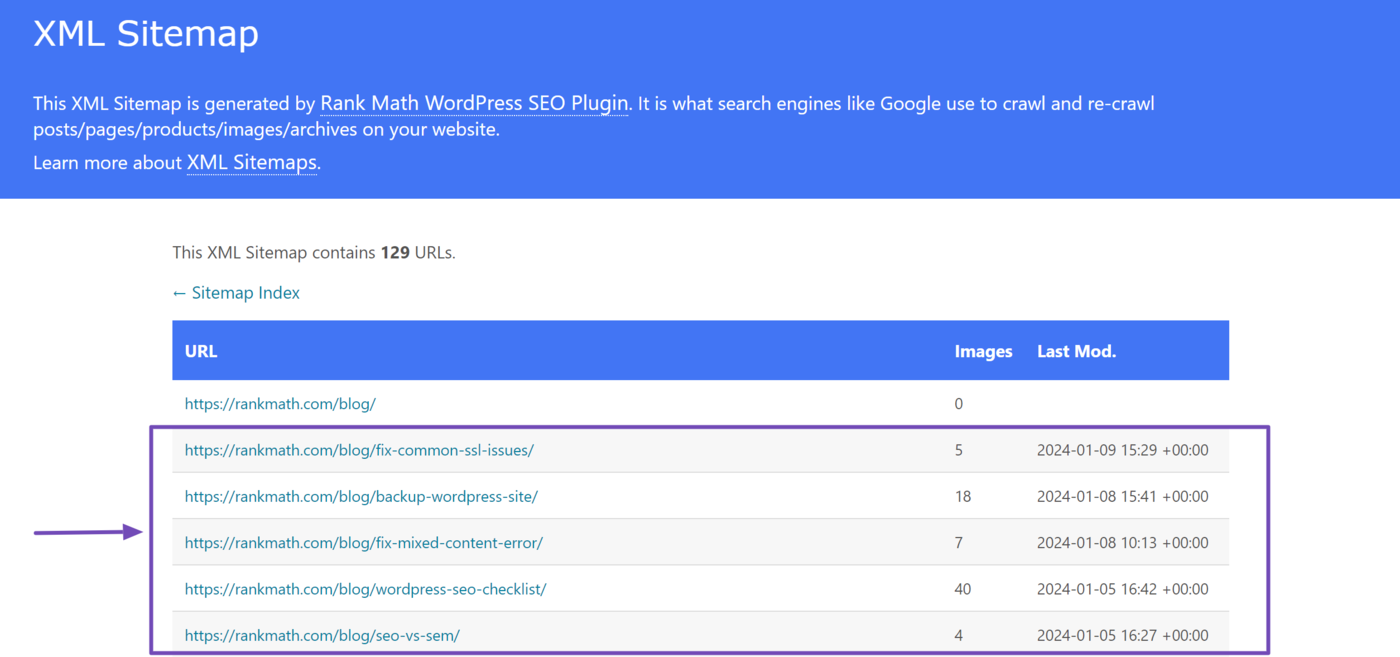
The image count specifies the number of images in the blog post. The URLs of the images are not present on the visible sitemap.
However, you can view them by clicking on any blank area of the webpage and clicking ページのソースを表示 (The exact wording may vary depending on the browser).
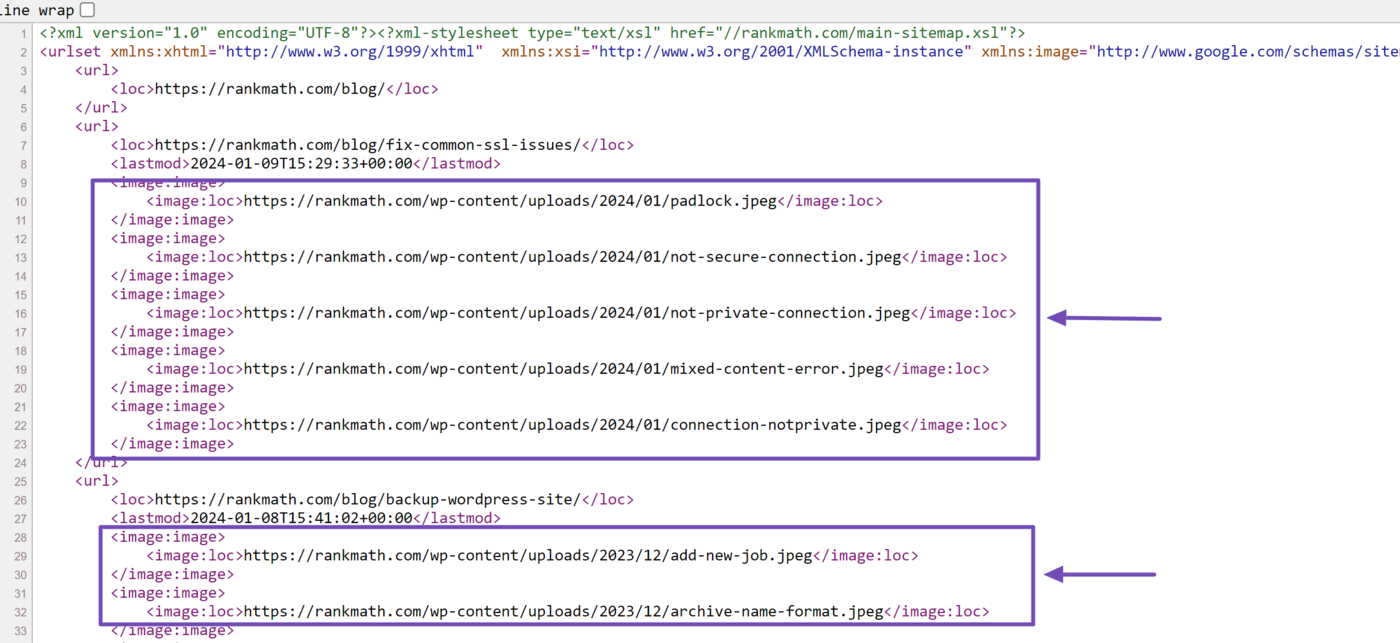
You will see that the image URLs will be visible, as shown below.
Importance of the Lastmod Tag in a Sitemap
The lastmod tag <lastmod>, short for last modified time, provides search engines with the date and time the sitemap entry was last updated.
The lastmod tag is optional, so some sites do not include them in their sitemap. However, it is recommended to include it in your sitemap as Google uses it to determine how frequently to crawl your site.
Bing also mentioned that the last mod is helpful for determining how frequently to crawl a site and what pages to index. Bing added that the lastmod tag should indicate the date the content was last updated and not when the sitemap was generated.
How to Add an XML Sitemap to Your Site Using Rank Math
You may create a sitemap manually. However, you will edit it whenever you publish, update, or delete content. So, instead of making one manually, you should use Rank Math to generate and add it to your site.
Rank Math adds a dynamic sitemap to your site. This means the sitemap is generated when search engine crawlers arrive at the sitemap URL. This ensures that your sitemap is created in real-time, is up to date, and contains your latest content at all times.
If you already have Rank Math, refer to this guide to setting up your XML sitemaps using Rank Math.
XML Sitemap Best Practices
1 Use Canonical URLs Only
Only include canonical URLs in your sitemaps. This minimizes the risk of duplicate content and ensures that search engines can identify and focus on the correct version of each page.
2 Use Absolute URLs Only
Use absolute URLs in your sitemap. While sitemaps can contain relative URLs like /what-is-yoga, they are not recommended as they could confuse search engine crawler bots, especially when used incorrectly. So, it is recommended to use absolute URLs like https://yourdomain.com/what-is-yoga.
3 Limit the Sitemap to 50MB or 50,000 URLs
Search engines have limits on the size of sitemaps they can process. So, it is recommended to keep your sitemap below 50MB or 50,000 URLs. If your site exceeds these limits, split the content into multiple sitemaps.
4 Include the <lastmod> Tag in the Sitemap
The lastmod tag <lastmod> helps search engines identify when a page was last modified. This makes it easier for them to determine whether a page needs to be recrawled. While optional, it is recommended to include the lastmod tag in your sitemap to specify the date and time the content was last updated.
5 Submit the Sitemap to Search Engines
Submit your sitemap to search engine services like Google検索コンソール と Bing ウェブマスター ツール. This is especially crucial for new sites as it ensures that search engines can find your site quicker than they ordinarily would.
6 Include the Sitemap in Your robots.txt File
Add your sitemap to your robots.txt file. This makes it easier for search engines to discover it quickly and easily. Without this, search engine crawlers will check the URLs it believes may contain your sitemap. This could slow the discovery, especially if your sitemap is not present at those locations.